How to create an Application Package
Here is a short explanation of how to create an application package.
Create new package by clicking right moutse button and select New - Package.
The package folder and package settings are created.
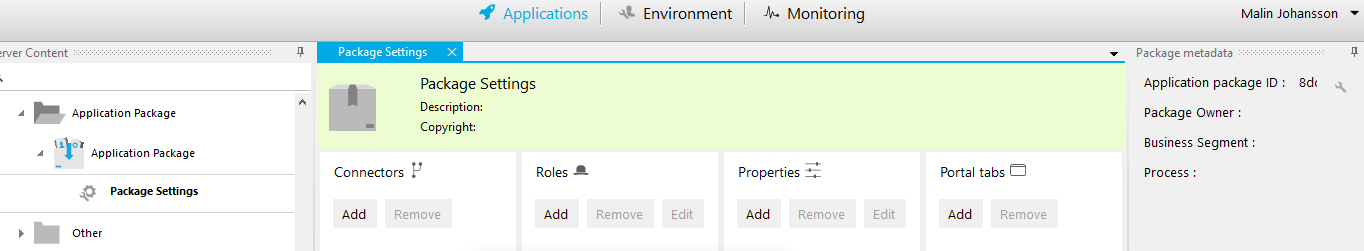
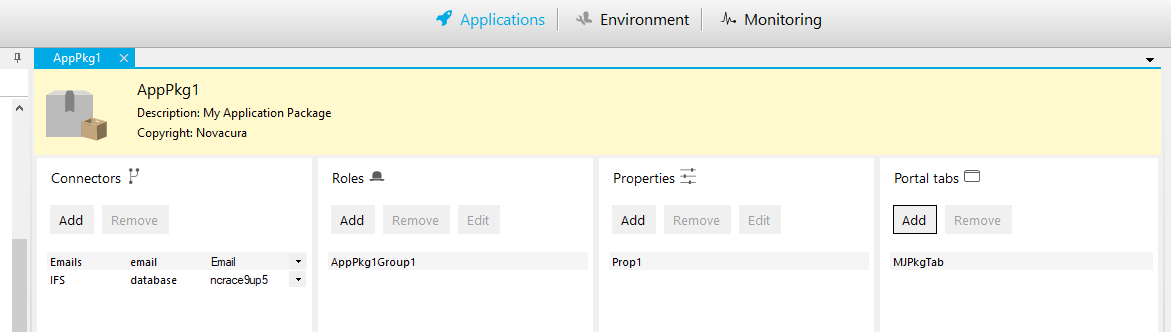
Change the package metadata.
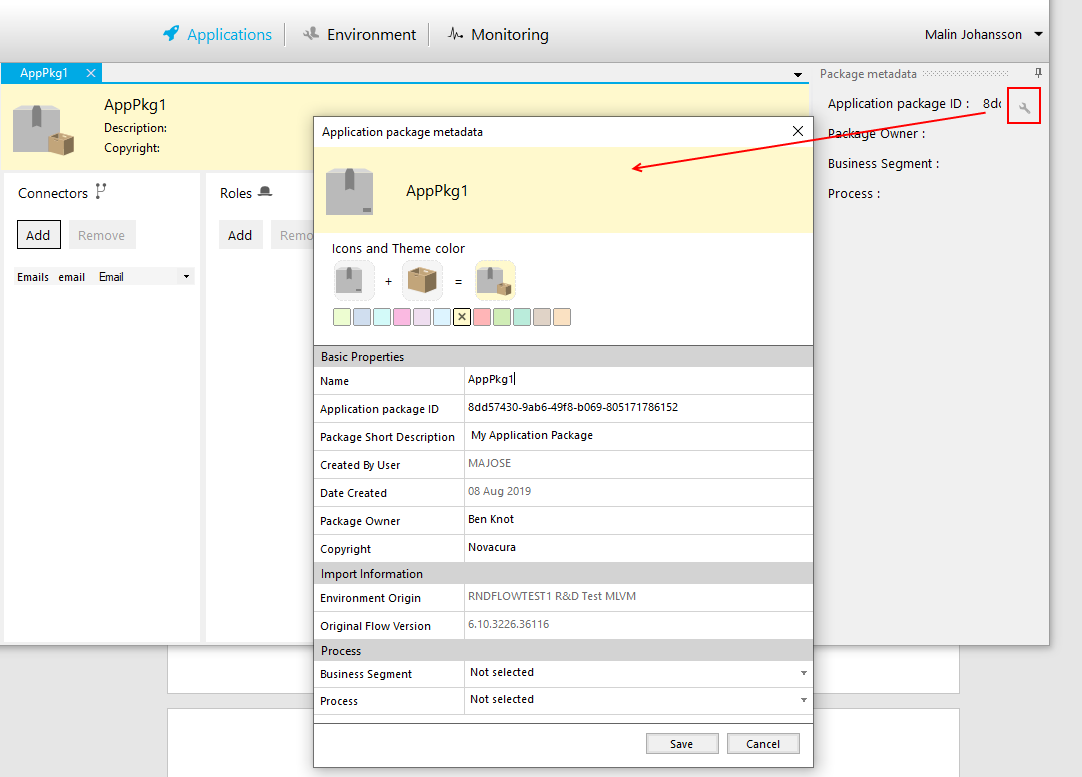
Add connectors.
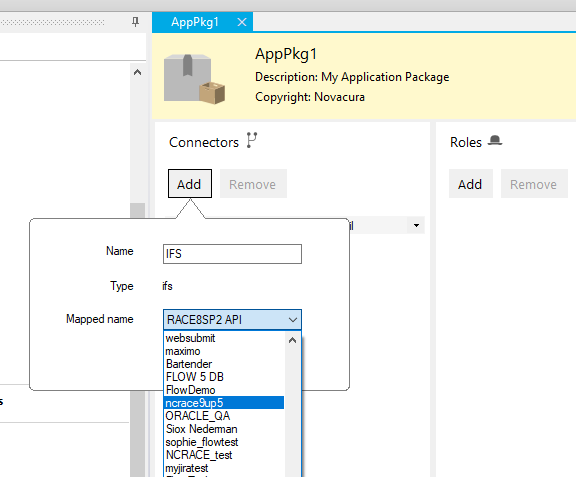
Add roles.
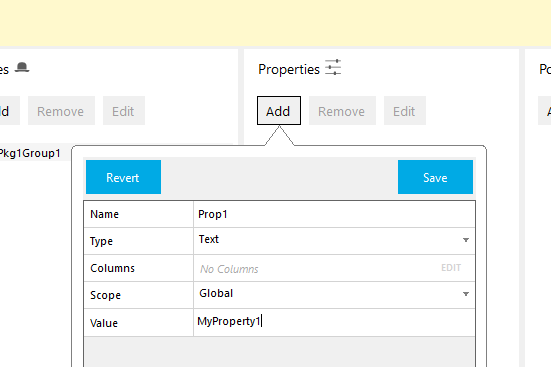
Add properties.
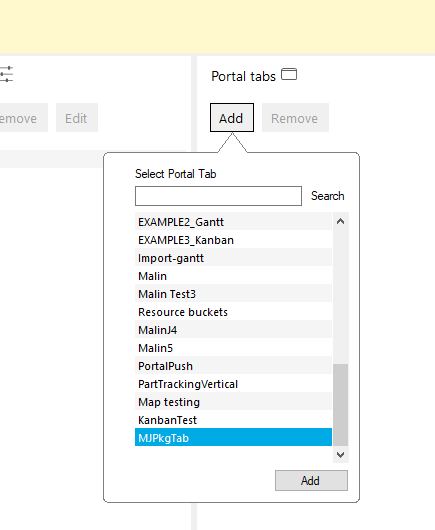
Add portal tabs.
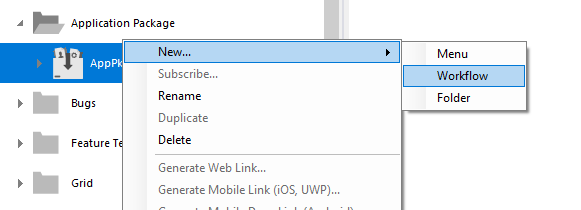
Create workflow in package.
Only the connectors defined in package settings can be selected in the workflow.
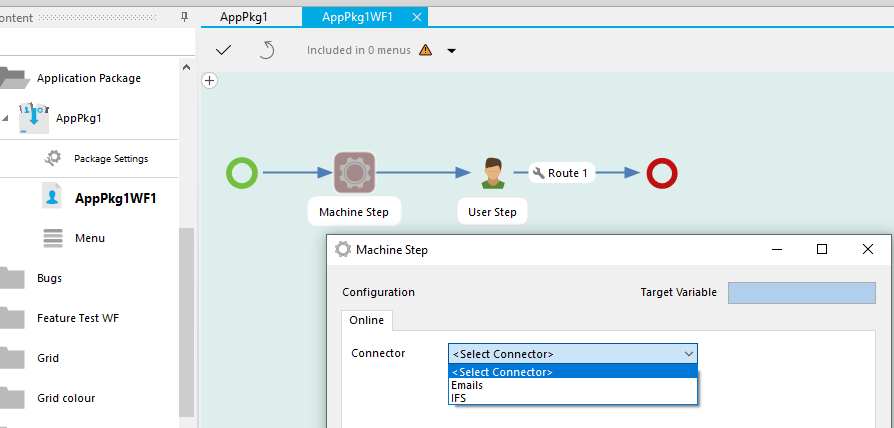
The package property can be used in the workflow.
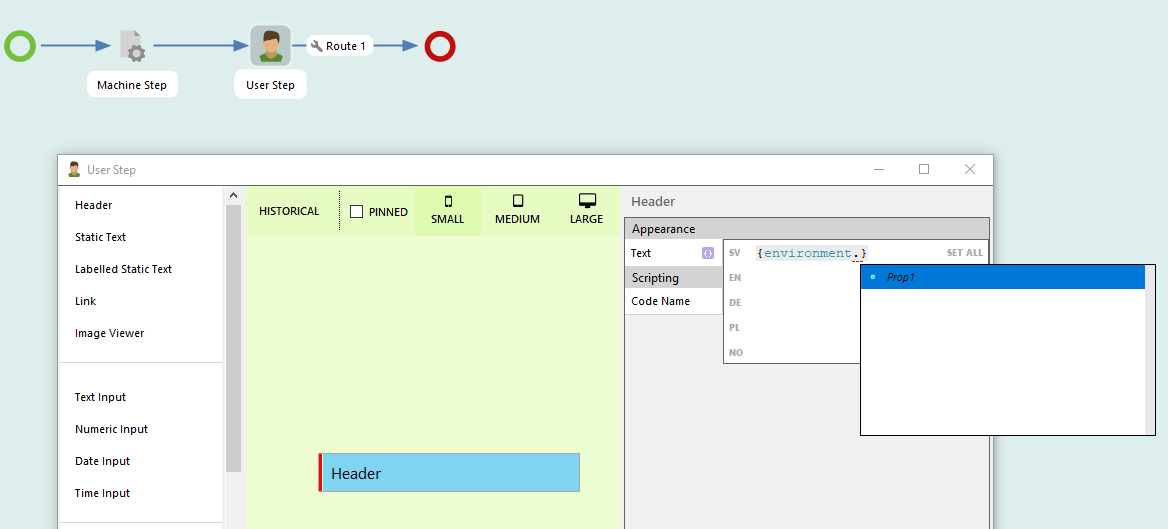
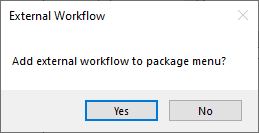
In the package menu it is possible add workflows that is not included in the package. If this is done, the user gets a warning message. External workflows are not included when exporting. Warning message:
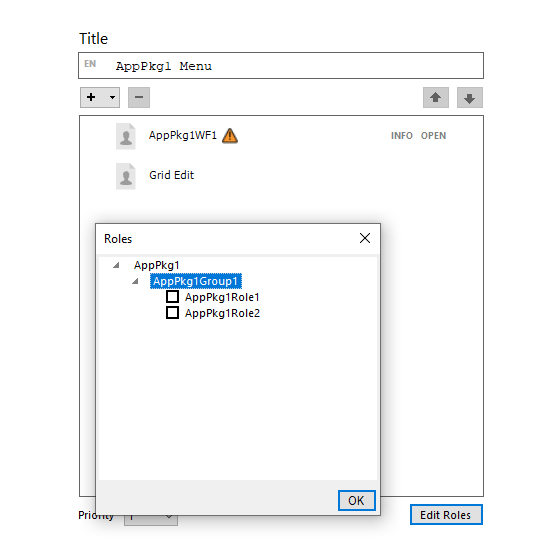
Add roles to the menu. Only package setting roles are available to be selected.
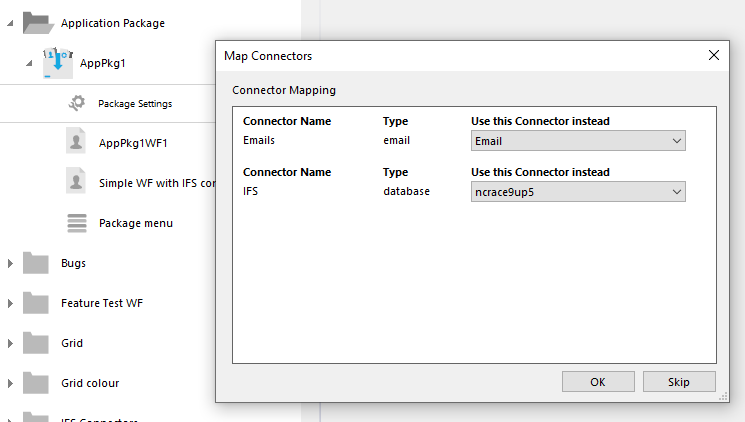
Drag and drop workflow as workflow into the package. Connector mapping is requested.
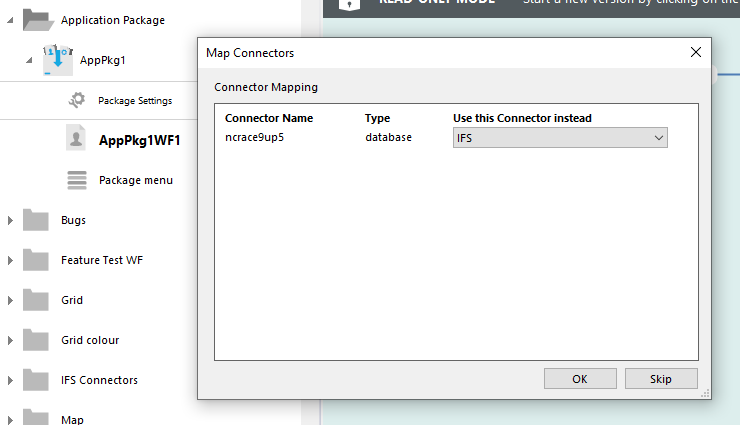
Export warning when menu contains workflow that is not in the package.
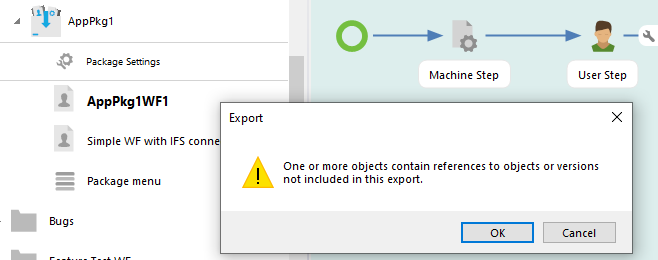
Export when workflows not published.
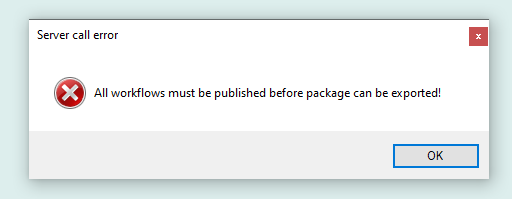
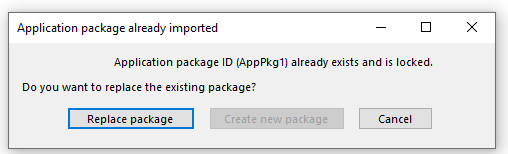
Import of existing package.
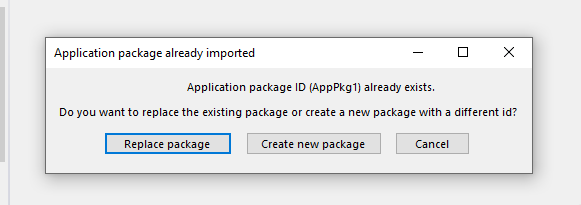
Connector mapping when creating new package at import.
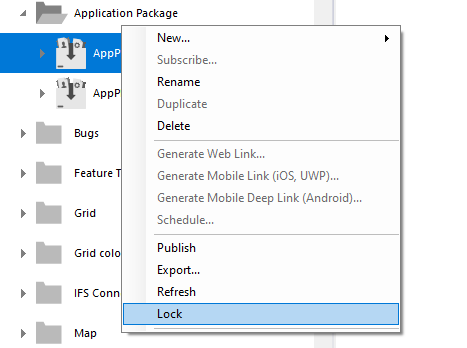
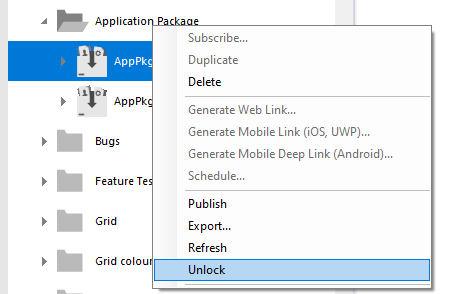
Lock package.
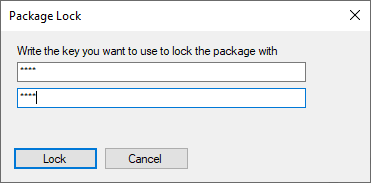
Enter and confirm password.
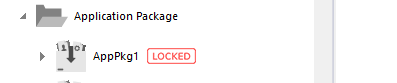
Package locked.
Unlock package
Inbox
There are two types of inboxes one can add to a menu, seed item and handover item.
Seed Item
How to configure a seed item in a workflow:
Connect a table or machine step with a data arrow to the start step.
A machine step is connected to the start step
Click on the start step and configure:
- Seed table: Choose a table
- Table key: Choose a column (from the data source)
How to configure seed item in an inbox:
Click on "+" and choose Seed Item and then select your workflow in the server content.
Step to select a seed item to the inbox
Example how Seed Item is set up in the inbox
How to configure inboxes:
- Title: The title is displayed on the inbox item.
- Description: The description is displayed under the title text on the inbox.
- Item Title: The title is displayed on the inbox item after clicking on the inbox.
- Description: The description is displayed under the title text after clicking on the inbox.
- Filter: Displays items after entered filter.
- Calendar: Displays items on a specific date in the calender tab in the inbox.
- Favorite: Displays items under the favorite tab in the inbox.
- Priority: Displays items under the priority tab in the inbox.
Example how an inbox with seed items can look in Universal Windows Client
Handover Item
How to configure handover item in an inbox:
Click on + and choose Handover Item and then select your workflow in the server content.
Step to select a handover item to the inbox
Menu
One or more menus needs to be configurated to make workflows available in the clients. A menu can have three different types of content Category, Workflow Item and Inbox.
- Category: A catecory will categorize workflows and menus in the clients.
- Workflow Item: Choose what workflows that should be available in the menu.
- Inbox: Add and configure an inbox to make seeded and hand overed workflows available for the user. Read more about how to configure an inbox here.
Edit Roles to assign the menu to those roles that the menu should be availalbe to.
Menu example
Generate Link
Generate link helps the user to construct a link to execute a workflow. This is supported for both User Workflows and Machine Workflows. Generate Link is located in the context menu in server content panel.
User Workflows
User workflow links points to the web client and provides a direct link to a workflow execution.
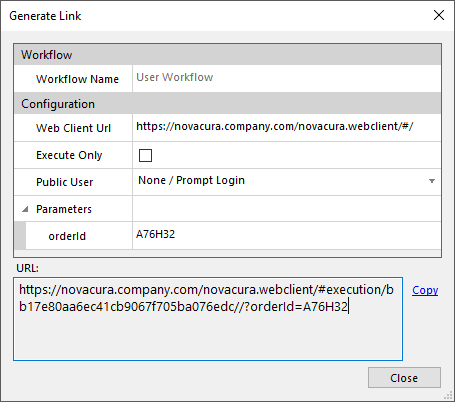
Configuration example
- Web Client Url this field should contain the url to the web client.
- Execute Only locks the user to the execution view and prehibit the user from quiting the workflow or returning to a menu after execution.
- Public User this option configures a public user to run the execution, when a public user is selected no credential prompt will be displayed.
- Parameters this sections show the input variables that are configured in the start event of the workflow. Only simple variables can be used in user workflows.
Mobile Link
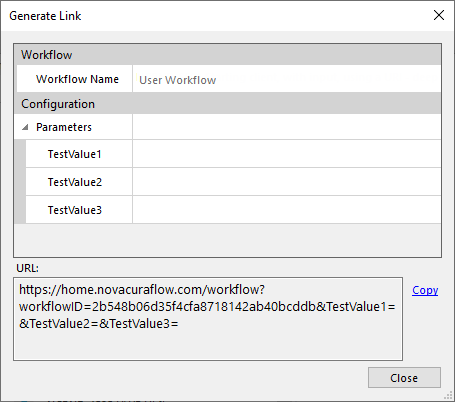
Configuration example
User workflow links points to the mobile client and provides a direct link to a workflow execution.
- Parameters these sections show the input variables that are configured in the start event of the workflow. Only simple variables can be used in user workflows.
Machine Workflows
Machine workflows can be executed over http request. These request are made directly to the flow server. The workflow is executed by a machine user and authentication is made by basic authentication.
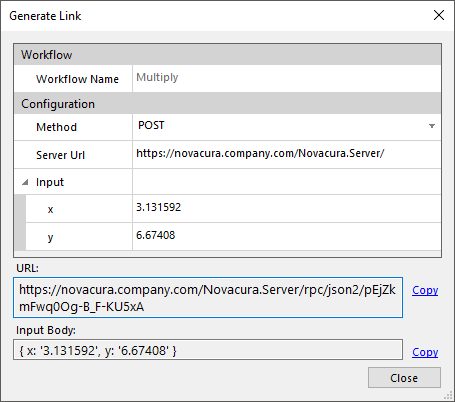
Configuration example
- Method supported methods are POST and GET, POST supports complexe structures as input and GET only supports simple variables feetched as query string values.
- Server URL url to server, must be accessible from where the request is made.
- Input in this section all simple variables are shown and provides a help function for constructing the input parameters. In POST requests the input should be sent as JSON in body content and GET should send input variables as part of the url.
Manually select BarTender document
With this operation you can manually select a BarTender document from your local file system.
The file is stored in the machine step and is not in any way synchronized with the file in your local file system. Once the file has been selected you can export the file by clicking on Export file....
Note that if you select another operation in the machine step the document will be lost and has to be selected from the file system again.
The same input and outputs as 'Print' applies, see Print for more information.
Database Connector
TODO
IFS Applications Connector
TODO
M3 Connector
TODO
Infor M3 REST Connector
The M3 Rest Connector is used to execute transactions in M3 via the M3-API-REST bulk API.
Press Select operation to select which transaction to execute.
Input
The input will of course depend on the transaction to execute. There is one common parameter that always is available though, readtimeoutmillis. In this parameter you can specify the amount of time to wait for response from job.
Another common feature for all transactions is the possibility to use an iterator. If you select a iterator it means that the transaction will be executed once for each row in the table specified as iterator. Using a iterator will change the output of the cogwheel to a table with the same number of rows as the iterator table, each row in the table is corresponding result of transaction execution for row in iterator table. You can of course map columns in iterator to parameters of transaction. Simply select an iterator, and for a parameter select I Iterator in dropdown menu for parameter and then select the suitable column of iterator table.
Output
Record (or table of records if iterator is used).
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HttpStatusCode | The status code returned from REST API. Typically 200 if request (not necessarily transaction) was successful. 401 if not authorized etc. |
| ReasonPhrase | HTTP ReasonPhrase, if any |
| AllHeaders | Simple variable containing all headers (with line feed between each header) returned by REST API. |
| OK | A record containing result of transaction if it was successfully executed. Will be empty if transaction failed. - Program - Simple variable containing the program executed - Transaction - Simple variable containing the transaction executed - Records - A table containing the records (if any) returned by transaction. The columns of the table will of course depend on the transaction, but you can always choose not the request particular columns by unchecking the Included checkbox. By doing that, it will not be requested from the REST API, which could boost performance. You can also specifiy a row limit on Records (default 100). |
| Error | A record containing error information if transaction failed for some reason. Will be empty if transaction was successfully executed. |
Note that if HttpStatusCode is 200, either OK or Error (never both) contains data. This can be used to take different paths in your workflow. Simply add a 'Decision Step' and add a script rule like transactionResults.Error != nil to check for errors.
Maximo Generic Connector
Maximo Generic connector communicates with Maximo Web Services.
Creating a Maximo Connector Machinestep
When connector is configured we can use it in machine steps. We have to do the following steps:
- Reload Maximo Web Services
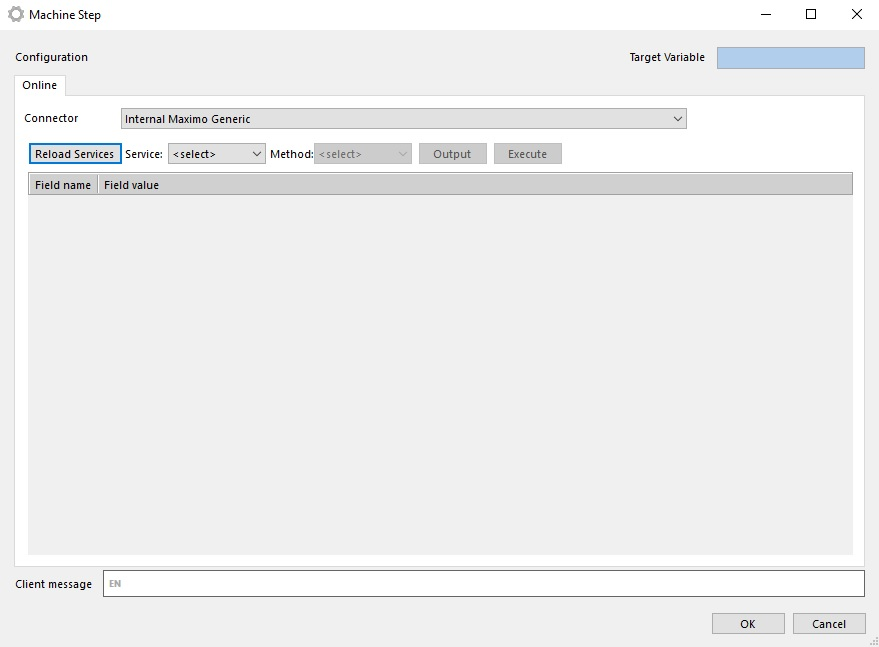
Connector reads WSDL from Maximo Main Web Services from MaximoWebServiceAddress (configuration):
for example: http://{MaximoWebServiceAddress}/meaweb/wsdl/MXWSREGISTRY.wsdl
After that it creates the web service dotnet client object and call Maximo Main Web Services.
Response from Maximo Main Web Service contains list with all available Maximo Web Services.
- Choose specific Maximo Web Service
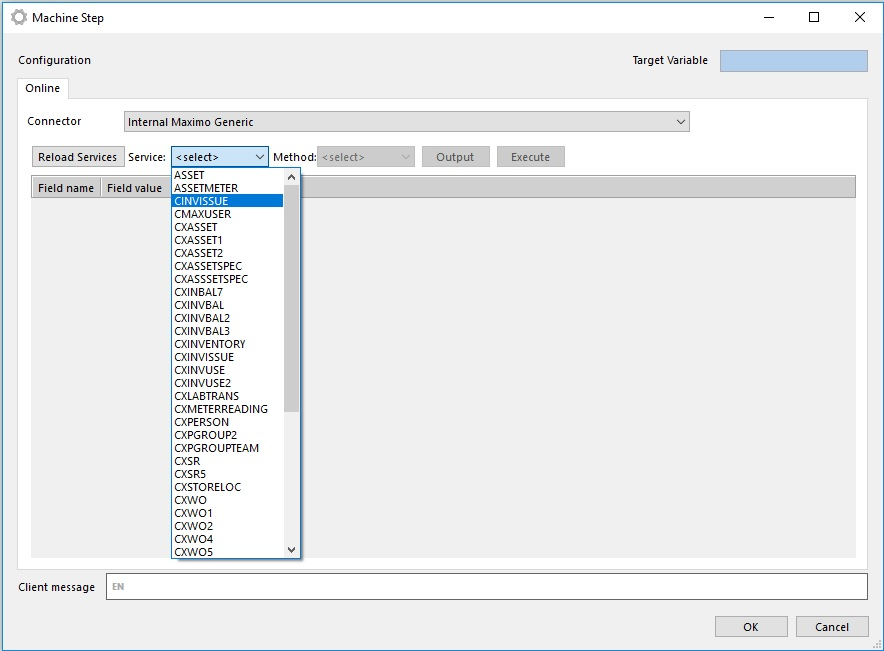
When specific web service is chosen the connector reads the WSDL for the SelectedWebService from MaximoWebServiceAddress (configuration):
for example: http://{MaximoWebServiceAddress}/meaweb/wsdl/{SelectedWebService}.wsdl
After that it creates web service dotnet client object and calls the selected Maximo Web Service.
Response from Selected Maximo Web Service contains list with all available methods and their parameters.
- Choose Method and fill method parameters
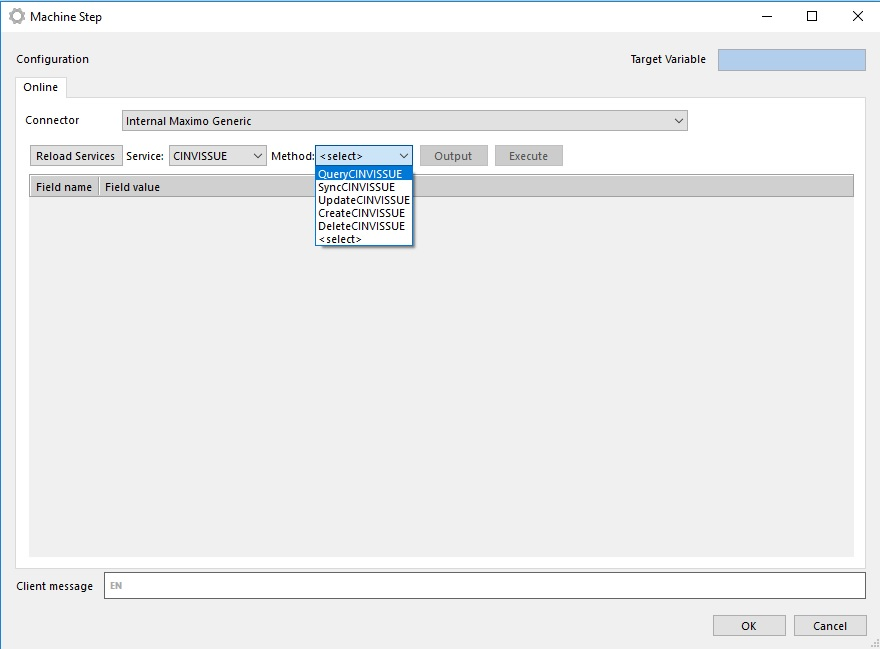
When specific web service method is chosen, the connector reads all input parameters from the method definition and displays it:
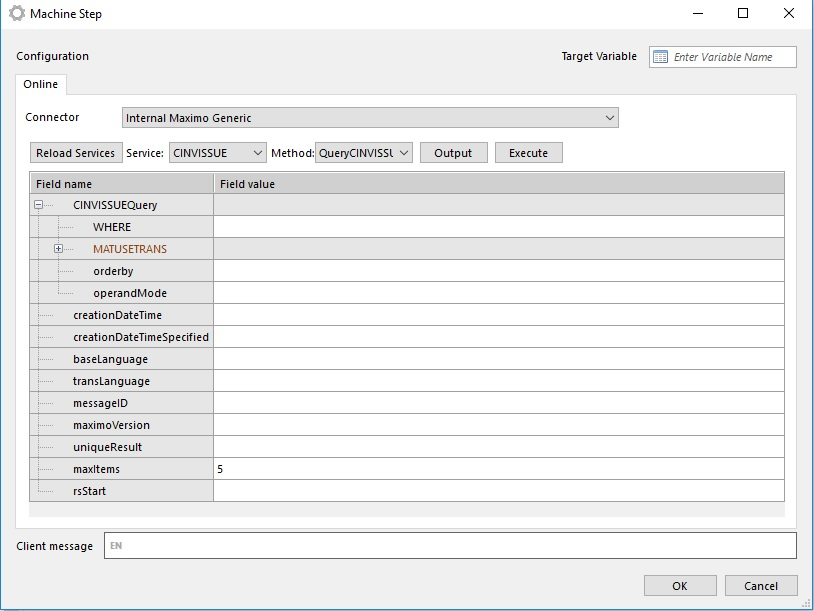
When all required parameters are set we can use connector (by running workflow or directly from Flow Studio to test it).
When Connector is executed it use web service dotnet client (created in point 2) and execute method and read response data.
Basic API
About the Novacura Flow Transporter Package
The Novacura Flow SAP connector will call a number of SAP BAPIs in order to retrieve the interface information. The following functions give the required information:
- ZNCFLOW_APPLICATION_COMPONENT: List BAPI application tree
- BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST: Returns a list of all available BAPI's in the SAP system.
- BAPI_INTERFACE_GETDOCU: Returns the help text documentation for a BAPI on different levels.
- RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE: Returns all parameters for a BAPI or function module in SAP.
- ZNCFLOW_DDIF_FIELDINFO_GET: Returns the data dictionary specification for parameter fields
BAPI: BAPI_INTERFACE_GETDOCU
With this BAPI you will get the documentation for the requested BAPI in the form of help text. This is useful for giving detailed descriptions of the BAPI on a general level or on the Method. If you give the Object you will get text on the object and if you give the object and the method you get details on the method. The fields in the input Is the same as the resulting table (BAPILIST) in the previous BAPI (BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST).
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJTYPE | Object type | I | CHAR10 | SFLIGHT |
| OBJNAME | Object name | I | CHAR32 | |
| METHOD | Method name of the object type | I | CHAR32 | GetDetail |
| PARAMETER | Name of parameter in method | I | CHAR32 | |
| FIELD | Field name in the parameter for F4 values | I | CHAR30 | |
| LANGUAGE | Language of the text to be displayed | I | LANG1 | |
| TEXTFORMAT | Format of the text to be displayed | I | CHAR3 | |
| LINKPATTERN | Convert SAPscript Hyperlinks to HTML | I | CHAR255 | |
| RETURN | Return messages | O | BAPIRET2 | |
| TEXT | Table for the text | T | BAPITGB |
Table: BAPITGB
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINE | Line in documentation text | CHAR255 |
BAPI: BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST
This BAPI returns information for BAPI's relating to the position in the BAPI application tree. Giving an * in the first input parameter will give a full list of all BAPI's.
The other parameters can be left blank thus letting the system using default values. It is possible to select BAPI's for a list of application nodes by sending in a table COMPONENTS2SELECT with rows of nodes in the field COMPONENT. This BAPI together with the first (ZNCFLOW_APPLICATION_COMPONENT) will give you enough information to draw the complete Application tree containing all BAPI's.
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJECTTYPE | Object type | I | CHAR10 | * (will result in full list) |
| SHOW_RELEASE | Release /Reference Release to Display | I | CHAR4 | Use default |
| BAPIS_POTENTIAL | Display Potential BAPIs | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| BAPIS_NEW | Display New BAPIs in Release | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| BAPIS_OLD | Display BAPIs from Previous Releases | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| RELEASED_BAPI | Release Status of BAPIs | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| RELEASED_FUNC | Release Status of Function Modules | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| RETURN | Return messages | O | BAPIRET2 | |
| COMPONENTS2SELECT | Application Components/Areas to Select | T | BAPIMONCOM | |
| SYSTEMS2SELECT | Original System of BAPIs to Select | T | BAPISRCSYS | Use default |
| BAPILIST | List of Selected BAPIs | T | BAPIMONSTR |
Structure: BAPIRET2
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| TYPE | Message type: S Success, E Error, W Warning, I Info, A Abort | CHAR1 | |
| ID | Message Class | CHAR30 | |
| NUMBER | Message Number | NUMC3 | |
| MESSAGE | Message text | CHAR220 | |
| LOG_NO | Application log: log number | CHAR20 | |
| LOG_MSG_NO | Application log: Internal message serial number | NUMC6 | |
| MESSAGE_V1 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| MESSAGE_V2 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| MESSAGE_V3 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| MESSAGE_V4 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| PARAMETER | Parameter Name | CHAR32 | |
| ROW | Lines in parameter | INT4 | |
| FIELD | Field in parameter | CHAR30 | |
| SYSTEM | Logical system from which message originates | CHAR10 |
Table: COMPONENTS2SELECT
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMPONENT | Application component ID | CHAR24 |
Table: BAPILIST
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| OBJECTTYPE | Object Type | CHAR10 | SFLIGHT |
| OBJECTNAME | Object name | CHAR32 | Flight |
| BAPINAME | Method name of BAPI | CHAR32 | GetDetail |
| ABAPNAME | Function module name | CHAR30 | BAPI_FLIGHT_GETDETAIL |
| COMP | Application component ID | CHAR24 | BC-DWB |
| CREA_REL | Release at Creation | CHAR4 | 610 |
| CREATOR | Author | CHAR12 | SAP |
| UDATE | Changed On | CHAR8 | 18.09.2001 |
| CHANGER | Last changed by | CHAR12 | SAP |
| SOURCESYS | Name of the SAP system | CHAR8 | SAP |
| BAPI_AG | Application area or BAPI work group responsible | CHAR5 | Basis |
| ISINTERFAC | Interface object type | CHAR1 | |
| BAPI_REL | Release status of BAPI method | CHAR1 | X |
| FUNC_REL | Release status of function module | CHAR1 | R |
| OBSOLETE | Release in which the status was set to obsolete | CHAR4 | |
| FM_DOCU | Documentation on function module exist | CHAR1 | |
| BO_DOCU | Documentation for business object exist | CHAR1 | |
| MESTYPE | Message type | CHAR30 | |
| VERB | Object type component | CHAR32 | GETLIST |
| BO_TEXT | Description | CHAR80 | Flight with connection data (SAP training) |
| BAPI_TEXT | Description | CHAR80 | Find list of flights |
BAPI: ZNCFLOW_DDIF_FIELDINFO_GET
This BAPI will return de definition of data dictionary objects. In this case the parameters for BAPI's or function modules returned from BAPI: RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE.
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TABNAME | Name of the Table (of the Type) for which Information is Required | I | CHAR30 | |
| FIELDNAME | Use Parameter LFIELDNAME Instead | I | CHAR30 | |
| LANGU | Language of the Texts | I | LANG1 | |
| LFIELDNAME | If Filled, only Field with this Long Name | I | CHAR132 | |
| ALL_TYPES | Take all Types into Consideration | I | CHAR1 | |
| GROUP_NAMES | Take Named Includes into Consideration | I | CHAR1 | |
| UCLEN | Unicode length with which runtime object was generated | I | RAW1 | |
| DO_NOT_WRITE | Write | I | CHAR1 | |
| X030L_WA | Nametab Header of the Table (of the Type) | E | CHAR30 | |
| DDOBJTYPE | Kind of Type | E | CHAR8 | |
| DFIES_WA | Single Information if Necessary | E | CHAR30 | |
| LINES_DESCR | Information about Other Referenced Types | E | DDTYPEDESC-TYPENAME (CHAR30)-TYPEKIND (CHAR4)-DFIES | |
| DFIES_TAB | Field List if Necessary | T | DFIES | |
| FIXED_VALUES | Description of Domain Fixed Values | T | DDFIXVALUES |
Table/Structure: DFIES_TAB
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| TABNAME | Table Name | CHAR30 | |
| FIELDNAME | Field Name | CHAR30 | |
| LANGU | Language Key | LANG1 | |
| POSITION | Position of the field in the table | NUMC4 | |
| OFFSET | Offset of a field | NUMC6 | |
| DOMNAME | Domain name | CHAR30 | |
| ROLLNAME | Data element (semantic domain) | CHAR30 | |
| CHECKTABLE | Table Name | CHAR30 | |
| LENG | Length (No. of Characters) | NUMC6 | |
| INTLEN | Internal Length in Bytes | NUMC6 | |
| OUTPUTLEN | Output Length | NUMC6 | |
| DECIMALS | Number of Decimal Places | NUMC6 | |
| DATATYPE | ABAP/4 Dictionary: Screen data type for Screen Painter | CHAR4 | |
| INTTYPE | ABAP data type (C,D,N,...) | CHAR1 | |
| REFTABLE | Table for reference field | CHAR30 | |
| REFFIELD | Reference field for currency and qty fields | CHAR30 | |
| PRECFIELD | Name of included table | CHAR30 | |
| AUTHORID | Authorization class | CHAR3 | |
| MEMORYID | Set/Get parameter ID | CHAR20 | |
| LOGFLAG | Indicator for writing change documents | CHAR1 | |
| MASK | Template (not used) | CHAR20 | |
| MASKLEN | Template length (not used) | NUMC4 | |
| CONVEXIT | Conversion Routine | CHAR5 | |
| HEADLEN | Maximum length of heading | NUMC2 | |
| SCRLEN1 | Max. length for short field label | NUMC2 | |
| SCRLEN2 | Max. length for medium field label | NUMC2 | |
| SCRLEN3 | Max. length for long field label | NUMC2 | |
| FIELDTEXT | Short Description of Repository Objects | CHAR60 | |
| REPTEXT | Heading | CHAR55 | |
| SCRTEXT_S | Short Field Label | CHAR10 | |
| SCRTEXT_M | Medium Field Label | CHAR20 | |
| SCRTEXT_L | Long Field Label | CHAR40 | |
| KEYFLAG | Identifies a key field of a table | CHAR1 | |
| LOWERCASE | Lowercase letters allowed/not allowed | CHAR1 | |
| MAC | Flag if search help is attached to the field | CHAR1 | |
| GENKEY | Flag (X or Blank) | CHAR1 | |
| NOFORKEY | Flag (X or Blank) | CHAR1 | |
| VALEXI | Existence of fixed values | CHAR1 | |
| NOAUTHCH | Flag (X or Blank) | CHAR1 | |
| SIGN | Flag for sign in numerical fields | CHAR1 | |
| DYNPFLD | Flag: field to be displayed on the screen | CHAR1 | |
| F4AVAILABL | Does the field have an input help | CHAR1 | |
| COMPTYPE | DD: Component Type | CHAR1 | |
| LFIELDNAME | Field name | CHAR132 | |
| LTRFLDDIS | Basic write direction has been defined LTR (left-to-right) | CHAR1 | |
| BIDICTRLC | DD: No Filtering of BIDI Formatting Characters | CHAR1 | |
| OUTPUTSTYLE | DD: Output Style (Output Style) for Decfloat Types | NUMC2 | |
| NOHISTORY | DD: Flag for Deactivating Input History in Screen Field | CHAR1 | |
| AMPMFORMAT | DD: Indicator whether AM/PM time format is required | CHAR1 |
Table: FIXED_VALUES
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOW | Values for Domains: Single Value / Upper Limit | CHAR10 | |
| HIGH | Values for domains: upper limit | CHAR10 | |
| OPTION | Option for domain fixed values | CHAR2 | |
| DDLANGUAGE | Language Key | LANG1 | |
| DDTEXT | Short Text for Fixed Values | CHAR60 |
BAPI: RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE
This BAPI will return all parameters and parameter attributes for a specific BAPI or function module. The function module name (FUNCNAME) is the same value that was returned for each BAPI in the call to BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST (field ABAPNAME in table BAPILIST).
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUNCNAME | Name of the function module | I | CHAR30 | BAPI_FLIGHT_GETDETAIL |
| LANGUAGE | Language of the parameter text | I | LANG1 | |
| NONE_UNICODE_LENGTH | Length is also supplied in Unicode systems in non-Unicode format | I | CHAR1 | |
| REMOTE_BASXML_SUPPORTED | BasXML Protokoll | E | CHAR1 | |
| REMOTE_CALL | Function module can be called Remote-Function | E | CHAR1 | |
| UPDATE_TASK | Function module is in the update | E | CHAR1 | |
| PARAMS | Parameter of function module | T | RFC_FUNINT | |
| RESUMABLE_EXCEPTIONS | Resumable Exceptions | T | RSEXC |
Table: PARAMS
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| PARAMCLASS | Parameter type | CHAR1 | I |
| PARAMETER | Parameter name | CHAR30 | AIRLINEID |
| TABNAME | Table Name | CHAR30 | BAPISFLKEY |
| FIELDNAME | Field Name | CHAR30 | AIRLINEID |
| EXID | ABAP Data Type | CHAR1 | C |
| POSITION | Position of field in structure (from 1) | CHAR10 | 1 |
| OFFSET | Field offset from beginning of structure (from 0) | INT10 | 0 |
| INTLENGTH | Internal length of field | INT10 | 6 |
| DECIMALS | Number of decimal places | INT10 | 0 |
| DEFAULT | Default value for import parameter | CHAR21 | |
| PARAMTEXT | Short text | CHAR79 | Airline Code |
| OPTIONAL | Optional parameters | CHAR1 |
BAPI: ZNCFLOW_APPLICATION_COMPONENT
This BAPI returns the BAPI application tree. The resulting table contains all nodes in the BAPI tree indicating what level the node is on and what the superior node is. The input parameter can list all nodes (giving only a *) or a specific component. Ending with an * can give all nodes starting with a specific name. For example AP-MD* will give all nodes starting with AP-MD. I.e all nodes below that node.
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMP | Application Component | I | CHAR24 | * (will result in full list) |
Table: COMPONENTS
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMP | Application component ID | CHAR24 | AP-MD-BF |
| NAME | Short text | CHAR60 | Master data |
| LEVEL | Numc3, internal use | NUMC3 | 002 |
| SUPERIOR | Application component ID | CHAR220 | AP-MD |
SAP BAPI Connector
Introduction
Novacura Flow is delivered with a API connector for SAP ECC (supporting version ECC 6 and newer), where Flow is communication with SAP through the SAP BAPIs.
In order to use the SAP connector in Flow, the connector needs a license for the current environment.
Getting started
There are a couple of things that needs to be done before you can start using the SAP connector.
In short, these four steps needs to be done prior to creating workflows with the SAP connector (assuming that you of course already have installed the Flow Server):
- Install the SAP GUI for Windows on the Flow server. This is necessary for Flow to be able to connect to SAP.
- Verify that the connection between the Flow Server and SAP works, using the SAP Logon Pad.
- Install the Novacura Flow Transporter package in the SAP environment you want to connect to. The Transporter package will install a couple of BAPIs that the connector need to generate an API tree in the Flow Studio. Download Transporter package here.
- Make sure you have a license for the SAP Connector, read more; here.
- Configure the SAP Connector in the Flow Studio, read more; here.
Steps 3 to 5 are described below.
Designing a SAP workflow
If you want an example of a SAP workflow, you can find a simple workflow here, using the ABAP workbench BAPIs for Flight Booking: http://community.novacuraflow.com/product/sap-flight-booking-example/
Make sure you have these BAPI in your SAP environment before you use this workflow.
When in the Flow Studio, adding a Machine Step to your workflow will let you create a connection to SAP. After selecting the SAP connector you have defined in Environment/Connectors, you will be able to configure a method call to SAP with the following steps.
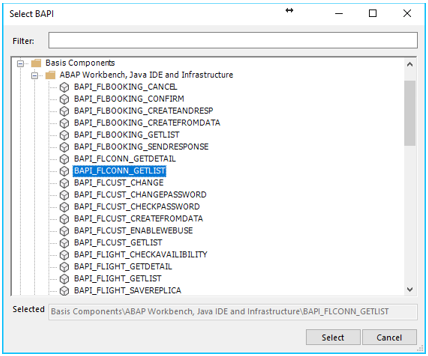
Get the list of BAPIs: When selecting youe SAP connector in the list of available connectors, press the button with the three dots. This will connect to your SAP environment and generate the entire BAPI tree in the connector. So whatever BAPIs you have in your installatione of SAP will be accessible directly from Flow.

Select a BAPI: After the generation of the BAPI tree is done, you will see all BAPIs arranged in a folder structure. You can find the BAPI you need by either browse through the structure or by searching for the BAPI using the Filter option.
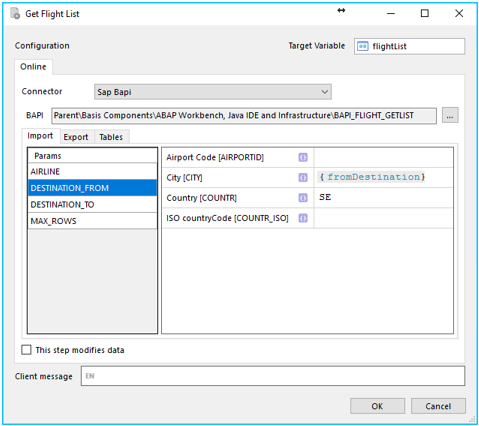
Configure the BAPI call (Input):
There are three tabs that can be used for configuration of the BAPI all:
- Import: input data do the BAPI
- Export: output data from the BAPI
- Tables: both input and output. One or many tables can be used here.
First, define the input. You can either set fixed data by just typing the value you need or by using existing (single) variables in the workflow. Note that Input can be set both on the Import and Tables tabs.
Configure the BAPI call (Output): All data coming out from the called BAPI will end up in the Target Variable, so the Target Variable must be set (as in all Machine Steps returning data). There are two tabs for output; Export and Tables. Export are singe variables returned from the BAPI. Tables are table variables returned from the BAPI. Depending on the BAPI, Export and Tables will look and function differently.

Configuring Commit step
Selecting check box This step modifies data will ensure that a BAPI commit step is executed. Check this box for any BAPI that updates or inserts data in the ECC system. For a BAPI that only reads data it can be left unchecked.
When you have configure the BAPI call, you can test it using the Play button on the top right of the Application Window in the Studio.

Error handling
SAP returns errors as output from the BAPI. This means that you will need to handle errors from SAP in the workflow. Like this:
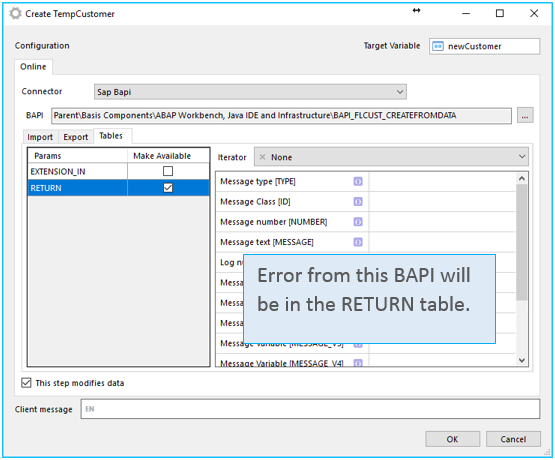

So, now you can create any app directly on top of your SAP environment!
Add attached file (from bytes)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Source bytes | Table (consisting of bytes) to read from |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from file system)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Local filename | Full path to file to upload. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have access to the file. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from stream)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Filename | Remote filename |
| Source stream | Simple variable containg a stream |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete all attached files
Delete all attachments on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete attached file
Delete an attachment on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
| 1000005 | File not found. |
List attached files
Lists all files attached to specified item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete item
Deletes item with given ID.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get items by query
Gets information about items by provided CAML Query
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| CAML Query | The query to send to SharePoint |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- StaticName
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List all items
Lists all items in Custom List app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Row limit | Limit on how many items to list. A value of -1 indicates no limit |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- StaticName
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List fields of items
Lists the fields that are available for items in Custom List app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Create new item
Creates a new item in a Custom List app. Returns the ID of created item in Results.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item name | Title of new item |
| Folder url | Url to folder to create item in. Leave empty for root folder. Example if adding item to folder 'folder1' in Custom List 'clist' in subsite 'subsite1': '/subsite1/Lists/clist/folder1' |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Create new item, with field values
Creates a new item in a Custom List app. Returns the ID of created item in Results.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item name | Title of new item |
| Field values | Table consisting of field values. Note that StaticName of fields needs to be provided, not Title |
| Folder url | Url to folder to create item in. Leave empty for root folder. Example if adding item to folder 'folder1' in Custom List 'clist' in subsite 'subsite1': '/subsite1/Lists/clist/folder1' |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Update item field
Updates a field of a given item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Field | Name of field/column (StaticName, not Title) |
| Value | New value of property |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Check in file
Checks in a file to SharePoint that the user has checked out
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Comment | Comment, must not exceed 1023 characters |
| Checkin type | Specifies check in type |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000002 | User has not checked out the file. |
Check out file
Checks out a file to the SharePoint user the connector is running as.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000003 | File already checked out. |
Discard check out
Undo a check out of a file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000002 | User has not checked out the file. |
Copy file
Copies a file from a Document Library to another (or the same) Document Library at the same SharePoint site.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Document Library Name | Name of source Document Library in SharePoint to copy file from |
| Source filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" to move |
| Destination Document Library Name | Name of target Document Library in SharePoint to copy file to |
| Destination filename | Name of file in destination Document Library |
| Overwrite | Specifies whether to overwrite destination file if it already exists |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Delete file
Deletes a file in the Document Library. If the file does not exist, the operation is considered succesful.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" to move |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Get file information
Gets information about a file provided as a releative url, example: '/subsite1/Shared Documents/file.doc'
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List files
Lists all files at the root of a Document Library
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Populate user members | Specifies whether to populate members that relates to SharePoint users, e.g. Author. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Move file
Moves a file from a Document Library to another (or the same) Document Library at the same SharePoint site.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Document Library Name | Name of source Document Library in SharePoint to move file from |
| Source filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" to move |
| Destination Document Library Name | Name of target Document Library in SharePoint to move file to |
| Destination filename | Name of file in destination Document Library |
| Move operations | Specifies move options. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Update file property
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder/file.txt". |
| Field name | Name of field or column |
| New value | The new value to set on field |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Create subfolder
Creates a new folder beneth specfied folder. If the folder already exists, the operations is considered succesful
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Parent folder | Name of folder to create sub folders in. E.g. "folder1" or "folder1/subfolder2" |
| Name of sub folder | Name of folder to create |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Delete folder
Deletes a folder by its relative url.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url of folder | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List files in folder
Lists all files in a specified folder.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Folder | Remote folder in Document Library, can include sub folders if applicable. E.g. "subfolder1/subfolder2" |
| Populate user properties | Specifies whether to populate members that relates to SharePoint users, e.g. Author |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List files in folder by relative url
Lists all files in a folder specified by relative url. Useful for instance if you got a Record containg folder information including its relative url and want to list those files.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder". |
| Populate user properties | Specifies whether to populate members that relates to SharePoint users, e.g. Author |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List folders in root of Document Library
Lists all folders in the root of the Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List subfolders of folder
Lists all subfolders of specified folder.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Folder | Name of folder to list sub folders of. E.g. "subfolder1/subfolder2" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Get subfolders by relative url
Lists all subfolders of specified folder provided by relative url. Useful for instance if you got a Record containg folder information including its relative url and want to list the sub folders of that folder.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file by url to file system
Downloads a single file by server relative url to file system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder/file.txt". |
| Local filename | Full path where to download file. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have write access to the file. If the file already exists, it is overwritten. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file by url to stream
Downloads a single file by server relative url to a simple variable (stream).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder/file.txt". |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file to file system
Downloads a single file from Document Library by path to file system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Remote filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Local filename | Full path where to download file. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have write access to the file. If the file already exists, it is overwritten. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file to stream
Downloads a single file to a simple variable (stream).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Upload file from bytes
Uploads a single file from a Table of bytes to a SharePoint Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source bytes | Table (consisting of bytes) to read from |
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename to use in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Overwrite if exists | Specifies whether to overwrite remote file if it already exists or abort |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Upload file from local file system
Uploads a single file from file system to a SharePoint Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | Full path to file to upload. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have access to the file. |
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Remote filename | Remote filename to use in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Overwrite if exists | Specifies whether to overwrite remote file if it already exists or abort |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Upload file from stream
Uploads a single file from a stream to a SharePoint Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source stream | Simple variable containg a stream |
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename to use in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Overwrite if exists | Specifies whether to overwrite remote file if it already exists or abort |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Set description
Set a new description on a Document Library
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| New description | New description to set on Document Library |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Set name
Set a new title on a Document Library
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| New title | The new title |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Add attached file (from bytes)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Source bytes | Table (consisting of bytes) to read from |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from file system)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Local filename | Full path to file to upload. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have access to the file. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from stream)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Filename | Remote filename |
| Source stream | Simple variable containg a stream |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete all attached files
Delete all attachments on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete attached file
Delete an attachment on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
| 1000005 | File not found. |
List attached files
Lists all files attached to specified task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get task information by ID
Get information such as start date, due date etc about a task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get task information by name
Get information such as start date, due date etc about all tasks with given name.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task name | Name of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Get task information by query
Gets information about tasks by provided CAML Query. Example to get all tasks that are 50% or more completed:
<View>
<Query>
<Where>
<Geq>
<FieldRef Name='PercentComplete' />
<Value Type='Number'>0.50</Value>
</Geq>
</Where>
</Query>
</View>
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| CAML Query | The query to send to SharePoint. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Get task property value
Gets the value of a field of a given task. This is an advanced operation that require deeper knowledge on how SharePoint works. The Property parameter is the identifier of a field, which might not be the same as is displayed in SharePoint. E.g use 'Body' as Property to update 'Description'.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Property | Name of property |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
List tasks
Lists all tasks.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Row limit | Limit on how many tasks to list. A value of -1 indicates no limit |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List fields of tasks
Lists the fields that are available for tasks in Task app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Include read only fields | Specifies whether to include fields that can only be read in the results of the operation |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List tasks assigned to current user
Lists all tasks assigned to current user. Optionally including finished tasks.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Include already finshed tasks | Specifies whether to also include completed tasks |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List tasks assigned to specific user
Lists all tasks assigned to specified user. Optionally including finished tasks.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| User ID | ID of user |
| Include already finshed tasks | Specifies whether to also include completed tasks |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Add predecessor
Adds an existing task as a predecessor to provided task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Predecessor task id | ID of predecessor task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get predecessors
Gets all predecessors of given task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Remove all predecessor
Removes all predecessor of provided task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Remove predecessor
Removes a predecessor of provided task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Predecessor task id | ID of predecessor task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Assign task to user (by username)
Assign a task to given SharePoint user (by username).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Username | Username of user to assign task to |
| Remove other assignees | Specfies whether to remove other assignees. Default true |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete task
Deletes task with given ID.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Set task as finished
Sets the percent complete to 100%.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Update task progress
Updates the progress of a given task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| New progress | New progress in % |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Update task property
Updates a field of a given task. This is an advanced operation that requires deeper knowledge on how SharePoint works. The Property parameter is the identifier of a field, which might not be the same as is displayed in SharePoint. E.g use 'Body' as Property to update 'Description'.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Property | Name of property |
| Value | New value of property |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Create new subtask
Creates a new subtask in a Task app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Parent Task ID | ID of parent task |
| Task name | Name of new subtask |
| Start date | When task is to be started |
| Due date | When task is to be finished |
| Percent complete | How much of task that is finished. Default 0 |
| Description | Description of task |
| Priority | Priority of task |
| Status | Status of task |
| Assigned to (user ID(s)) | User ID to assign task to, if any |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Create new task
Creates a new task in a Task app. Returns the ID of created task in Results.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task name | Name of new task |
| Start date | When task is to be started |
| Due date | When task is to be finished |
| Percent complete | How much of task that is finished. Default 0 |
| Description | Description of task |
| Priority | Priority of task |
| Status | Status of task |
| Assigned to (user ID(s)) | User ID to assign task to, if any |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Assign user to group
Assigns a user to a group
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Group id | Id of group |
| Login name | Login name of user, not id |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Detach user from group
Detaches the user from the group
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Group id | Id of group |
| Login name | Login name of user, not id |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List site groups
Gets and list all site groups
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List users by group id
List all users assigned to a group.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Group id | Id of group |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Get user by ID
Get information about a SharePoint user.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| User ID | ID of user |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Get user by Login name
Get information about a SharePoint user.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Login name | Login name of user, not id |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List users
Get list of all users at site.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Microsoft SharePoint 2013
The SharePoint 2013 connector can be used to integrate with various apps in SharePoint 2013.
Business systems
Email Connector
User the email connector to send email in your workflow. It is possible to use Flow script in the email connector to make the email more informative.
TODO
Create directory
Creates a directory at the FTP server. It is not possible to create several levels of directories in one step. If you want to create the directory "./dirA/dirB", the directory "./dirA" must exist. Otherwise you have to do it in two steps; first creates directory "./dirA" and the second one created "./dirA/dirB".
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to the directory to create. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete empty directory
Deletes specified empty directory. Note if directory contain a file it will return an error.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to directory to delete |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if directory exists
Determains whether directory at specified path exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if directory exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
List directory
Lists all files and directories in a specified path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
| Mask | Mask to use when filtering items in directory. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B" |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Include files | Specifies whether to include files in the listing. |
| Include directories | Specifies whether to include directories in the listing. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also search in subdirectories. |
Output
A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file or directory. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since
6.3
See also
Download single file
Downloads a file from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded file. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download multiple files
Downloads multiple files from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to downloaded files from. |
| Remote mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded files. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| File copy mode | Specifies what to do with the file after download has been completed. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to download files from sub directories recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download stream
Downloads a file from FTP server and store it as Flow variable.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
Output
Simple value (binary stream).
Since
6.3
See also
Delete file
Delete a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to file to delete. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete files
Delete multiple remote files based on mask.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path where to delete files. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to delete files recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if file exists
Checks if a remote file exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if file exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Get file time
Get a remote file time.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
Output
Simple value, Date.
Since
6.3
See also
Get list of files
Get list of files in a directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
Output
A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since
6.3
See also
Get size of file
Gets the size, in bytes, of remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | File of interest. |
Output
Simple value, numeric.
Since
6.3
See also
Rename file
Renames a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Old path | Current name of file. |
| New path | New name of file. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Set file time
Changes a remote file time.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
| New time | New time for the file. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Clear Command Channel
Clears command channel encryption state, turning off SSL/TLS encryption.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Graceful SSL Closure | Send closure notification to the server. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Get Server System
Get server system operating system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output
Single value, text.
Since
6.3
See also
Send Command
Sends a command to the FTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Send Command | Command to send. Send NOOP for a dummy message. |
Output
Single value, text. Returs a error code.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload single file
Uploads a single file from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | File to upload. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the file. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload multiple files
Uploads multiple files from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local path | Path where to upload files from. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to upload. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Remote path | Path where to upload the files. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also upload from subdirectories. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload stream
Uploads the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream. This can for instance be used to upload data from a camera input.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local stream | Stream to read data from. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the data. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
FTP
The FTP Connector is used to upload and download files from an FTP server. It can also perform other operations such as creating remote directories and list files and directories on the FTP server.
Configuration
- Address. Address to FTP server.
- Port. Port to use, usually 21.
- Username. Username for a user on the FTP server.
- Password. Password for a user on FTP server.
- Communication settings
- Transfer type. ASCII or Binary (recommended), default is Binary.
- Concurrent connections.
- Concurrent connections.
- SSL / TSL settings
- Use SSL / TLS. To enable a secure connection between client and server. Enabled is recommended.
- Encrypt data channel. If enabled the data transfer will be encrypted, otherwise only command channel will be encrypted.
- SSL Mode.
- Implicit the connection is performed to the dedicated port (usually 990), and immediately starts SSL negotiation (without sending AUTH command).
- Explicit the client connects to the generic FTP port (21), and then sends AUTH command.
- ExplicitManual mode
- Client certificate patch. Path to the clients certification.
- Auth command. Specifies an authorization command that should be sent to server to request an explicit SSL session. Different servers support different commands, so in most cases it is a good idea to set this to Auto.
- Auto. Try to specify command supported by server automatically.
- AuthTLS. Use AUTH TLS command.
- AuthSSL. Use AUTH SSL command.
- AuthTLSP. Use AUTH TLS-P command (protected data channel).
- AuthTLSC. Use AUTH TLS-C command (clear data channel).
- Validate server. If enabled the client validates server.
- Server certificate path. Path to the server certification.
- FTP Version. The secure version of SSL or TLS. Default SSL Version 3 and TLS Version 1.0. -Validation options.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of FTP Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the FTP Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
Operations
| Directory operations |
|---|
| Check if directory exists |
| Create directory |
| Delete empty directory |
| List directory |
| Download operations |
|---|
| Download multiple files |
| Download single file |
| Download stream |
| File operations |
|---|
| Check if file exists |
| Delete file |
| Delete files |
| Get size of file |
| Rename file |
| Set file time |
| Get time of file |
| Get list of files |
| Upload operations |
|---|
| Upload multiple files |
| Upload file |
| Upload stream |
| Server operations |
|---|
| Send Command |
| Clear Command Channel |
| Get Server System |
Modbus
All commands can be sent in synchronous or asynchronous mode. If a value is accessed in synchronous mode the program will stop and wait for slave to response. If the slave didn't answer within a specified time a timeout exception is called. The class uses multi threading for both synchronous and asynchronous access. For the communication two lines are created. This is necessary because the synchronous thread has to wait for a previous command to finish.
Operations
| Read operations |
|---|
| Read Coils Inputs |
| Read Digital Inputs |
| Read Holding Register |
| Read Inputs Register |
| Write operations |
|---|
| Read Write Multiple Holding Register |
| Write Multiple Coils |
| Write Multiple Holding Register |
| Write Single Coil |
| Write Single Holding Register |
Read Coils
Reads Coils
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values, true or false.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Digital Inputs
Read Digital Inputs
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values, true or false.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Holding Register
Read Holding Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Input Register
Read Input Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Write Multiple Holding Register
Read Write Multiple Holding Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
| First address to be written | Length of data. |
| Holding register inputs to be written | Contains the register information. |
Output
Return table with values.
Since
6.4
See also
Write Coil
Write Coil
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
Write Single Register
Write Single Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data written begins. |
| Holding register input to be written. | Value to write on the address. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
Write Multiple Coils
Write Multiple Coils
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data written begins. |
| Number of addresses to be set. | Values to be set. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
Write Multiple Registers
Write Multiple Registers
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Values to write. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
External Oauth 2.0 provider
There are no settings, only choose what variable you would like to output the token to. This variable can be used in conjuction the REST connector to access Oauth 2.0 authenticated resources, like azure graph api
Create directory
Creates a directory at the SFTP server. It is not possible to create several levels of directories in one step. If you want to create the directory "./dirA/dirB", the directory "./dirA" must exist. Otherwise you have to do it in two steps; first creates directory "./dirA" and the second one created "./dirA/dirB".
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to the directory to create. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete directory
Deletes specified directory. Note that the directory must be empty unless Recursive is set to true.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to directory to delete |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also delete all files and subdirectories. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if directory exists
Determains whether directory at specified path exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if directory exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
List directory
Lists all files and directories in a specified path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
| Mask | Mask to use when filtering items in directory. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B" |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Include files | Specifies whether to include files in the listing. |
| Include directories | Specifies whether to include directories in the listing. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also search in subdirectories. |
Output
A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file or directory. |
| IsDirectory | True if the item is a directory, false if it is a file. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
| LastAccessTime | Last time item was accessed. |
| LastModifiedTime | Last time the item was modified. |
| CreationTime | Time of item creation. |
Since
6.3
See also
Download single file
Downloads a file from the SFTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded file. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download multiple files
Downloads multiple files from the SFTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to downloaded files from. |
| Remote mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| File copy mode | Specifies what to do with the file after download has been completed. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to download files from sub directories recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download stream
Downloads a file from SFTP server and store it as Flow variable.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
Output
Simple value (binary stream).
Since
6.3
See also
Copy remote file
Copies a remote file into the selected destination.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote source path | Path where to copy from. |
| Remote destination path | Path where to copy to. |
| Overwrite if already exists | True or false. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete file
Delete a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to file to delete. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete files
Delete multiple remote files based on mask.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path where to delete files. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to delete files recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if file exists
Checks if a remote file exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if file exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Get size of file
Gets the size, in bytes, of remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | File of interest. |
Output
Simple value, numeric.
Since
6.3
See also
Rename file
Renames a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Old path | Current name of file. |
| New path | New name of file. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload single file
Uploads a single file from the Flow Server to the SFTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | File to upload. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the file. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload multiple files
Uploads multiple files from the Flow Server to the SFTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local path | Path where to upload files from. |
| Local mask | Mask used to filter which files to upload. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Remote path | Path where to upload the files. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also upload from subdirectories. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload stream
Uploads the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream. This can for instance be used to upload data from a camera input.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local stream | Stream to read data from. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the data. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
SFTP
The SFTP Connector is used to upload and download files from an SFTP server. It can also perform other operations such as creating remote directories and list files and directories on the SFTP server.
Operations
| Directory operations |
|---|
| Check if directory exists |
| Create directory |
| Delete directory |
| List directory |
| Download operations |
|---|
| Download multiple files |
| Download single file |
| Download stream |
| File operations |
|---|
| Check if file exists |
| Copy remote file |
| Delete file |
| Delete files |
| Get size of file |
| Rename file |
| Upload operations |
|---|
| Upload multiple files |
| Upload file |
| Upload stream |
Siox
Before using the Siox connector you need the Siox driver from the Siox website. You can also find the documentation for all the operation if you download the Siox SDK.
Communication
BarTender 2016
The BarTender 2016 connector can be used to integrate with BarTender, typically to print BarTender documents.
32-bit version of BarTender 2016 R8 Automation Edition or Enterprise Automation Edition needs to be installed on the same machine as Flow Server.
List printers
Lists all printers available.
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a table with information about printers |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Print BarTender Document
Prints a BarTender document to specified printer or to an image (printing to image requires Enterprise Automation Edition).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Printer | Printer to print to, leave empty to use default printer |
| Print job name | Name of print job, can be omitted |
| Document password | If applicable, the password to use in order to print the document |
| Number of identical copies to print | If supported, specifies how many identical copies to print |
| Embedded data | Values to embedded data can be provided here. The members of this record parameter depends on the BarTender document. See this for example of usage |
| Text file database | If the document reads data from a text file, this section can be used to configure it. More information about this parameter below. |
| Database connection | If the document reads data from a database, this section can be used to configure it. More information about this parameter below. |
| Print to image preview | This section can be used to configure that the document should be printed to an image instead of a printer. Requires Enterprise Automation Edition of BarTender |
Text file database
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| File name | File to use as input. Relative to Flow Server or, if not a complete path, relative to where the BarTender document is located. |
| Delimitation | Specifies how fields are separated in text file |
| Field delimiter | Specifies what character is used to delimit fields if Delimitation is Custom |
| Number of fields | The number of fields to consider when reading text file (if file contains more data than needed) |
| Use field names from first record | Specifies whether the first row of the file contains the field names. |
| Flow table | If specified, overrides File name and data is read from the provided table. See this for example of usage |
Database connection
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of database |
| User ID | Database user to login to the database with, if applicable |
| Password | Password for given database user, if applicable |
| SQL Statement | Specifies the SQL to execute. |
| File name | Specifies path to file, if applicable, for instance if Microsoft Access or Microsoft Excel is used. |
| Server | The database server to connect to, if applicable |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a message from BarTender, typically information about the printing |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occurred |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | Failed to print. |
| 1000002 | Failed due to timeout. |
Print from BTXML script (from file)
Sends a BTXML Script to BarTender.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Filename | Full path to file containing BTXML Script |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a record with the xml response from BarTender and a table with messages from BarTender |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Structure of Results
Results- Text
- ID
- Severity
- Category
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Print from BTXML script (from string)
Sends a BTXML Script to BarTender.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Script value | String containing the BTXML Script |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a record with the xml response from BarTender and a table with messages from BarTender |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Structure of Results
Results- Text
- ID
- Severity
- Category
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Html to PDF Connector
Use the PDF connector to create PDF files in your workflow. The connector uses Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) to define the layout of your PDF pages and fully supports using FlowScript.
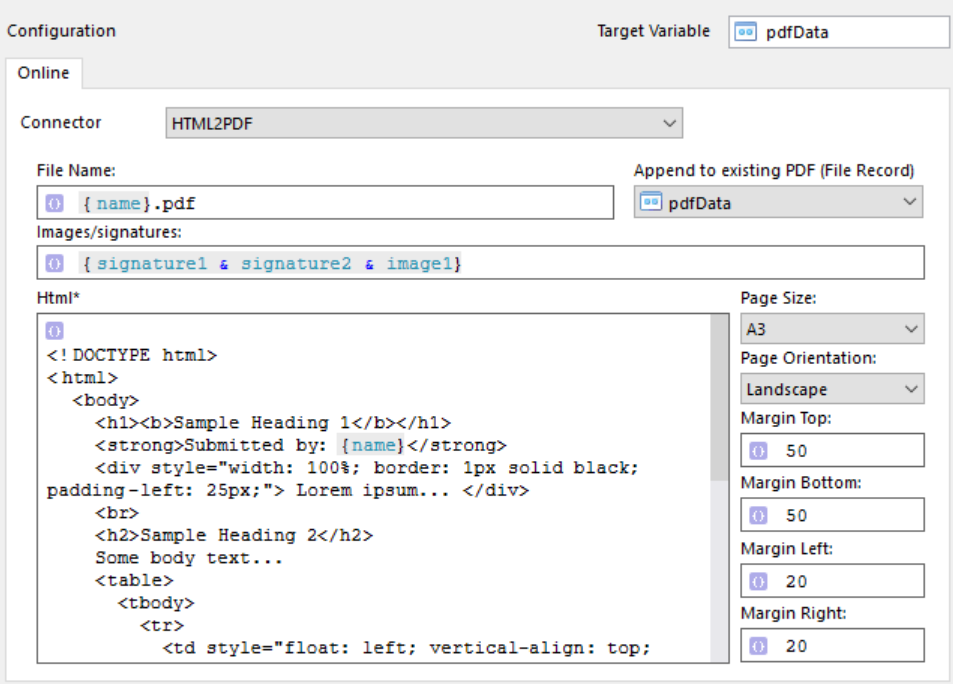
Connector Output
The output from the connector is a standard file record: [filename:the_file_name, data:binary_pdf_data].
General Tips & Tricks
In most use cases, you want to take control over the page breaks in your document. In order to achieve this, you need to specify a maximum length for all dynamic data in your workflow and specify the height of the elements which contains the dynamic data using the HTML DOM Style height property. If you do not to this, the document will grow with its content and you might get undesirable page breaks.
Tip: Create a simple workflow with a PDF connector and a user step. In the user step, add a file gallery with the generated PDF document(s)
and use the workflow for designing and debugging your page layouts.
Another good practice is to use one machine step per page and then supply the previous PDF document (file record) as input parameter for the next PDF task (see Append a new page to an existing PDF below).
Settings
This chapter describes the available settings in the PDF connector.
File Name
This string defines the filename-key value of the target file record (see Connector Output).

Append new page to an existing PDF
The connector optionally takes a file record containing a PDF file as an input variable. If suppied, the new page(s) created in the current machine step will be appended to the existing PDF file. The target variable will contain the merged PDF file as a standard file record.
To keep the file name from the previous PDF step, just re-use the filename value from the previous PDF file record:

Margins
The margin size in points (one inch = 72 points).

Page Size
Page Orientation
Choose between Portrait and Landscape orientation. The default orientation is Portrait.
Images / Signatures
If you need to display images or signatures in your PDF pages, you need to make sure to have them available in your flow as file records. Signatures from the signature input provider is by default a file record with some extra fields and are supported by the PDF connector. The Images / Signatures field takes either a file record or a table of file records. The image below gives an example of two signature records being passed to the PDF connector.
In order to be able to differentiate between the images/signatures in the HTML code, you might need to override the filename
component of the file records and give them unique and identifiable file names prior to passing them to the PDF connector. The image below shows a file name being overriden in an assignment step.
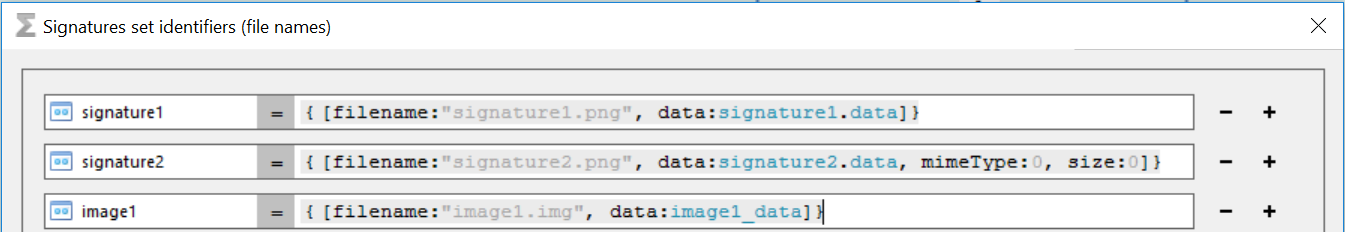
To position your image/signature in the document, the HTML IMG tag is used. I.e. <img src=your_file_name.jpg
height=40
>. See the image under the HTML headline below.
HTML
The document layout is defined using HTML. It's recommended to keep the code as simple as possible and build the layout using a bottom-up approach. If you are new to HTML, visit https://wordhtml.com/. However if you use the generated code directly you will get disappointed as there are some important aspects to keep in mind. Most importantly, you need to use percentages instead of absolute values for width. Keep the total width of your columns at about 95%.
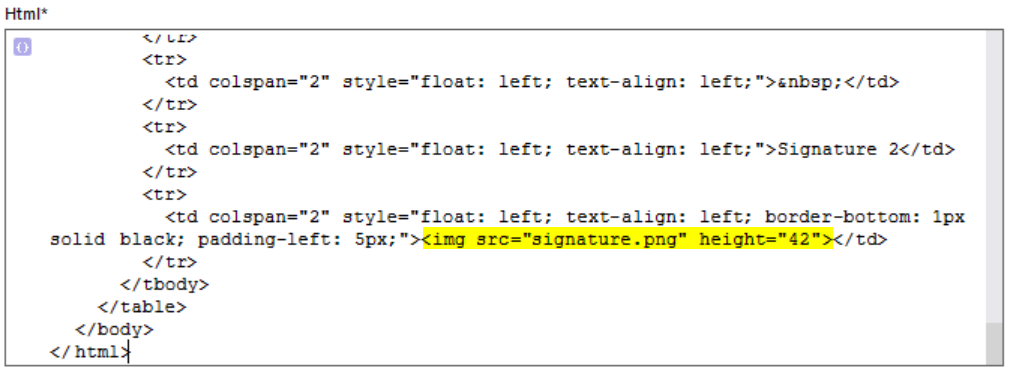
NiceLabel
Printing
Create directory
Creates all the directories at specified path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to create. Allow subdirectories on path will also be created if they do not exist. |
| Allow Everyone to have full control over directory | If set to True, all users have full control over directory. If set to False, only the user the Connector is running as can access the directory. Default True. |
Output
Simple value containing the path to the newly created directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Delete directory
Deletes directory at provided path. Directory must be empty unless 'Also delete all subdirectories (and files)' is true.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to delete. |
| Also delete all subdirectories (and files) | If set to True, all files and subdirectories will be deleted. If set to False, the directory must be empty in order to delete it. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if directory was successfully deleted. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Delete files in directory
Deletes all files in directory matching specified pattern.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to the directory to delete files from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match files against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. Default value "*". |
Output
Simple value, number of files deleted.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if directory exists
Determains whether directory at specified path exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if directory exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Get directory modification times
Gets a record containing directory modification times.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get modification times from. |
| As UTC | True to get the modification times in UTC |
Output
Record with members 'CreationTime', 'LastWriteTime' and 'LastAccessTime'.
Since
6.0
See also
Get all subdirectories of directory (full path)
Gets the full path of all subdirectories of given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get file names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match directories against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. Default value "*". |
| Also get directories in subdirectories | Specifies whether to also include directories in subdirectories of Path. Default value False. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is a full path to directory in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Get name of all subdirectories of directory
Gets the names of all directories in given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get directory names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match directories against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is the name of a directory in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Get name of files in directory
Gets the names (including extension) of all files in given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get file names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match files against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is the name of a file in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Get files in directory (full path)
Gets the full path of all files in given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get file names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match files against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. Default value "*". |
| Also get files in subdirectories | Specifies whether to also include files in subdirectories of Path. Default value False. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is a full path to file in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Move directory
Moves a directory to a new location.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source path | The path to directory to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Destination path | The path to directory to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Overwrite destination directory if it exists | If set to True and destination path already exists, it is overwritten. If set to false and destination path already exists, no move operation is done. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if directory was successfully moved. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Appends all lines to file
Appends all provided lines to a file. If the file does not exist, it is created.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to append lines to. |
| Lines | Lines to append. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the lines in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Appends all text to file
Appends all provided text to a file. If the file does not exist, it is created.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to append text to. |
| Text to append | Text. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the text in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Copy file
Copies a file to a new location.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source | The file to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Destination | The location of the file. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Overwrite if destination file exists | If set to True and destination file already exists, it is overwritten. If set to false and file already exists, no copy operation is done. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file was successfully copied. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Delete file
Deletes file at provided path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to file to delete. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file was successfully deleted. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Check if file exists
Determains whether file at specified path exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to the file to check. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Get files modification times
Gets a record containing files modification times.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get modification times from. |
| As UTC | True to get the modification times in UTC. |
Output
Record with members 'CreationTime', 'LastWriteTime' and 'LastAccessTime'
Since
6.0
See also
Move file
Moves a file to a new location.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source | The file to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Destination | The location of the file. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Overwrite destination file if it exists | If set to True and destination file already exists, it is overwritten. If set to false and file already exists, no move operation is done. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file was successfully moved. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Read all bytes from file
Reads all bytes from a file and puts it a Table variable. Reading too large files can cause performance issues.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to source file to read lines from. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is one byte from source file.
Since
6.0
See also
Read all lines from file
Reads all lines from a file and puts it a Table variable. Reading too large files can cause performance issues.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to source file to read lines from. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to read the file in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is one line in source file.
Since
6.0
See also
Read all text from file
Reads all text from a file and puts it a simple value variable. Reading too large files can cause performance issues.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to source file to read text from. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to read the file in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
Simple value variable (string), with all content of file in it.
Since
6.0
See also
Write all bytes to file
Writes all provided bytes to a file. If the file already exist, it is overwritten.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to append text to. |
| Bytes | A Table containing one column, value, with numeric values (byte, 0-255). |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Write all lines to file
Writes all provided lines to a file. If the file already exist, it is overwritten..
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to write lines to. |
| Lines | Lines to write. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the lines in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Write all text to file
Writes all provided text to a file. If the file already exist, it is overwritten.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to write text to. |
| Text to write | Text. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the text in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.1.6
See also
Write stream to file
Writes the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream to a file. This can for instance be used to write data from a camera input to the file system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to write stream to. |
| Source stream | Stream to write. Must be a Flow variable. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.2
See also
Add single file to zip
Compresses a single file and adds it to a zip file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| File | File to add to archive. |
| Path to zip file | Zip file to add file to. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
| Replace mode | Specifies what to do if a specific file already exists in the archive. |
| Compression level | Specifies the level of compression, valid values are 1-9 where 9 indicates highest level of compression (and slowest). Default value is 6. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Add stream to zip
Compresses the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream. This can for instance be used to compress data from a camera input.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Stream | Stream to read data from. |
| Filename for stream in zip file | The name of the file in the archive the content of the stream should be written to. |
| Path to zip file | Zip file to add stream content to. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
| Replace mode | Specifies what to do if a specific file already exists in the archive. |
| Compression level | Specifies the level of compression, valid values are 1-9 where 9 indicates highest level of compression (and slowest). Default value is 6. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Extract files from zip
Extracts all files from a zip file which matches provided mask.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path to zip file | Zip file to extract from. |
| Destination path | Path where to extract files to. If file or directory already exists at destination path, it is skipped (not overwritten). The directory should exist before this operation is called. |
| Filter | Filet to use when filtering items in archive. Example "*.txt". |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Extract file to stream
Extracts a single file to a stream. The entire file will be loaded into memory, so do not use this operation with large files.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path to zip file | Zip file to extract from. |
| Filename | The name of the file in the archive to extract. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
Output
Simple value, read-only binary stream trinket.
Since
6.3
See also
Add folder to zip file
Zips all files and subfolders in a folder into a zip file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to read files and folders from. |
| Path to zip file | Zip file to add folder content to. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
| Replace mode | Specifies what to do if a specific file already exists in the archive. |
| Compression level | Specifies the level of compression, valid values are 1-9 where 9 indicates highest level of compression (and slowest). Default value is 6. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
File System
The File System connector can be used to perform directory and file operations on any file system which the Flow Server can access.
Operations
| Zip operations |
|---|
| Add folder to zip file |
| Add single file to zip |
| Add stream to file |
| Extract file to stream |
| Append all text to file |
Read/Write to Flow Environment
The Flow Environment Connector can be used to read information from the flow 6 database, it can also write new data to said database.
Operations
These are the functions that the connector supports, the flow connector can fetch data and write/update data to the flow 6 database. All operations either returns a table, row or a true/false boolean depending on if the operation was successful or not.
Connector
- Get connector name and species - Fetches a table of each connector with its type (species) and name.
Language
- Get Languages - Fetches a table of all languages set in the environment.
- Add or update language - Set a new language with two parameters/use record with parameters in it:
Code: Language code e.g "SV"Name: Name of the language e.g "Swedish"
- Delete Language - Delete an existing language set in the environment/use record with parameter in it:
Code: Language code e.g "SV"
Properties
- Get properties - Fetches all properties.
- Get user properties - Fetches all properties their types and values connected to the user ID provided:
User ID: The Flow User you wish to get property information from.
- Get user type properties - Fetches the name of all properties that are not global.
- Get global type properties - Fetches the name of all properties that are global
- Add property - Adds a new property:
Name: the name of the propertyType: table or textColumn only used in table: name of the column/sScope: global or userValue only used in global scope: static value
- Get property types - Returns what types of properties that are present in the environment.
- Get property scopes - Return what property scopes that are present in the environment.
- Delete property - Deletes a property using the property name:
Name: the name of the property that is to be deleted
- Set value of global property - Sets the value of a global property:
Name of property: the name of the property that the value is added toNew value: the value of the property
Roles
- Add or update/delete Role Group - Adds/deletes or update an existing role group:
Group ID: Id of the role groupGroup Name: Display name of the role groupInherit Children: true/false if the role group will inherit children
- Add roles to Role Group/Delete roles from role group - Adds/deletes roles to a role group:
Group ID: id of the role group the roles will belong toRoles: a table containing the columns "Path" and "DisplayName"Path points towards the Rolegroup/Role e.g "Administrators/ITadmins" where Administrators is the rolegroup and the ITadmins is the role. Displayname is the displayname of the role
- Get Role group by group ID - Returns a row containing Name, DisplayName, Inheritchildren and a table containing all role paths.
- Get role groups - Returns a table containing Name, DisplayName, Inheritchildren and a table containing all role paths.
- Add/delete roles to user - Assigns/deletes a role to a user:
User ID: User ID that is to receive the roleA table containing: Path - path to the role in the format "RolegroupID/Role" DisplayName - The displayname of the role
- Get assigned user roles - Returns a table with Path and DisplayName columns.
Users
- Add or update user/from record - Adds or updates a user:
Name: mame of the userActive: true/false if the user is activeUser ID: the User ID of the userAccess level: sets the access level of the user e.g "Work"Group: assigns the user to a groupType: assigns the user to a user-type e.g "FullUser"Password: sets a password for the userEmail: sets the email for the userLanguage: sets the language of the user by using lang codes e.g "SV"
- Delete user - Deletes a user in the environment:
User ID: which User ID that is to be deleted
- Get user by User ID - Returns a row with all user values.
- Get access levels - Returns a table with all access levels.
- Get types - Returns a table with all types.
- Get users - Returns a table of all users.
- Get user groups - Returns a table with all user groups.
- Set value of property on user - Sets the value of a property on a user:
User ID: the user to receive the property valueProperty Name: the name of the propertyValue: the value that is to be added (tables are not supported yet)
- Get value of property on user - Returns the value of a property:
User ID: the user to fetch the property fromThe property name to fetch the value from
- Set connector properties for user - sets the login/password for the connector:
User ID: the user id that will get the connector login/password addedConnector Name: the connector that is getting values addedConnector Username: the username for the connectorConnector Password: the password for the connector
PDF Connector
Use the PDF connector to create PDF files in your workflow. The connector uses Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) to define the layout of your PDF pages and fully supports using Flow Script.
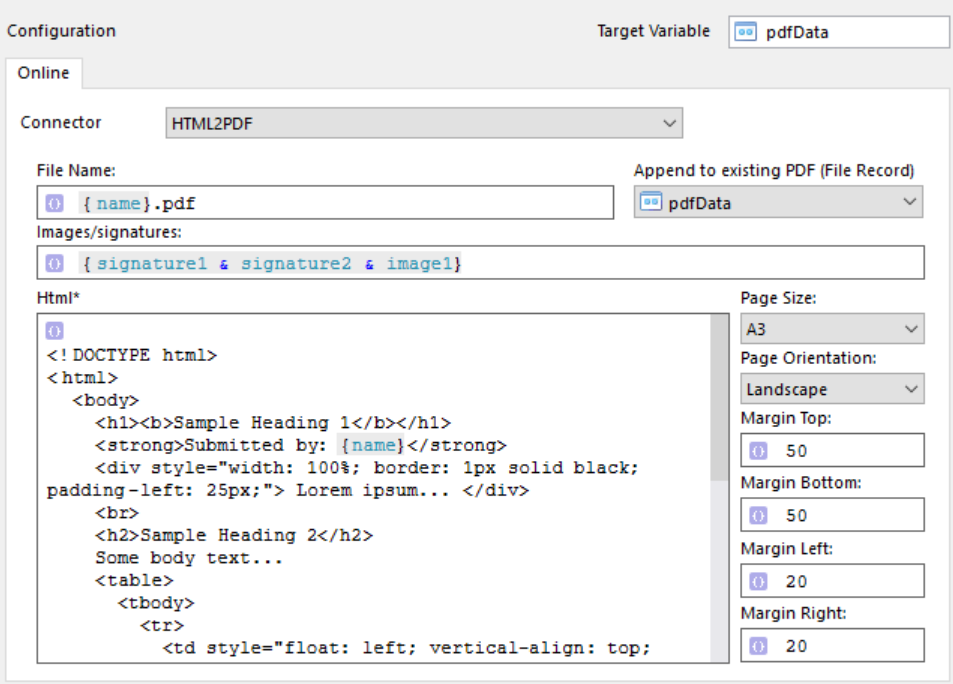
Connector Output
The output from the connector is a standard file record: [filename:the_file_name, data:binary_pdf_data].
General Tips & Tricks
In most use cases, you want to take control over the page breaks in your document. In order to achieve this, you need to specify a maximum length for all dynamic data in your workflow and specify the height of the elements which contains the dynamic data using the HTML DOM Style height property. If you do not to this, the document will grow with its content and you might get undesirable page breaks.
Tip: Create a simple workflow with a PDF connector and a user step. In the user step, add a file gallery with the generated PDF document(s)
and use the workflow for designing and debugging your page layouts.
Another good practice is to use one machine step per page and then supply the previous PDF document (file record) as input parameter for the next PDF task (see Append a new page to an existing PDF below).
Settings
This chapter describes the available settings in the PDF connector.
File Name
This string defines the filename-key value of the target file record (see Connector Output).

Append new page to an existing PDF
The connector optionally takes a file record containing a PDF file as an input variable. If suppied, the new page(s) created in the current machine step will be appended to the existing PDF file. The target variable will contain the merged PDF file as a standard file record.

To keep the file name from the previous PDF step, just re-use the filename value from the previous PDF file record:

Margins
The margin size in points (one inch = 72 points).

Page Size
Page Orientation
Choose between Portrait and Landscape orientation. The default orientation is Portrait.
Images / Signatures
If you need to display images or signatures in your PDF pages, you need to make sure to have them available in your flow as file records. Signatures from the signature input provider is by default a file record with some extra fields and are supported by the PDF connector. The Images / Signatures field takes either a file record or a table of file records. The image below gives an example of two signature records being passed to the PDF connector.
In order to be able to differentiate between the images/signatures in the HTML code, you might need to override the filename
component of the file records and give them unique and identifiable file names prior to passing them to the PDF connector. The image below shows a file name being overriden in an assignment step.
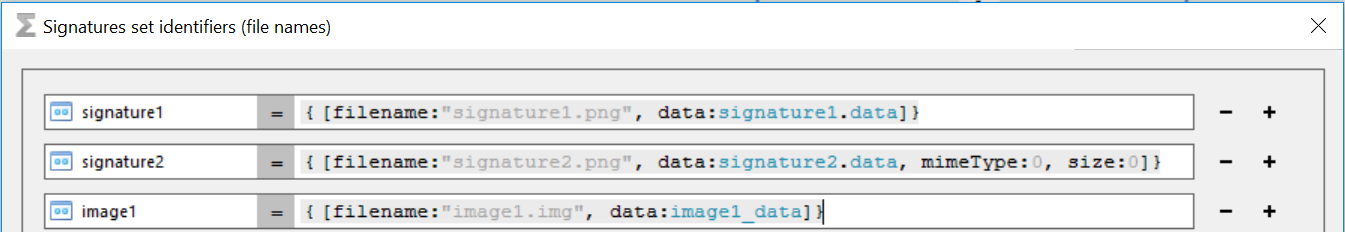
To position your image/signature in the document, the HTML IMG tag is used. I.e. <img src=your_file_name.jpg
height=40
>. See the image under the HTML headline below.
HTML
The document layout is defined using HTML. It's recommended to keep the code as simple as possible and build the layout using a bottom-up approach. If you are new to HTML, visit https://wordhtml.com/. However if you use the generated code directly you will get disappointed as there are some important aspects to keep in mind. Most importantly, you need to use percentages instead of absolute values for width. Keep the total width of your columns at about 95%.
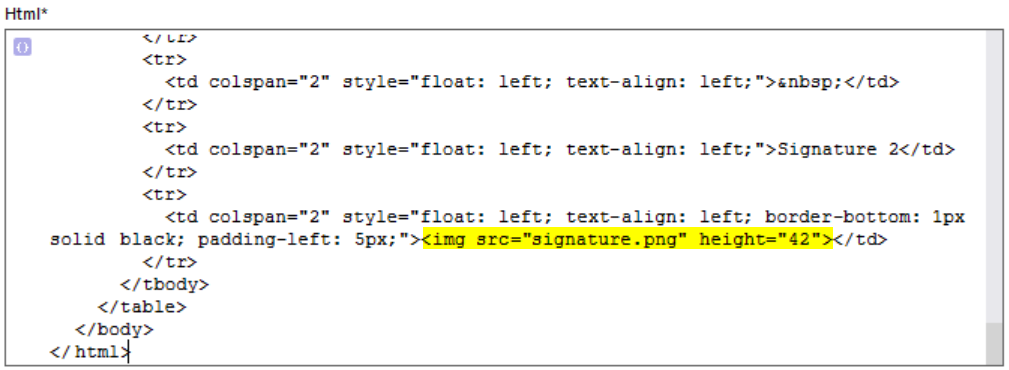
Utility
Pinned User Step
A pinned user step are an information
It is only possible to use Header, Static Text, Labeled Static Text, Link and List Presentation in pinned user steps, this because a pinned user step is only a why to show the user information.
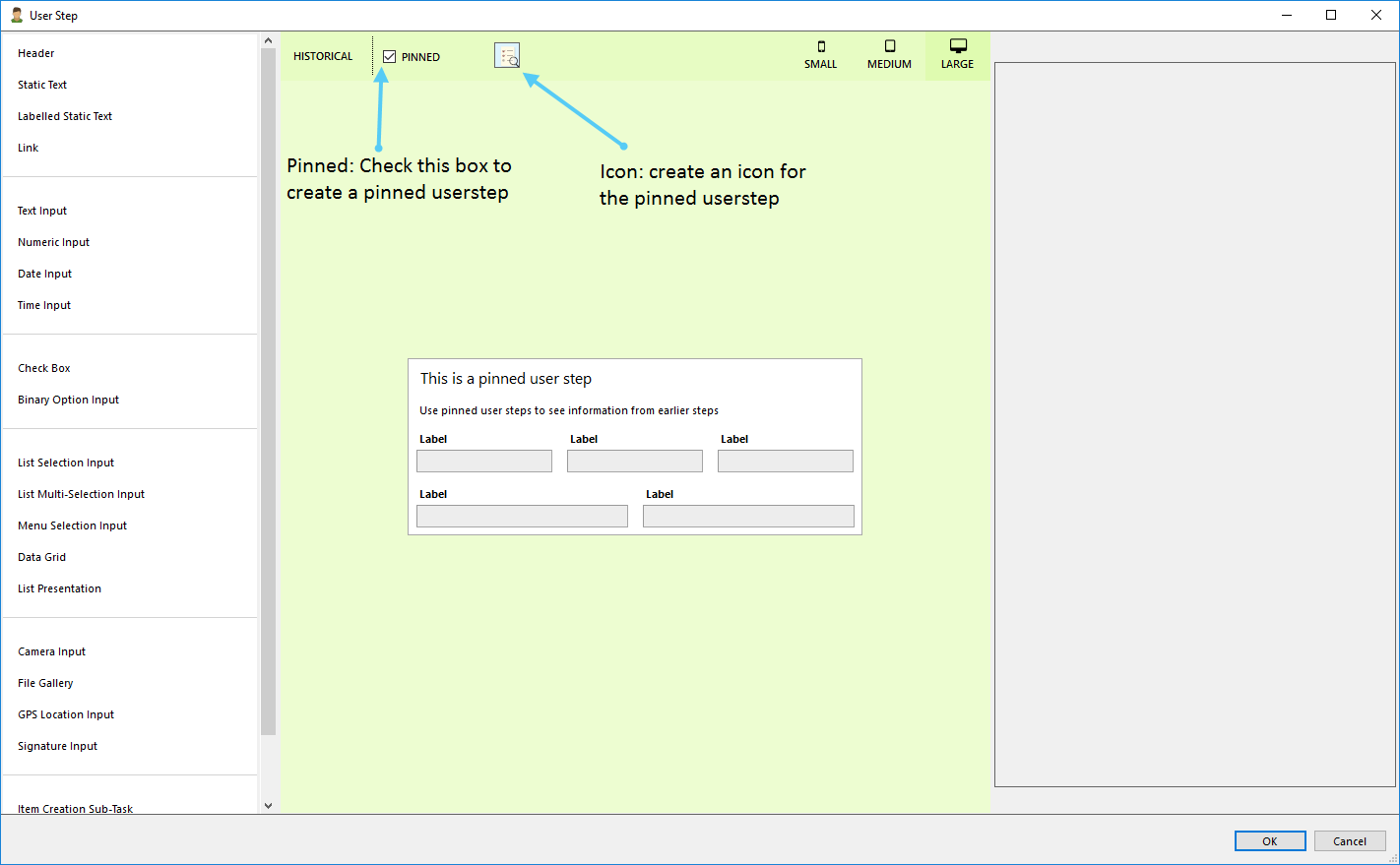
Configure a pinned user step
The pinned user step will show up in the side of the screen, and the user need to tap/click on the icon to extend or colaps the pinned user step. In the below picture is the pinned user step to the left and the regular user step to the right. If there is more then one pinned user step in the workflow, will the pinned user step be replaced when the user steps over another pinned user step.
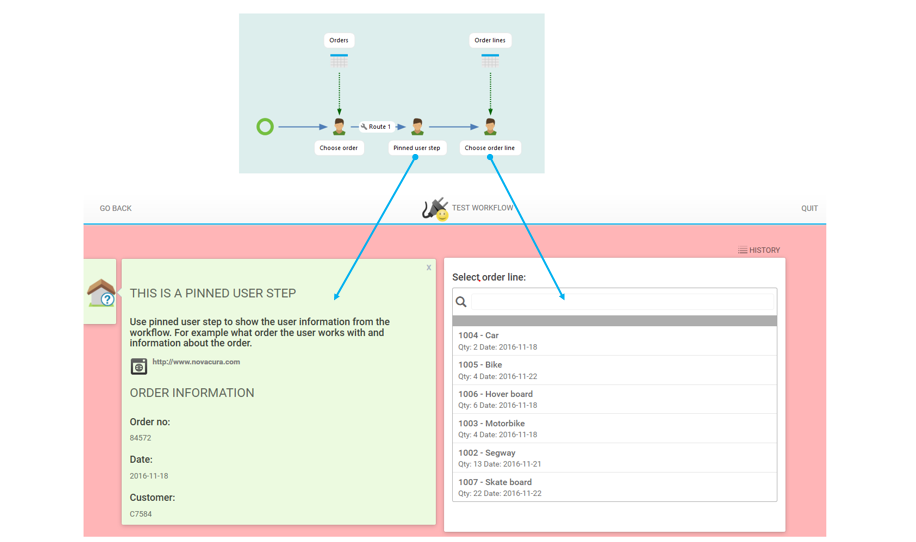
Pinned user step in the web client
Create an offline resource
Use an Offline resource to make data available in an offline workflow. When an offline resource is used, the button Offline data will be available in the clients. Under Offline data can the end user download data to the local device that will be used when executing offline workflows. For every Offline resource used in workflows available for the end user will one row show up under My offline data.
Use an Offline resource to get data in offline workflows.

Create a machine workflow that fetches the data needed and connect the Machine workflow to the Offline resource. The Machine workflow must be created as an Offline resource.
Use the output variable from the Offline resource to use the data from the Machine workflow.
Create an offline seed inbox
Seeded inbox can also be fetched from an offline resource. Create an offline resource and connect a machine workflow that fetches the data needed for the seed inbox. Add a machine step and connect the machine step to the start event with a data arrow. In the machine step refer to the output of the offline resource.
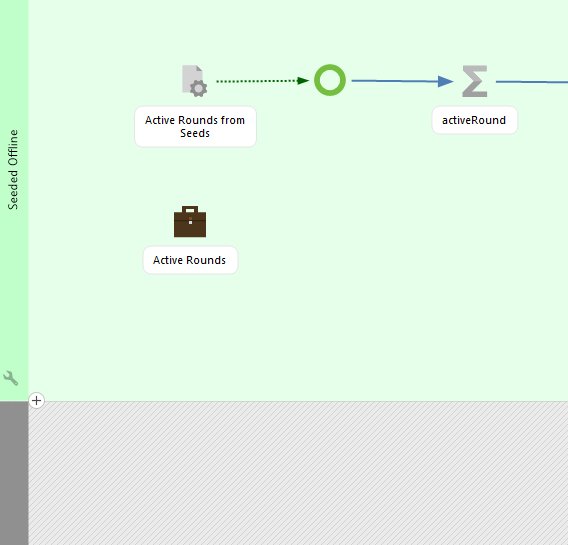
For every fetched row will an inbox item appear in the inbox.
Read more about how to setup a seeb inbox here
Create an offline workflow
When developing an offline workflow, all machine steps that writes data to a system must be placed in a machine swimlane to be able to create offline transactions; start with creating a regular User workflow.
Add one swimlane to the workflow with the plus sign. Change the mode for one of the swimlanes to offline and the mode of the other swimlane to machine.
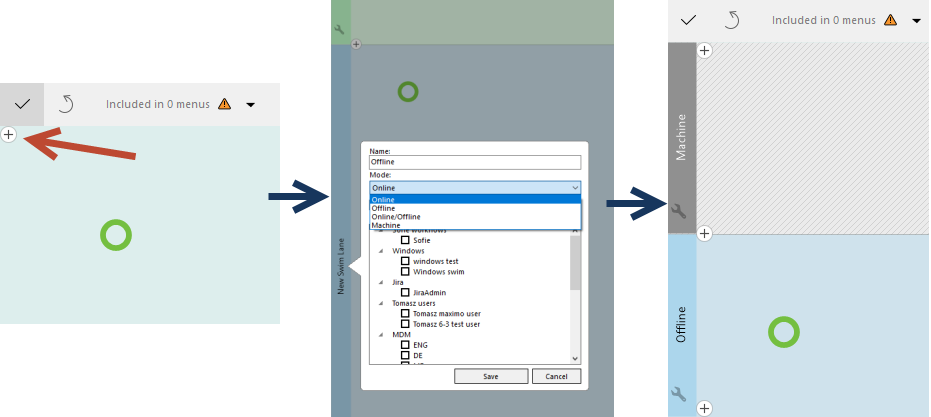
Create an offline transactions
All machine step that writes data to a system must be placed in the machine swimlane in the offline workflow. It is possible to either use the split step or end the workflow in the machine swimlane. A transaction will be created for every swimlane crossing that is executed.


Offline workflow
Two different levels of offline:
Built-in semi-offline:
- The fat clients only need connectivity when passing a cogwheel.
- Seed inbox items are downloaded and can be accessed without connectivity.
- Less network dependency and better mobile performance.
- Push cogwheels to the start and end events ? and you can be offline in between.
Constant offline:
- Offline Resources are used for supporting data (User Info, Equipment Structures, Lists etc.)
- Machine Swimlanes executes cogwheels on the server.
- A background job on the client handles data and transactions whenever there is connectivity.
- The user do not have to think about going online or offline.

Binary Option Input
A binary option interaction item is used when the operator needs to choose between two values. For example; they are used in conjunction with a decision step to allow the operator to pick a path through the workflow.
Binary option input have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which to store the chosen value of either option 1 or 2. - Option 1 text
The text to be displayed for option 1. - Option 2 text
The text to be displayed for option 2. - Default value
Enter a default value (value of option 1 or 2) as a default value. - Option 1 value
The value that should be put into the target variable for the option 1. - Option 2 value
The value that should be put into the target variable for the option 2. - Refuse option 1
The operator is only allowed to move forward through the workflow if he/she chooses the second option.
Calendar
A calendar with entries that can be viewed, added, edited and removed. Same table setup as in Data grid.
Blurbs
Use blurbs to present day specific data.
Enter a title of the blurb and either use text, variables or FlowScript to visulize data in the value field.
Use FlowScript to for example summarize data from the grid part of the calender control, and when the user enter the numbers in the grid the summarized value in the blurb will be live updated.
Examle:
Title: Reported
Value: {sum((dayEntries where internalQuantity > 0).internalQuantity)}
Configuration
Calendar start: Start date of the calendar.
Enter a date, example: 2018-05-05 or {now()-10}Calendar end: End date of the calendar.
Enter a date, example 2020-05-05 or {now()+10}Unavailable days: An unavailable day will be grey and not clickable.
Enter a date, example {selectedDay = "2018-05-05"} Enter multiple dates from a table, example {selectedDay in blocked.days}Selected date: This date will be selected by default when entering the step with the calendar view.
Enter a date, example 2018-05-05 or {now()-1}Read-only days: A read-only day will be red when it is choosed and it will not be possible to add, delete or edit the data grid for those days.
Enter a date, example 2018-05-05 or {now()-1} Enter multiple dates from a table, example {(selectedDay where status = 'Confirmed').days}
Style
Use a case statement to decide what color the columns should have based on a variables value.
Example:
{case when SelectedDay in table.column then "RED" else "" end}Or to mark a date that got entrie write for example:
{case when any(dayEntries) then "RED" else "" end}Edit columns:
First column in "edit columns" is grayed out. It's possible to choose source, edit title and include and enter output variable.
Camera Input
If the device has a camera the user will be able to take a picture with the camera input. If the camera input runs in a device without a camera the user will be able to choose a picture-file on the device.
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which the data stores. - Prompt
The label displayed above the camera input.
Example of the camera input in the Android client
Check Box Input
A boolean input interaction item is used when the operator needs to answer a true/false question of lesser importance. Boolean inputs show up as check boxes in the Flow Client.
Boolean inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which to store the choice entered. A positive choice (checked) creates a variable value of true, while a negative choice (unchecked) creates a variable value of false. - Prompt
The label to display over the check box input field. - Default Value
Either false (unchecked), true (checked) or a variable reference to a value of either false or true.
Sub Workflows
A sub workflow is put into a User Step
There are three types of sub workflows:
 Check List: Executes one workflow for each record in a list of things to do.
Check List: Executes one workflow for each record in a list of things to do.
Item Creation: Creates a new item for each time the sub workflow is executed.
Verb: A side track in the workflow where the sub workflow can be executed one or many times.
Check List Sub Task
A sub workflow is created from a User Step. Create a new User Step and add a sub workflow element. Configure the appearance of sub workflow in the client.
Set the following:
- Title: Title of the check list.
Icon: The icon that will be showed in the check list.
Target Variable: Enter a name for the output variable. The output from the sub workflow will end up in this new table variable.
- Source: Choose a table from the list of available table variables. Each row in the result from the table variable will be a row in the check list.
- Row Variable: Enter a varibale name, this vaiable will hold the source data of the choosen check list row and make the data available in the sub workflow.
- Sub Task Text: Text on the check list row.
Pills: The indicator on the sub workflow button.
- Pre-Blurbs: Information to the user, before taping/clicking on the check list row.
Post-Blurbs: Information to the user, after taping/clicking on the check list row.
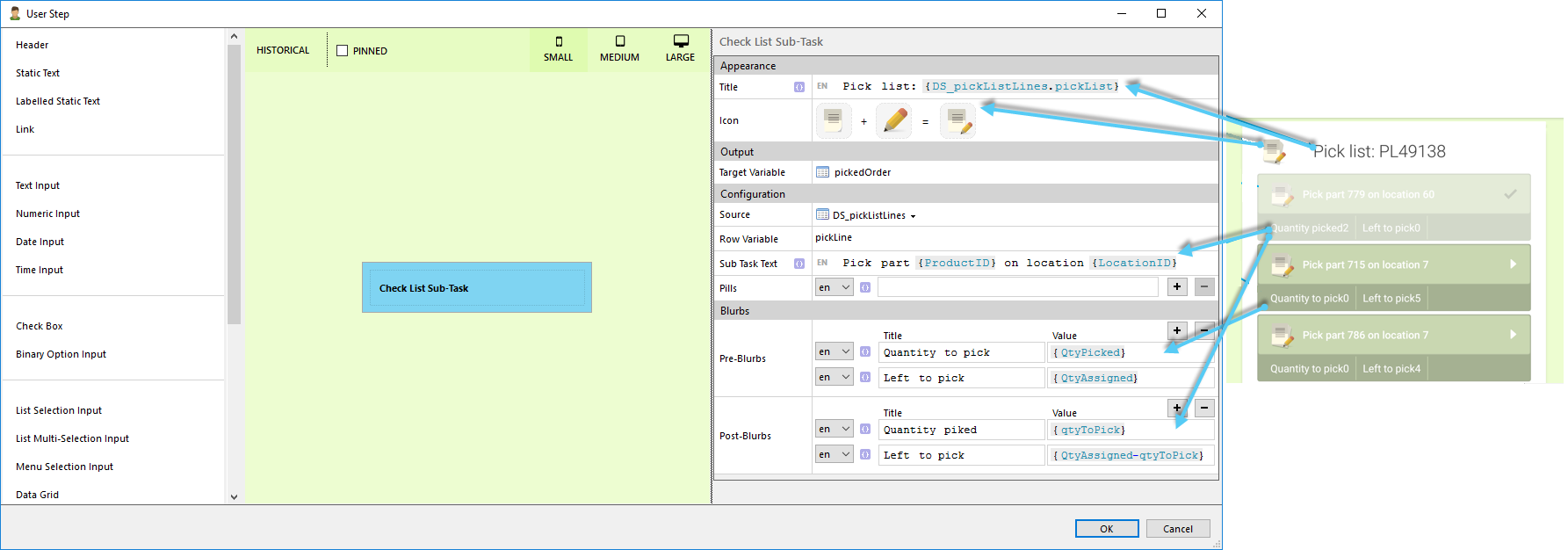
Item creation sub task example
Close the User Step, an icon will now appear that representing the added sub workflow. Double click on the sub workflow icon to open the (empty) sub workflow. Create a workflow, all variables from the main workflow are available in the sub workflow. Return data back to the main workflow, by configuring the End step in the sub workflow.
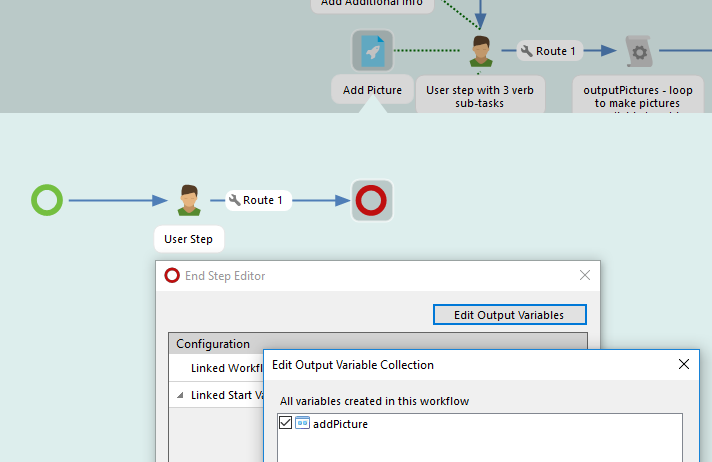
Configure sub workflow end task
Data Grid
A table that is possible to edit direct in the ongoing workflow.
- Prompt
The label displayed above the data grid. - Source
Choose a source or leave it empty. - Columns
Click on edit to add or modify columns in the grid. Read more about configuration of columns below. - Allow Add
Check this box if it should be possible to add new rows to the data grid. - Allow Delete
Check this box if it should be possible to delete rows from the data grid.
- Use Change Tracking
A variable RowState will appear when this checkbox is checked, this variable can have four different states:- Unchanged - when the row in the data grid is unchanged
- Changed - when the user have change something on the row in the data grid
- Added - When the user have added a new row (when the row is new)
- Removed - When the user have removed the row
Use the variable RowState to handle new, modify and delete in scripts.
Example:
If @RowState = 'Changed' Begin Update OrderLines Set Qty = @Qty Where OrderNo = @OrderNo and OrderRowId = @OrderRowId End;If @RowState = 'Removed' Begin Delete from OrderLines Where OrderNo = @OrderNo and OrderRowId = @OrderRowId End; - Row Selection Mode
Enables the possibility to select one or multiple rows:- No selection - not possible to select any row
- Single selection - only possible to select one row
- Multi selection - one or more rows can be selected
The grid is by default set to No selection. Calendar grid and grid in CE client are out of scope.
Selected rows are fetched in a Scrip Step (or Assignment Step) after the grid User Step using the variable IsSelected. The target variable from the script step is then used in as the source when the selected data is to be used.
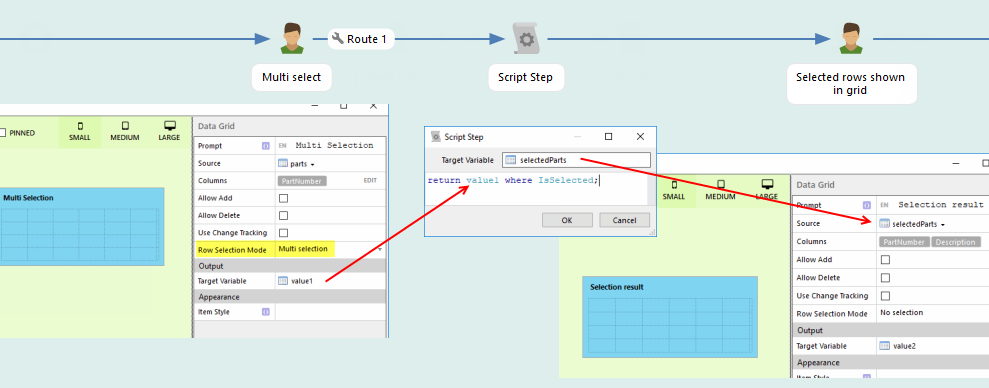
Row Selection
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which the data is stored as a table.
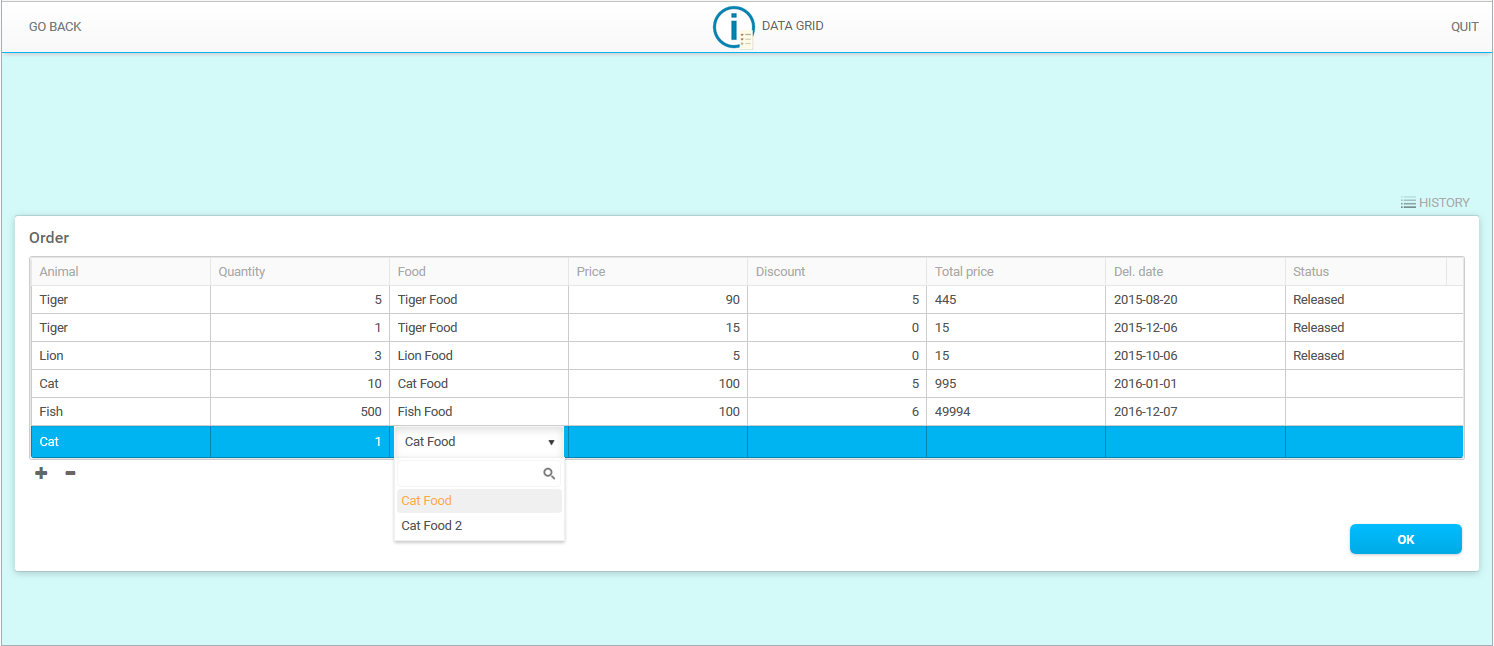
Data grid example
Item Style
Use a case statement to set row color based on a condition. Also see Cell Color under All Columns. CE client is out of scope.Example:
{case when objStatus = 'Planned' then 'PURPLE' when objStatus = 'Released' then 'GREEN' when objStatus = 'Rested' then 'RED' else '' end}Colors: GREEN, RED, YELLOW, BLUE and PURPLE
Columns
Click EDIT to configure the columns in the grid. The Add All Columns button will add all columns in the Source in one click, Remove All Columns will remove them all. Use + or - respectively to add or remove a single column. In a calendar grid a mandatory date column is always added by default, this column is not affected by the Add/Remove All functionality and is not possible to remove.
Edit columns settings:
- All Columns
The following settings are available for all column types:- Title: Enter a title for the column.
- Size Mode: Size mode can be set to Break, Clip or Fit (for CE client Clip and Fit are available):
- Break - Break works like word wrap, ie the column width is defined by the Size setting and the text then continues on multiple rows to the maximum height of 85% of max grid height. Uses ellipsis function to indicate omission of text.
- Clip - Clip mean that the text is clipped according to size setting. No wordwrap. Uses ellipsis function to indicate omission of text.
- Fit - Fit means that the column width is fitted to the largest value displayed in the column - up to approx. 85% of grid width. Fit overrides the Size setting. Uses ellipsis function to indicate omission of text.
- Break - Break works like word wrap, ie the column width is defined by the Size setting and the text then continues on multiple rows to the maximum height of 85% of max grid height. Uses ellipsis function to indicate omission of text.
- Size: Decide what width of the column. Sizes: Small, medium, large.
- Cell Color: Use a case statement to set cell color based on a condition, also see Item Style above. Available colors are: GREEN, RED, YELLOW, BLUE and PURPLE. CE client is out of scope.
- Title: Enter a title for the column.
- Text Column
Enter a title of the column and a variable name, for example First name as the title and firstName as the variable name. Choose a value type, which represents that type of data that the column should hold. Decide the appearance of the column if the data should be editable, hidden and/or mandatory.- Hidden: Check this if the column should be hidden and not showed to the user.
- Editable: Check this if the column should be editable for the user.
- Default Value: Enter a default value.
- Editable For New Rows: Check this if the column only should be editable when adding new rows.
- Hidden: Check this if the column should be hidden and not showed to the user.
- Numeric Column
Enter a title of the column and a variable name, for example First name as the title and firstName as the variable name. Choose a value type, which represents that type of data that the column should hold. Decide the appearance of the column if the data should be editable, hidden and/or mandatory.- Format String: Numeric format strings are used to format common numeric types. Using the C modifier in the format string area converts the numeric input into local currency. Also the hashtag symbol (#) represents one number in the total numeric value, so one can format the 6-digit value 123456 with inputs in the following way:
First two numbers: ## Second two numbers ## Last three Numbers ##Result: First two numbers 12 Second two numbers 34 Last three numbers 56Read more about formating here - Hidden: Check this if the column should be hidden and not showed to the user.
- Editable: Check this if the column should be editable for the user.
- Default Value: Enter a default value.
- Editable For New Rows: Check this if the column only should be editable when adding new rows.
- Format String: Numeric format strings are used to format common numeric types. Using the C modifier in the format string area converts the numeric input into local currency. Also the hashtag symbol (#) represents one number in the total numeric value, so one can format the 6-digit value 123456 with inputs in the following way:
- Value List Column
Enter a title of the column and a variable name, as in below example Food as the title and food as the variable name, check Include in Output to include the variable in the target variable of the grid.- Table Expression: Connect a table to the value list, the result of the below example will be based on what the user have choosed in the catalog value list.
- Row Text: Enter the variable that represents the value that should be showed in the value list.
- Key Expression: Enter a variable here (for example an id) and use Output Key Only to just get the one variable insted of a record.
- Output Key Only: Check this to get a variable with the Key Expression.
- Editable For New Rows: Check this if the column only should be editable when adding new rows.
- Table Expression: Connect a table to the value list, the result of the below example will be based on what the user have choosed in the catalog value list.
- Computed Column
Enter a title of the column and a variable name, for example sum as the title and sumValue as the variable name. The computed column can for example be used as a summary column. If the grid have one column with a price and one with a discount, then the columns can be summarized in the computed column. Do the calculation ({price - discount}) of the variables price and discount in the template field and choose what value type the column should have.- Value Templete:
- Hidden: Check this if the column should be hidden and not showed to the user.
- Checkbox Column
Enter a title of the column and a variable name, for example Invoice as the title and invoice as the variable name. Decide if the checkbox should be check by default or not.- Editable: Check this if the column should be editable for the user.
- Default Value: Enter a default value.
- Editable For New Rows: Check this if the column only should be editable when adding new rows.
- Editable: Check this if the column should be editable for the user.
Date Input
A date input interaction item is used when the operator is required to pick a calendar date.
Date inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which to store the date entered. Dates are stored in the YYYY-MM-DD format. - Prompt
The label to display over the date input field. - Default Value
The default value must be in YYYY-MM-DD format. If no default value is supplied, today's date will be displayed by default. - Allow Empty Input
If set to True, the operator is allowed to move forward in the workflow without entering anything into the date field.
File Gallery
With the file gallery is it possible to show files that the user can open and use on their device. The user can also add files to the gallery.
- Target Variable
The name of the new table variable in which the data stores. - Prompt
The label displayed above the file gallery. - Source
Choose a source table that contains files. - Uploads
Choose upload type, singel or multiple upload.- Single: if the user only should upload one file.
- Multiple: if the user should be able to upload more then one file (or zero files).
- Single: if the user only should upload one file.
- Allow File Endings
Enter file endings for those type of files that should be allowed to add to the file gallery. For example; .doc, .xls - Target Image Size
Use target image size to scale images or make it possible for the user to decide what size the image should be scaled to.- Original: All attached images will not be scaled.
- Small (25%): All attached images will be scaled to the size of 25% of the original size.
- Medium (50%): All attached images will be scaled to the size of 50% of the original size.
- Large (75%): All attached images will be scaled to the size of 75% of the original size.
- User defined: The user will be able to decide if the image should be scaled and what size it should be scaled to.
- Original: All attached images will not be scaled.
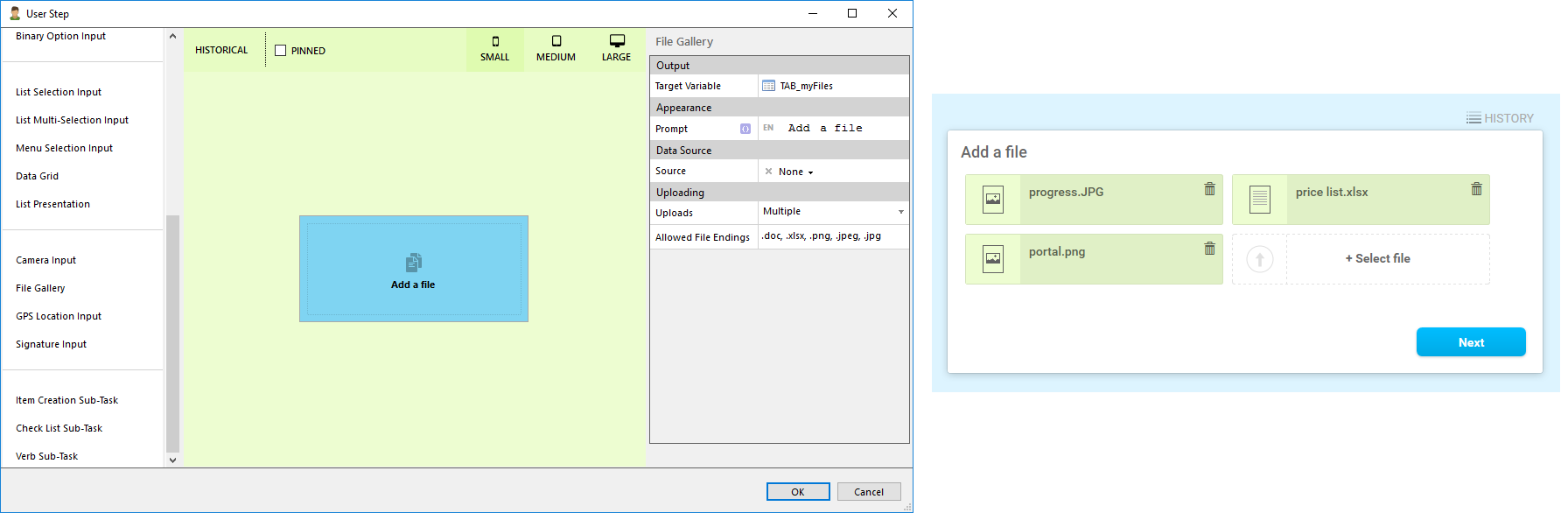
A configuration of the file gallery in the designer, and how it looks in the web client
GPS Location Input
The GPS location input catches the device/users location coordinates.
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which the GPS coordinates stores. - Text
The label displayed above the GPS input. - Failure text
Enter a text that will be shown to the user if it is not possible to catch the coordinates. - Allow failure
Check the box if failures should be allowed.
Header
A text header is used to display a bold, non-editable, single-line text block to the user. Use your variables (with {}) and Flow script to make your texts generic.
Text headers only have one property:
- Text
The text to be displayed in the header.

Image Selection Input
The Image Selection Input is used to show a list of images that are selectable, it supports both single- and multiple selections.
Images that are selected are imported from image URLs > e.g "http://www.genericimageuploader.org/picture.jpg"
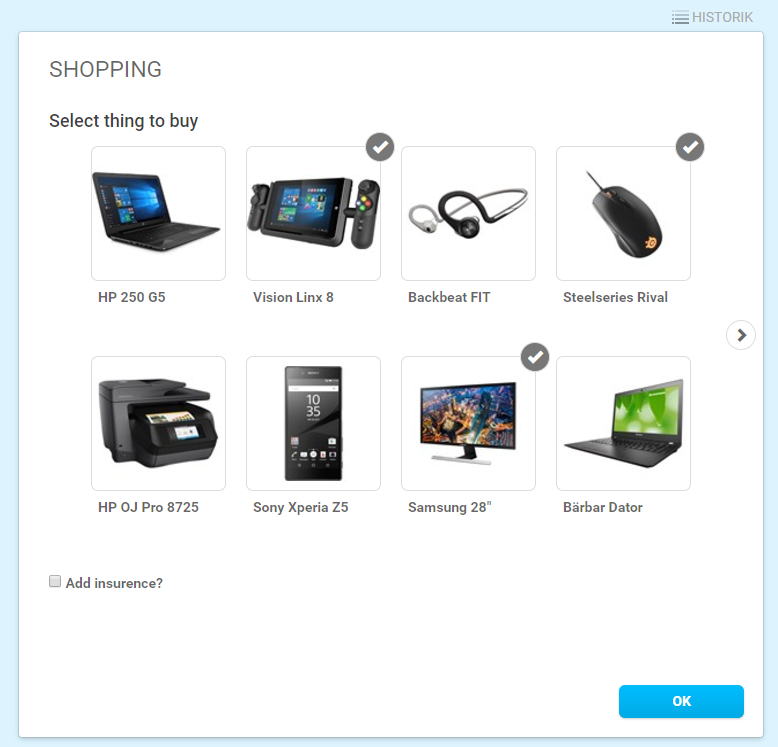
Image Selection
Configuration
One can import a table with an URL-column of several images to list several images, item description and etc.
- Output
- Target Variable - Output table of images selected and their properties(Text).
- Data Source
- Table Variable - Input table of image-URLs and their properties.
- Default Selection - adding a source from input table such as {Column2} will preselect all images contained in that column.
- Appearance
- Prompt - A text prompt.
- Item Text - Text for the images, can import text from a column from the source table.
- Image Source - Where the image is imported from, can be a standard URL text, or a column in a table with URLs.
- Allow Multiple Selections - TRUE/FALSE checkbox if the userstep supports multiple image selections.
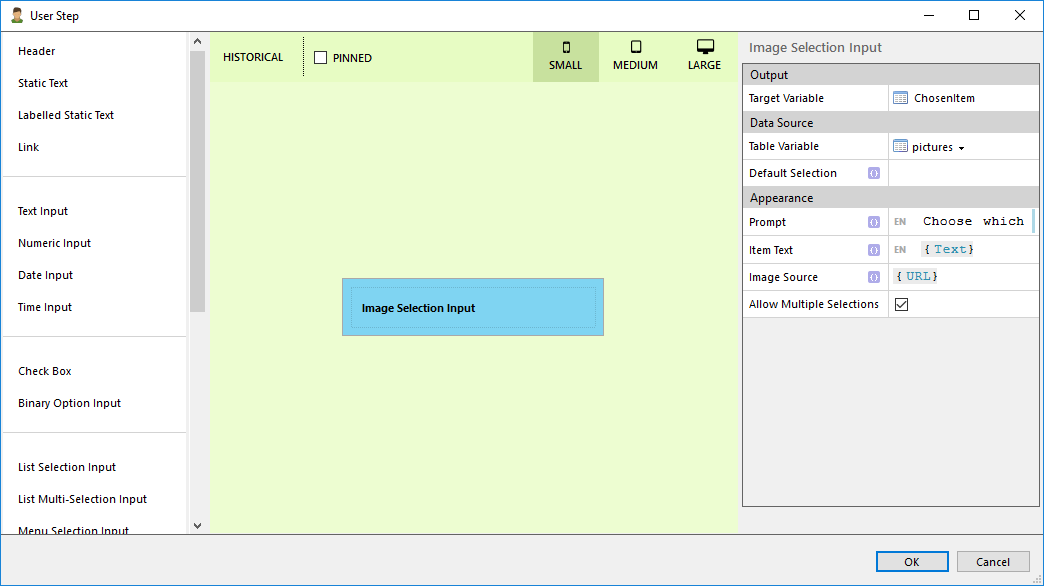
Image selection userstep settings
Image Viewer
The Image Viewer is used to display images in the User step.
In order to display an image the following has to configured
URL - The source url from which the image will be fetched.
All clients must have direct access to the image source
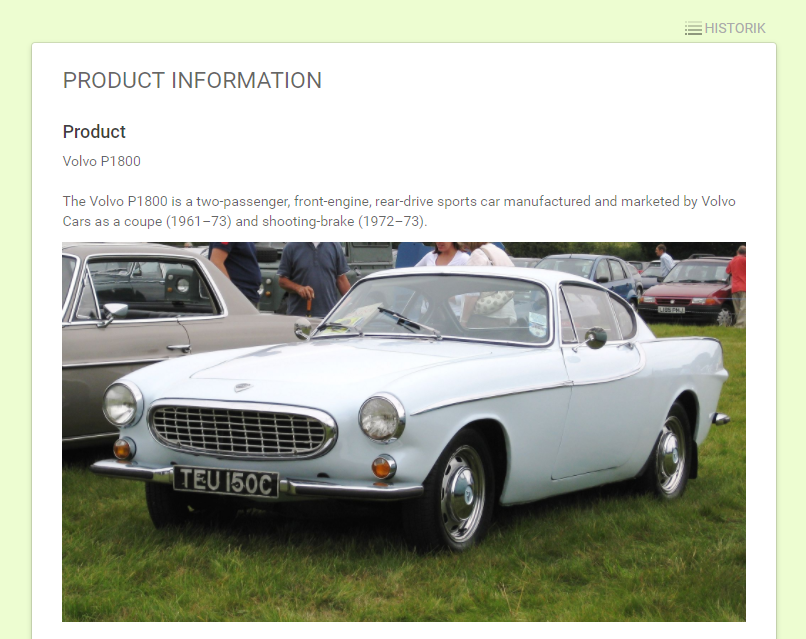
Image Viewer
Sub Workflows
A sub workflow is put into a User Step
There are three types of sub workflows:
 Check List: Executes one workflow for each record in a list of things to do.
Check List: Executes one workflow for each record in a list of things to do.
Item Creation: Creates a new item for each time the sub workflow is executed.
Verb: A side track in the workflow where the sub workflow can be executed one or many times.
Item Creation Sub Task
A sub workflow is created from a User Step. Create a new User Step and add a sub workflow element. Configure the appearance of sub workflow in the client.
Set the following:
- Target Variable: Enter a name for the output varibale. The output from the sub workflow will end up in this new table variable.
- Title: Text on the sub workflow button.
- Icon: Icon one the on the sub workflow button.
- Sub Task Text: Text on the Item (e.g. the Time Report) that has been created. Varibles can be added later.
- New text: Text on the New button, to add new item (e.g. a new Time Report)
- Pills: The indicator on the sub workflow button
- Post-Blurbs: Info parts on a created Item.
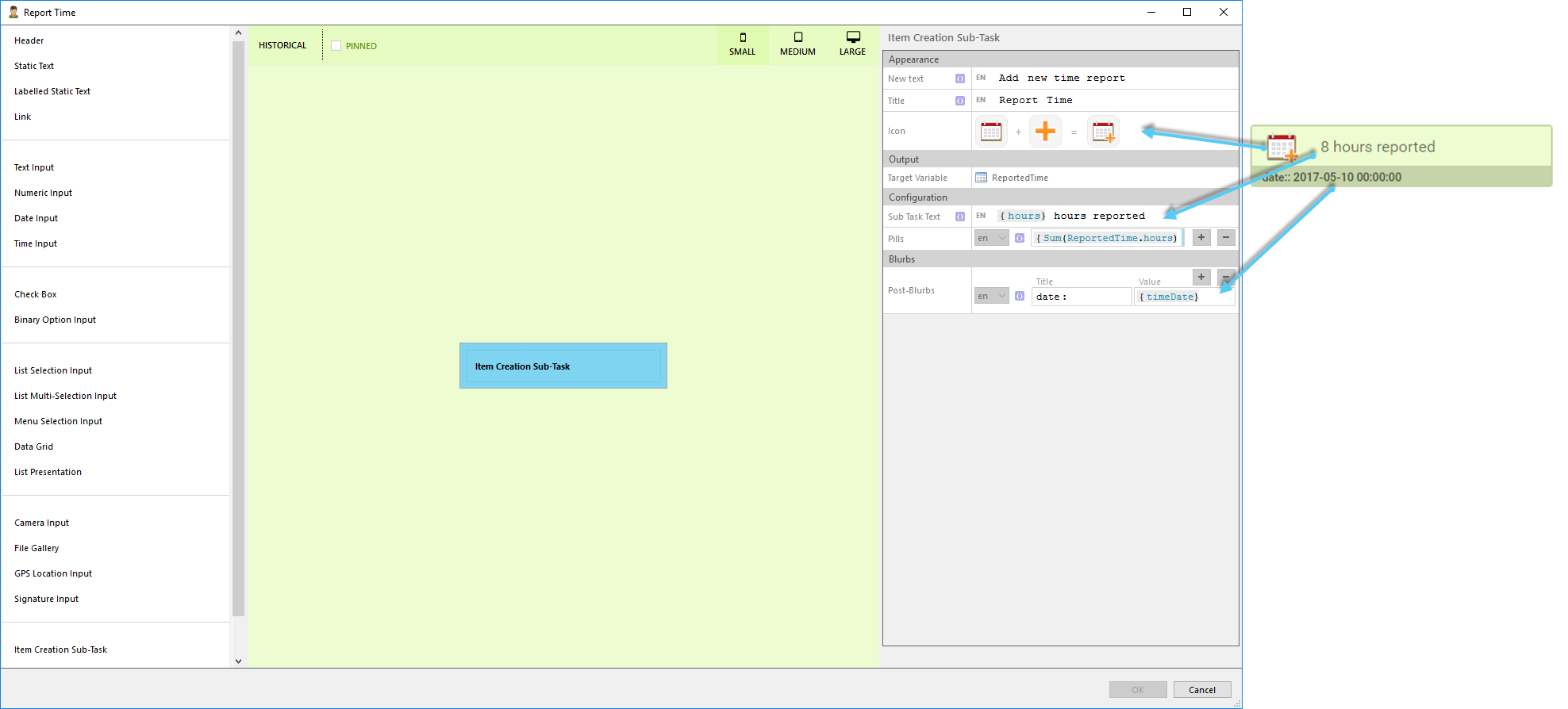
Item creation sub task example
Close the User Step, an icon will now appear that representing the added sub workflow. Double click on the sub workflow icon to open the (empty) sub workflow. Create a workflow, all variables from the main workflow are available in the sub workflow. Return data back to the main workflow, by configuring the End step in the sub workflow.

Configure sub workflow end task
Labeled Static Text
The labeled static text control can be used to structure data in a good way on the screen.
For example: Label = "Order no:" and text = "{orderNo}" (a variable for the order number). The result will look like this:
Use your variables (with {}) and Flow script to make your texts generic.
- Label
Enter a text that will be displayed to the user. - Text
Enter a text that will be displayed to the user. - Use Large Font
Check the box to make the font size of the text larger.
Labeled static text in the web client
Link
- Large Text
Enter a text to describe the uri, this text will be shown in large text. - Small Text
Enter a text to describe the uri, this text will be shown in small text. - URI
Enter a URI. An URI can for example be a name, location or URL. Link Type
- Document:
- Web: the uri link will be open as a web site in the users default web browser.
- Email: the uri will be open as an email message window where the uri will be placed in the to field.
- Phone: the phone number will be called if the uri is opend on a mobile device.
- Address: if the uri is opened in a mobile device with a GPS app, the GPS will be opend and show the address.
Example of links in the Android client
List Multi-Selection Input
A list multi-selection input is used when it should be possible to choose more then one record in a list. It can also be left with no chosen value.
If a barcode scanner is used in a list multi-selection input, the Flow Client will search the data source for a record where the Key field matches the scanned value and select the corresponding line in the list. If no match is found, the Flow Client will attempt to match the other fields on the data source to the scanned value and select the first line where a match is found.
List selection inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable(s) in which to store the selected records. (The output variable type will be a table.)
- Table Variable
Choose the table that will be the data source in the list. Default Selection Use Flow script to do a default selection of values.
Example:{objectStatus = 3}- Prompt
The label displayed at the top of the list. - Large Text
Enter text and variables that should be displayd in the list (can be left empty but observe that either large or smal text need to be configured to show something in the list). Use {} to get a list of available variables from the source table. - Small Text
Enter text and variables that should be displayd in the list (can be left empty but observe that either large or smal text need to be configured to show something in the list). Use {} to get a list of available variables from the source table. - Group Rows By
If the list should be grouped choose a column from the source table to group the list by. Set to "none" to not group the list.
- Show Automatically
If set to True the list will be open direct when the user steps in to the user step (only in mobile clients) so the user not need to open the list and after that choose from the list, and in that way make the workflow more user friendly. Item Style
Use a case statement to decide what color the columns should have based on a variables value.
Example:{case when objStatus = 'Planned' then 'PURPLE' when objStatus = 'Released' then 'GREEN' when objStatus = 'Rested' then 'RED' else '' end}Colors: GREEN, RED, YELLOW, BLUE and PURPLE
Log on to the Flow community to download an example workflow of item style: http://community.novacuraflow.com/product/670/
Example of list selection configuration
If the list looks like it is empty, make sure that varibales from the list is entered in the large and/or small text field.
List Presentation
A list presentation item is used to display a list without requiring the user to select any record. Therefore it is no Target Variable property.
- Table Variable
Chose a data source with the data to display in the list. - Prompt
The label displayed at the top of the list. - Large Text
Enter text and variables that should be displayd in the list (can be left empty but observe that either large or smal text need to be configured to show something in the list). Use {} to get a list of available variables from the source table. - Small Text
Enter text and variables that should be displayd in the list (can be left empty but observe that either large or smal text need to be configured to show something in the list). Use {} to get a list of available variables from the source table. - Row Hyperlink Template
Enter a variable here to get hyperlinks in the list.
Item Style
Use a case statement to decide what color the columns should have based on a variables value.
Example:
Colors: GREEN, RED, YELLOW, BLUE and PURPLE{case when objStatus = 'Planned' then 'PURPLE' when objStatus = 'Released' then 'GREEN' when objStatus = 'Rested' then 'RED' else '' end}
Log on to the Flow community to download an example workflow of item style: http://community.novacuraflow.com/product/670/
Group Rows By
If the list should be grouped choose a column from the source table to group the list by. Set to "none" to not group the list.
List Selection Input
A list selection input is used to select a record or value from a data source.
List selection inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable(s) in which to store the record selected. - Table Variable
Choose the table that will be the data source in the list. Default Selection Use Flow script to do a default selection of values.
Example:{customerNo = 5}Result Transformation Use this if the output record variable differ from the selected target variable.
Example:{[column1: orderNo, column2: orderDate]}- Prompt
The label displayed at the top of the list. - Large Text
Enter text and variables that should be displayd in the list (can be left empty but observe that either large or smal text need to be configured to show something in the list). Use {} to get a list of available variables from the source table. - Small Text
Enter text and variables that should be displayd in the list (can be left empty but observe that either large or smal text need to be configured to show something in the list). Use {} to get a list of available variables from the source table. Item Style
Use a case statement to decide what color the columns should have based on a variables value.
Example:{case when objStatus = 'Planned' then 'PURPLE' when objStatus = 'Released' then 'GREEN' when objStatus = 'Rested' then 'RED' else '' end}Colors: GREEN, RED, YELLOW, BLUE and PURPLE
Log on to the Flow community to download an example workflow of item style: http://community.novacuraflow.com/product/670/- Group Rows By
If the list should be grouped choose a column from the source table to group the list by. Set to "none" to not group the list.
- Show Automatically
If set to True the list will be open dirct when the user steps in to the user step (only in mobile clients) so the user not need to open the list and after that choose from the list, and in that way make the workflow more user friendly. - Match By
Rows: If a barcode scanner is used in a list selection input, the Flow Client will search the data source for a record where the Key field matches the scanned value and select the corresponding line in the list. If no match is found, the Flow Client will attempt to match the other fields on the data source to the scanned value and select the first line where a match is found.
Specific Columns: Enables Match Columns.
Match Columns
Click Edit to open the Match Columns pop up. In Match Columns it is defined which columns should be matched when scanning and in which order (top to bottom). When Specific Columns has been selected the scanning is on exact match only, regardless of client settings. Letters in upper or lower case are seen as separate values.
Example of list selection configuration
Example of Match Columns
If the list look is empty, make sure that varibales are entered in the large and/or small text fields.
Menu Selection Input
A menu selection input is used to select a key field value from a machine task or a table. Menu selection inputs take up less space than list selection inputs, but are less practical for large data sources with lots of information in each record.
Menu selection inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable(s) in which to store the selected value. The data that will be stored in the varibale is the value frpm the seleced variable in "Field to select". - Table Variable
Choose the table that will be the data source in the list. - Prompt
The label displayed at the top of the list. - Row Text
Enter text and variables that should be displayd in the list. Use {} to get a list of available variables from the source table. - Default Value
Enter a default value based on the values of the variable entered in Field to Select. - Field to Select
The target variable will contain the value of this field. - Show Empty Option
The list will be empty when the user enter the user step.
- Text of Empty Option
Enter a text for the empty option (optional). - Allow Empty Option Selection
If set to True, the operator is allowed to move forward in the workflow without entering anything into the text field.
Numeric Input
A numeric input interaction item is used when the operator is required to supply numeric information, either manually (using a keyboard) or with the aid of a barcode scanner. Numeric inputs treat both points (.) and commas (,) as decimal separators.
Numeric inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which to store the number entered. - Prompt
The label to display over the numeric input field. - Default Value
The number that will be entered as default when the operator first enters the user task. - Allow Empty Input
If set to True, the operator is allowed to move forward in the workflow without entering anything into the numeric field.
Pinned User Step
A pinned user step are an information
It is only possible to use Header, Static Text, Labeled Static Text, Link and List Presentation in pinned user steps, this because a pinned user step is only a why to show the user information.
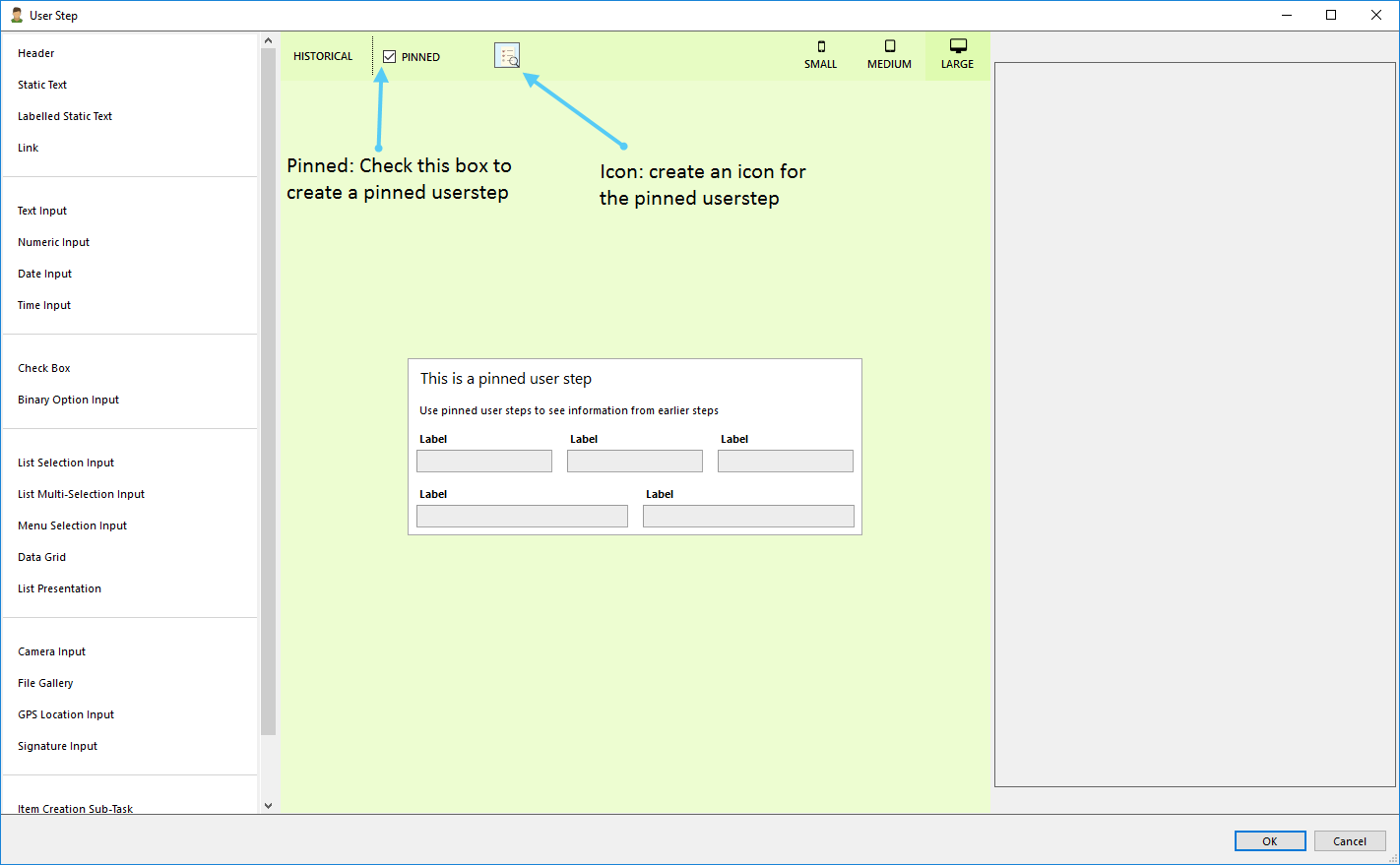
Configure a pinned user step
The pinned user step will show up in the side of the screen, and the user need to tap/click on the icon to extend or colaps the pinned user step. In the below picture is the pinned user step to the left and the regular user step to the right. If there is more then one pinned user step in the workflow, will the pinned user step be replaced when the user steps over another pinned user step.
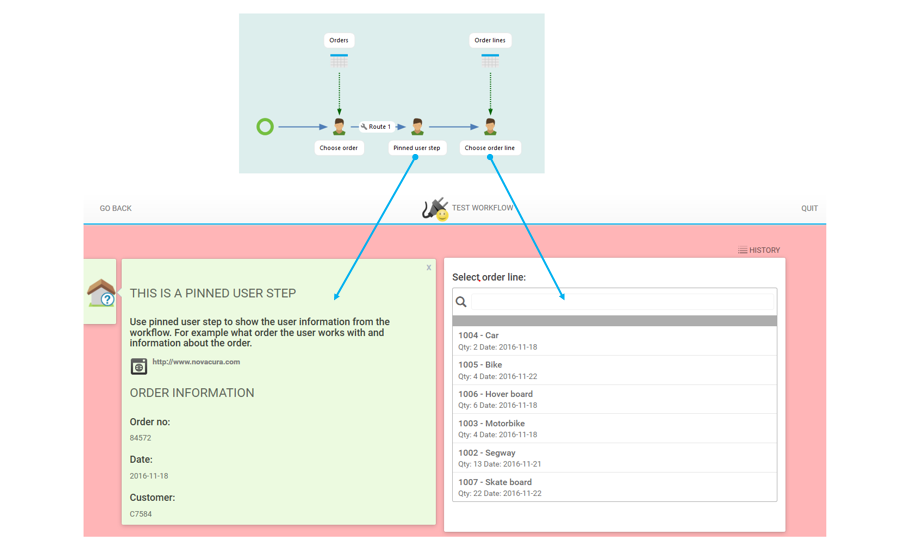
Pinned user step in the web client
Signature Capture Input
The signature capture input allows the user to write their signature directly on the device.
- Target Variable
The name of the variable that store stores the signature in PNG-format. - Prompt
The label to display over the signature area.
Example of the signature capture input on Android
Static Text
A static text is used to display a non-editable multi-line text block to the user. Use your variables (with {}) and Flow script to make your texts generic.
- Text
Enter a text that will be displayed to the user. Use the pipe sign (|) to insert line breaks in the text.
Text Input
A text input interaction item is used when the user is required to supply textual information containing letters and/or digits, either manually (using a keyboard) or with the aid of a barcode scanner.
Text inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which to store the text entered. - Prompt
The label to display over the text input field. For readability, it's often better to use a Text Header interaction item in user tasks with a single text input. - Default Text
The text that will be entered as default when the user first enters the user task. - Allow Empty Input
If set to True, the user is allowed to move forward in the workflow without entering anything into the text field. - Multiline
If set to True, the text box will expand into a multi-line text editor allowing line breaks. - Force Uppercase
If set to True, the contents of the text input will automatically be translated into UPPERCASE before being stored in the target variable. - Enable Text Correction
If set to True, the text input will be enabled for spell checking, word suggestions and auto correction, on host systems that support such features. Use this only for human language text fields (e.g. work order error descriptions). - Trim Input Automatically
If set to True, the contents of the text input will be trimmed (leading and trailing whitespace removed) before being stored in the target variable. - Use Password Mask
If set to True, the text entered will show up as bullets like in a password input field.
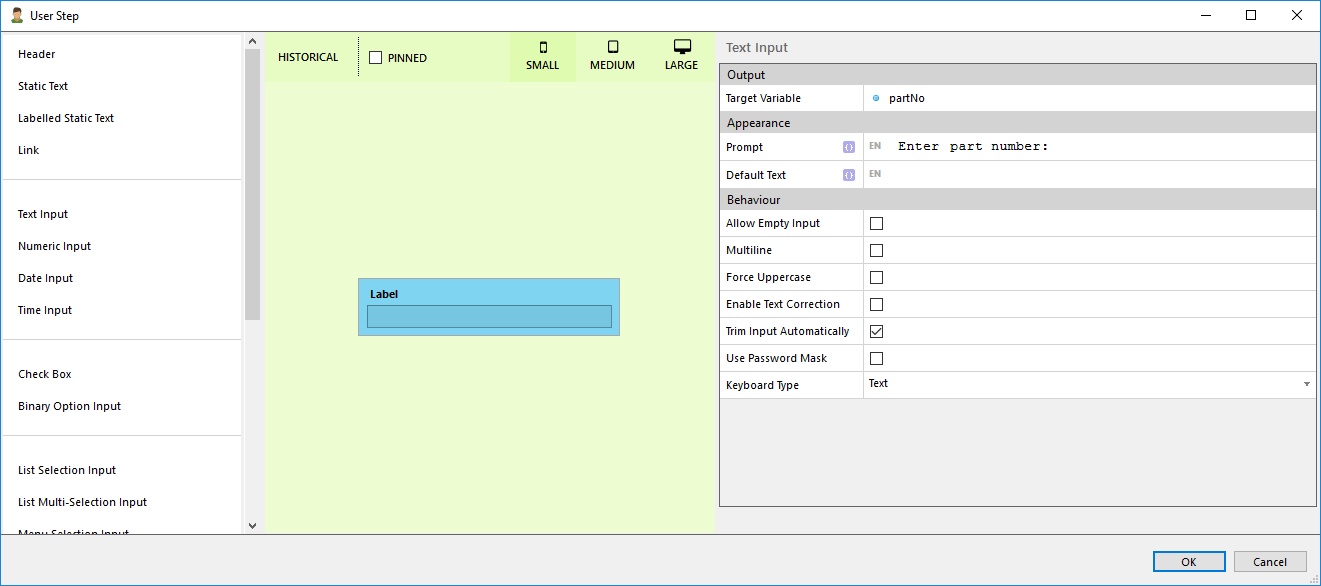
Text input example
Time Input
A time input interaction item is used when the operator is required to enter a time input.
Time inputs have the following properties:
- Target Variable
The name of the new variable in which to store the time entered. Time are stored in the HH-MM format. - Prompt
The label to display over the time input field. - Default Value
The default value must be in HH-MM format. If no default value is supplied, the present time will automatically be displayed by default. - Allow Empty Input
If set to True, the operator is allowed to move forward in the workflow without entering anything into the time field.
Sub Workflows
A sub workflow is put into a User Step
There are three types of sub workflows:
 Check List: Executes one workflow for each record in a list of things to do.
Check List: Executes one workflow for each record in a list of things to do.
Item Creation: Creates a new item for each time the sub workflow is executed.
Verb: A side track in the workflow where the sub workflow can be executed one or many times.
Verb Sub Task
A sub workflow is created from a User Step. Create a new User Step and add a verb sub-task element. Configure the appearance of verb sub-task element in the client.
Set the following:
- Title: Text on the verb sub-task element button.
- Icon: Icon one the on the verb sub-task element button.
- Allow Multiple Runs: This should be check to allow the verb sub-task element to be run multiple times whist in the same user step in the main workflow.
- Pills: Pill on the sub workflow button. One or multiple pills can be configured on the verb subtask, the pill can display a text or a count of how many times the verb sub-task has been run*
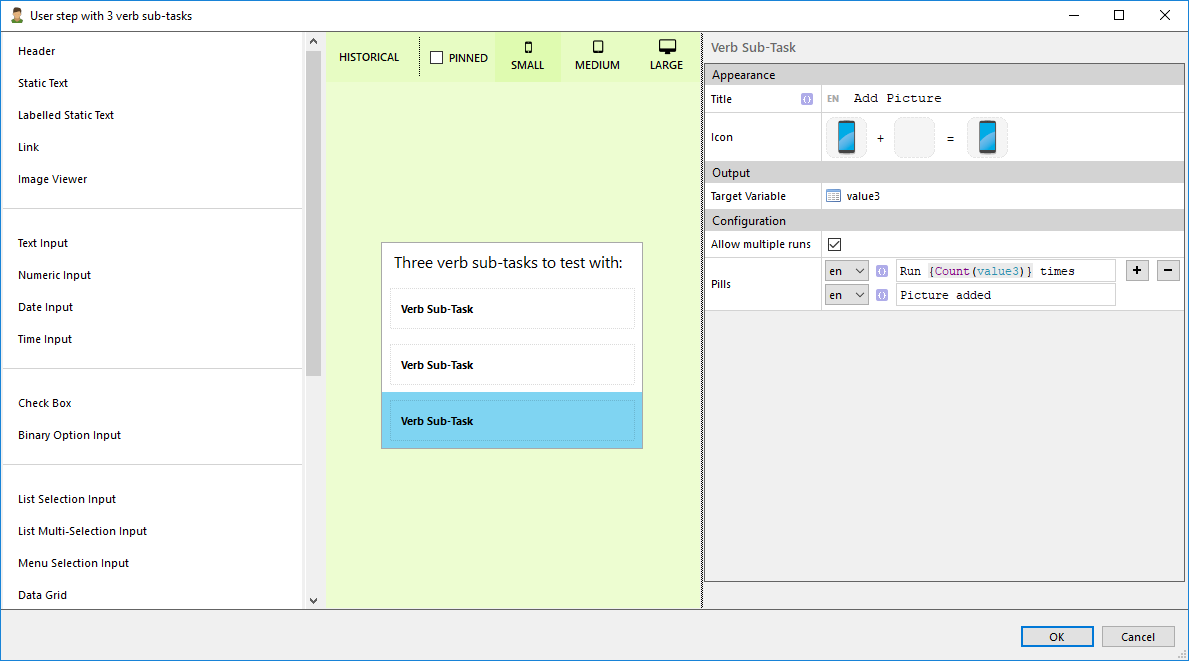
Close the User Step, an icon will now appear, representing the added sub workflow.
Double click on the sub workflow icon to open the (empty) sub workflow.
Create a workflow, all variables from the main workflow are available in the sub workflow.
Return data back to the main workflow by configuring the End step in the sub workflow. The output from the sub workflow is put in the target variable of the verb sub-task element. The sub workflow output is available once the user has moved on from the user step the verb sub-task is located in, i.e. it is not possible to use the data in the user step the sub workflow is started from.
The output from a sub workflow will always be in grid format.

Verb sub-task output example
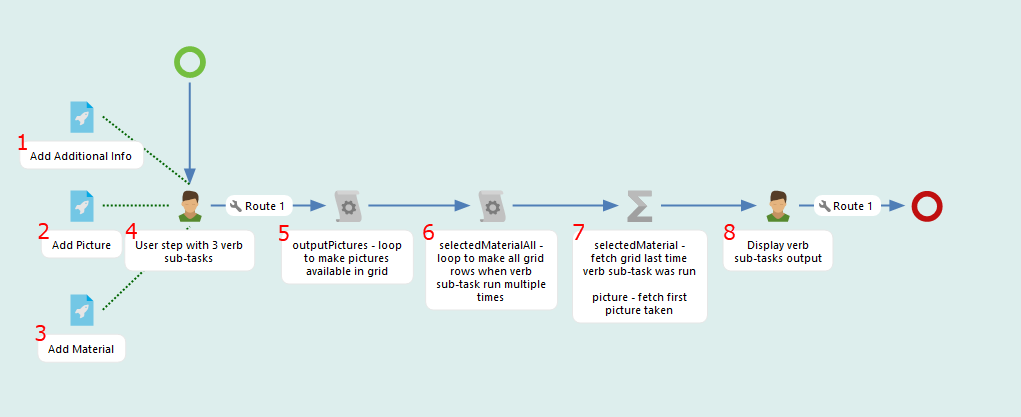
The user step contains three verb sub-tasks with the following content:
1. Add Additional Info
a. addInfo ? text input
b. finishDate ? date input
2. Add Picture (Allow multiple runs = TRUE)
a. addPicture ? camera input
3. Add Material (Allow multiple runs = TRUE)
a. gridMaterial ? data grid
4. User Step: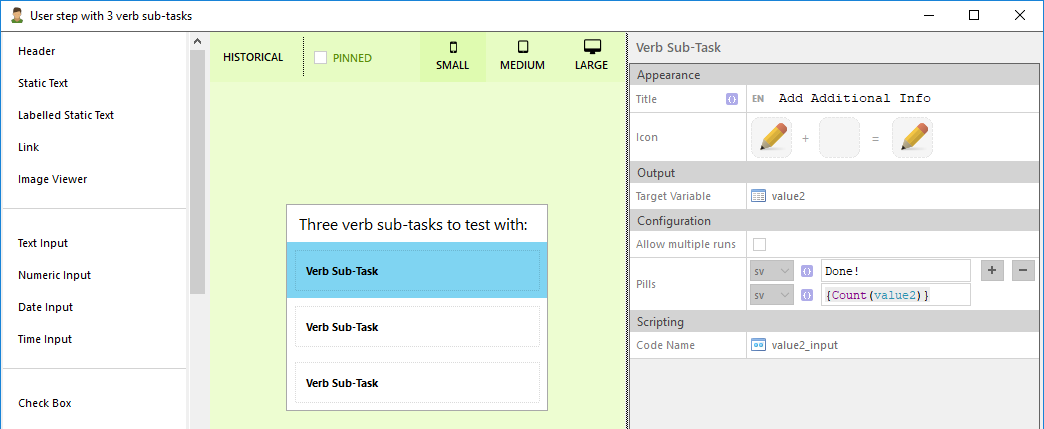
5. Script Step: outPutPictures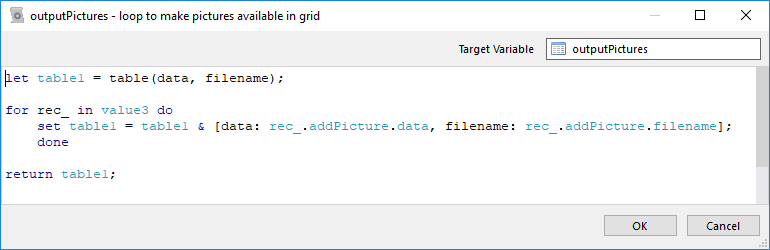
6. Script Step: selectedMaterialAll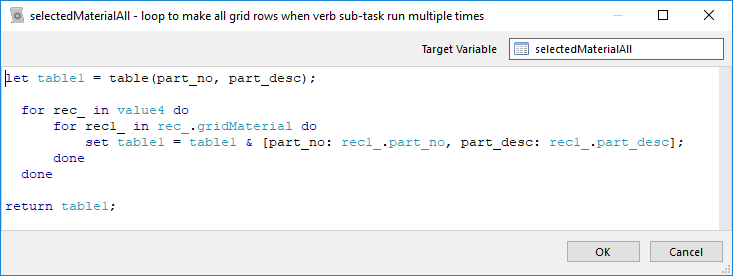
7. Assignment: selectedMaterial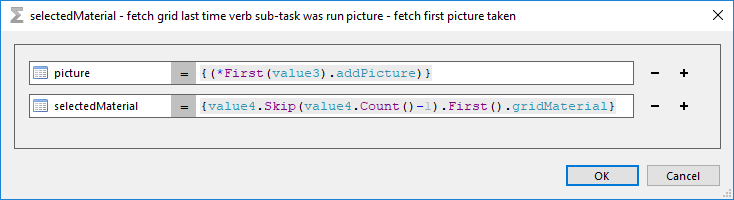
8. User Step
Sub verb-tasks run in iOS - Pills:
Flow script examples
Scrip Step - Add pictures to table:
let table1 = table(data, filename);
for rec_ in value3 do
set table1 = table1 & [data: rec_.addPicture.data, filename: rec_.addPicture.filename];
done
return table1;Scrip Step - Grid ? verb sub task run multiple times (loop in loop):
let table1 = table(part_no, part_desc);
for rec_ in value4 do
for rec1_ in rec_.gridMaterial do
set table1 = table1 & [part_no: rec1_.part_no, part_desc: rec1_.part_desc];
done
done
return table1;Assignment ? fetch first picture:
Picture = {(*First(value3).addPicture)}Assignment ? fetch last grid:
selectedMaterial = {value4.Skip(value4.Count()-1).First().gridMaterial} Annotation
Annotation
Use the annotation element to add a comment to the workflow. The comment is not visible to end users.
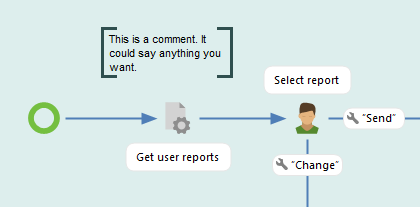
Annotation Example
 Assertion Step
Assertion Step
Assertion steps are used to perform "sanity checks" on variables in the workflow. An assertion step consists of one or many conditions (see Decision steps) and an error message to be shown to the operator in case the conditions are satisfied.
If an assertion step generates an error message, the operator is automatically returned to the most recent user step.
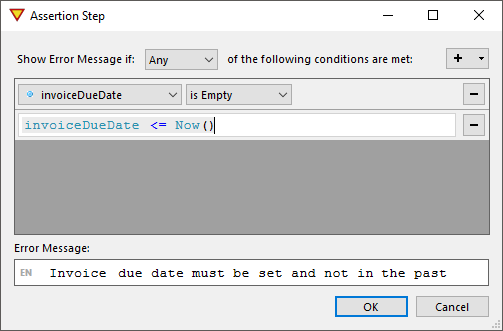
Example
 Assignment
Assignment
Use the assignment to create one or many new variables and assign values to them. It is possible to use Flow script to assign a value to the variable.
 Checkpoint
Checkpoint
A checkpoint will notis the user with the message that is configurated in the checkpoint step.
- Title: Enter a title for the message.
- Text: Enter a text for the message.
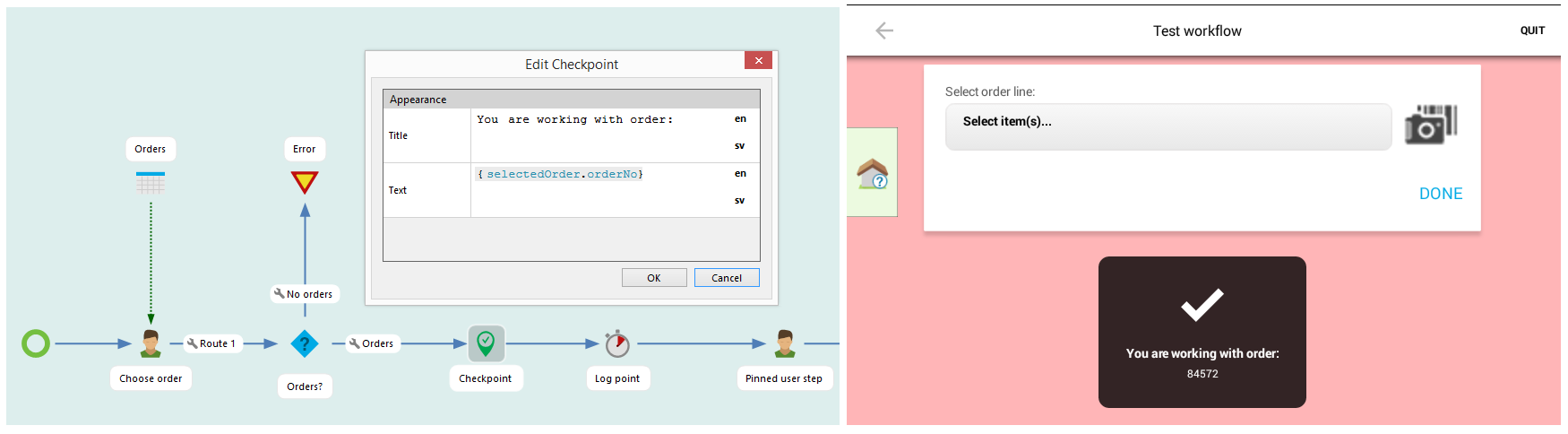
Checkpoint example
 Decision Step
Decision Step
Decision steps are used to take different routes through the workflow depending on the contents of variables or data sources.
Decision steps are invisible to the operator. To allow the operator to decide which route to take in a workflow, use a User step in conjunction with a decision step.
Outgoing routes
To configure the outgoing routes for a Decision step, start by connecting the decision step element to two or more items, then double-click on the little cogwheels that appear after the decision step. Route conditions
Each route has to define one or more conditions for when the route should be taken. The order in which these conditions are evaluated is not defined, except that the default route is always taken last. (See below.)
Conditions come in two types: Binary and unary. Binary conditions compare one value (L-value or left hand side value) to another value (R-value or right hand side value). A natural language example would be "if A equals B" where A is the L-value and B is the R-value. Unary conditions only have an Lvalue; an example would be "if A exists".
The following condition types are available for variables:
- Equals: Holds true if the variable is equal to the comparison value.
- NotEquals: Holds true if the variable is different from the comparison value.
- GreaterThan and LessThan: Hold true if the variable is greater or less than the comparison value (only works for numeric values).
- IsTrue: Holds true if the variable value is different from 0.
- IsFalse: Holds true if the variable value is 0.
- IsNull: Holds true if the variable is empty.
- IsNotNull: Holds true if the variable is not empty.
The following condition types are available for data sources:
- IsEmpty: Holds true if the data source is empty (e.g. the underlying SQL query returns no results).
- IsNotEmpty: Holds true if the data source is not empty.
Decision step example
 End
End
The end step represents where the workflow is ending. It's possible to have one or multiple end steps in a workflow. Double-click on the end step to edit the output variables or linked workflows.
Linked workflow
Linked workflow is used to connect a workflow to an existing one. The linked workflow will be runned after the original workflow. Go into the end step to configure the linked workflow.
Example of how a linked workflow looks like
- Pick: Select a created workflow
- New: Create a new workflow
- Clear: Clear the added workflow
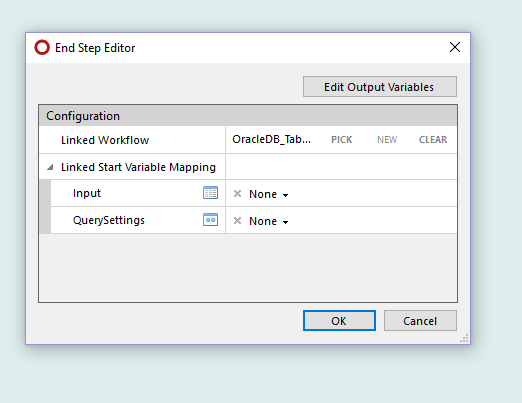
Example how the end step editor looks
 Included Workflow
Included Workflow
A workflow fragment is a type of workflow that can be reused in serveral user workflows. Use the Included Workflow step to connect a workflow fragment to a user workflow.
Create a workflow fragment by clicking on File in the main menu and choose New, choose type Workflow fragment.
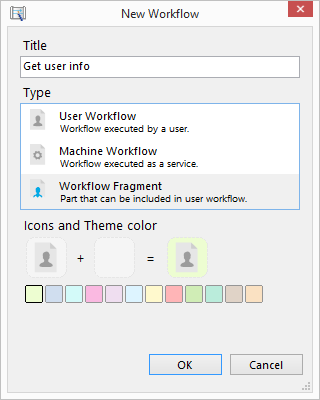
Develop the fragment workflow as wanted. Enter variables in the start step to get input parameters to the fragment workflow and select the output variables in the end step. A fragment must have an end step otherwise there will be an error in the workflow.
 Join
Join
Use the join task to join....
Example where join is used
 Log Point
Log Point
The log point can for example be used to measure time or debug workflows. Log points capture the value of the checked variables and can be stored in a database thru a connected workflow in system events.
Download a basic log point workflow and a Sql server database here:
Log Point Workflow - Sql Server 2012
Log Point Workflow - Sql Server 2014
- If needed Sql server express can be downloaded here:
- Restore the database backup in sql server express management studio.
- Create a connector to the database.
- Import the machine workflow (LogPointWorkflow) in the Flow studio.
- In Environment -> System Events, pick the machine workflow (LogPointWorkflow) for the log point system event and choose a user that will execute the log point system event.
- Now should data be logged when the workflow steps over a log point.
1. Create a machine workflow. This workflow will run every time a workflow steps over a log point.
- Use imparameters to get the log point data into the machine workflow. Download the example above to see how the imparameters should be configured or look at the picture of the workflow below.
- Create a record variable named LogPoint, with variable; Name, TimeStamp, WorkflowName and a table Data with variable Key and Value.
- Create a record variable named LogPoint, with variable; Name, TimeStamp, WorkflowName and a table Data with variable Key and Value.
- Use a connector to the database where the logged data will be stored. Download the example above to get a database (other types of databases can also be used).
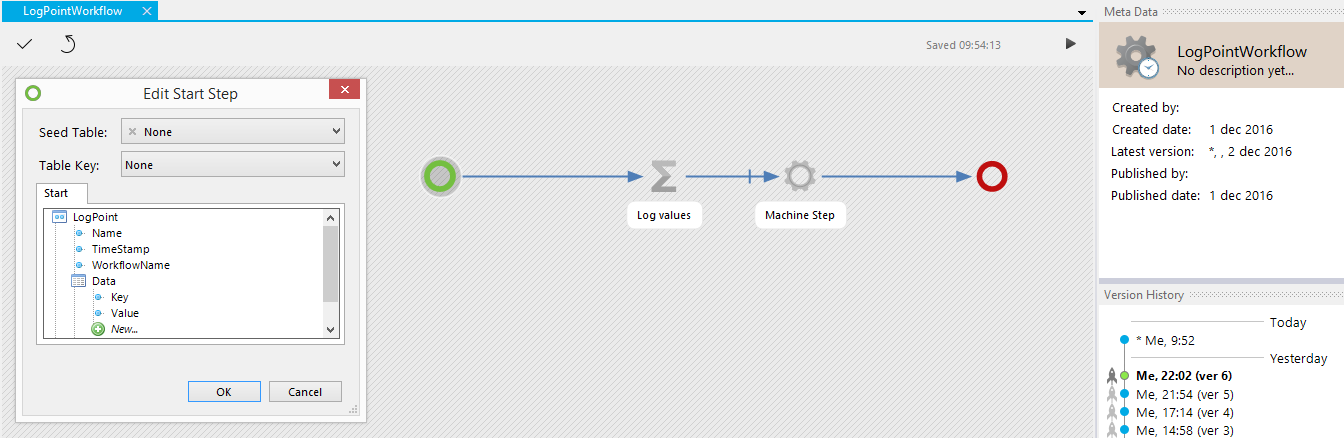
2. Go to Environment -> System Events, and pick the machine workflow for the log point system event and choose a user that will execute the log point system event.

3. Add log points in workflows to log data.
 Machine Step
Machine Step
A machine step is used to read or write data from/to other systems, or to modify the variables in a workflow. Machine steps are invisible to the operator except when something goes wrong (e.g. the ERP system responds with an error message). If a machine step goes wrong, the operator gets an error message and is transported back to the most recent user step.
Machine steps that potentially modify data in another system are called non-reversible. Incoming connections to non-reversible machine steps are adorned with an orthogonal line indicating that an operator will not be able to user the back button in the flow client once this step has been successfully executed.
A user step followed by a non-reversible machine step
Avoid consecutive non-reversible Machine steps, because each machine step is executed atomically (in its own transaction), any changes to underlying systems are committed as soon as the step is completed. Therefore, in case a transaction has already been committed, the Flow Client cannot go back to the previous user step without risking data inconsistency. If this happens, the operator is forced to exit the workflow right away.
In the example below (see picture), the operator would be forced to exit the workflow if machine step B executed successfully but machine step C failed.
A user step followed by two non-reversible machine step
Connectors:
Read more about connectors here.
 Offline Resource
Offline Resource
Use an Offline resource to make data available in an offline workflow. When an offline resource is used, the button Offline data will be available in the clients. Under Offline data can the end user download data to the local device that will be used when executing offline workflows. For every Offline resource used in workflows available for the end user will one row show up under My offline data.
Use an Offline resource to get data in offline workflows.

Create a machine workflow that fetches the data needed and connect the Machine workflow to the Offline resource. The Machine workflow must be created as an Offline resource.

Use the output variable from the Offline resource to use the data from the Machine workflow.

 Script Item
Script Item
This item is used to execute a FlowScript program and assign the target variable with the script result.
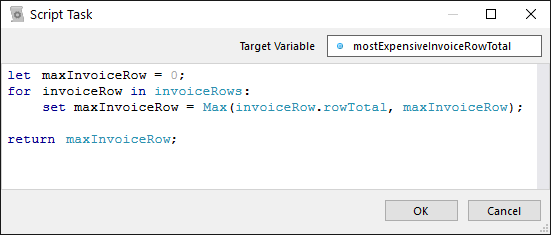
Script task example
 Split
Split
Use the split task to split....

Example where split is used
 The Start step
The Start step
The start step is created automatically and cannot be deleted. It represents the first step of the workflow and can be configured with start parameters. Double-click on the start step to edit the start parameters.
TODO Seed table
Swimlane start position
Swimlanes
Use swimlanes to involve several users in one flow execution.
The swimlanes can be configured so only a specified role can access a specific swimlane, the remaining swimlanes will still be accessable by the default menu role.

Configuration
The swimlanes can be configured to work online, online & offline, offline, or machine.
When using an offline swimlane, the same restrictions apply as when using offline workflows. You need to fetch the data before going offline, and the transactions will be stored and executed first when you go online again.
In configuration one can also assign names to the swimlanes, access roles and swimlane colour.
Crossing Swimlanes
When crossing swimlanes there will be an swimlane crossing event, in this event you can configure what will happen when the crossing happens.
Task name is the name of the task that is handed over to the recipient.
Push notifications enables iOS & Android client to notify the recipient when a new item is handed over to their inbox. Recipients is where one can select who receives these notifications.
Override Recipient is where you can choose a specific flow user or all users belonging to a role to get this push notification.
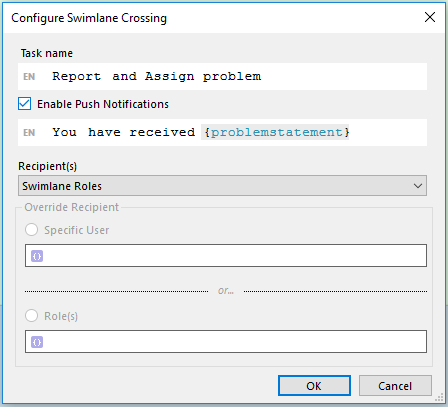
Split/Join
When working with swimlanes, sometimes parallel user inputs need to be made.
To do this, use the workflow element "Split" to split the executions into to parallel workflows, this way the original user can continue working in the workflow while the new user works on their swimlane.
When the new user is done you can use "Join" to join the two parallel executions into one again.
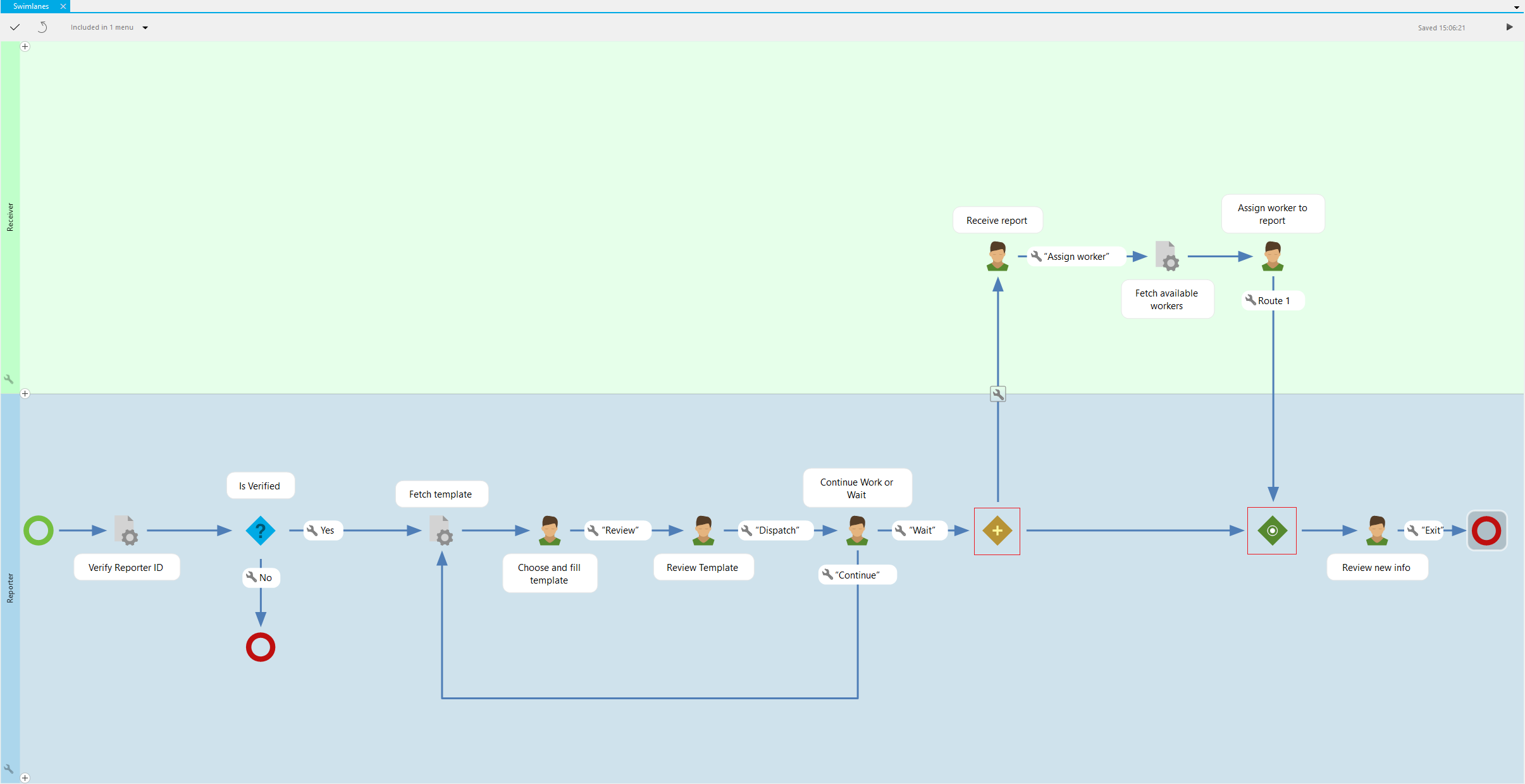
 Table
Table
A table is used to make internal tables with stored data just for that specific workflow.
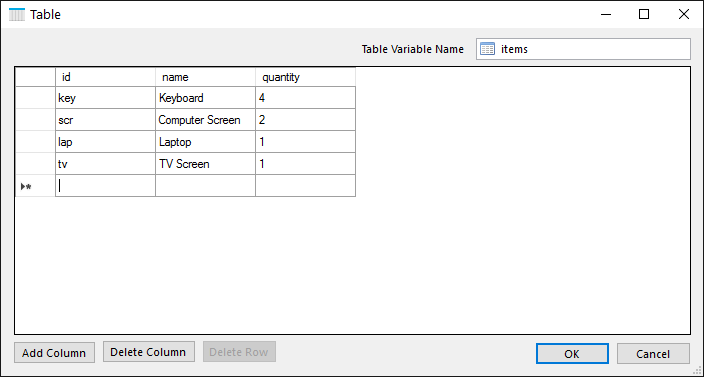
Table example
 User Step
User Step
A user step contains a sequence of interaction items, like input controls, lists and static texts. Each interaction item type has a number of properties and preferences. Extend User step in the tree beside to read about all the different user controls.
Multi exits
A user step can have multiple exits that will appear like buttons in the clients. There is no restriction on how many exits that it is possible to have, but too many buttons in the client (especially in the mobile clients) can look messy, therefore it can sometimes be better to use a sub workflow instead of a button.
If a user step got one exit step it's automatically set to default but when having more than one exit you have to manually set one exit to default, otherwise no exit will be selected automatically when using enter or scanning in a workflow.
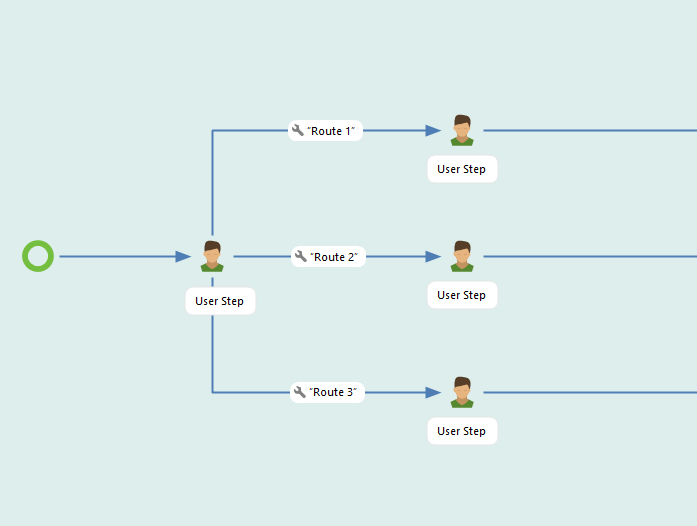

The first exit button is set to default in the Web Client and the priority of the buttons is set to show in which order they should be displayed.
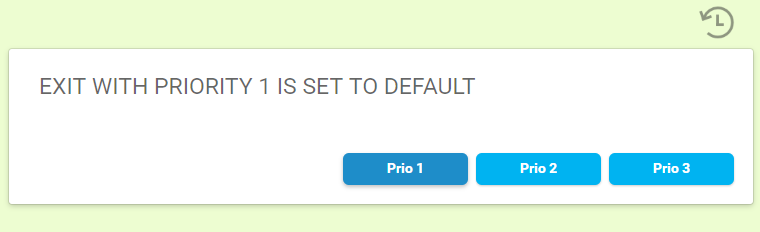
Always enabled exit
Tick the box Always Enabled if an exit should be available even if mandatory data in the user step is missing.
If data is partly entered in the user step from which an always enabled exit is used, the data is not cleared but can be used later in the workflow. The workflow designer should take care when using always enabled exit so the next step is not dependent of data from the exited step.
Pinned user steps
A pinned user step are an information
It is only possible to use Header, Static Text, Labeled Static Text, Link and List Presentation in pinned user steps, this because a pinned user step is only a way to show the user information.

The pinned user step will show up in the side of the screen, and the user need to tap/click on the icon to extend or collapse the pinned user step. In the below picture is the pinned user step to the left and the regular user step to the right. If there is more then one pinned user step in the workflow, will the pinned user step be replaced when the user steps over another pinned user step.

History
From the user step it's possible to edit the text that is displayed in the historical view in the clients.
Click on historical to configure the historical view. Then enable show in history to be able to see the text in the clients. Enter the preferred text into the text, title and value field.
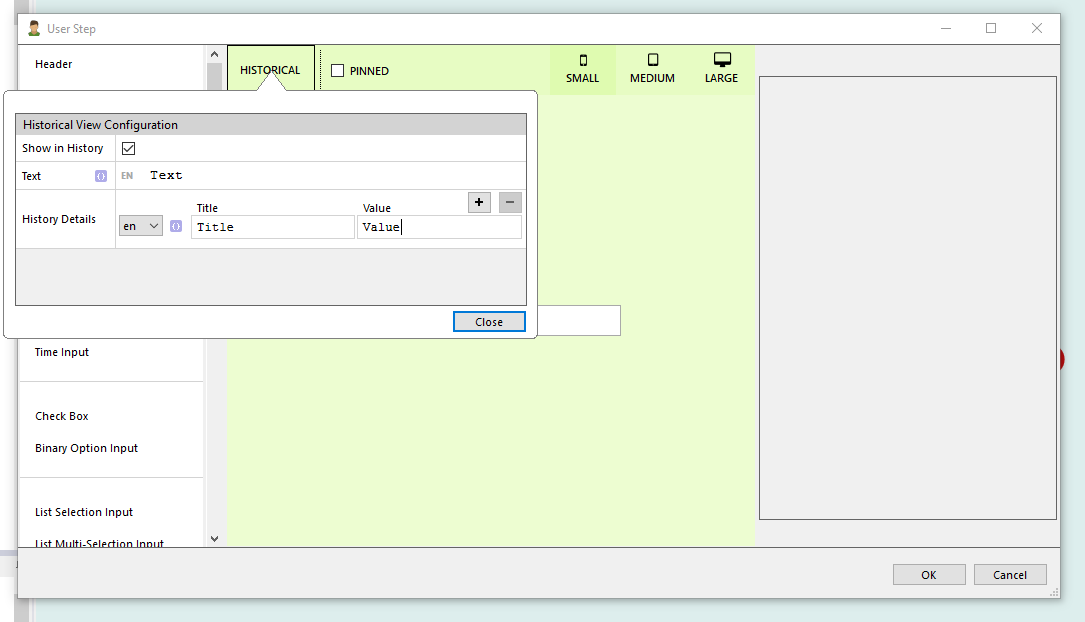
In Universal windows client the configured history step looks like this:

Designer
The designer allows for drag-and-drop interaction with the user step. The user can simply drag one item on the left bar and drop it inside the design area. The designer allows for 1, 2, 3 and 4 columns to be added in one row. The web client will expand or shrink depending on the amount of columns added in the designer step.
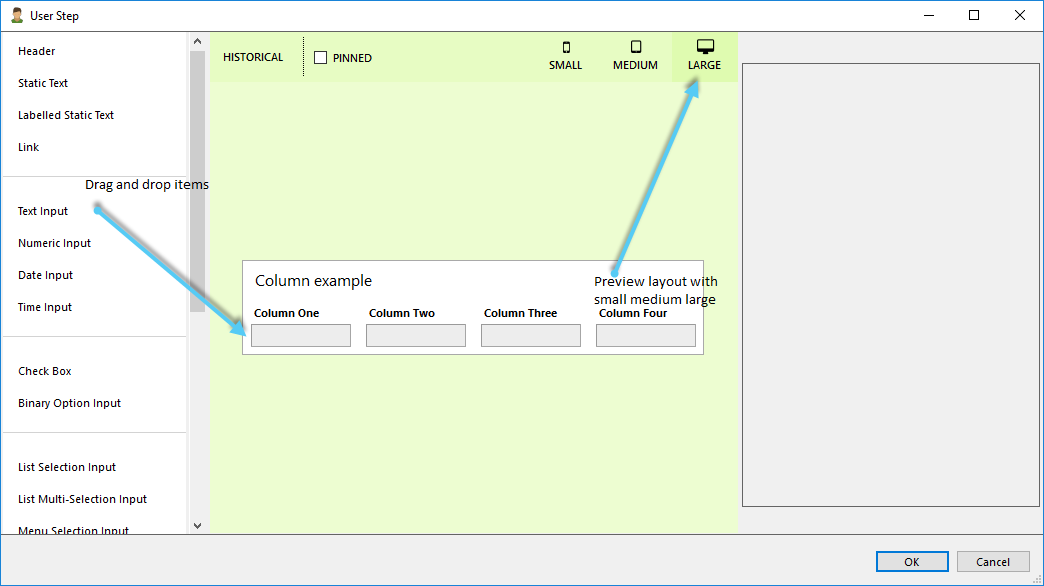
Workflow
The Workflow area is where workflows can be created, published and maintained for the Novacura Flow platform.
A workflow is a visual representation of a sequence of steps, some of which are to be performed by an user, typically on a mobile device. The workflow consists of user steps, which require the user to do something; machine steps, which connects to underlying systems and databases thru connectors; various flow control steps, which for example tell the workflow how to proceed from the current step to the next.
The sequence of steps is determined by flow sequence arrows that bind them together.
Below image shows a workflow with a start step, two user steps and a machine step. Above the first user task is a machine step that only retrieves data and it is connected to the user task with a sequence data arrow. To the right of the sequence data arrow is a text annotation.
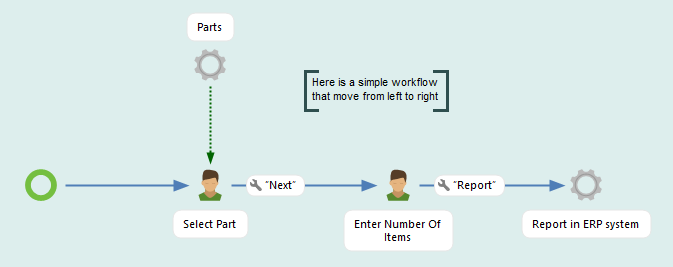
Workflow example
Get started
Under the File menu is it possible to create new, open, close and save workflows in the same way as in most other Windows application. When creating a new workflow, you will be a prompted to enter the title and type of the workflow. It is also possible to choose theme color and compose an icon.

The title and description are shown in the main menu of the Flow Clients and can be changed under the Meta Data panel in the Flow studio. If the workflow should be available in more than one language, add other languages under Languages found in the environment part of the Flow studio.
Managing workflow elements:
Create a new workflow element by dragging and dropping an element from the toolbox to the workflow canvas, or right-click on the workflow canvas and select the element type you wish to create from the contextual menu.
- To insert a new workflow element between two existing, connected elements, right-click on the sequence arrows and choose the element from the Insert menu.
To insert an existing workflow element between two connected elements, drag the element to insert onto the sequence arrow and drop it when the arrow turns green.
- To delete a workflow element, right-click on it and select Delete from the contextual menu or mark the workflow element and press the delete button.
- To edit the configuration for an element double-click the element or right-click the element and select "Edit Configuration..." from the contextual menu.
If there is an error in the element configuration a error message will appear in the Problems panel.
Managing sequence arrows:
- To add a sequence arrow from one element to another, right-click the source element and select Add Sequence arrow from the contextual menu.
- To remove a sequence arrow, right-click on it and select Remove arrow from the contextual menu.
- To change the target element of an existing sequence arrow, click on the target point, move the mouse to the new target element and click on it.
- To change the source element of an existing sequence arrow, click on the source point, move the mouse to the new source element and click on it.
- To add a joint point to a sequence arrow, right-click on the sequence arrow and select Add point from the contextual menu, or hold down the shift key and click on the sequence arrow.
To remove a joint point from a sequence arrow right-click on the joint point and select Remove point from the contextual menu, or hold down the shift key and click on the joint point
- While creating or editing a sequence arrow, use the escape key on the keyboard to cancel the current operation.
- While adding or modifying a sequence arrow, use the backspace key on the keyboard to remove the joint point closest to the mouse cursor.
While creating a new sequence arrow, create a new target element directly by right-clicking on the empty canvas background and selecting a element to create from the contextual menu.
Configuring sequence arrows:
To control the behaviour of a Sequence Arrow, double click on the arrow text. The following window should then appear.
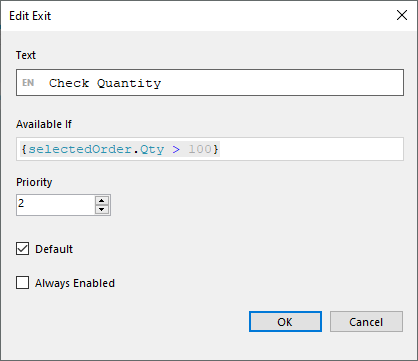
For the Sequence Arrow configuration, you can do the following:
- Text: Change the name of the user step exit. This name is what the User will see as text on the exit button in the current User Step. The name of the exit can be set for each of the used language. What text the User will see depends on which language the User is using.
- Available if: Use this configuration if you want to control when an exit should be available for the User. When the given expression evaluates to True, the exit will be available. Flow Script including any variable from the workflow which can be used in the User Step, can be used to create an expression. Variables defined in the current User Step cannot be used for the Available if expression. If no expression is given, the exit will always be available.
- Priority: Use Priority to control in which order the exit button in the User Step appears.
- Default: This option can be used if the User Step has many exits and one of the exits should be set as the default exit. The Default option is especially useful when scanning is used to execute the workflow. If this option is checked, the current exit will automatically be selected when the User moves from the last input control on the User Step. This works the same regardless if you move forward using scanning or press Enter on your keyboard to move forward.
Data in the workflow
Workflows are all about collecting and consuming data. Pieces of information supplied by the user or fetched from a system or database are stored in named variables in the workflow.
For example, a user step may prompt the user to scan a part number. We may choose to store this information in a variable called, for instance, partNo. The partNo variable would then be available to all steps from this user step where the variable is created (that is, steps that can be deterministically reached by following the arrows from the user step).
The Flow studio automatically checks the workflow to ensure that variables are used correctly; making sure that a variable cannot be consumed before creating it. However, unlike in some programming languages, variables don't need to be explicitly declared beforehand - assigning to a variable (in a user step or machine step) automatically brings it into existence.
When using variables in the user steps (for example in texts and lists) use {} to get a lists of all available variables or write the name of the variable in {} like the picture below. In the machine steps is the syntax of how to get the variables different dependent on what connector that is used, read more about what syntax to use under machine step.
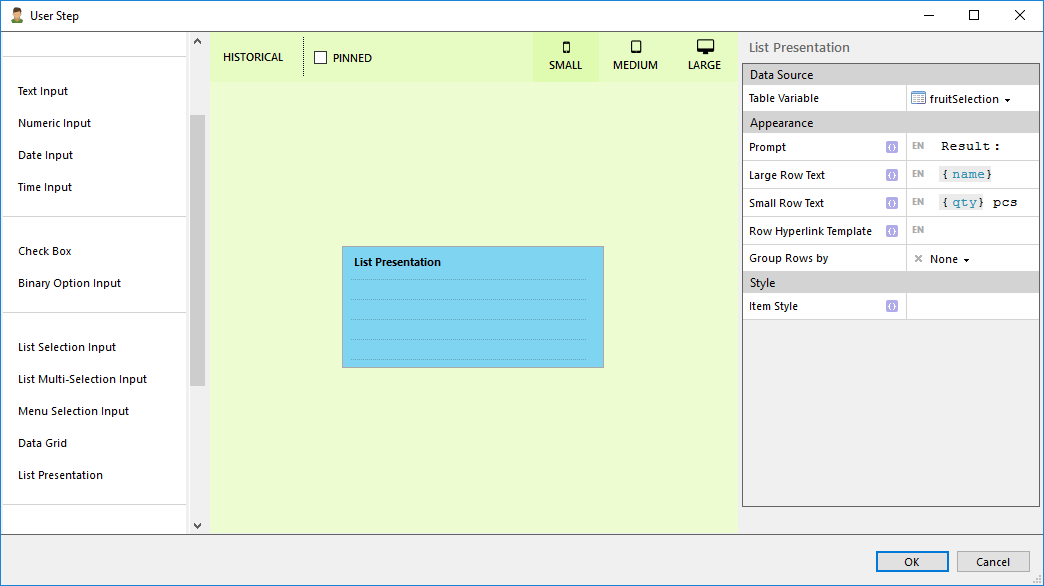
Navigation
To move the view focus to the start item, press the home button on your keyboard.
Scrolling through the workflow:
- The Navigation panel, drag the red square to show differnt parts of the workflow
- Hold down the ctrl key on your keyboard and drag the mouse on the workflow canvas
- The arrow keys on your keyboard
Zooming the workflow in or out:
- The scroll wheel on your mouse
- The View menu
- Ctrl and + or ctrl and -
Image/PDF export
- To export the workflow as a PDF file, select "Export as PDF..." from the File menu
- To export the workflow as a more print friendly PDF file, select "Export as PDF(print)..." from the File menu
- To export the workflow as an image file, select "Export as Picture..." from the File menu
Applications
Application tab gathers all features that is needed to create and develop workflows. Users with type AdministerWorkflows or AdministerBasicData can access this tab.
Application Package
Application Package is a way to package, license and lock specific solutions.
A package can contain workflows, package roles, package properties and portal tabs and can, if licensed, be used by users connected to user type FullUser and AppUser. If the package is unlicensed, it is available to FullUsers.
Package Settings
Metadata
Icons and Theme color: Select the icons and banner color for the package.
- Name: The Name of the package
- Application Package ID: The ID of the application package. This ID is when licensing the package.
- Package Short Description: Enter the description for the package here
- Create by User: The Flow ID of the user that created the package
- Date Created: The date the package was created
- Package Owner: Editable field into which the package owner can be entered. This is useful
- Copyright: Editable field for copyright
- Environment Origin: The name of the environment on which the package was originally created
- Original Flow Version: The Flow version on which the package was originally created
- Business Segment: Possible to set business segment for the package, drop down list
- Process: Possible to set process for the package, drop down list
Connectors
The connectors tab defines which connectors can be used in the package. The technical set up of a connector is still done in Environment - Connectors, the package only contains a mapping.
- Name: The name of the connector. This name is what is seen in the connector drop down list when creating or moving workflows into the package.
- Type: The type of connector. Value if fetched when mapping the connector.
- Mapped name: Drop down list showing all connector available to be selected from. Once added, it is possible to change the mapped connector but only to connector of the same type.
Roles
The Roles tab shows the package access roles. The roles can be added, removed and edited. The roles structure is the same as in the rest of Flow, with a group ID and roles connected to the group.
Properties
Package specific properties are added removed and edited in the Properties tab. A package property is set up the same as in Environment - Properties but are only available within the package.
Portal Tabs
The portal tab shows the Flow Portal tabs connected to the package. Portal tabs can be added or removed. It is only possible to connect whole portal tabs to a package, not individual portlets.
Workflows
Application package workflows are created the same way as normal with the difference that the available connectors are only the ones defined in the Package Settings - Connectors tab. Workflows can be dragged and dropped into a package, the user is then asked to map the connectors used in the workflow to the ones package settings.
Menu
A package can contain one or more menus. A package related menu is configured the same way as a non-package menu, ie workflows and inboxes can be added, and roles connected. The roles available for a package menu are the ones defined in package settings.
Workflows however, are not just limited to the ones in the package but all workflows can be added. An info message is displayed to notify the user if a workflow is not in the package - ?Add external workflow to package menu?, yes or no will either add the workflow or about the action. Package workflows can also be added in external Menus.
Folders
A package can contain folders in multiple levels. All workflows and menus in the folders will belong to the same package and have the same package settings data available.
Package Actions
Import and Export
A package can be exported and imported using the right mouse button options in the navigator.
Export: it is the that package content that is exported. External workflows connected to a menu will not be included in the export. All workflows in the package must be committed and published before the package can be exported.
Import: at import, the user will be asked to map all package connectors. If the package already exists, the user gets the options to replace the existing package or to create a new. New packages created will get a new package id. The rest of the metadata remains the same.
If a new package is created and the original package contains portal tabs, the portal tabs are not duplicated but the mapping is to the same tabs as the original package.
Individual workflows are exported and imported outside the package.
The application package only contains connector mappings and not the full connector. Before importing into a new environment, it is recommended to check that all relevant connectors exist.
Lock
An application package can be locked by right mouse clicking on the package, selecting Lock. All workflows in a package must be committed before it can be locked. Any package content open in the studio will be closed when the package is locked.
If a package is locked it is not possible to open workflows or change metadata.
For a locked package the following is still editable:
- Menu: add and remove workflows, inbox and category
- Menu: add and remove package roles
- Package settings - Connectors: possible to change the connector mapping to enable the customer to maintain connect settings themselves
A locked package is exported and imported as locked.
If importing into an environment where the package id already exists, the user will not get the option to create a new package but only the possibility to replace the existing one.
Forgotten password
It is possible to unlock the package for which the password has been forgotten. Contact support for assistance.
Find
This panel can be used to search in the active workflow. Do a search by entering a search term in the search text field and pressing the search button or the enter key. The search results will be displayed in the list below the search field. The search function will search in workflow items and their configurations (including scripts). Note that each workflow item will only be displayed once in the search result (even if it has more than one occurrence of the search term).
The checkboxes in the upper left corner can be used to filter the search result. For example, in the screenshot below, we have filtered the search to display only variable assignments and usage of variables containing the phrase workOrder.
Search result example
Tip Double click a search result item to navigate to that item, works even for items in sub workflows.
Markdown File
Navigation
Navigation panel shows an overview of the active workflow and provide a rapid way to navigate in the workflow by dragging the camera around to change view.
Red box indicate the current view box in workflow
Problems
The Flow Designer will check the workflow for possible errors at regular intervals (or if the F5 key is pressed). Errors are displayed in a list which as of default is located below the workflow, and workflow steps with errors are rendered with a red background.
Workflows with errors can not be published. Workflows with warnings can be published but is not recommended.
Most type of errors/warnings can be double clicked and it will highligt the failing step. Some errors/warnings is related to more than one step and in that case a search will be performed when double clicking that row, the search result will be shown in the Find Panel
Example with both errors and warnings
Public variables
Public Variables are visible from outside the current workflow, and are used to provide instance-specific information when configuring the template for an Inbox.
To create public variables:
- Navigate to metadata in your workflow.
- Open the panel for public variables.
- Create a new public variable.
- Choose a name for the new public variable.
- Confirm and create the new variable.
To assign a value to the public variable:
- Navigate to Workflow->Public Variables
- Click on public variables.
- Select your public variable and map it to a system variable.
- Press ok to save changes.
Workflow Scheduler
Machine workflows and User workflows* can be started from a schedule in Novacura Flow. This is useful when a workflow should be run at a certain time or/and with a certain recurrence. This function is suitable when moving data between systems or doing system checks that may result in user tasks.
All scheduled workflows which will be ran in the future are indicated with a clock icon in server content panel. Each scheduled workflow saves a last run status which is shown in the configuration windows. This windows can be found in the server content context menu for each workflow, i.e. Right click on the workflow and select Schedule....
Server content example
*User workflows must start in a machine swim lane but can later do a handover to an end-user.
Configuration
- Machine User: Sets which machine user account that will be used when executing the workflow.
- Repeat every: Sets the repeat interval (if any). The start point is used for calculating the cycles.
- Start: Date and time for the first execution.
- End: Date and time for when the execution should stop repeating. This will not stop any started executions.
- Enable: Sets if the scheduling is active or not.
Example configuration
Note: This function is depending on the Novacura Flow windows service which is installed along with all Novacura Flow server installations. This service will check for scheduled workflows on a 10s interval, which means that the granularity can never be more precise than 10s.
Tips
More complex repeat patterns can be achived with FlowScript that restrict the execution. For example running a workflow every Monday, Wednesday and Friday at 03AM can be achived by settings start time to 03AM and repeat interval to 24 hours. The workflow should then start with a decision step that checks which day it is. See example below.
Example every Monday, Wednesday and Friday
Best practices
Avoid long running workflows. Workflows can never be run longer than 60min and each machine steps should never take more than 100s.
Don't run multiple instances at the same time. If a workflow take more time (in worst case scenario) than the repeat interval then it will start parallel executions which may result in unexpected behavior.
Troubleshooting
If a workflow wasn't executed as expected follow these steps:
- Check the status field, if the execution ended in an error that should be stated here.
- Workflow should have a clock icon, or else the configuration is incorrect.
- Press Run now... to see that it can be executed with that user and has a published version.
- Make sure that windows service is running and correctly configured.
- Change log level to info on Novacura Flow server and wait for next execution.
Server Content
The Server content panel shows the server content that is stored on the currently connected server. Content can be folders, workflows or menus.
To create new content right click anywhere and select New... from the context menu. To move the contents, drag and drop the content onto the folder that it should be moved to.
Export: To export an item and save it as a file, right click on it and choose Export. You can export a single workflow or menu, or right click on a folder to export everything in the folder.
An exported workflow will get suffix .flow, a menu will get suffix .mflow and a folder will get suffix .wap.
Import: To import an exported item, right click in the server content panel and choose Import, or choose Import to server from the File menu. Novacura Flow 6 supports import of workflows from version 5.10 and above.
Server content example
Folder: A folder can contain different types of workflows and menus.
Workflow: A regular workflow. The icon is grey when no one is working with it. The icon is blue when the logged in user has the workflow in edit mode. When another user is working on the workflow, it will show a padlock icon.
Machine Workflow: A machine workflow. The icon is grey when no one is working with it. The icon is blue when the logged in user hae the machine workflow in edit mode. When another user is working on the workflow, it will show a padlock icon.
Workflow Fragment: A fragment workflow, and the icon is grey when no one is working with it. The icon is blue when the logged in user have the fragment workflow in edit mode. When another user is working on the fragment, it will show a padlock icon.
Menu: A menu needs to be configurated to make workflows available in the clients.
Subscribe
The subscribe function is used to share applications between different Novacura Flow server environments. This makes the transition of workflows from test to prod very simple.
We recommend that applications are developed in a dev/test environment, and subscribed in the production environment.
Share
Share the workflow by clicking on the share icon, right to the edit and publish.
Enter a comment and click on share.
Copy the url.
The workflow need to be published to be able to be shared.
Subscribe
Subscribe to an application by right-clicking in the server contect panel area and choose subscribe.
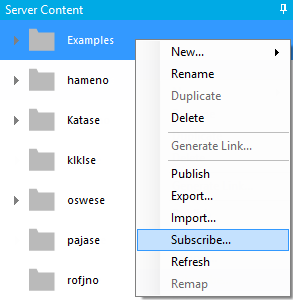
Enter the copied url for the application that should be subscribed and click OK.
Subscribed workflows will get a specific icon as in the below picture.
It is not possible to edit subscribed workflows.
Update to new version
When a shared workflow is updated and published with new functionality to a new version, click on the share icon and enter a comment and click share.
The new version of the application will now be available in all environments where it is subscribed.

In the environment where the application is subscribed will the application get a star icon, indicating that there is a new version avalibale.
Right-click on the application and choose update. This will update the application to the latest version.

Test Bench
Test Bench is a powerful tool for dynamic workflow analysis, making it possible to detect errors, problems and misbehaviours. By using it, you can follow the execution of your workflow step-by-step with live information about all used variables, inputs and tasks.
Test Bench panel is divided into two areas: on the left there is a simulation how the step will be presented in the clients; on the right there is a panel with variables available in this step with their values.
Test Bench overview
User can start the test bench by clicking on the Play button in the top right of your workflow window. Current element being debugged is highlighted on yellow, if two or more swimlanes are present both paths are being highlighted and user can switch between them by choosing proper tabs in the test bench.
When using several swimlanes, the test bench can impersonate as another user in the other swimlane(s) from this window that shows up when the workflow moves to another swimlane
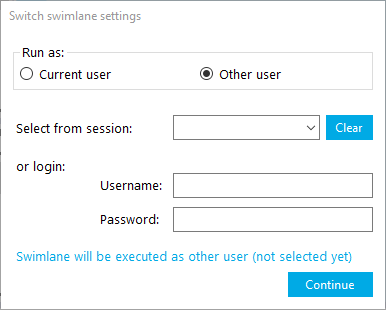
Swimlane user settings
User can go to the next step by clicking the button on the preview window. If step requires some action (eg. demands user to provide some text) you cannot move forward without providing it, just like in real execution. By providing different inputs and data user can test the workflow to make sure it works as it is expected.
If two or more swimlanes are present some steps must be completed before others to make it possible to move forward. Test Bench will prompt the user if action on another swimlane is needed.
Test session can be stopped by going through the workflow to the end or at any time by clicking the Stop button on the top right corner of the workflow.
Missing features
- Support for Log Points
Version Panel
Start a new workflow version by clicking the Edit button, this will lock the workflow and prevent other users from starting new versions. To indicate edit mode, the server content shows a blue icon to the current user and a lock icon for other users.
When editing a workflow in edit mode all changes will be saved to the server automatically. In the case when the server can not be reached changes will be saved to local copy and uploaded when server is available. When the changes of the workflow are done click on the Commit button. The commit button is enabled once there is a change in the workflow. If no change is required for a workflow in edit mode, click the Revert button to go back to the previously committed version.
At commit it is possible to enter a commit message. The commit message is option but is possible to make mandatory by ticking the Force Commit Message box in the workflow metadata.
When a new version is committed is it possible to publish the new version and make is available for the end-users by clicking on the Publish button.
- Edit button
- Commit button
- Revert button
- Publish button
The version panel will show a list of versions. Any version can be opened by double click. Each version can be in a number of different states.
In order to create a new version that is based on a historical version just open the old version and click the Edit button. This will be shown as a break line. In the example below Version 3 is based on Version 1.
Version jump example
Archive
When a workflow has more than five (as default, this can be adjusted in the server configuration) versions only the five latest versions will be shown and loaded as default. This enables faster loading since older versions are achieved. Double click on Load all versions to load and show all previous versions.
Version handling example
Elements
From this panel, elements can be dragged to the workflow canvas.
Tip The panel adjusts its layout to its size; experiment with different sizes!
Novacura Flow Android client
Novacura Flow is an innovative, rule changing software with one sole purpose: to improve your critical business processes. With Novacura Flow, we put the business and the user in focus, allowing you to create intelligent and user friendly business applications in three simple steps: Design, Configure, Run.
System requirements
The Android Client requires Android version 5.0 - 7.0.
Installation
There are two ways of installing the Novacura Flow Android Client:
- Download the client from Google Play store: Search for Novacura Flow 6 or use this link.
- Download the client from your server: The server address should be https://[your servername]/Novacura.flow.server. Ask your administrator for the server name.
Note! If you download the Android client from your server, you need to enable installation from Unknows Sources on your device. This setting is typically found under Settings/Security.
Connect and Log In
In order to be able to run your Novacura Flow applications, you first need to connect to the correct Flow environment.
When you first start the Novacura Flow app you will get to this screen:
There are three ways of connecting to your Flow environment:
- Scan Code: Scan the QR Code on the Server Page. The server address should be https://[your servername]/Novacura.flow.server.
- Enter Pin: Enter the Pin Code visible on the Server Page.
- Enter server address manually:. Enter the server address above manually to connect.
When you have connected to your Novacura Flow environment, you should get to the login page.
Here you enter your Novacura Flow user name.
Depending on the set up, you will be prompted to enter one or many passwords. These passwords is either your Flow login password OR passwords for logging in to any connected system. The login can therefore be different for different users.
For User setup, see User configuration.
Get started
Open the Novacura Flow client and enter your Flow server address and press OK. Enter your username and choose environment and language and press Enter to log on.
All menus are displayed in lists which can be opened to display all workflows that are attached to the menu. Users can only see menus they are allowed to see by assigning the menu to dedicated roles and the same for the user.
To log out, go offline/online or reload the workflows use the menu in the top right corner.
Start a new workflow by tapping the workflow you want to run under the Workflow tab. Pause or quit a running workflow with the arrow in the left corner. Online mode If any transactions is done when a workflow is quit, all transactions will still be done as far as the step you are in, no rollback will be done. When the workflow is paused the workflow will be available in the Ongoing tab. Start a paused workflow by taping it the workflow under the Ongoing tab. To delete paused workflow from the Ongoing tab, press and hold on the workflow you wish to kill the ongoing execution on (observe that all transaction that is done in the workflow will not be deleted). When a workflow is completed it will appear with a check mark in the History tab.
Offline mode
When working with offline applications in the iOS Flow clients, all transactions that are produced by the workflow are put in a queue. This queue can be found in the Offline Data section, under MY WORK. The transactions are executed automatically in the background when the device have access to internet. Always download or update the offline data under Offline Data -> MY OFFLINE DATA, after that is done, then it will be possible to execute a workflow without internet connection.
Help request
Transactions that is done in offline applications will normally execute without any problems and then disappear from the queue. However, if a workflow transaction has failed, then is possible to send a Help Request to an Administrator, so that the problem can be fixed. The Administrator can then either correct the problem in the back-end system or correct the data in the workflow transaction. When the Administrator has sent back the transaction can the transaction be executed again, and if the problem is fixed will the transaction execute without any errors.
- If there is an error in a transaction a warning will show up next to the Offile data button.
- Workflow error details are registered in the MY WORK section under Offline data.
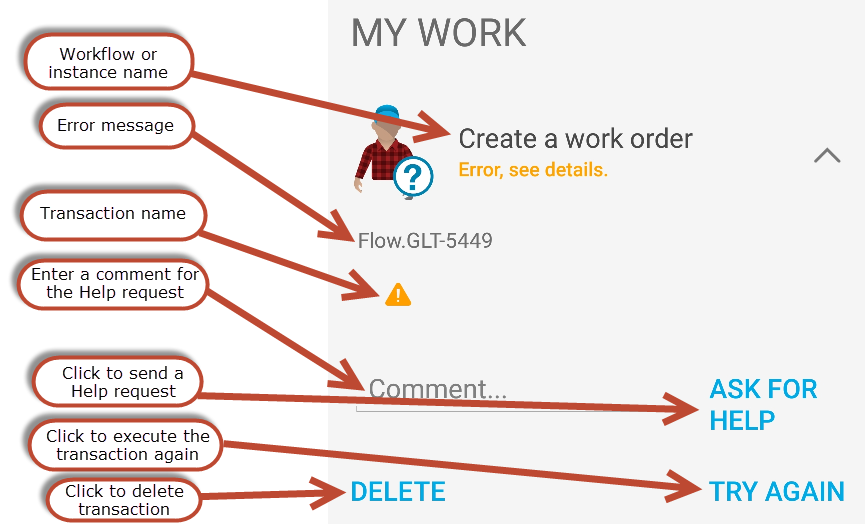
- To send a Help request for a transaction that has an error, fill in the optional Comment field and click on ASK FOR HELP, the Help request will be sent to an Administrator that will take care of the issue.
- When the Help request is sent, then will the status for the transaction change to Waiting for response.
- A notification will be sent when an Administrator has started to work with the Help request, and another notification will arrive when the Help request is sent back to be executed again.
- To execute the transaction again, go to MY WORK section under Offline data, find the transaction that is fixed and click in TRY AGAIN.

The User can use the following options:
- ASK FOR HELP: Send a Help request to and Administrator
- TRY AGAIN: Retry a transaction without asking for help
- DELETE: Delete the transaction (observe that all data for that transaction will be deleted)
Scanning
Scanning functionality levels:
FULL SUPPORT: We can scan in all applicable controls (text inputs, list selections, etc.). The workflow moves forward automatically when appropriate.
LIMITED SUPPORT: We can scan in text inputs. The workflow does not move forward automatically, and scanning may not work in list selections and other non-textual controls.
NO SUPPORT: Scanning will not work at all.
- Honeywell CT50: FULL SUPPORT.
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge with semicolon character as pre-and postfix and send the scanned characters as key events: FULL SUPPORT.
- Unfortunately, there is no way of knowing whether the scanner sends key events. The only way is to test it.
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge: LIMITED SUPPORT.
Novacura Flow iOS client
Novacura Flow is an innovative, rule changing software with one sole purpose: to improve your critical business processes. With Novacura Flow, we put the business and the user in focus, allowing you to create intelligent and user friendly business applications in three simple steps: Design, Configure, Run.
System requirements
Requires the latest two major versions of iOS. Compatible with iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch.
Installation
To install the Novacura Flow iOS Client:
- Download the client from app store: Search for Novacura Flow 6 or use this link.
Connect and Log In
In order to be able to run your Novacura Flow applications, you first need to connect to the correct Flow environment.
When you first start the Novacura Flow app you will get to this screen:
Screen for connecting to your Flow Environment
There are three ways of connecting to your Flow environment:
- Scan Code: Scan the QR Code on the Server Page. The server address should be https://[your servername]/Novacura.flow.server.
- Enter Pin: Enter the Pin Code visible on the Server Page.
- Enter server address manually:. Enter the server address above manually to connect.
When you have connected to your Novacura Flow environment, you should get to the login page where you can enter your Novacura Flow user name.
Depending on the set up, you will be prompted to enter one or many passwords. These passwords is either your Flow login password OR passwords for logging in to any connected system. The login can therefore be different for different users.
For User setup, see User configuration.
Get started
Open the Novacura Flow client and enter your Flow server address and press OK. Enter your username and choose environment and language and press Enter to log on.
All menus are displayed in lists which can be opened to display all workflows that are attached to the menu. Users can only see menus they are allowed to see by assigning the menu to dedicated roles and the same for the user.
To log out, go offline/online or reload the workflows use the menu in the top right corner.
Start a new workflow by tapping the workflow you want to run under the Workflow tab. Pause or quit a running workflow with the arrow in the left corner. Online mode If any transactions is done when a workflow is quit, all transactions will still be done as far as the step you are in, no rollback will be done. When the workflow is paused the workflow will be available in the Ongoing tab. Start a paused workflow by taping it the workflow under the Ongoing tab. To delete paused workflow from the Ongoing tab, press and hold on the workflow you wish to kill the ongoing execution on (observe that all transaction that is done in the workflow will not be deleted). When a workflow is completed it will appear with a check mark in the History tab.
Offline mode
When working with offline applications in the iOS Flow clients, all transactions that are produced by the workflow are put in a queue. This queue can be found in the Offline Data section, under MY WORK. The transactions are executed automatically in the background when the device have access to internet. Always download or update the offline data under Offline Data -> MY OFFLINE DATA, after that is done, then it will be possible to execute a workflow without internet connection.
Help request
Transactions that is done in offline applications will normally execute without any problems and then disappear from the queue. However, if a workflow transaction has failed, then is possible to send a Help Request to an Administrator, so that the problem can be fixed. The Administrator can then either correct the problem in the back-end system or correct the data in the workflow transaction. When the Administrator has sent back the transaction can the transaction be executed again, and if the problem is fixed will the transaction execute without any errors.
- If there is an error in a transaction a warning will show up next to the Offile data button.
- Workflow error details are registered in the MY WORK section under Offline data.
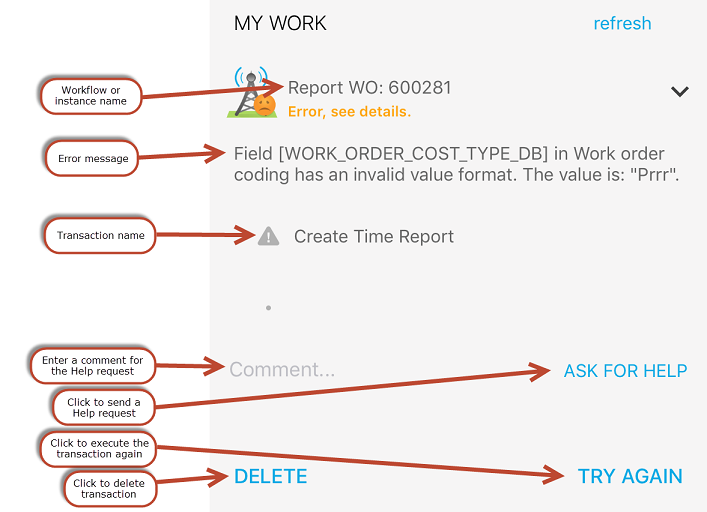
- To send a Help request for a transaction that has an error, fill in the optional Comment field and click on ASK FOR HELP, the Help request will be sent to an Administrator that will take care of the issue.
- When the Help request is sent, then will the status for the transaction change to Waiting for response.
- A notification will be sent when an Administrator has started to work with the Help request, and another notification will arrive when the Help request is sent back to be executed again.
- To execute the transaction again, go to MY WORK section under Offline data, find the transaction that is fixed and click in TRY AGAIN.
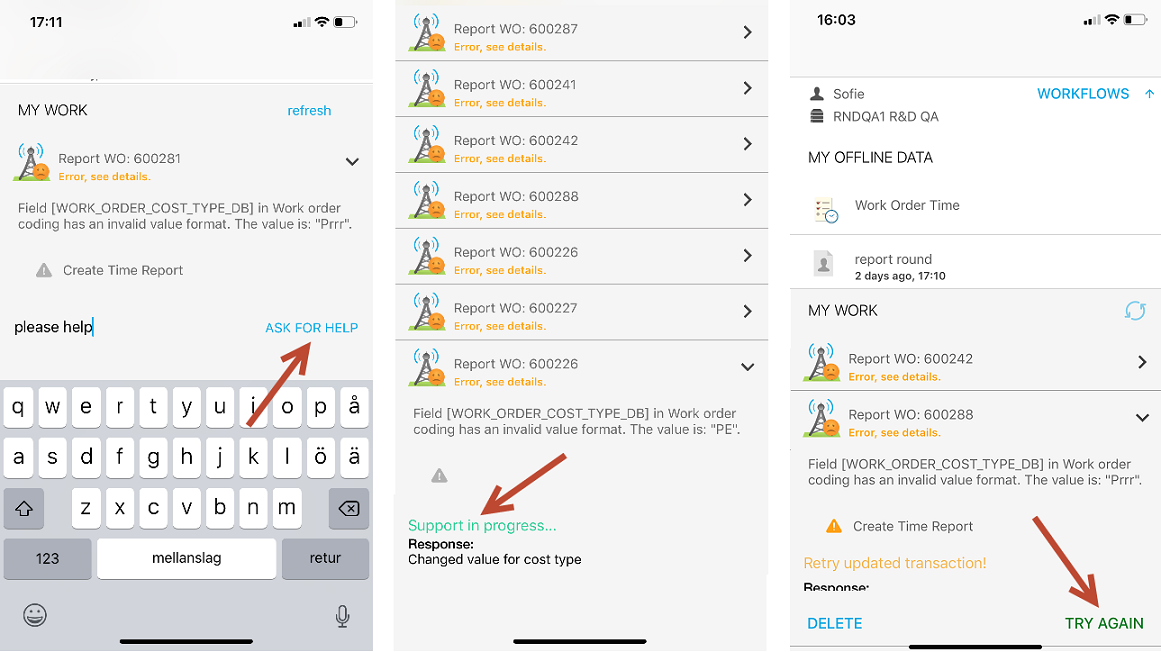
The User can use the following options:
- ASK FOR HELP: Send a Help request to and Administrator
- TRY AGAIN: Retry a transaction without asking for help
- DELETE: Delete the transaction (observe that all data for that transaction will be deleted)
Scanning
Scanning functionality levels:
FULL SUPPORT: We can scan in all applicable controls (text inputs, list selections, etc.). The workflow moves forward automatically when appropriate.
LIMITED SUPPORT: We can scan in text inputs. The workflow does not move forward automatically, and scanning may not work in list selections and other non-textual controls.
NO SUPPORT: Scanning will not work at all.
- Linea Pro: FULL SUPPORT
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge (scanning into any application): LIMITED SUPPORT
- Other scanners which do not support keyboard wedge: NO SUPPORT
Content Access Management
Content Access is used to control which tabs in the portal that a flow user can access. The access is granted by their assigned flow roles meaning that depending on which flow role(s) a flow users is connected to, the flow user will gain access to a specific set of tabs in the portal.
By defining specific flow roles for portal content access, one can control what tabs a user can access in the portal.
Flow Roles
Flow Roles are defined in the Novacura Flow Administration interface and can be used for a variety of purposes. The Roles are organized in a tree structure and can inherit be set to inherit its parents or children. Flow Users can be connected to one or many flow roles. See more about Roles in the Novacura Flow Administration interface
Set up content access
- Choose the flow role which the user needs to access.
- Check which tabs the role should have access to.
- Press save.
Document Access Management
Included in the Flow Portal, is a simple Document Manager. Documents are saved in a Folder structure and access to documents is controlled by granting access to different Folders. This means that depending on which Flow Role(s) a Flow User is appointed to, the Flow User will gain access to a specified set of Document Folders and the documents it contains.
In the Document Manager Folders all Documents are managed (i.e. created, updated or deleted) by using workflows. All the business logic around document management is thereby defined by the workflows used by the Portal.
Global Variables management
Global variables are used to set a global context to the portal with one or many variables that are set in the URL to the portal.
This allows the usage of the global variables as parameters to affect the data that is displayed to the user in many of the portlets.
Example of URL with parameters:
http://www.myflowportal.com/#/?GlobalVariable1=ValueA&GlobalVariable2=ValueB
In this example the global variables GlobalVariable1 and GlobalVariable2 are defined with the values ValueA and ValueB.
Global Variables
This is where one defines a list of global variables that are available for usage. By pressing create the user will be forwarded to the definition window to be able to specify a new global variable.
Definition
This is where one defines the new global variable, by entering a variable name in the text field Code, one assigns the variable name.
To save the variable the save button is used and the new variable will be displayed in the Global variables list.
By selecting a variable in the list and pressing delete in the definition window, one can delete a global variable.
Icons
Icon Library for Portal
Import/Export
Export allows the user to export the current settings in the portal including values and translations in the portal, tabs, portlets.. there is also an option to export the document folder structure.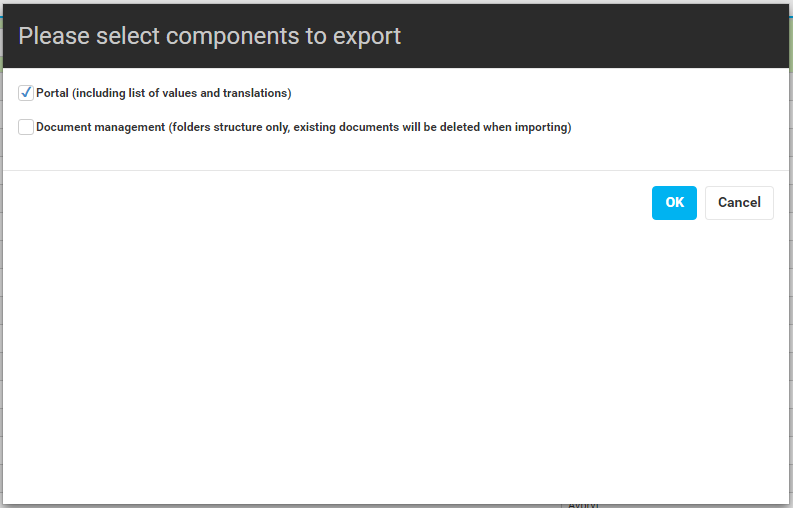
NOTE that existing documents will be deleted when importing, so one can not export/import and expect to keep the documents inside the folder structure.
Import allows the user to import a preconfigured portal from a .json file. When importing the system will ask the user to map the connectors used in the .json file to the corresponding ones in the current server.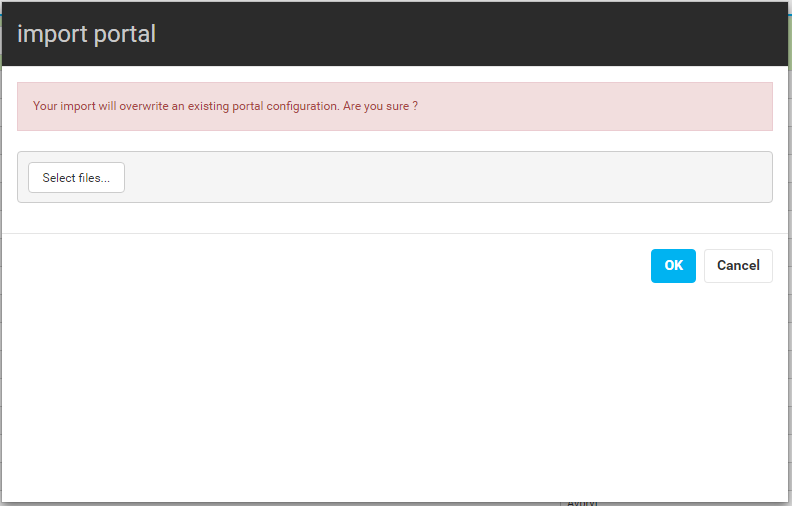
List of values management
In the Table and Record View Portlets, there is a possibility to use a List of Values (a drop-down list with a set of predefined values) when you create or edit a record directly in the Portlet. The List of Values will then define what a user can enter in a specific field.
The List of Values can also take an input, so that the list could be filtered depending of an existing value in the current record.
What the list of values are to contain is defined here.
List of Values
Name - Select a name in the list to display the list settings to the right in the Definition window.
Create - Resets the definition window to the right, so one can create a new list of values.
Definition
Code - Display name of the list.
Query - A query to select a set list of values.
Database Connector - The connector to the database where the query is to be executed.
Text Column - Text Column is what is shown to the User in the List of Values.
Value Column - Value column is the actual value chosen when a value is selected in the List of Values.
Save/Delete - Saves the current definition of the lov or Deletes the selected lov.
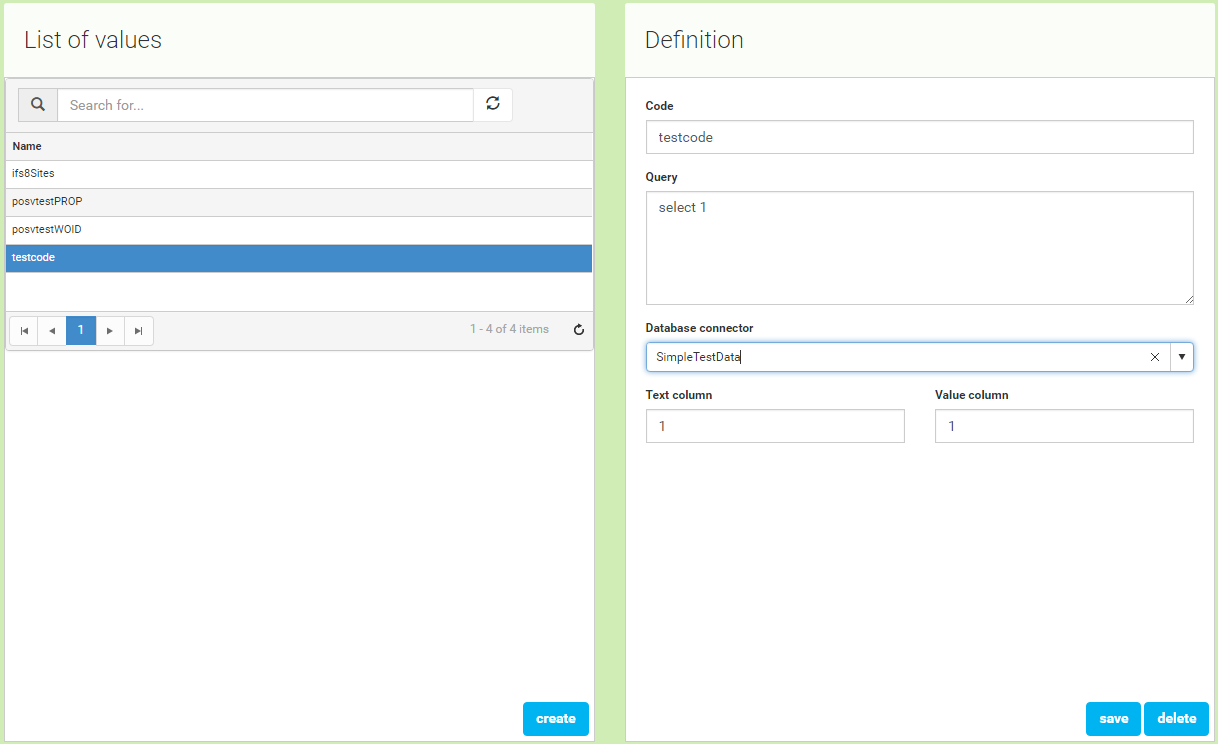
Portal Push
Portlets can be automatically updated by using the Portal Push functionality. If an updated is done in one portlet, a push event can trigger updates to connected portlets. A portal push rest connector must be configured to access this functionality.
Studio - Workflow
- Create a table element with two columns (use the exact column names):
- PortletInternalName
- Action
- In the PortletInternalName column enter the internal names of the portlets that are to be refreshed
- In the Action column enter REFRESH
- Create a Machine step to trigger the push event, using the PortalPush connector.
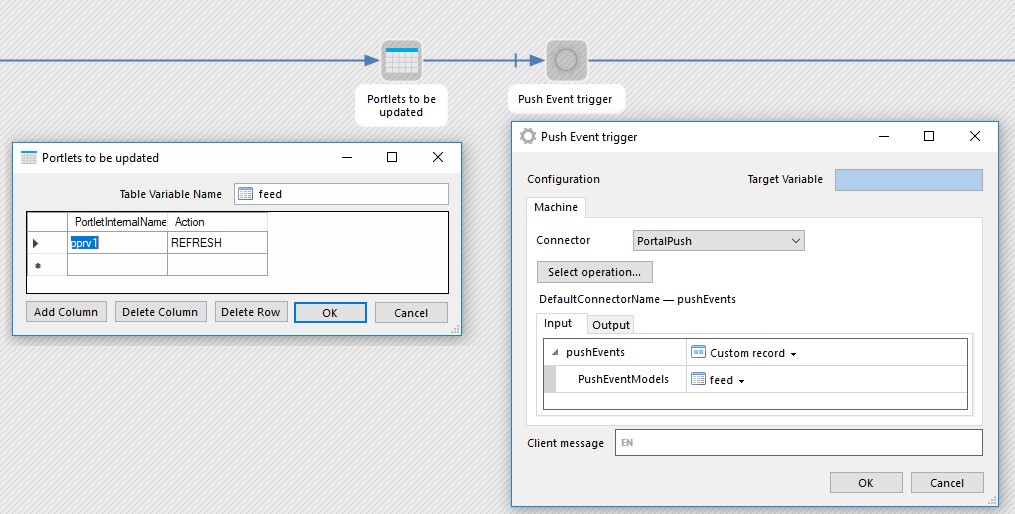
Create PortalPush Rest Connector
- Log on to Flow Studio, go to Environment - Connectors and click Add
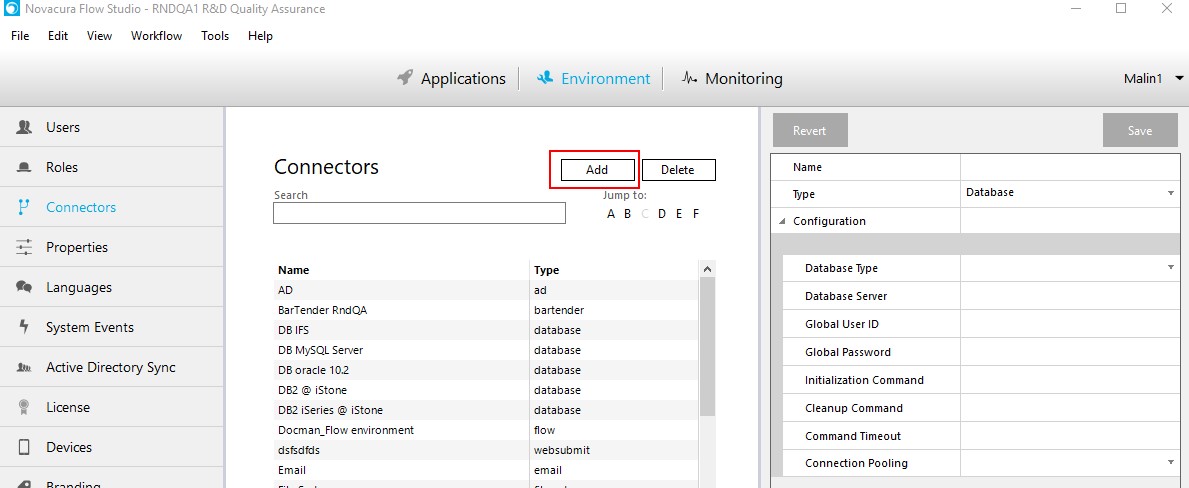
- Set up:
- Name = The name of the connector
- Type = Rest Service
- Base address = XX (in example: http://localhost/Trunk.NovaCura.Portal.Web/api)
- Encoding for url parameters = Unicode (UTF-8)
- Cache metadata = No
- Save
- Click on REST connector project - EDIT
- Set up:
- Connector name = XX (in example: DefaultConnectorName)
- Connector description = the description of the connector
- Base path = XX (in example: http://localhost/Trunk.NovaCura.Portal.Web/api)
Click Create/update connector button
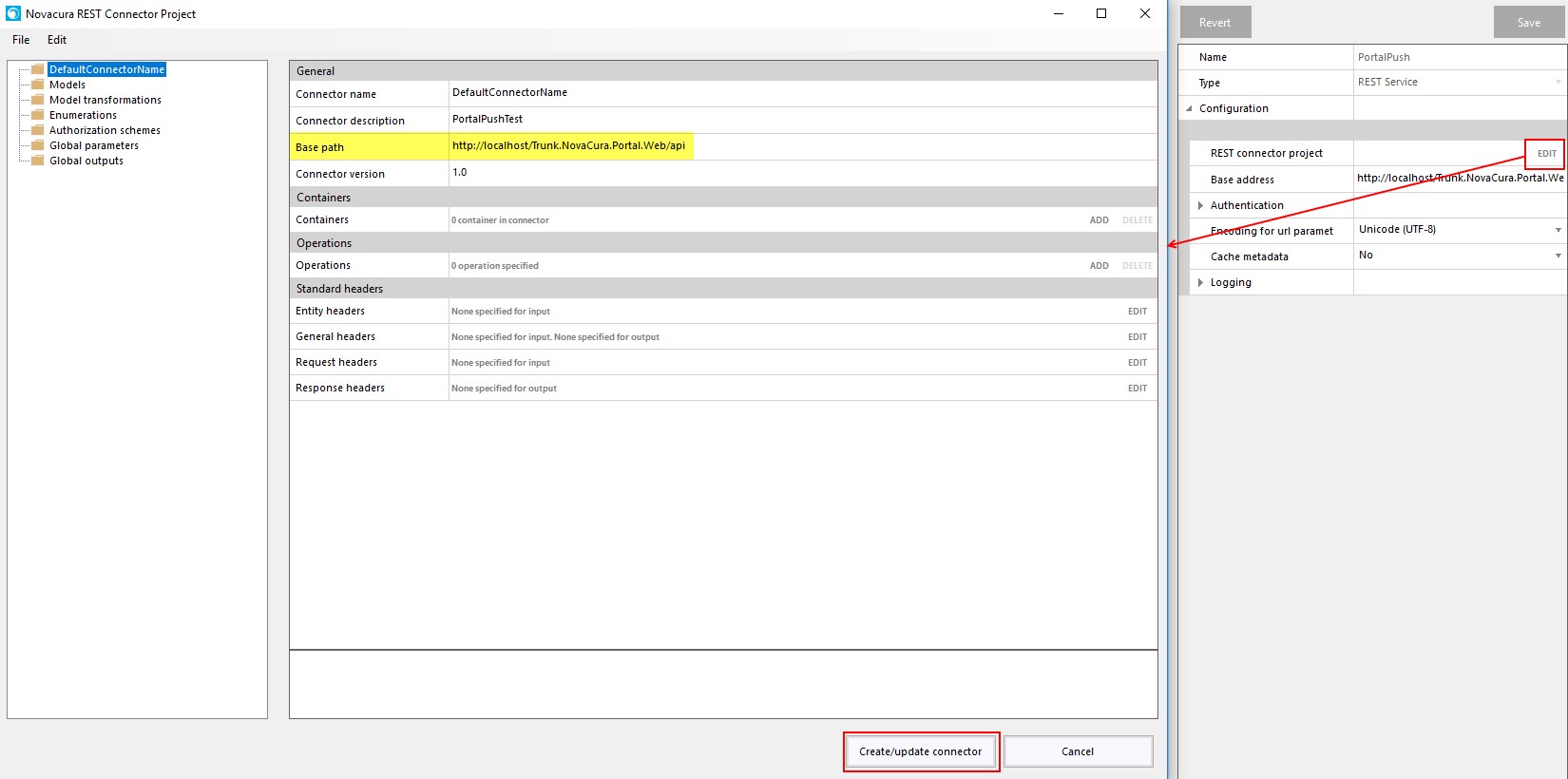
5. Click Save button in top right corner.
- Click on REST connector project - EDIT again
- Click on Models in the navigator tree
- Click on NEW FROM JSON
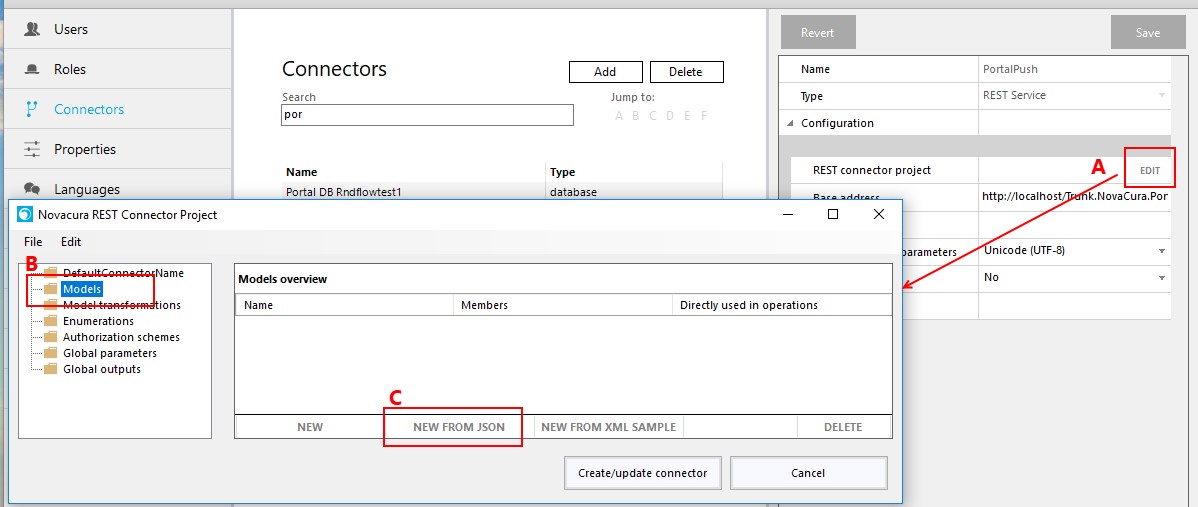
Use following JSON to generate required models:
{ "PushEventModels": [ {"PortletInternalName":"pptbl1","Action":"REFRESH"}, {"PortletInternalName":"pprv1","Action":"REFRESH"} ] }
You can change one of the new created model name from NEWMODEL to for example PUSHMODEL
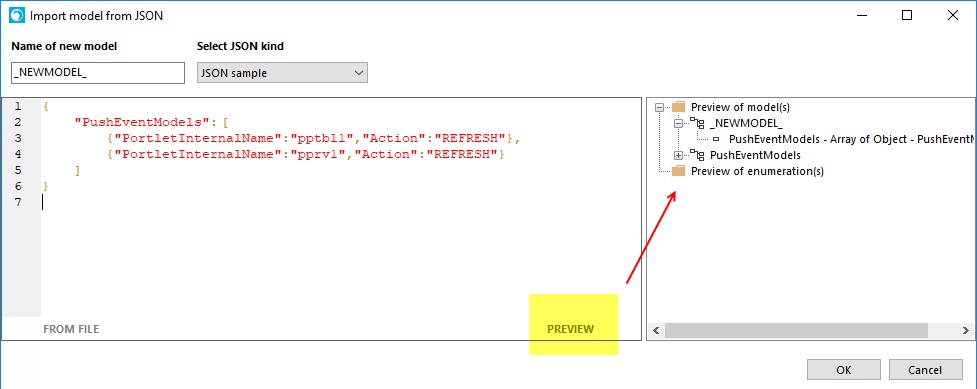
7. Click on DefaultConnectorName and ADD in Operations to create operation. When the requested parameters have been entered click OK.
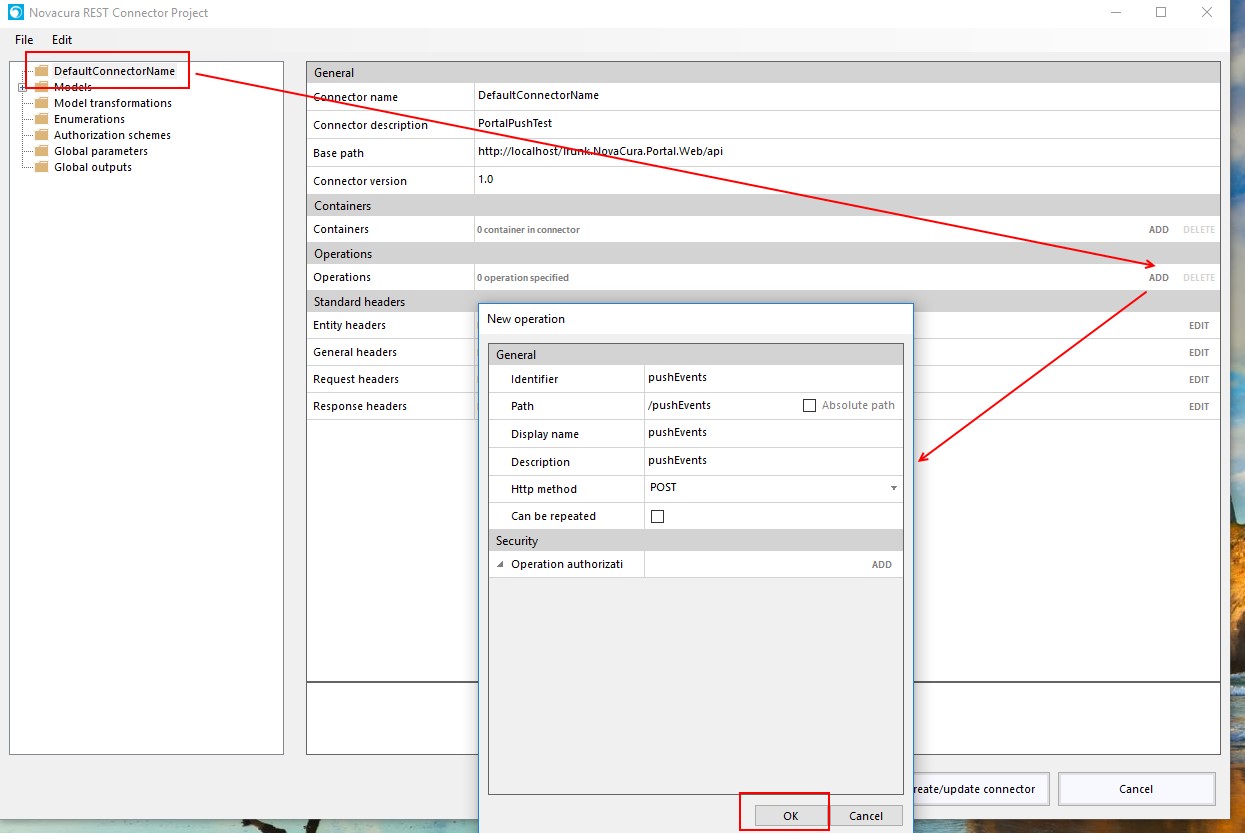
8. Click on Parameters and NEW BODY
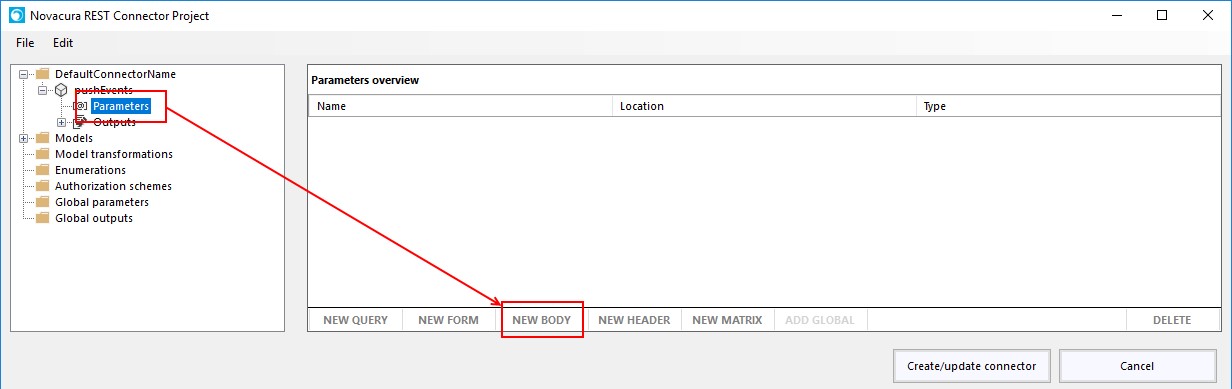
9. Enter Body data, click OK and then Create/update connector
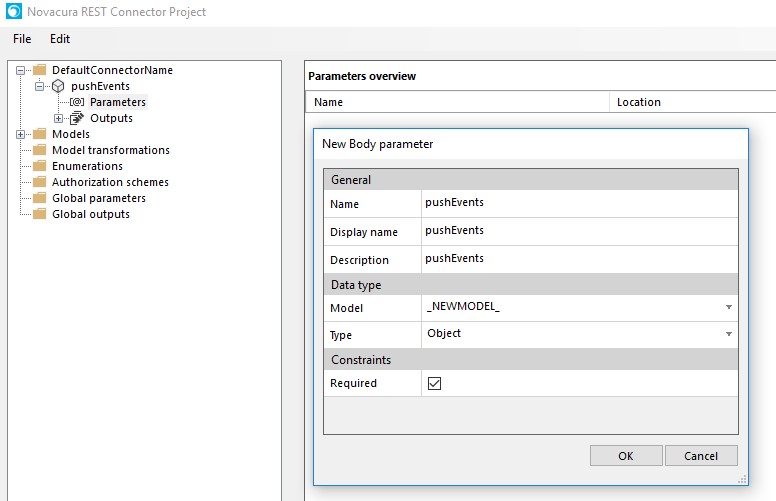
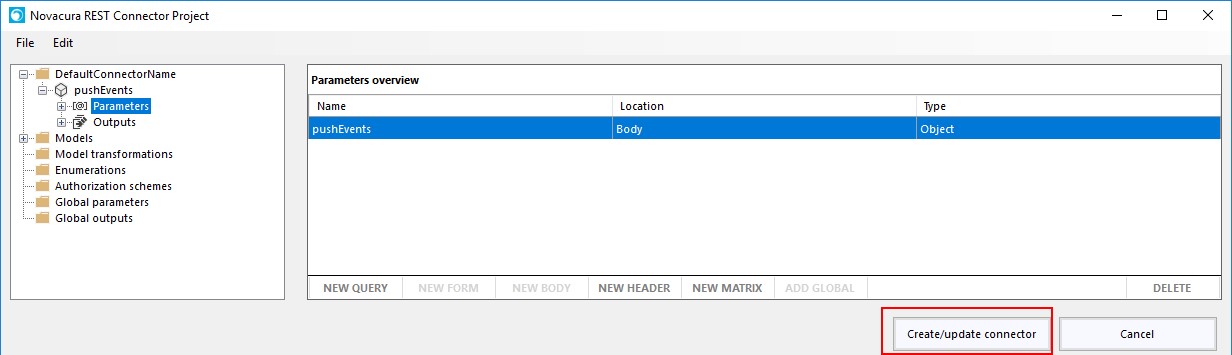
10. If asked for content type for rest requests, select Set content-type to application/json and click ok
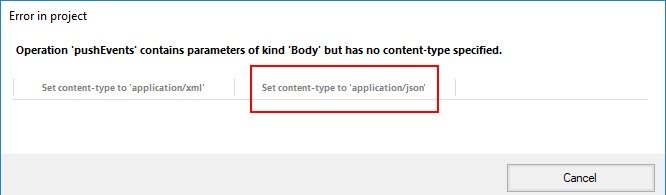
11. Save the connector
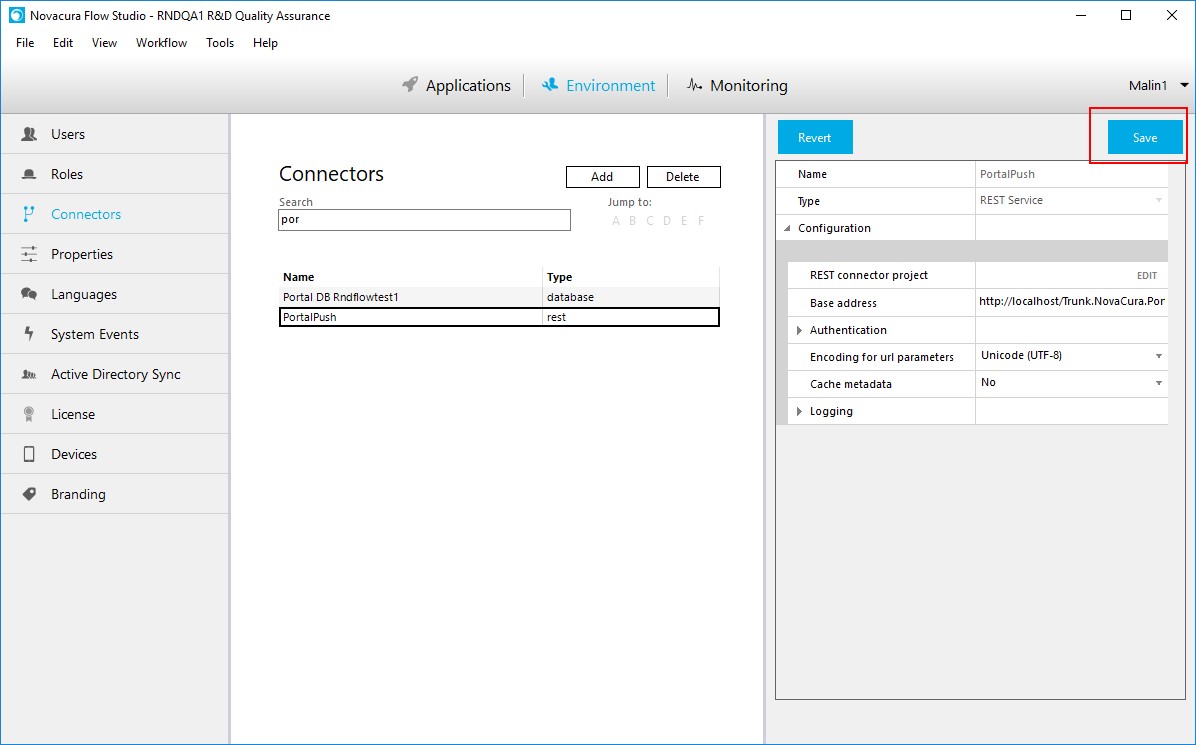
Settings
The portal settings allows the control of different aspects of the portal.
There are currently two configuration options available:
- Title - Controls the value shown in the header on the upper left side of the portal page.
- Margins - Control the distance between the left and right edge of the portal area.
Translations management
The translation management shows a grid of the current translations and its context. This allows for an easy way to customize the language in the portal.
Show translations by
This is where one can choose which translation rows that will be displayed.
Import/Synchronize
Import button allows the user to import translated tables of data from an external source.
Export button exports the translation data as an excel file(.xlsx).
The synchronize button updates the current data with the current set of data from the translation source.
Portal Administration Options
Todo
Portal Administration Options
To the top right is the options drop-down list, it contains:
Data Visualizer Card Portlet
The Data visualizer card portlet allows visual representations of data with different types of cards. The usage of this portlet allows the user to get an easy overview of performance figures by viewing live data.
Currently there are three different types of cards that can be used with this Portlet; Default, Process Card and Speedometer. These three layouts are shown below.

Default Style

Process Style
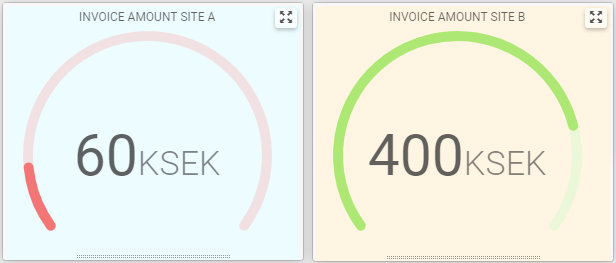
Speedometer Style
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
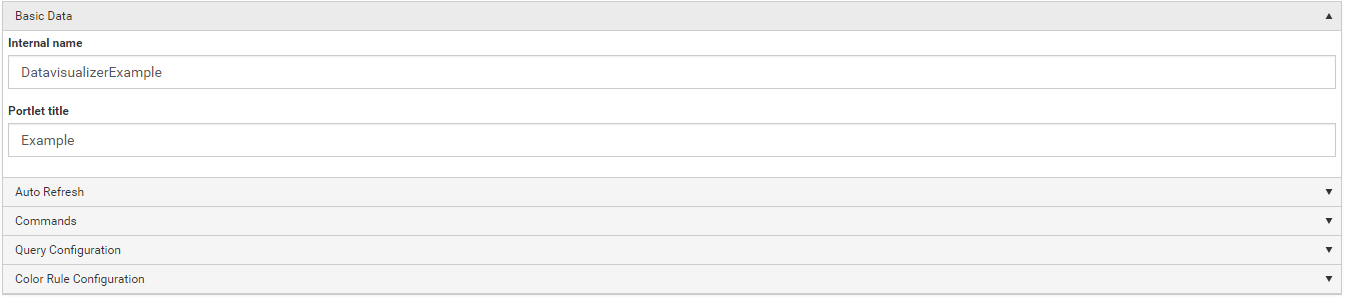
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.
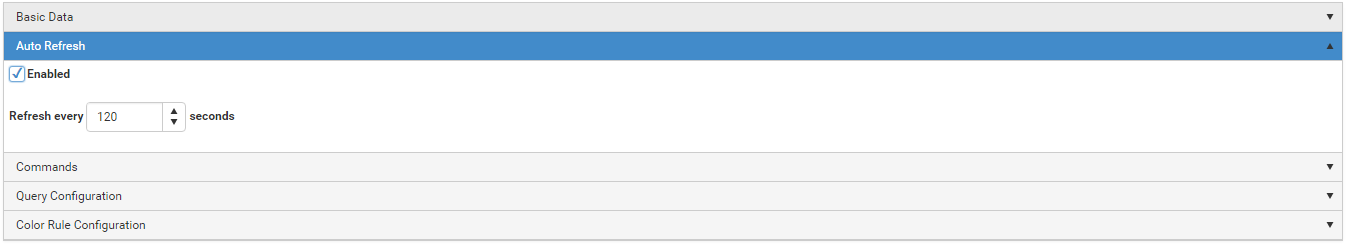
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onRefresh
- onFilter
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
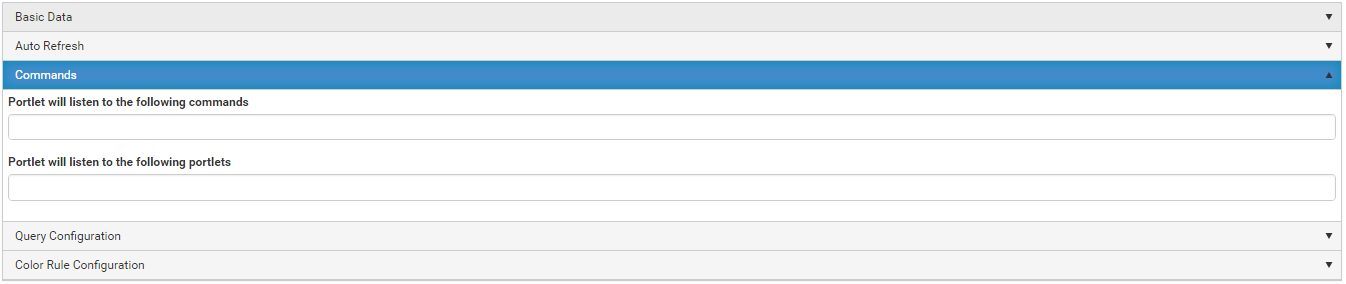
Data Source Configuration
As in all other data based Portlets there are two options to retreive data to the portlet; Database and Workflow.
To use Database as data source, select a database from the Database connector drop-down and then write your query in the Your query textbox.
The data retrived from the database should match what is needed in the Output Datasource Configuration section, which is described below.
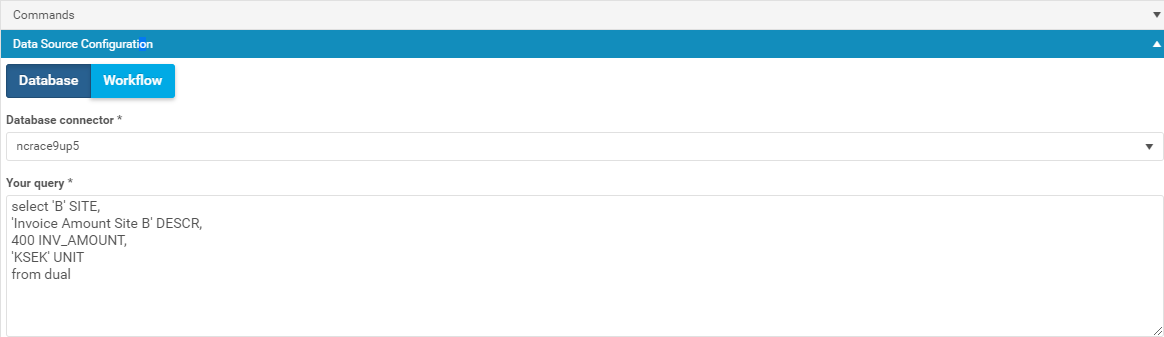
For more information how to set up a Workflow Data Source, please read this section: Fetching data from workflows
The data retrived from the workflow should match what is needed in the Output Datasource Configuration section, which is described below.
Output Data Configuration
This configuration defines what information to show in the Cards.
- Description - The column in the table that represents the KPI name.
- Description Default - If there is no value chosen in Data, this will replace that text
- Data - The column that represents data, can be used for e.g. "Amount of orders picked".
- Unit - The kind of unit the Data is measured in.
- Priority Value - A field that can represent the level of priority the card represents.
- Trend Value - The current trend of the KPI, value needs to be between -2 and 2.
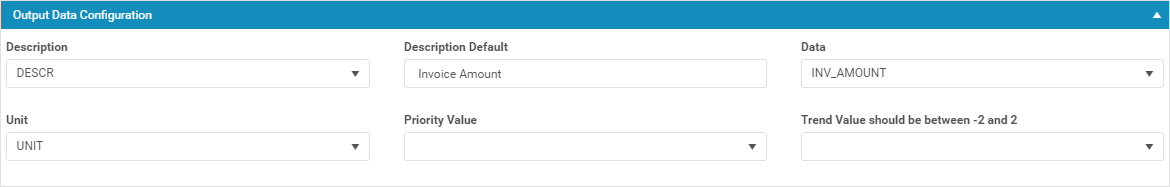
Display Configuration
There are three different card styles that can be used for displaying data; Default, Process Card and Speedometer.
Select the one that should be used.
Depending on style, the Display Configuration offers different possibilities.
Default and Process Card style
For the Default or Process Card styles, the following configuration can be made.
- Background - Color of the background in the card.
- DefaultColor - If no other criteria is fulfilled this will be the default color.
- Color Rules - A color which will be used as background when criteria is fulfilled.
- First Value - A value which will be used for comparison.
- Func - A function that will used for the comparison calculation. e.g. "Greater than" "Less than" "Equals"
- **Second Value* - The value that will be compared to the first value using "Func"
- Text - Color of the text in the card.
Speedometer Card style
For the Speedometer Card style, the following configuration can be made.
- Thickness - The thickness of the speedometer line.
- Min - Minimum value for the speedometer. Scale will start on this value.
- Thickness - Maximum value for the speedometer. Scale will end on this value.
- Line foreground color - Default color on the speedometer line. Will be applied if none of the line color rules is matched.
- Line foreground color rules - Color for the speedometer line will be set according to these rules. The top-most rule has the highest priority and will be applied first.
- Pos - Drag and drop to change the order of the color rules.
- Colour - Select which colour should be applied with this rule.
- First Value - A value which will be used for comparison. Use "{}" for expressions, e.g. {INV_AMOUNT} to use the value from the column INV_AMOUNT coming from the applied query or workflow.
- Func - A function that will used for the comparison calculation. e.g. "Greater than" "Less than" "Equals"
- **Second Value* - The value that will be compared to the first value using "Func". Same expression as in First Value can be applied here.
- Line background color - Default color on the background of the speedometer line. Will be applied if none of the line color rules is matched.
- Line background color rules - Color for the speedometer line background will be set according to these rules. The top-most rule has the highest priority and will be applied first.
- Pos - Drag and drop to change the order of the color rules.
- Colour - Select which colour should be applied with this rule.
- First Value - A value which will be used for comparison. Use "{}" for expressions, e.g. {INV_AMOUNT} to use the value from the column INV_AMOUNT coming from the applied query or workflow.
- Func - A function that will used for the comparison calculation. e.g. "Greater than" "Less than" "Equals"
- **Second Value* - The value that will be compared to the first value using "Func". Same expression as in First Value can be applied here.
- Background color - Default color on the background of the entire Card. Will be applied if none of the color rules is matched.
- Background color rules - Color on the background of the entire Card will be set according to these rules. The top-most rule has the highest priority and will be applied first.
- Pos - Drag and drop to change the order of the color rules.
- Colour - Select which colour should be applied with this rule.
- First Value - A value which will be used for comparison. Use "{}" for expressions, e.g. {INV_AMOUNT} to use the value from the column INV_AMOUNT coming from the applied query or workflow.
- Func - A function that will used for the comparison calculation. e.g. "Greater than" "Less than" "Equals"
- **Second Value* - The value that will be compared to the first value using "Func". Same expression as in First Value can be applied here.
- Text color - Default color on the texts in the Card. Will be applied if none of the color rules is matched.
- Text color rules - Color on the texts in the Card will be set according to these rules. The top-most rule has the highest priority and will be applied first.
- Pos - Drag and drop to change the order of the color rules.
- Colour - Select which colour should be applied with this rule.
- First Value - A value which will be used for comparison. Use "{}" for expressions, e.g. {INV_AMOUNT} to use the value from the column INV_AMOUNT coming from the applied query or workflow.
- Func - A function that will used for the comparison calculation. e.g. "Greater than" "Less than" "Equals"
- **Second Value* - The value that will be compared to the first value using "Func". Same expression as in First Value can be applied here.
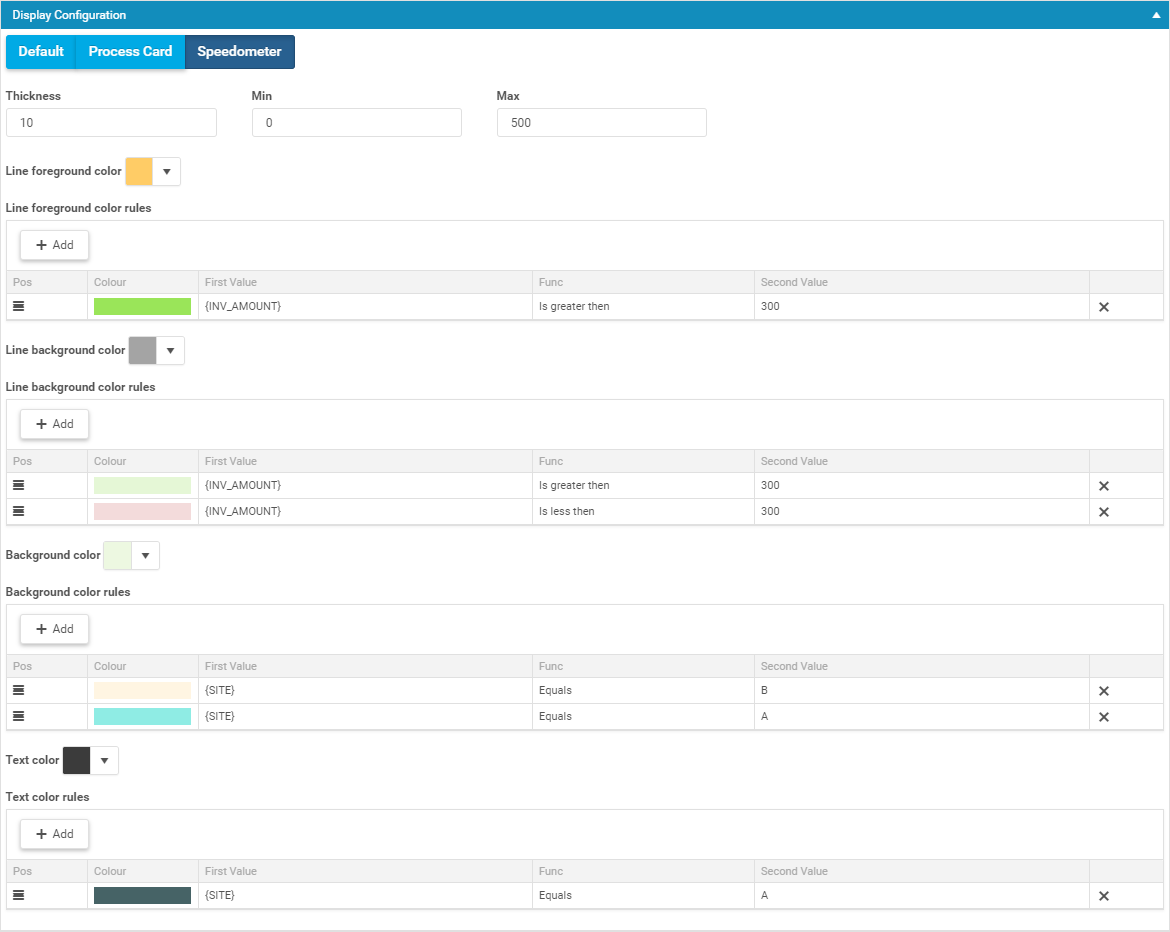
Data Visualizer Navigator
The Data Visualizer Navigator shows preconfigured Data Visualizer Cards together to easier get an overview of the processes the cards represents.

Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.
Cards
Select Cards specifies which visualization cards that are to be shown in the navigator portlet (the cards need to be preconfigured in any other portlet container as Data Visualizer Portlet).

Document List
The Document list displays the documents stored in the internal document management database. It can be connected to the Document Tree portlet to display all documents contained inside the selected folder in the Document Tree portlet.

Basic Data
Internal name - Unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - Title of the portlet, does not have to be unique. Include subfolders - Allows the portlet to include subfolders and their content of the document tree. View Documents - Not yet implemented.
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.

Query Configuration
Start node value - todo.
Page Size - Amount of results showed per page.

Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- updateDocumentManagementList
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.

Document Tree
The Document Tree displays the document folder tree stored in the internal document management database. It can be connected to the Document List portlet to display all documents contained in the highlighted folder in the Document Tree portlet.

Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.

Document Viewer
The document viewer displays the documents contained in the folder structure of the document tree. It connects to the document list to display selected documents inside the portlet.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.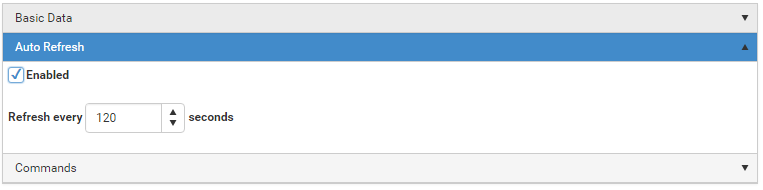
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- updateDocument
- onRefresh
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
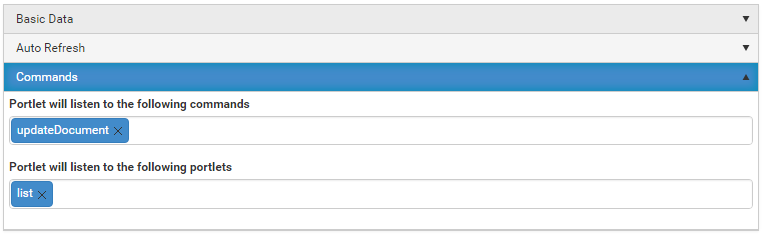
Filter Portlet
The Filter portlet allows for customized filter lists and buttons to apply towards other portlets. With this one can choose from a preconfigured list of values or manually typed in a value to send a filter request with the chosen criteria.

Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
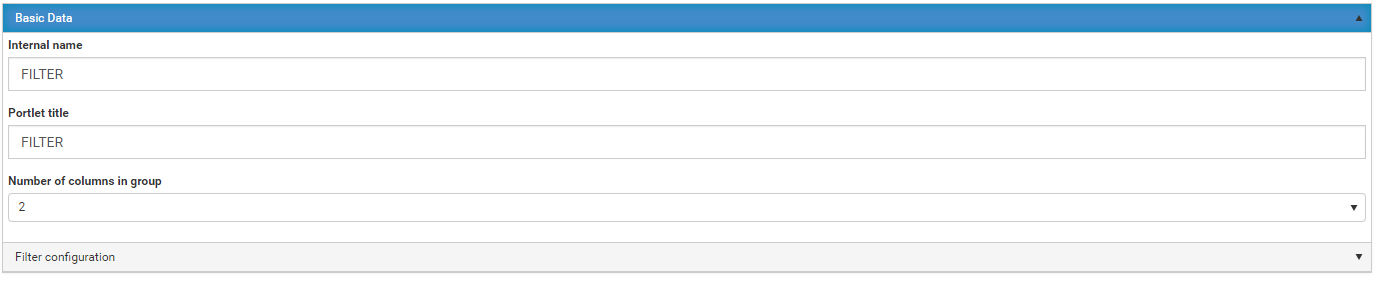
Filter configuration
Group Headers
- Group name - a value shown as display name of a group that contains column mappers.
- Header visible - if the display name is to be displayed or not.
- Align group - up or down arrow to realign in which order the groups are to be displayed.
Column Mappers
- Display name - The display name of the value field.
- Filter parameter - The column of the target portlet that the filter will be applied to.
- Column size - Width of the column list.
- Group - Which group the column mapper should be assigned to.
- Lov - A list of values (that can be set up in Options) to apply as filter value. Only works when Editor type is LOV.
- Editor - What kind of input one can type into the input box.
- Length - Only when using decimal in editor, specifies the amount of decimals that can be entered.
- Multiline - When using textinput and not Lov to filter, this enables the textwindow to have support for multiple lines.
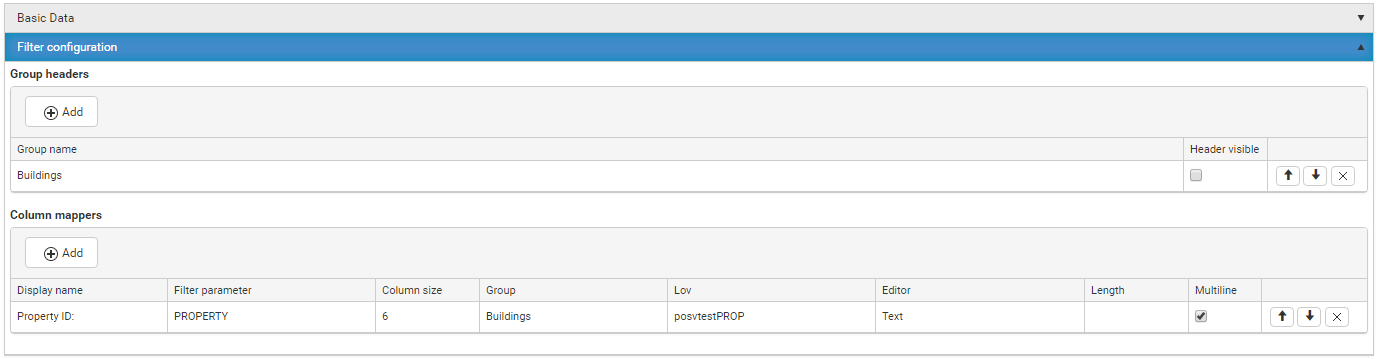
Setting up the portal
The portal consists of three elements:
- Tabs
- Containers
- Portlets
These are all required to set up an functional portal.
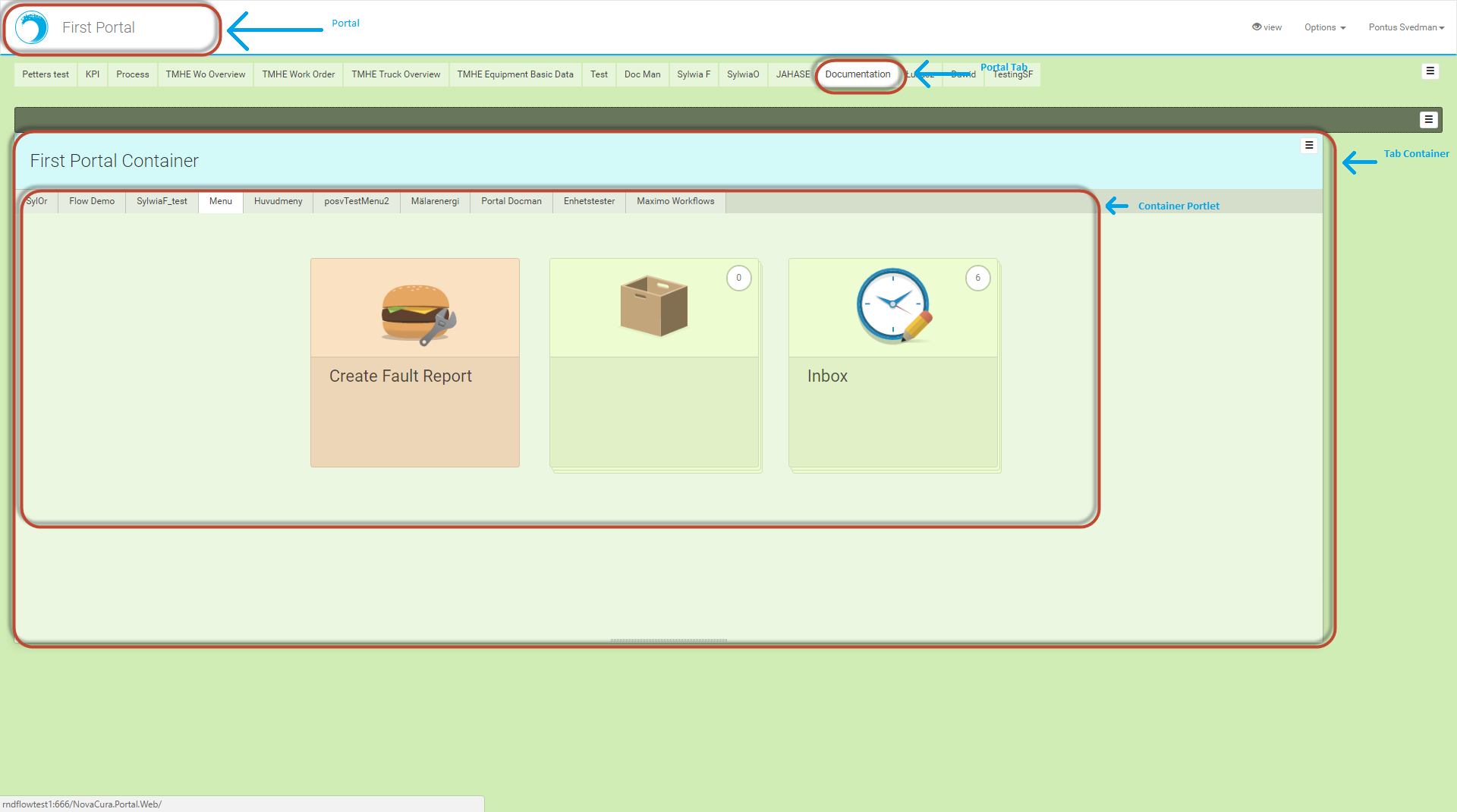
Portal Tab
The tabs is a window that can contain one or several containers, each container in turn can contain several portlets. This is to give the portal an easy to use and understand structure.
On the top right under the user name is an three-line menu, click it and select "add new tab"
Internal name - choose an unique string to identify this tab. Tab title - choose an title of the tab, does not have to be unique. Tab Description -Write an description that shows up when you hover over the tab. Content access group - select which flow roles that can access this tab.
Container
Inside the tab there are containers, each one of these can host several portlets. Click the top right three-line menu of the tab header to create a container
Internal name - unique string to identify this container. title - title of the container, does not have to be unique. Disable header - wether the header should show or not. Layout - Choose between row or tab layout, grid is strictly for data visualizer plugin. Header background color - choose which color the header background should be in. Header text color - choose the text color in the header. Width - the tab is a total of 12 "units" in width, a container therefore max be 12 in width, with this logic you can for example have 2 container with 6 in width on the same row.
Portlet container
Inside a container you can have portlets, these are the applications that visualize, calculate or creates something in the portal.
In this example we are going to use the flow client as a portlet.
- On the top right of the container, choose the three-line menu and select "Add new portlet to portlet container".
- Select "Flow Client" under "You can create a portlet from scratch".
- Enter a unique portlet name and a portlet title.
- Try try out your new flow client inside your portal.
Now you can experiment yourself by for example creating several containers and tabs, create other kinds of portlets and using the Portal documentation for more assistance.
Gantt Chart Portlet
The Gantt chart gives you a time-based view of your projects and tasks; What tasks are planned and when are they to be executed. In the Gantt chart you can also see dependencies between tasks and who is assigned to a task.
A Gantt chart allows you to see at a glance:
- Project start and end dates
- Task start and end dates
- What the task is
- Who is assigned to the task
- If tasks overlap
- Dependencies between tasks
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet.
Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Checkbox options
- Enable header - enables the portlet header, ie makes it visible in the portal. It is possible select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header background color - select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header color text - select a header text color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Show work days - tick the box to show only work days in the Gantt chart. Work days are Monday to Friday.
- Show work hours - tick the box to show only work hours in the Gantt chart. Work hours are 08:00 - 17:00.
- Show task selector - tick the box to enable a drop-down box where it is possible to search for tasks
Height - sets the height of the activity display window
List Width - sets the width of the activity navigator list
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh - enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed in the columns the table wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.
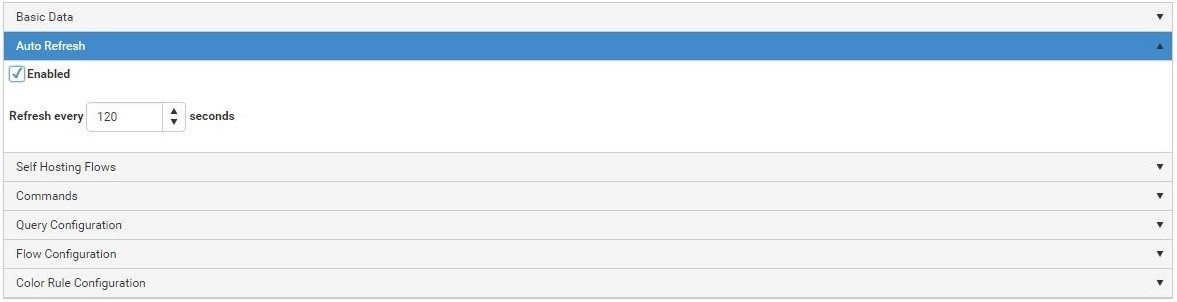
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows - enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.
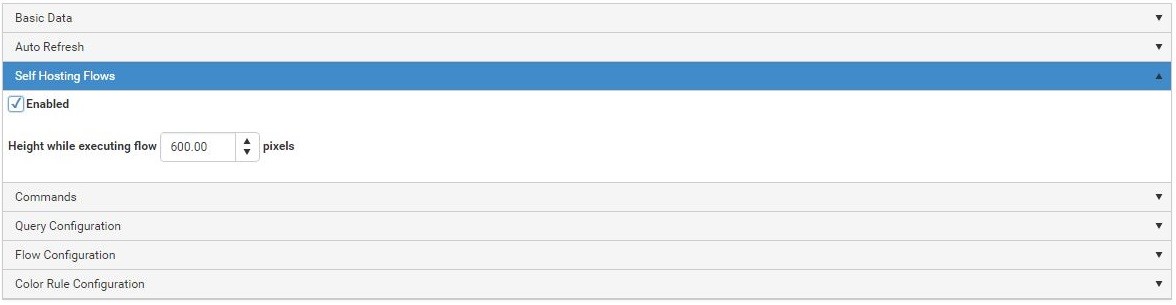
Commands
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
Data Source configuration
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute a specified query towards the chosen database connector to fetch data, or fetch data from a workflow.
Fetching data using database query
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute a specific query to the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query should execute against
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
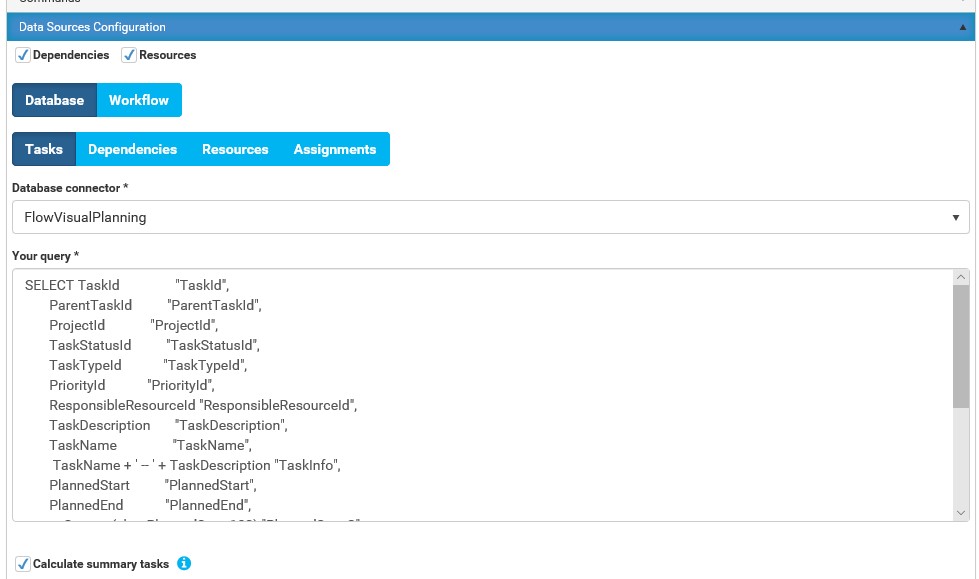
Fetching data using workflows
It is possible to use workflows to fetch data.
Read more about Workflow Source in: Workflow source.
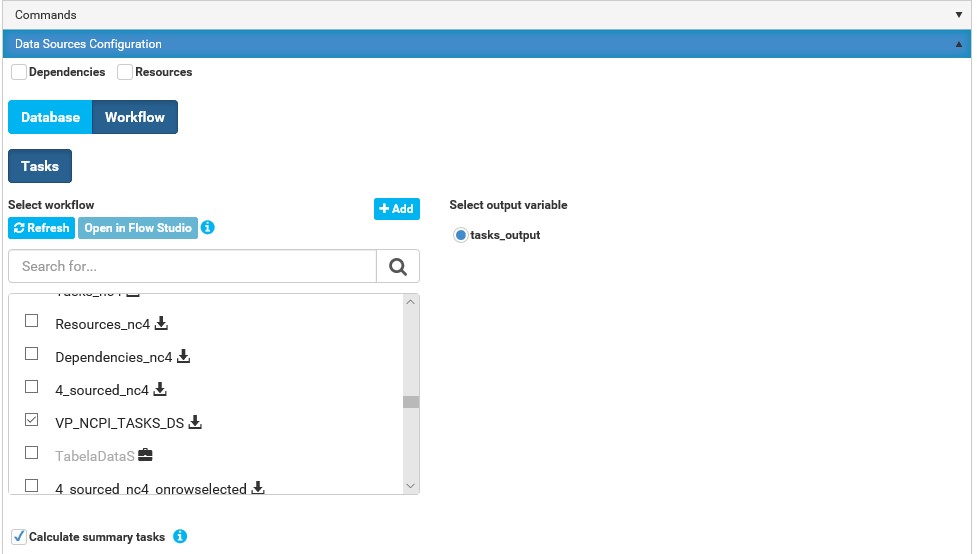
Checkbox option
- Calculate summery task - When enabled nullable start date. end date and summery columns will be populated based on task child tasks (Parent id column)
Map the data columns that are to be displayed in the portlet.
- Task identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the task
- Title column - The task title that is to be displayed
- Start date column - The date the Gantt task starts
- End date column - The date the Gantt task ends
- Parent id column - The id of the parent task. Required for child tasks
- Order column - The position of the task relative to its sibling tasks
- Is summery column - If set to true, the task has child tasks
- Percent column - The task percentage of completion
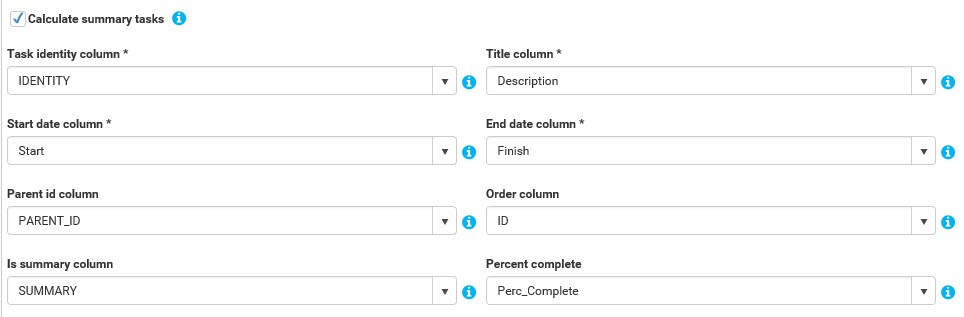
Dependencies
In the tab Dependencies it is possible to enter a query or workflow to define the dependencies between tasks.
- Dependency identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the dependency
- Predecessor identity column - The mandatory id of the predecessor task
- Successor identity column - The mandatory id of the successor task
Type column - The type of dependency. The type is a value between 0 and 3, representing the four different dependency types:
- 0 - Finish-Finish
- 1 - Finish-Start
- 2 - Start-Finish
- 3 - Start-Start
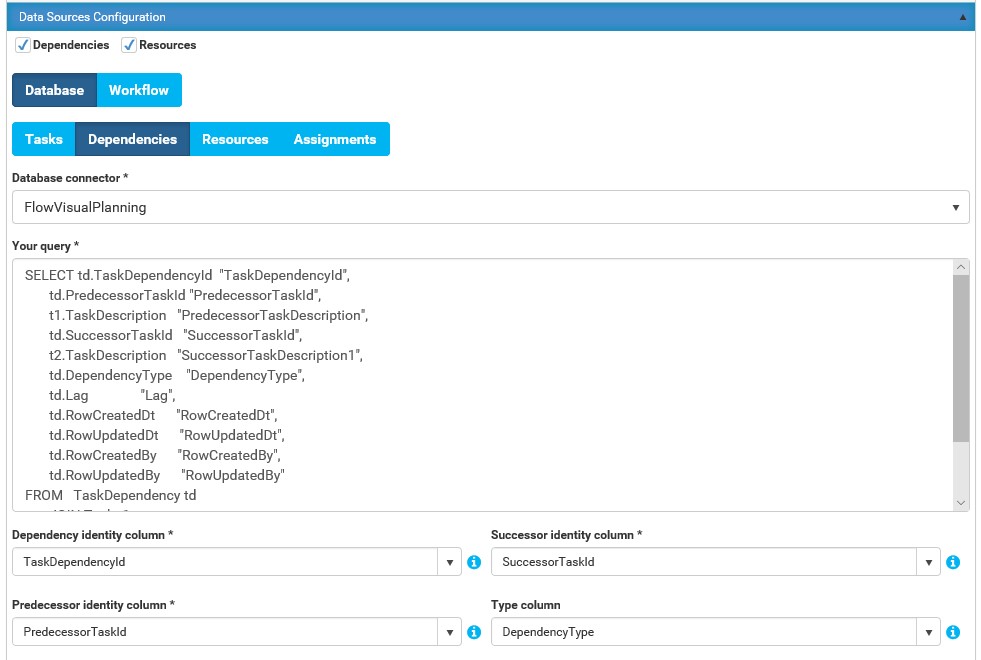
A dependency relationship between tasks is indicated by an arrow, as shown in the picture below. If the parent or child task is moved in the Gantt charge, the dependent task will follow accordingly.
Resources
The Resources tab fetches the list of employees, resources, that will be assigned to the task in the Gantt chart.
- Resource identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the resource
- Title column - The title of the resource
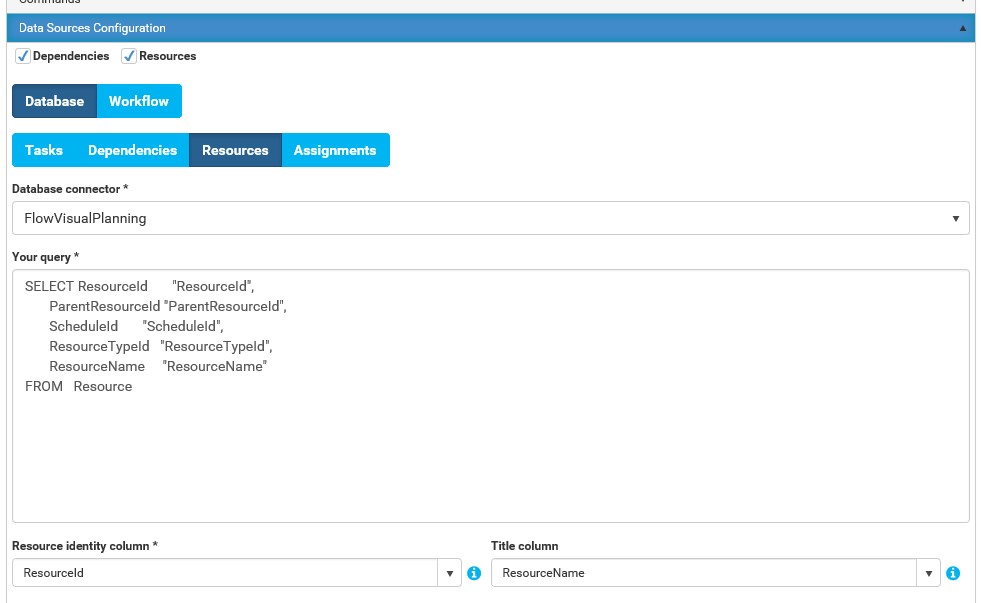
Assignment
The Assignment is the information which task is assigned to which resource (based on data provided in Task data source and Resources data source).
- Assignment identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the assignment
- Task identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the task
- Resource identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the resource
- Unit column - Describes how much of each resource is taken up by the current task
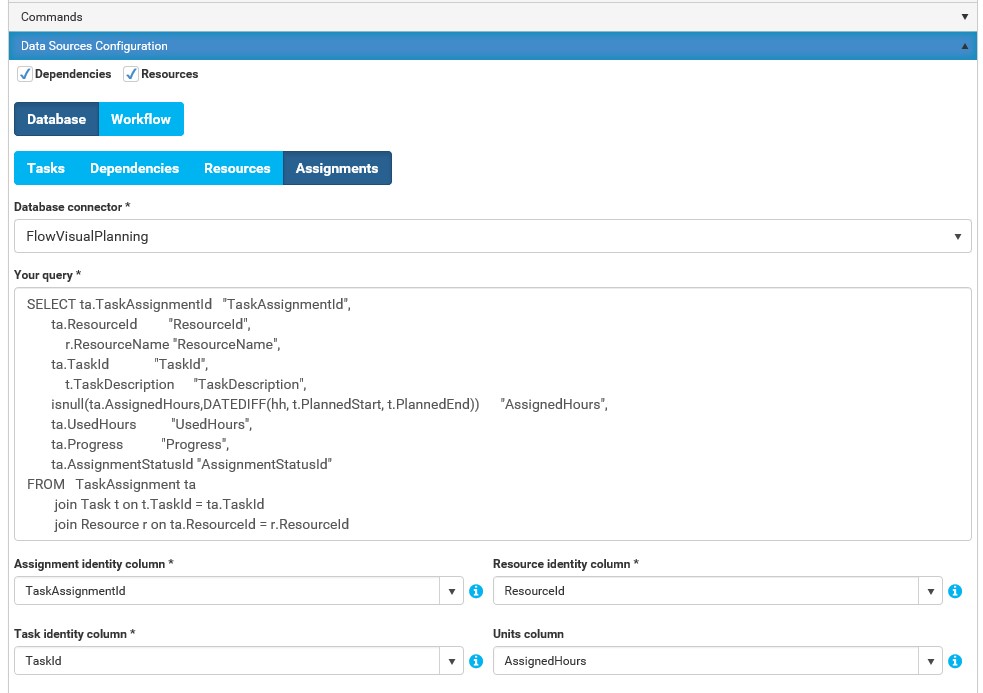
Flow Configuration
See Flow Configuration in Table Portlet.
Column Configuration
In column configuration the column which are to be displayed in the Gantt chart are added. It is possible to change the column order by using the up and down arrows. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
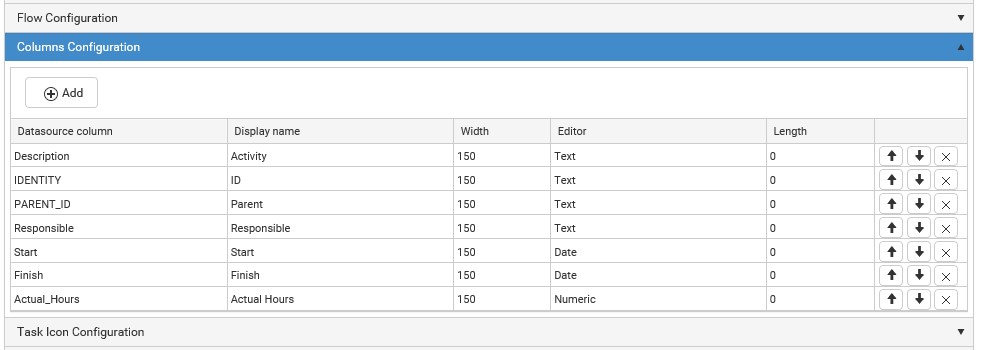
The columns will be shown in the same order as in the configuration:
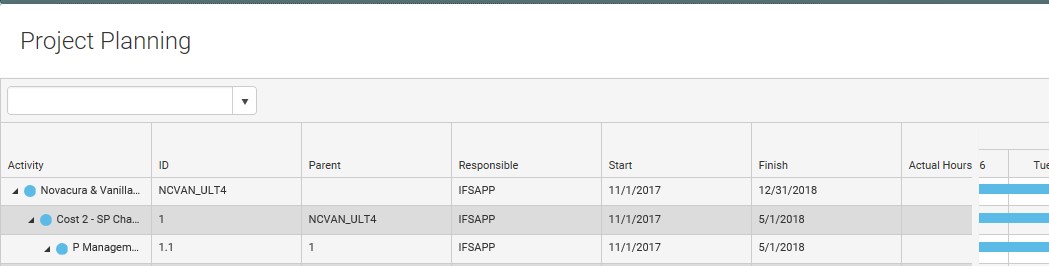
Task Icon Configuration
It is possible to display icons on the activities in the Gantt chart.
Default Icon - field where a default icon value can be added.
Icon rules - add a row here to enter icons with conditions. It is possible to enter multiple conditions. The first condition that an activity fulfills is the icon that will be displayed on the activity. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
The icon Bug shown on a task in the Gantt chart:
Task Color Configuration
Activates in the Gantt can be configured in to be displayed different colors. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
Color rule setup:
- First value - variable.
- Func - parameter to consider.
- Second Value - the value to be measured against the variable.
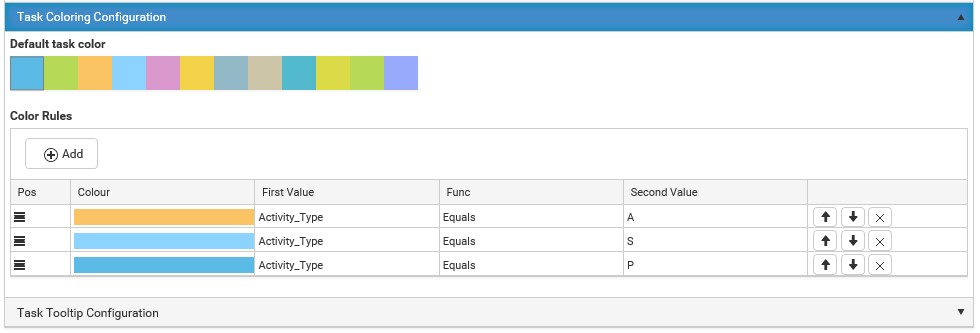
Task Tooltip Configuration
In tooltip configuration enter the text and the variables that are to be seen in the Gantt tool tip when the cursor hovers above an activity.
Fields - add the columns where the data mapper is required, for example remove the time stamp when a date is displayed
Tooltip - add the text and variables, using {}, which are to be displayed
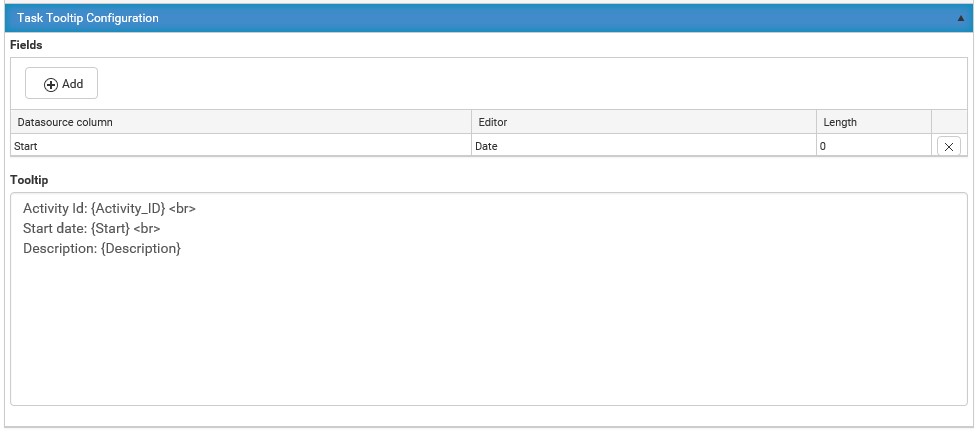
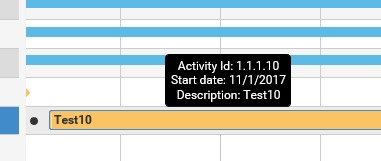
Generic Document Viewer
The Generic Document Viewer can display documents from any database, it supports most document formats and image formats.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.
Query Configuration
Query Configuration enables the portlet to execute specified queries towards the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query will execute against.
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
- Data column name - Select in which column the document data is stored.
- Mime type column name - Select in which column the mime type of the document is stored.
- File name column -Instead of mime type column name, choose this for formats such as ".jpg, .gif, .txt".
- Default mime type - Also an alternative if all documents share the same mime type one can define it here.
Mime types are defined in the following format: e.g "application/pdf"
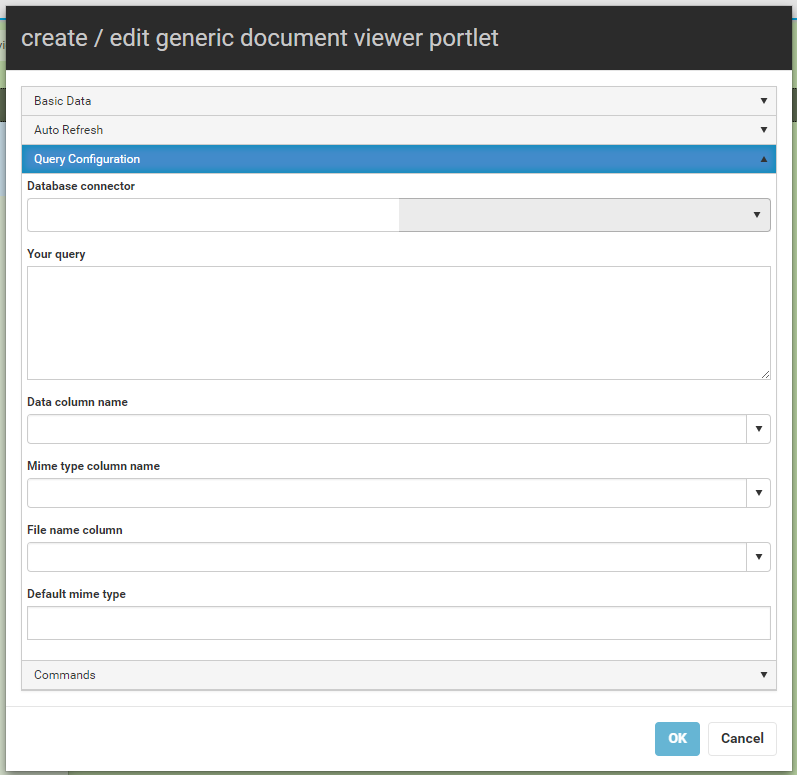
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRefresh
- onRowSelected
- onGenericTreeNodeSelection
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
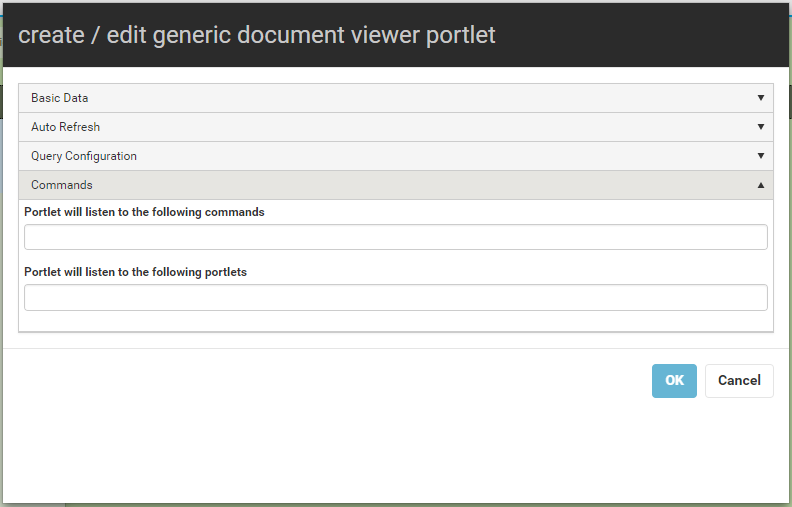
Generic Document Viewer URL
The Generic Document Viewer from URL can display documents from an URL, it supports most document formats and image formats.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
URL
URL - Where the url to the document is added. Mime-type - What kind of type of document (pdf, jpg etc) that is to be shown. Needs to be formated as a mime e.g application/pdf.
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRefresh
- onRowSelected
- onGenericTreeNodeSelection
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
Generic Document Viewer
The Generic Document Viewer can display documents from any database, it supports most document formats and image formats.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.
Query Configuration
Query Configuration enables the portlet to execute specified queries towards the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query will execute against.
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
Start node value - Select from which node to display tree structure.
- Parent node - Name of the parent node column.
Node - Name of the column the start node value fetches value from. Example: Id
Id would mean that start node value would look for values inside the column I.d * Node title - Decides where the portlet will fetch the titles for each node fetched.
Mime types are defined in the following format: e.g "application/pdf"
HTML portlet
The HTML portlet allows the usage of HTML code inside the portal. It can execute SQL queries and use the result with HTML to get a customized presentation of the data.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
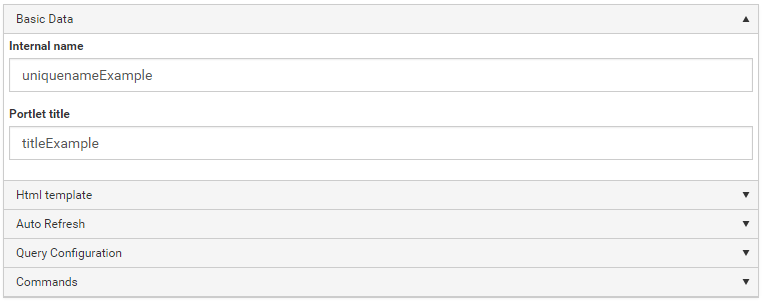
HTML Template
The HTML template is where the user can customize how the portlet will be displayed. It supports HTML5.
Header - format the html portlet with a header. Can take in variables from the SQL query e.g. "Welcome {name}" where {name} is fetched from the SQL query. Body - format the html portlet with a body. Can also take in variables from the SQL query.
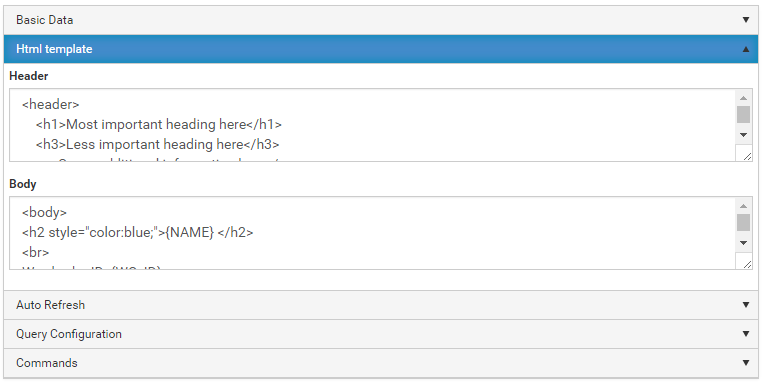
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.
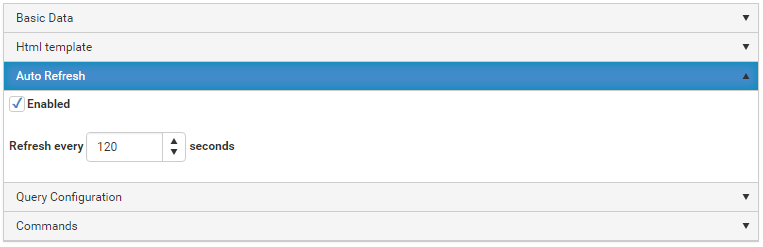
Query Configuration
Query Configuration enables the portlet to execute specified queries towards the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query will execute against.
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
- Page Size - Amount of rows showed on each page
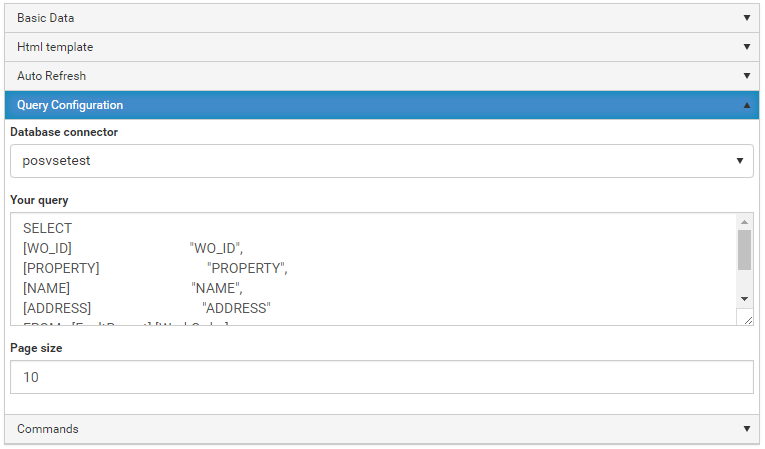
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onGenericTreeNodeSelected
- onRefresh
- onFilter
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
Iframe portlet
The Iframe portlet displays a website.

Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
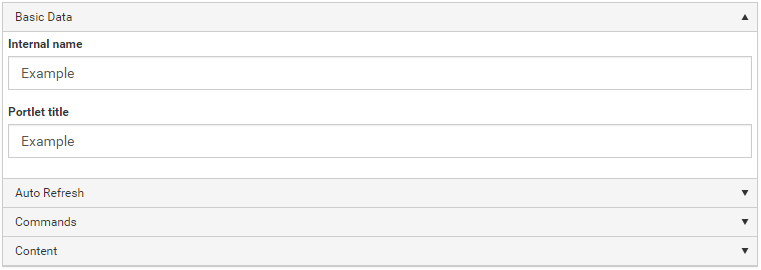
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.
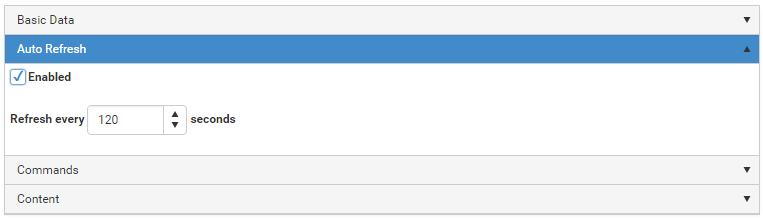
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onRefresh
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
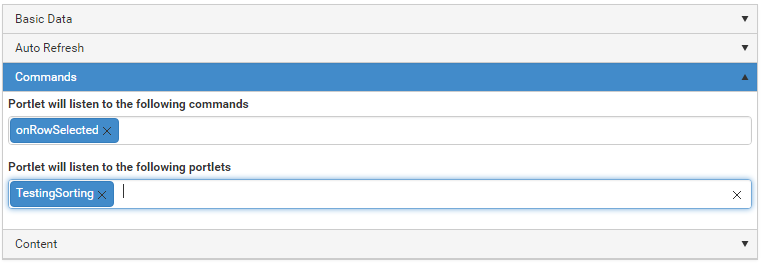
Content
URL An valid URL-link.
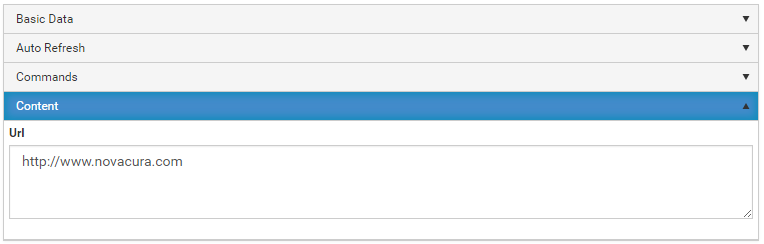
Inbox portlet
The inbox portlet displays an inbox from a workflow menu. It can be used to see items sent to the inbox.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Please Select Inbox - Select which inbox that is to be displayed.
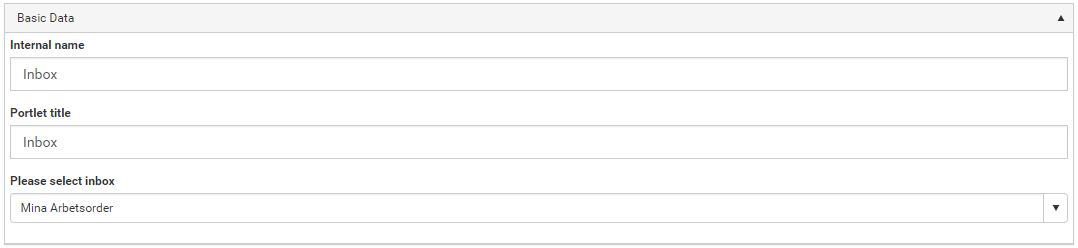
Kanban Portlet
The Kanban portlet is a work and workflow visualization portlet that enables you to optimize the flow of your work. It gives you a process based view of your activities and shows where in the process are your activities right now.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet.
Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Checkbox options
- Enable header - enables the portlet header, ie makes it visible in the portal. It is possible select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header background color - select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header color text - select a header text color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh - enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed in the columns the table wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.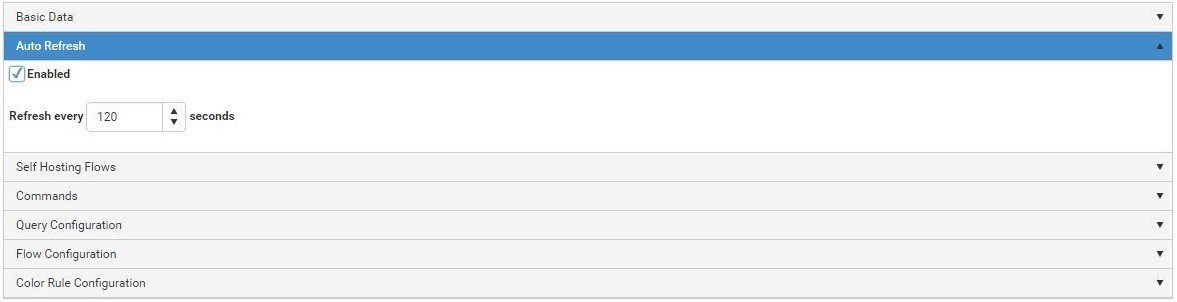
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows - enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.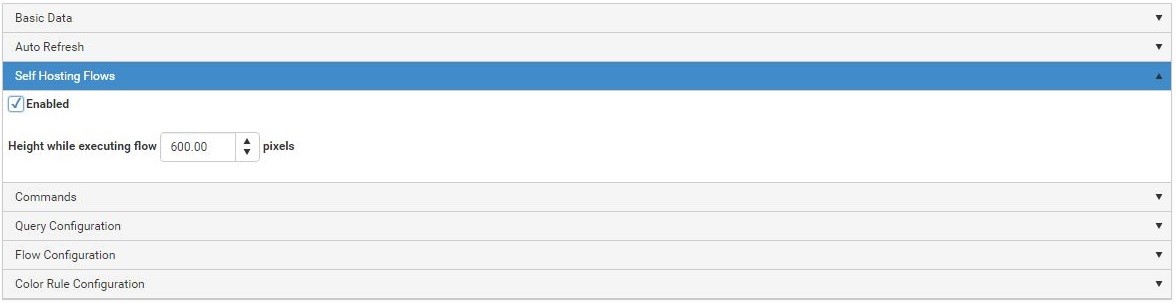
Commands
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.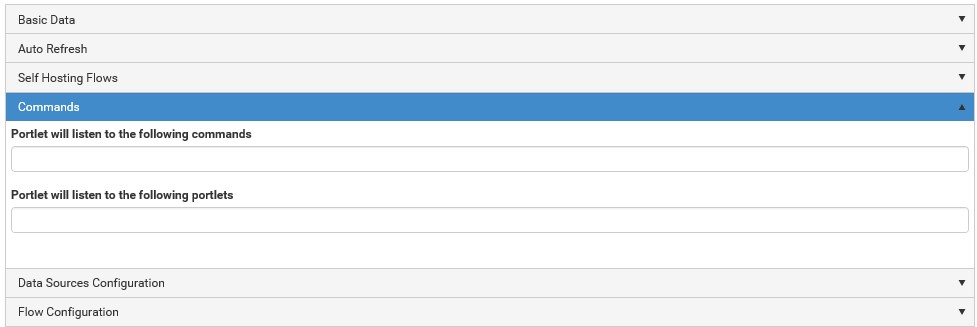
Data Source configuration
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute specified query towards the chosen database connector to fetch data, or fetch data from a workflow.
Fetching data using database query
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute a specific query to the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query should execute against
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
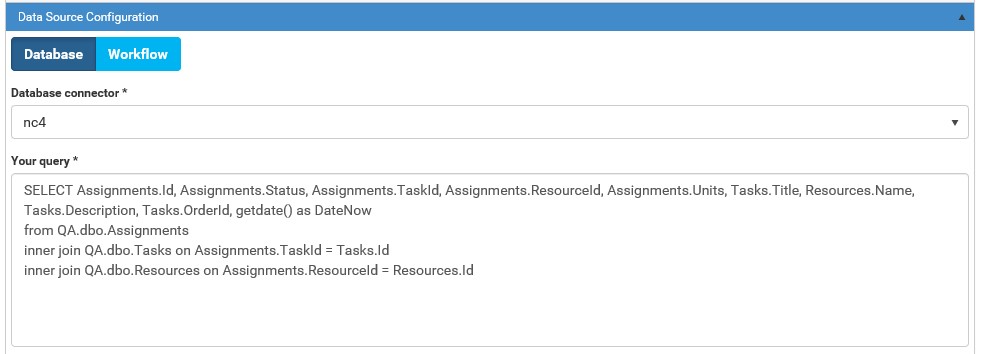
Fetching data using workflows
Workflow option allows for any type of data table to be retrieved as data that the portlet can show.
Read more about Workflow Source in: Workflow source.
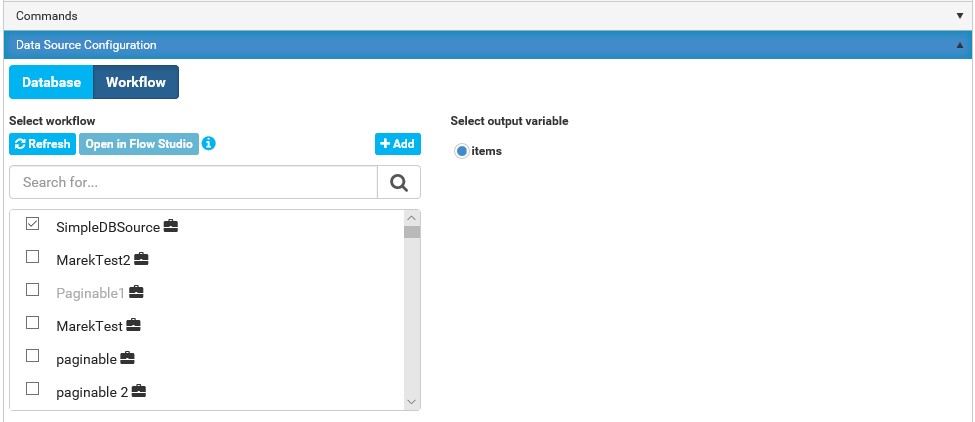
Map the data columns that are to be displayed in the portlet.
- Task identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the task
- Task status column - The status of the task that is displayed
- Task order id column - The position of the task relative to its sibling tasks
- Task order sort direction - Default way of sorting cards
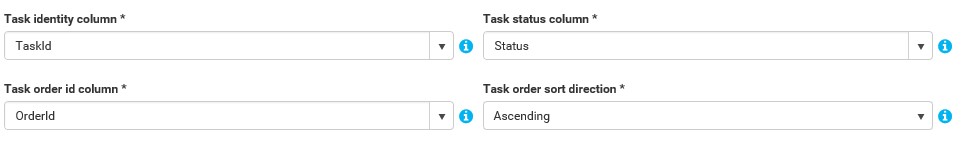
Column Configuration
In column configuration the column which are to be displayed in the Kanban are added. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.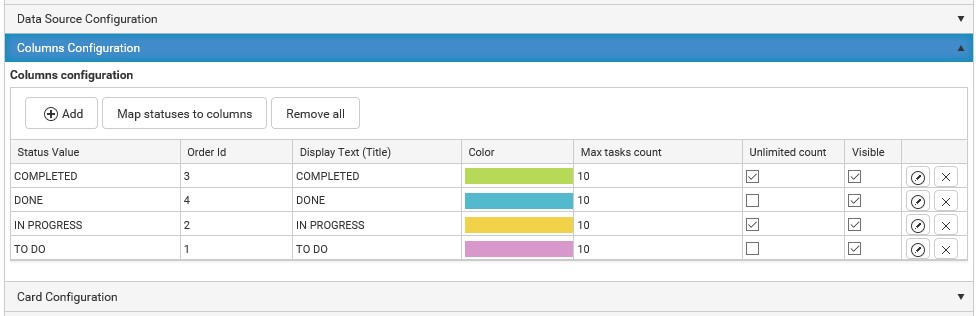
Card Configuration
Column Configuration
Add the columns that are to be displayed in the portlet and set the Display Text and header color.
Task Tooltip Configuration
In tooltip configuration enter the text and the variables that are to be seen in the Gantt tool tip when the cursor hovers above an activity.
Fields - add the columns where the data mapper is required, for example remove the time stamp when a date is displayed
Tooltip - add the text and variables, using {}, which are to be displayed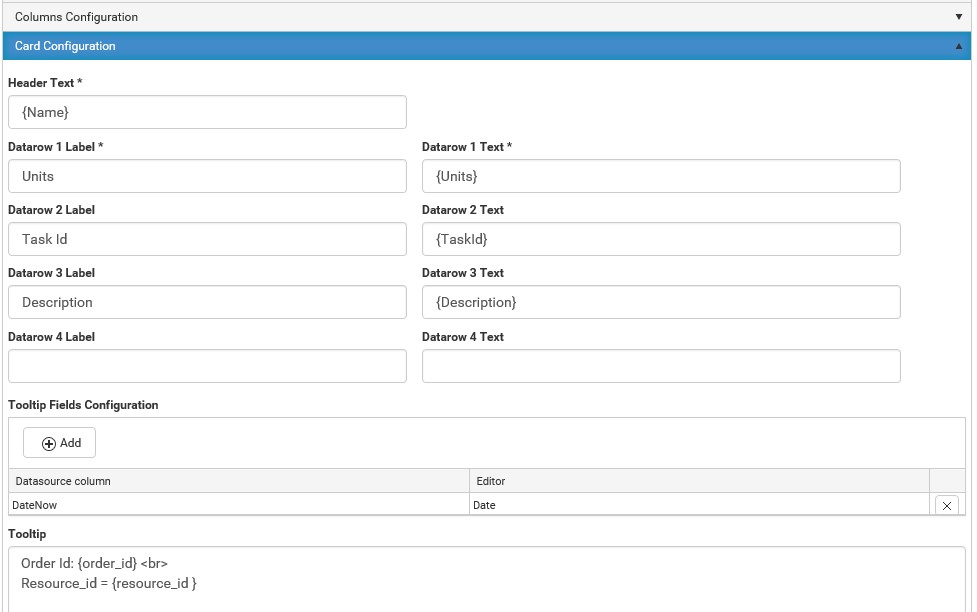
Flow Configuration
See Flow Configuration in Table Portlet.
Task Icon Configuration
It is possible to display icons on the activities in the Kanban.
Default Icon - field where a default icon value can be added.
Icon rules - add a row here to enter icons with conditions. It is possible to enter multiple conditions. The first condition that an activity fulfills is the icon that will be displayed on the activity. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.Task Color Configuration
Activates in the Kanban can be configured in to be displayed different colors. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
Color rule setup:
- First value - variable.
- Func - parameter to consider.
- Second Value - the value to be measured against the variable.
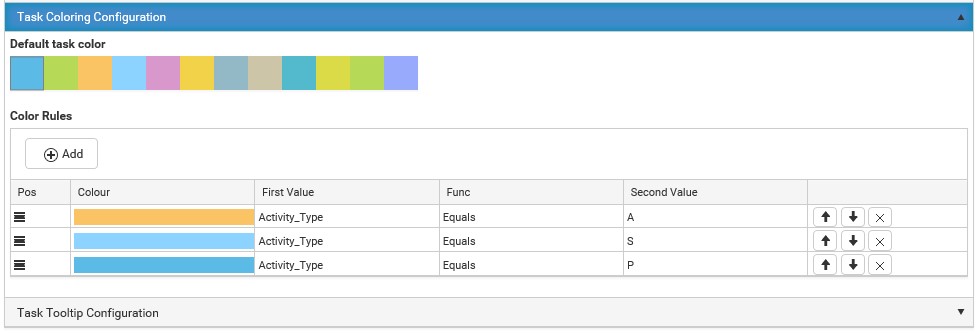
Map Portlet
The Map portlet shows a geographical map into which markers can be placed based on their longitude and latitude values from the marker basic data. A marker can for example represent a work order from the ERP system. OpenStreetMap is used as the base map.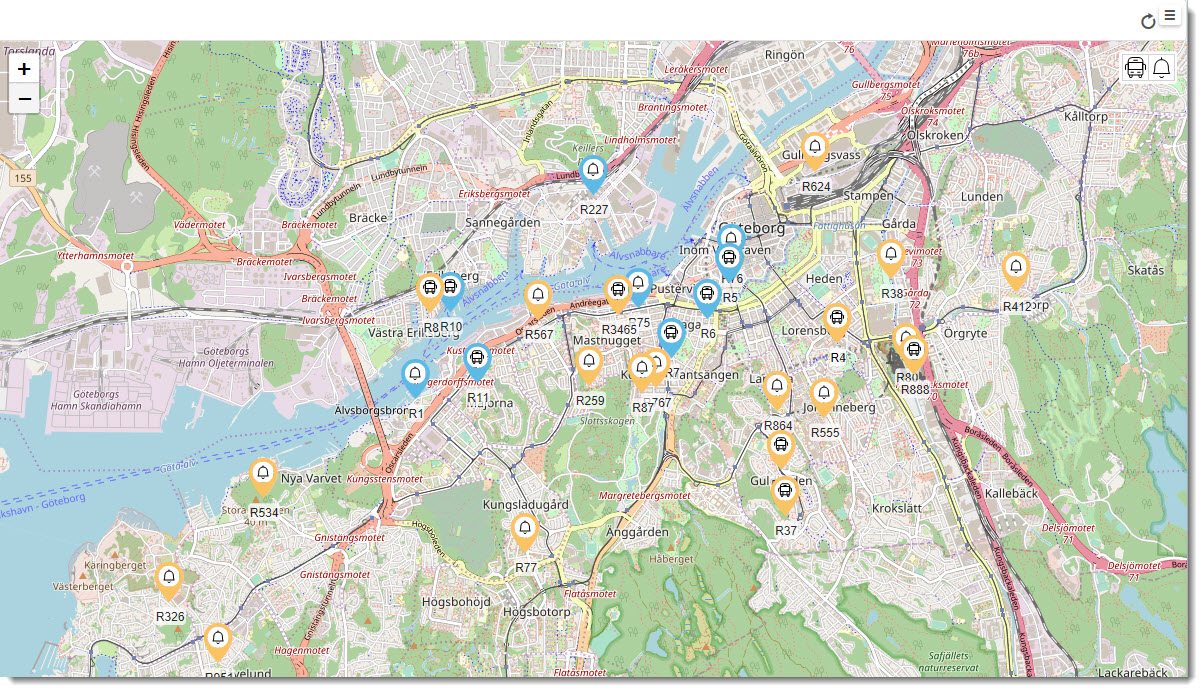
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet.
Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Checkbox options
- Enable header - enables the portlet header, ie makes it visible in the portal. It is possible select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header background color - select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header color text - select a header text color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh - enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed in the columns the table wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows - enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onGenericTreeNodeSelected
- onRefresh
- onFilter
The portlet will listen to the following portlets: Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
Show rows when onRowSelected empty - Tick the box if the portlet is to be populated when no selection is sent from triggering portlets.
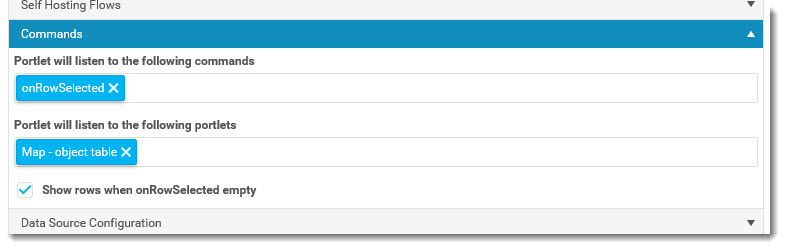
Data Source configuration
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute specified query towards the chosen database connector to fetch data, or fetch data from a workflow.
Fetching data using database query
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute a specific query to the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query should execute against
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
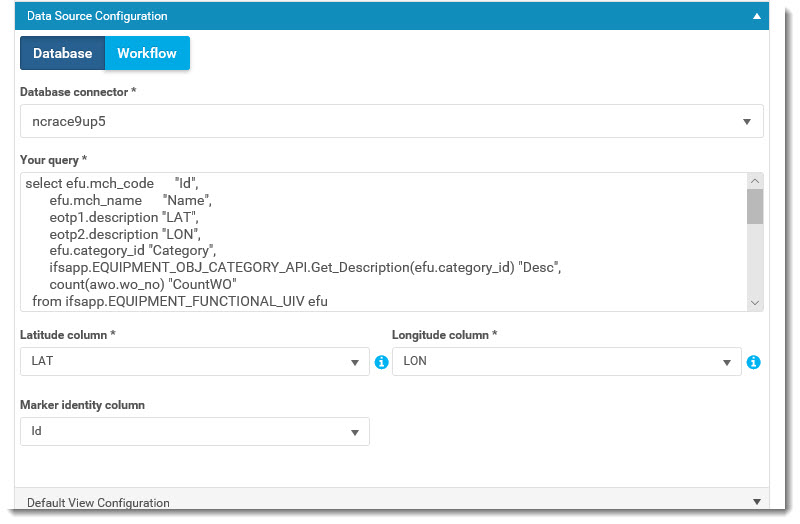
Fetching data using workflows
Workflow option allows for any type of data table to be retrieved as data that the portlet can show.
Read more about Workflow Source in: Workflow source.
Map the data columns that are to be displayed in the portlet.
- Latitude column - The mandatory unique identifier of the latitude value
- Longitude column - The mandatory unique identifier of the longitude value
- Marker identity column - The id of the marker, not mandatory
Default view configuration
When a map has got markers, the default view is to show all markers with maximum possible zoom. It is possible to set a fixed default view by entering values set longitude and latitude values under the Manual tab.
Tick the box Remember current state if the map, position and zoom level, should remain unchanged when the portlet is refreshed.
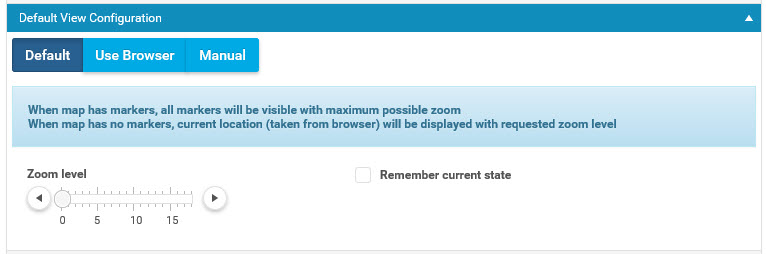
Flow Configuration
See Flow Configuration in Table Portlet.
Marker Icons Configuration
It is possible to use icons as markers in the Map.
Default Icon - field where a default icon value can be added. Tick the box Show in Legend if the default icon is to be shown there.
Icon rules - add a row here to enter icons with conditions. It is possible to enter multiple conditions. The first condition that an activity fulfills is the icon that will be used as the marker. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove. It is possible to configure if the icon is to be shown in the legend or not by setting Show in Legend column to Yes or No.
Marker Coloring Configuration
Basic markers in the Map can be configured in to be displayed different colors. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
Color rule setup:
- First value - variable.
- Func - parameter to consider.
- Second Value - the value to be measured against the variable.
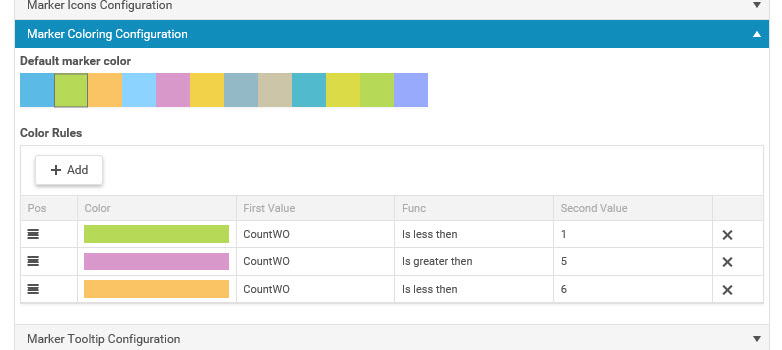
Overlay Configuration
Overlay map data is fetched from a workflow. The format must be GeoJson.
Select the workflow by ticking the box in the list. Select the output output variables and map the overlay identity column and GeoJSON column.
It is possible to set the overlay map to a default color and to configure different color rules.
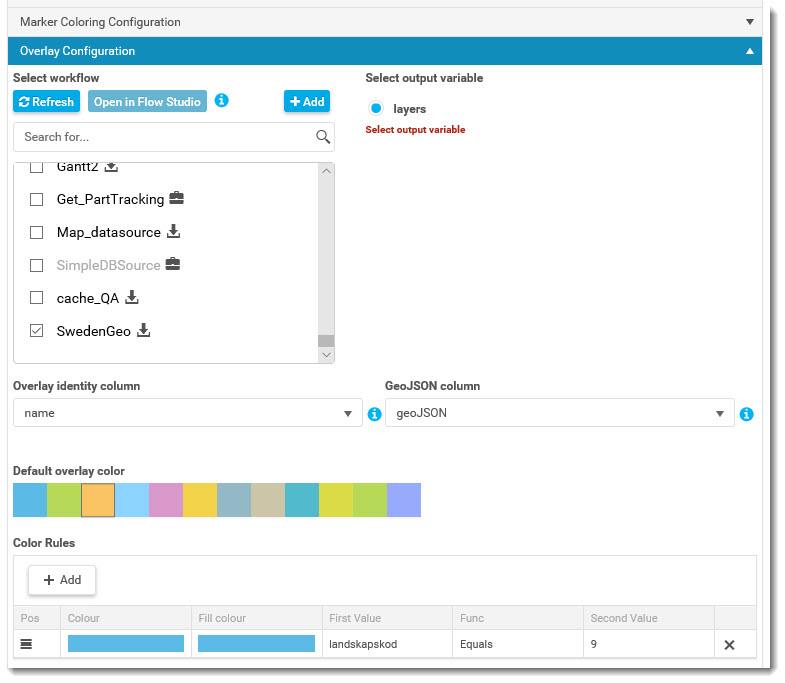
Marker Tooltip and Label Configuration
In tooltip configuration enter the text and the variables that are to be seen in the Map tool tip when the cursor hovers above a marker. The Label is the static text shown under the marker
Fields - add the columns where the data mapper is required, for example remove the time stamp when a date is displayed
Tooltip - add the text and variables, using {}, which are to be displayed
Label - add the text and variables, using {}, which are to be displayed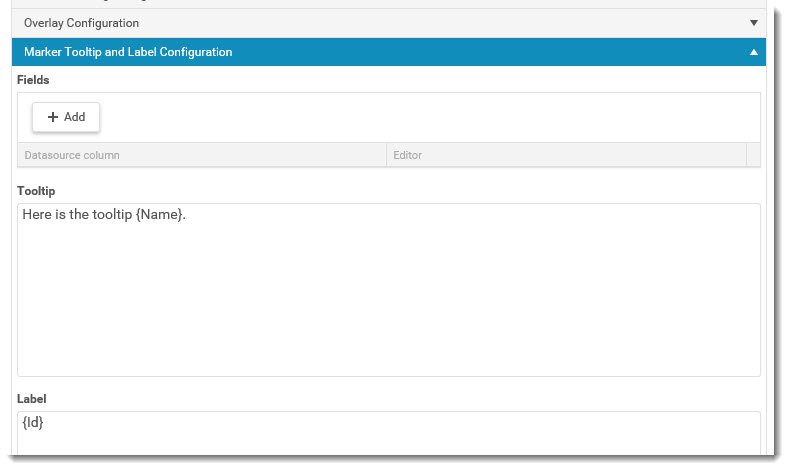
News Viewer
The news viewer portlet displays a news seed from a workflow menu. It can be used to see items sent to the inbox.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Display
Display Comments - Wether to display comments or not in the news viewer. Page Size - How many news items that are shown on each page.
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second.
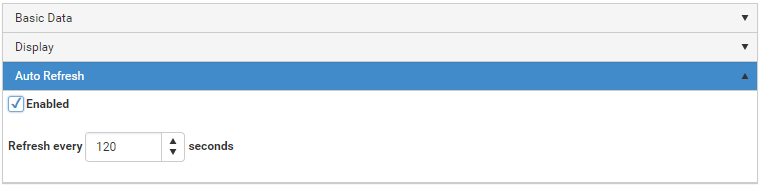
Process Overview Portlet
The Process Overview portlet can show information in data cards that allows for an easy overview of data from a single or several queries. The portlet can be used to see e.g. statuses in current running processes, employees planned for work on workdays.
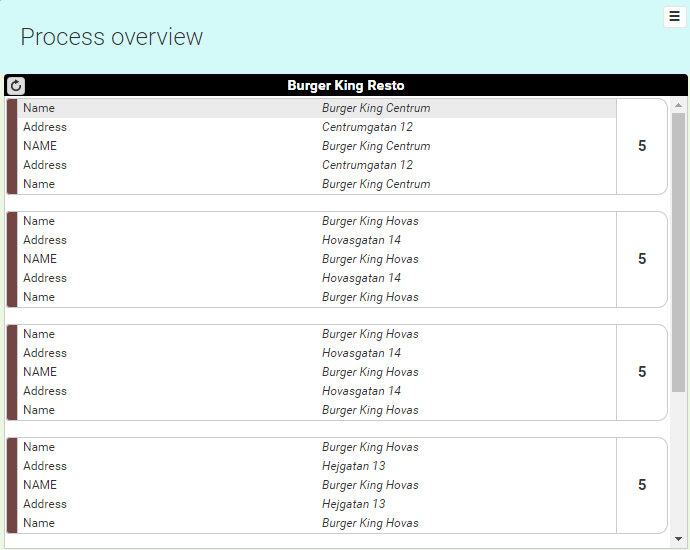
Basic Data
Internal name - Unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - Title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
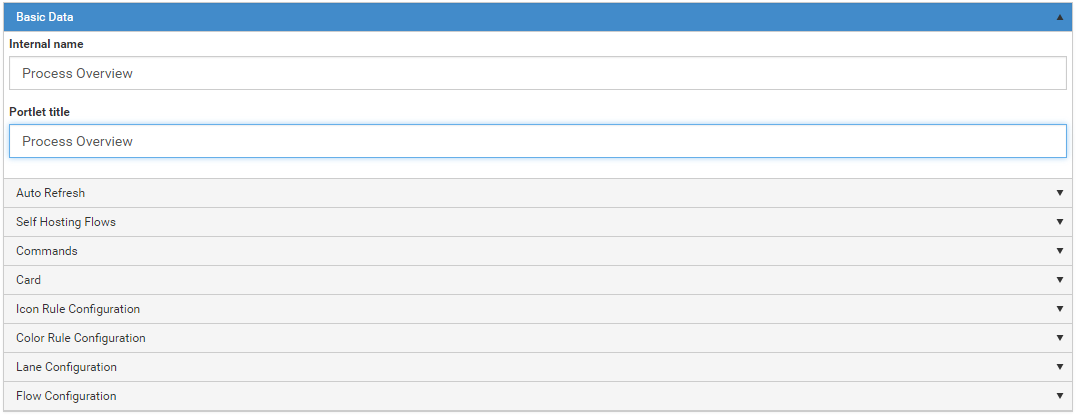
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed in the columns the table wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.
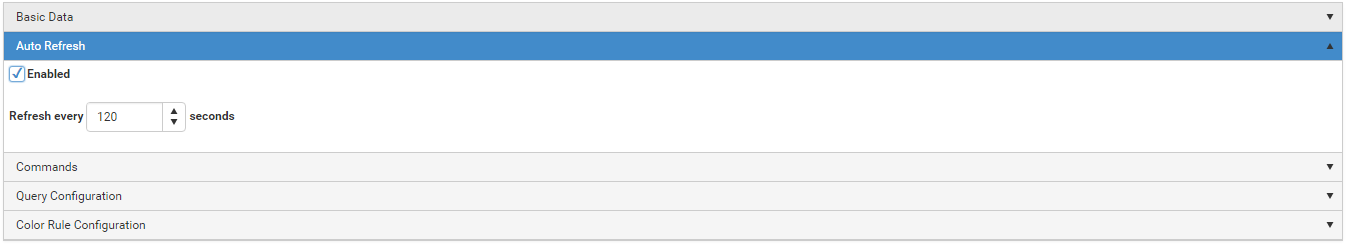
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.
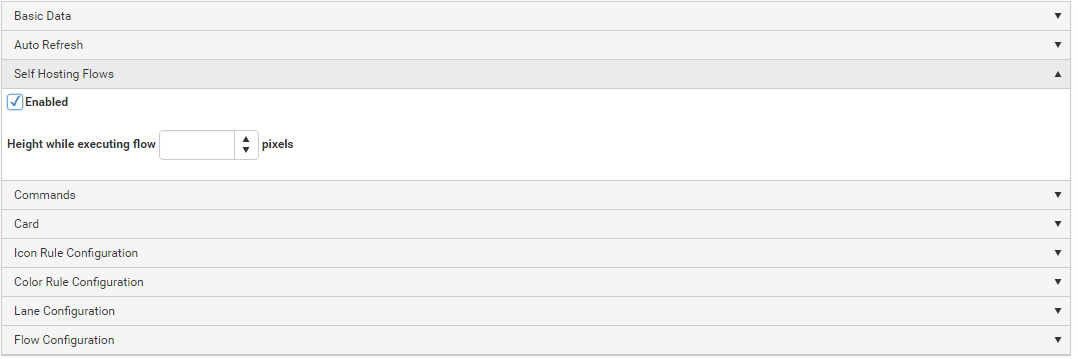
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. This can be used e.g. showing more information from one of the data cards.
The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onFilter
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
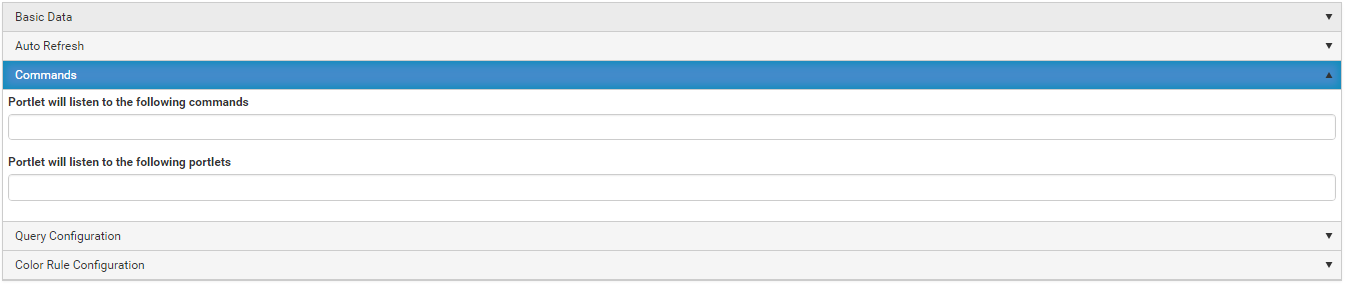
Card
Card Options
- Card height in pixels - The height of the data card when shown.
- Card Column Widths - The width of the data card when shown.
- Datarow Header Displayname - Name of the value Datarow Header Data shows
- Datarow Header Data - Value of data, can be constant or a value from an sql query specified in the lane configuration step
- Tooltip - Show the specified message when hovering pointer over any data card.
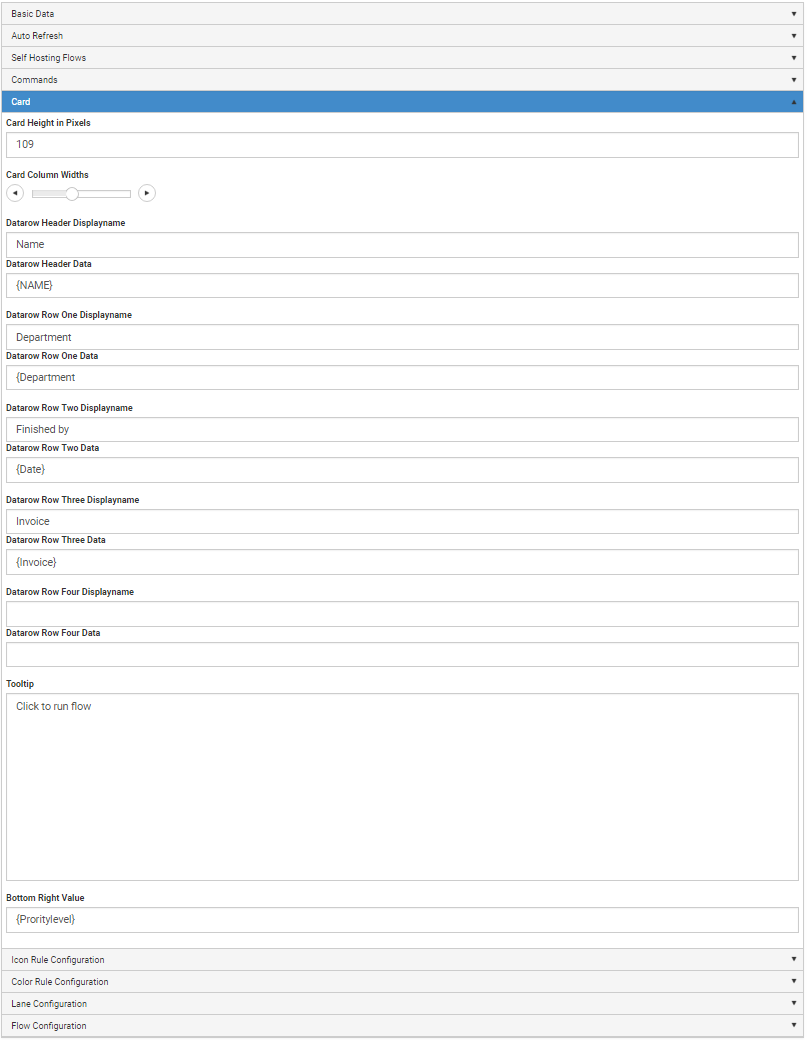
Icon Rule Configuration
Configure Icon rules on data cards.
Icon rule configuration
- Icon - Not yet implemented
- First value - Variable.
- Func - Parameter to consider.
- Second Value - The value to be measured against the variable.
Color Rule Configuration
Configure Color rules on data cards.
DefaultColor - the color on the bar to the left side of the data cards.
Color rule configuration
- Colour - The color that is to be implemented when the rule is applied.
- First value - Variable.
- Func - Parameter to consider.
- Second Value - The value to be measured against the variable.

Lane Configuration
Query Configuration enables the portlet to execute specified queries towards the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector/database that the query will execute against.
- Lane Width - The width of the data card lane
- Cards per request / Initial card count - todo
- Card Shown - The default amount of cards to show when loading the portlet.
- Cards shown in Fullscreen - When in fullscreen mode, how many cards that are shown by default.
Lanes
- Title - The title shown in the top bar.
- Background - The Background color in the top bar
- Text - The color of the text in the top bar
- Query - Text field where queries can be written
- OrderBy - Select a column to order the table. Will be ordered by the selected column.
- Direction - Descending or Ascending direction the OrderBy command will order by.

Flow Configuration
Double Click Workflow - This option enables a button that runs Machine Workflows, if User Actions is checked you can also choose User Workflows.

Record Viewer portlet
The Record Viewer portlet displays one row in a table per page in the portlet. The portlet supports attaching workflows to the record page to be able to edit the data or for customized usage e.g. Dispatching a technician in the selected record.

Basic Data
Internal name - Unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - Title of the portlet, does not have to be unique. Read Only - Disable the option to edit the displayed data. Number of columns in group - todo
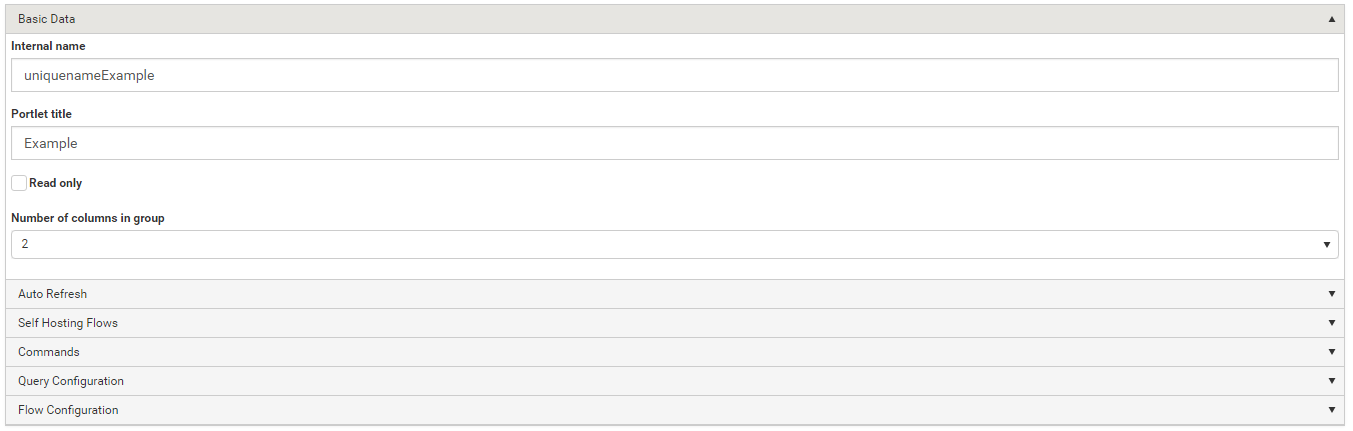
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed the portlet wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. This can be used e.g. showing more information from one of the data cards.
The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onGenericTreeNodeSelected
- onRowSelected
- onFilter
- onRefresh
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
Query Configuration
Group Headers
- Group name - a value shown as display name of a group that contains column mappers.
- Align group - up or down arrow to realign in which order the groups are to be displayed.
Column Mappers
- Display name - The display name of the value field.
- Database Column - The column where the data to be displayed will be fetched from.
- Group - Which group the column mapper should be assigned to.
- Lov - A list of values (that can be set up in Options) to apply as filter value.
- Editor - todo
- Length - todo
- Hidden - Wether or not this column will be displayed.
- Editable - Wether or not this column will be editable.
- Multiline - When using textinput and not Lov to filter, this enables the textwindow to have support for multiple lines.
- Align group - up or down arrow to realign in which order the groups are to be displayed.

Flow Configuration
Save Workflow choose the machine workflow that will save the edited data to the corresponding database.
Custom Workflows
- Display Name - The displayed name of the button
- Custom Flow - The workflow that will be mapped to the button. By default only machineworkflows can be chosen, but with User actions ticked one can choose user workflows too.
- User actions - Enable the use of user workflows as custom workflows.

Resource bucket Portlet
The Resource Buckets portlet gives you a new and innovative way to easily see who is doing what.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet.
Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Checkbox options
- Enable header - enables the portlet header, ie makes it visible in the portal. It is possible select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header background color - select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header color text - select a header text color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
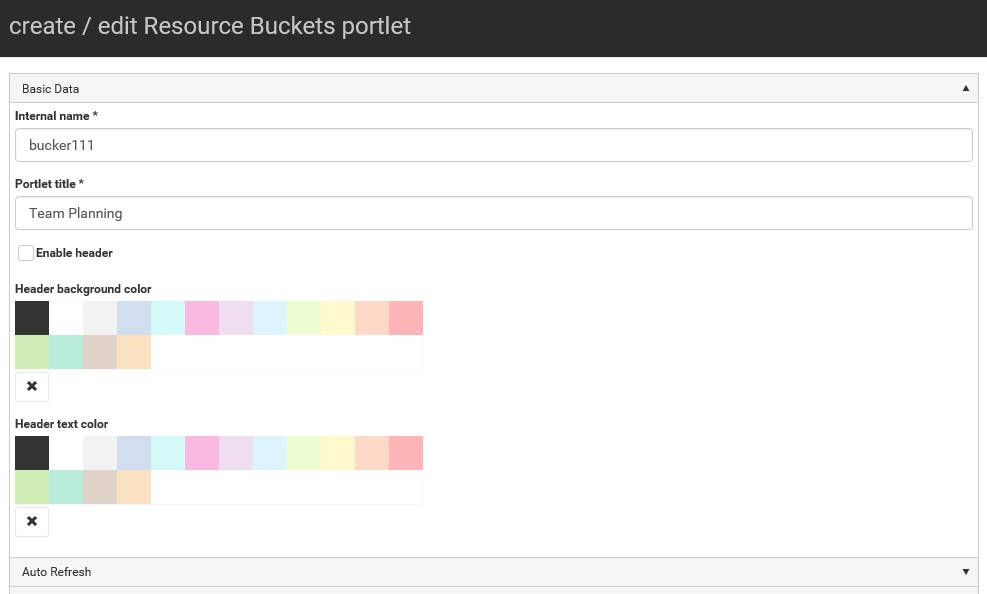
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh - enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed in the columns the table wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.
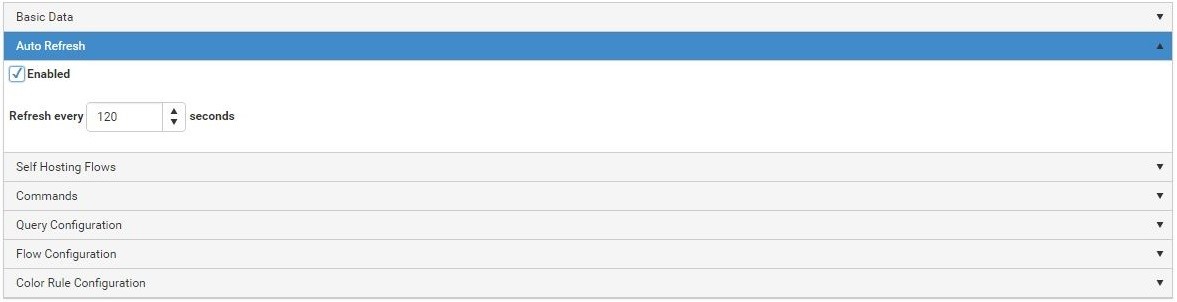
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows - enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.
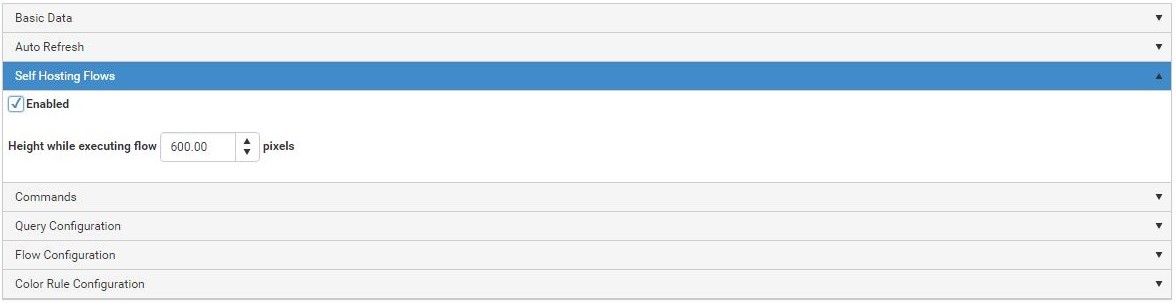
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onGenericTreeNodeSelected
- onRefresh
- onFilter
The portlet will listen to the following portlets: Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
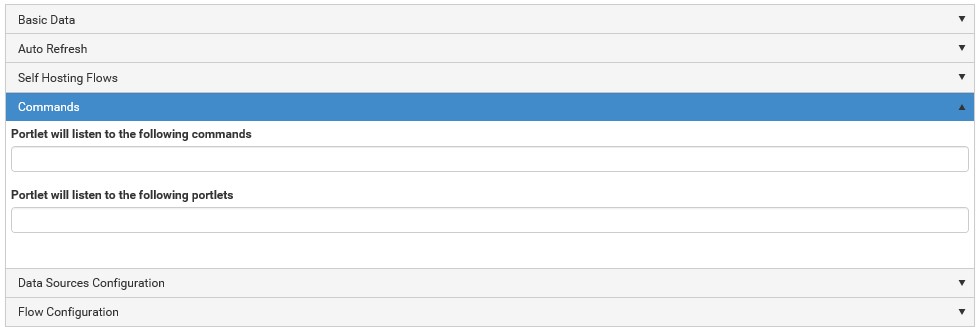
Data Source configuration
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute specified query towards the chosen database connector to fetch data, or fetch data from a workflow.
Fetching data using database query
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute a specific query to the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query should execute against
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
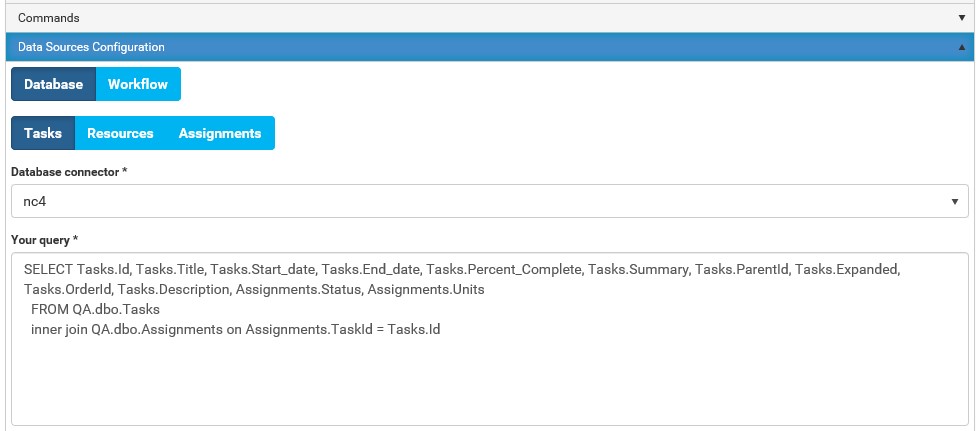
Fetching data using workflows
It is possible to use workflows to fetch data. For more information about using workflows as the data source go to: Workflow source
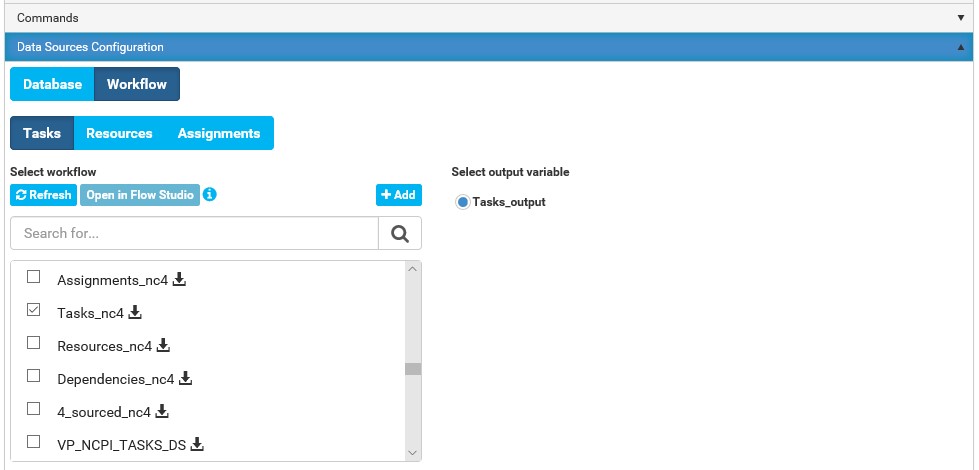
Checkbox option *
Map the data columns that are to be displayed in the portlet.
- Task identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the task
- Title column - The task title that is to be displayed
- Start date column - The date the Gantt task starts
- End date column - The date the Gantt task ends
- Status column - The status of the task
- Description column - The description of the task
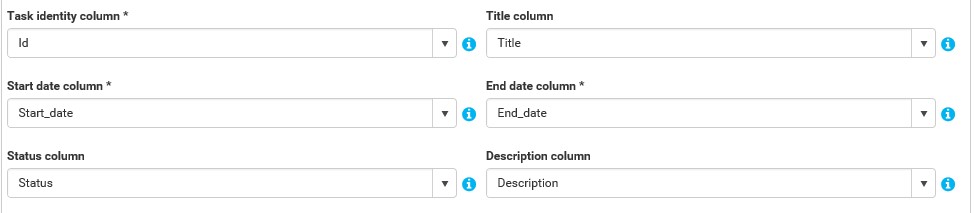
Resources
The Resources tab fetches the list of employees, resources, that will be assigned to the task in the Gantt chart.
- Resource identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the resource
- Title column - The title of the resource
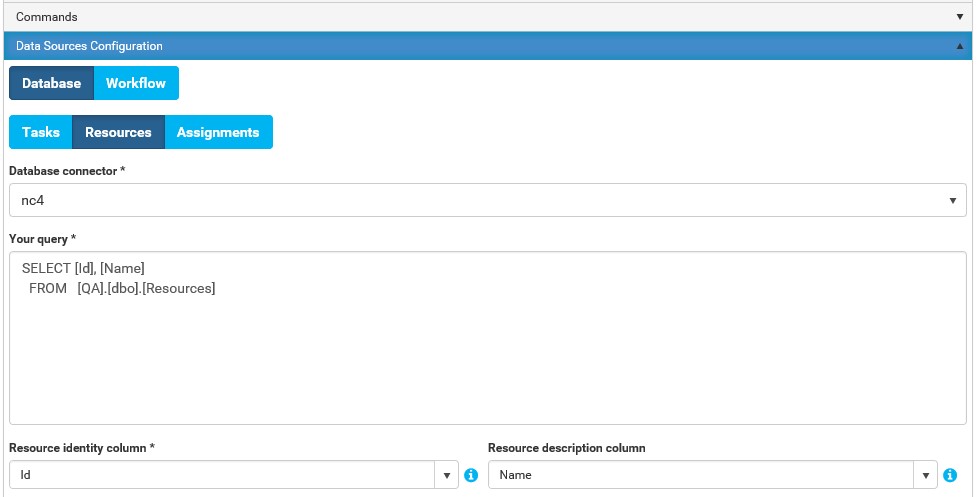
Assignment
The Assignment is the information which task is assigned to which resource (based on data provided in Task data source and Resources data source).
- Assignment identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the assignment
- Task identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the task
- Resource identity column - The mandatory unique identifier of the resource
- Unit column - Describes how much of each resource is taken up by the current task
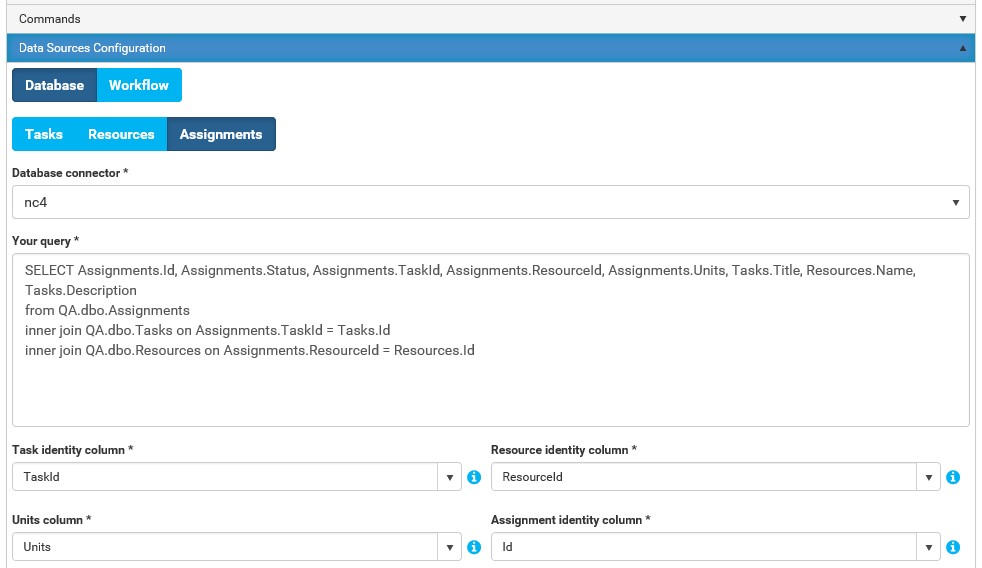
Scope Configuration
In scope configuration it is possible to configure how the portals is going to look by defining the time scale and number of buckets shown in the portlet.
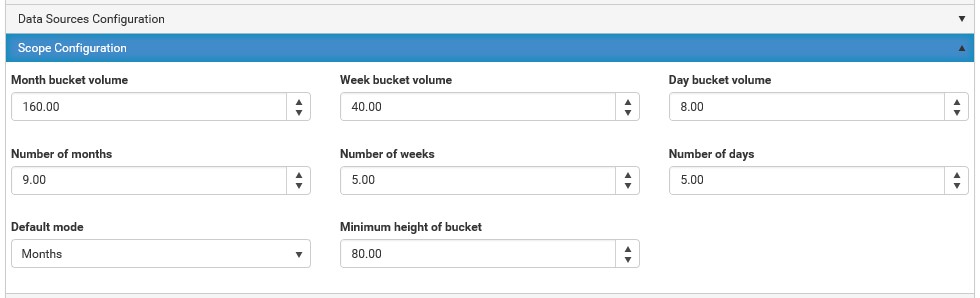
Card Configuration
The data displayed on the card is by default the title and description columns from the data source configuration. Card configuration adds the possibility for users to configure what data is to be displayed and the order of said data. The data available is what is selected in Tasks. The text is only visible when the card size is a minimum of 200 x 140 pixels.
Fields - add the columns which need to be formatted, for example dates without formatting will be displayed as text so they need to set to Date or DateTime to be displayed in the correct manner.
Add the variables and text that are to be displayed in the portlet. A datarow wraps to a maximum of two rows and uses an ellipsis function to indicate omission of text. Header text and Labels display font is bold.
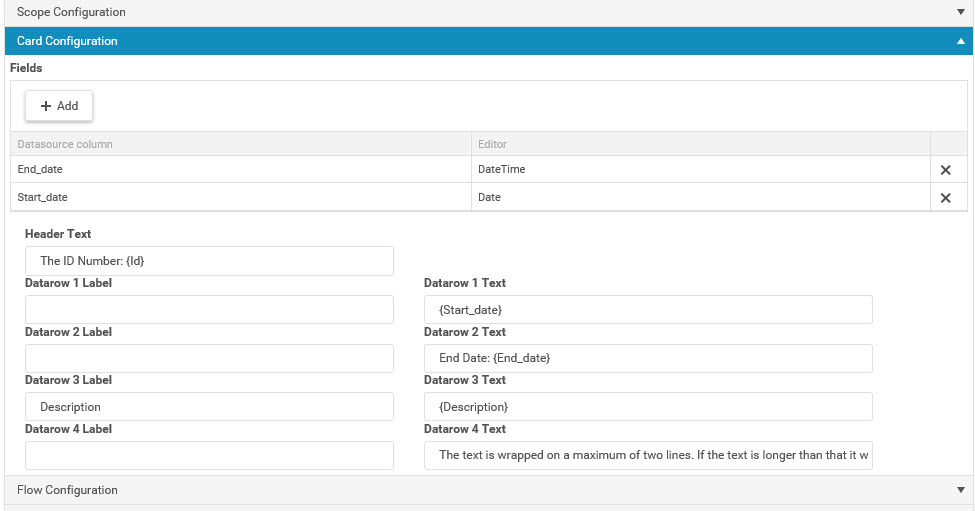

Flow Configuration
See Flow Configuration in Table Portlet.
Task Icon Configuration
It is possible to display icons on the Resource Buckets tasks.
Default Icon - field where a default icon value can be added.
Icon rules - add a row here to enter icons with conditions. It is possible to enter multiple conditions. The first condition that an activity fulfills is the icon that will be displayed on the activity. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
Legend/Color configuration
The Legend for the Resource Bucket is set up in Legend/Color configuration and configured in to be displayed different colors. The Legend name is used in Flow Configuration/Create task Workflow to identify the task type created. Use the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
Color rule setup:
- First value - variable.
- Func - parameter to consider.
- Second Value - the value to be measured against the variable.
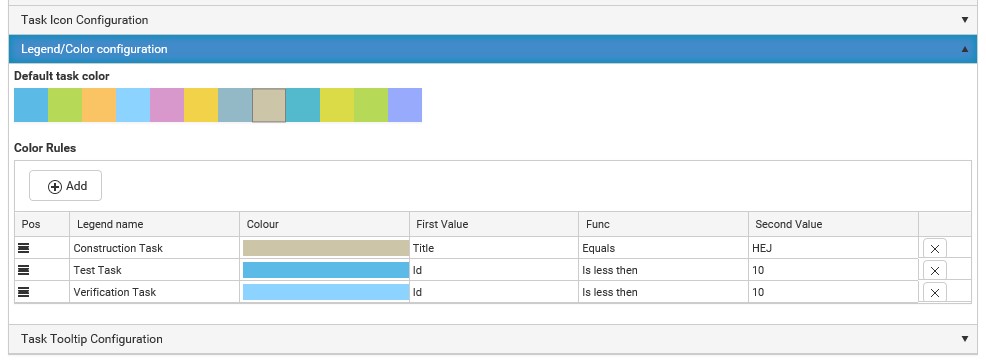
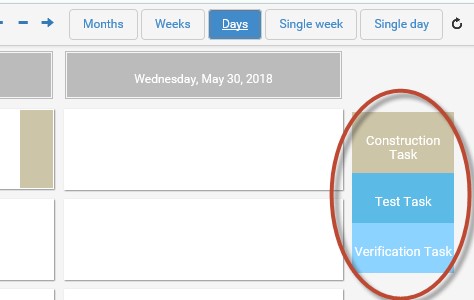
Task Tooltip Configuration
In tooltip configuration enter the text and the variables that are to be seen in the tool tip when the cursor hovers above a task.
Fields - add the columns where the data mapper is required, for example remove the time stamp when a date is displayed
Tooltip - add the text and variables, using {}, which are to be displayed
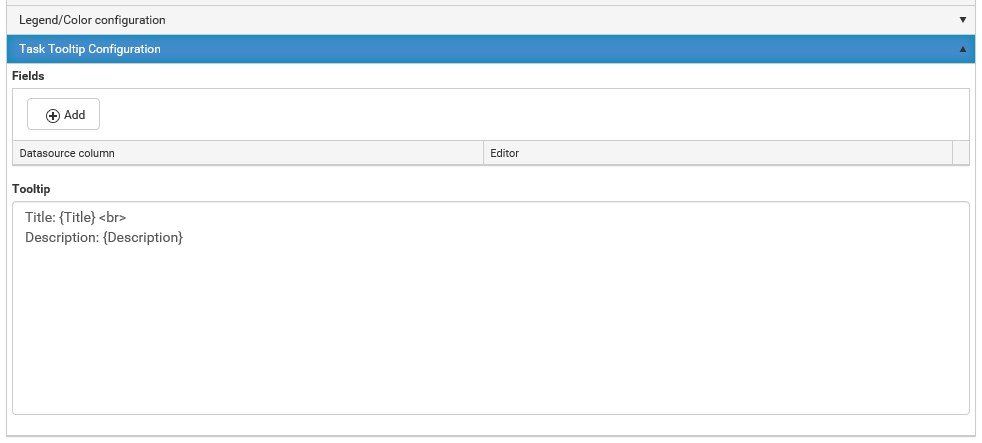
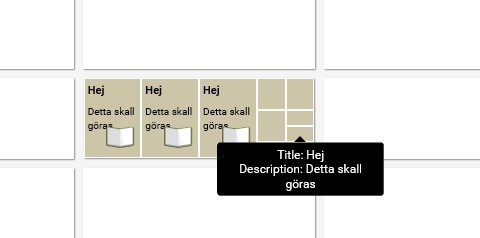
Scheduler Portlet
The scheduler portlet allows the user to easily schedule, display and edit appointments or tasks. It can be in different time views; day, week, month, timeline, agenda or customized view, and can be grouped horizontally and vertically.
The scheduler is based on three tables; Resource, Task and Assignment, where the Resource is the who or where, the Task is the what and the Assignment is the connection of the Resource and Task. A resource can be a person that is to perform certain task, or the resource can be a room in which a meeting (the task) is to take place.
Delete task must be handled by a workflow, consistant with how the other visual planning portlets work.
Important time zone information: The scheduler is expecting the time standard to be UTC (Coordinated Universal Time). Any adjustments due to server location and setting must be handled in the workflows.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet.
Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Checkbox options
- Enable header - enables the portlet header, ie makes it visible in the portal. It is possible select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header background color - select a header background color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
- Header color text - select a header text color by clicking on one of the color in the color palette, remove the color by pressing the X underneath the palette
Scheduler View and Custom Timeline
Height - the height of the scheduler shown in the portlet.
Major tick - the number of minutes each time header represents, ie the setting 60 means the headers will be full hours, 120 every second hour and 1440 a full day. See major tick example below.
The start time of the week and day views - the first hour the scheduler should show when in day or week views.
The end time of the week and day views - the last hour in the scheduler when in day or week views.
Start of the work day - the first hour of the work day. In day and week views it is possible to in the portlet to select to show only business hours.
End of the work day - the end hour of the work day. In day and week views it is possible to in the portlet to select to show only business hours.
Scheduler views - configure which views that are to be available to the user. It is possible to select one or multiple.
Horizontal grouping - tick the box if the resource is to be shown horizontally instead of vertically.
Show times in header - untick if time is not to be shown in header.
Custom timeline title - the title that will be shown to the user for customTimeline if included in Scheduler View.
Custom timeline column width - the width of the columns.
Number of days to show in custom timeline - the customer timeline will start two days before today so if this field is set to 7, the day before yesterday, yesterday, today and the future four days will be shown. The idea with custom timeline is that the customers can create a rolling timeline configured to their needs when planning etc.
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh - enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed in the columns the table wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.
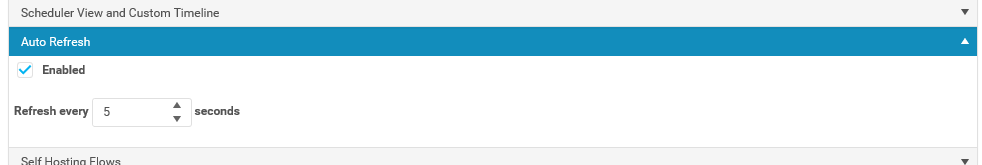
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows - enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.
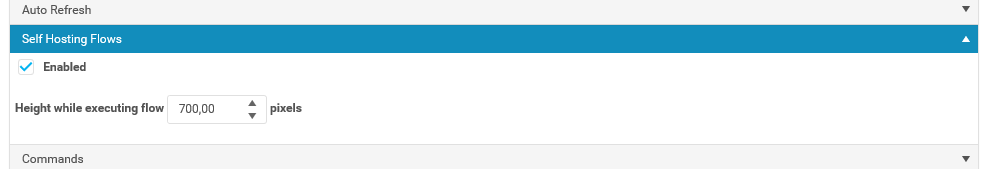
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onGenericTreeNodeSelected
- onRefresh
- onFilter
The portlet will listen to the following portlets: Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
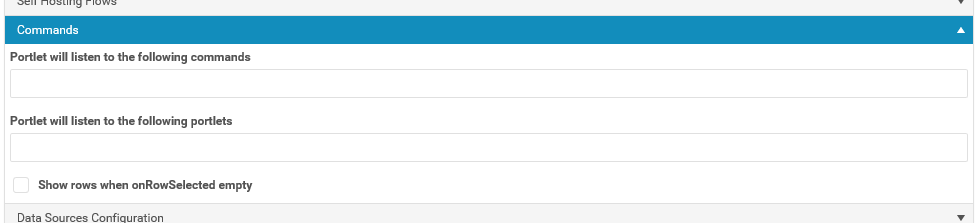
Data Source configuration
The scheduler is to be configured with tasks, resources and assignment data.
Tasks - the datasource must include a unique task identifier, a title and the start and end date and time.
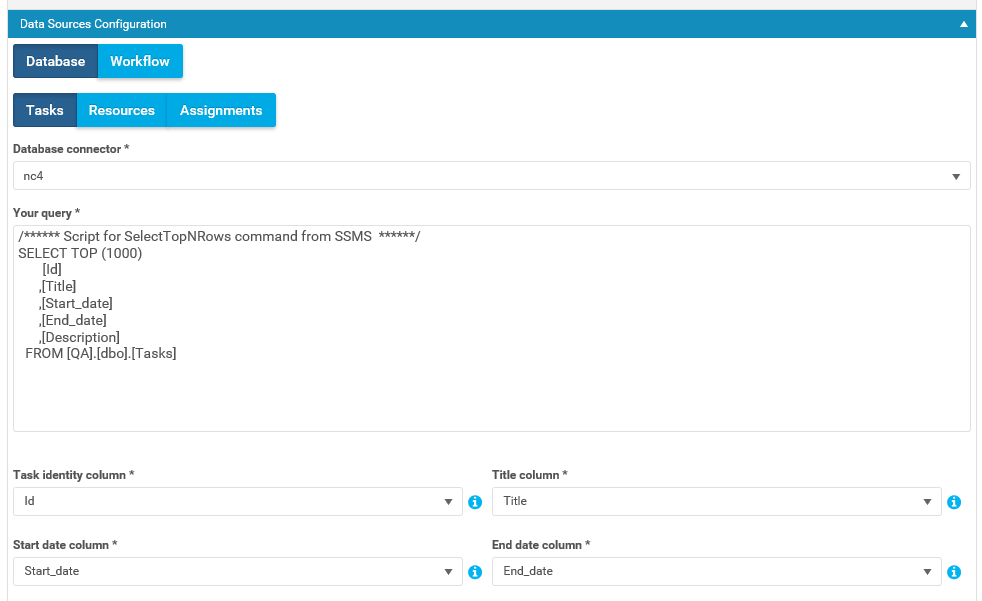
Resource - the data source must include a unique resource identifier and as optional a title and a group. The group can be used as a scheduler specific filter, see Filtering Options - Group further down in the text.
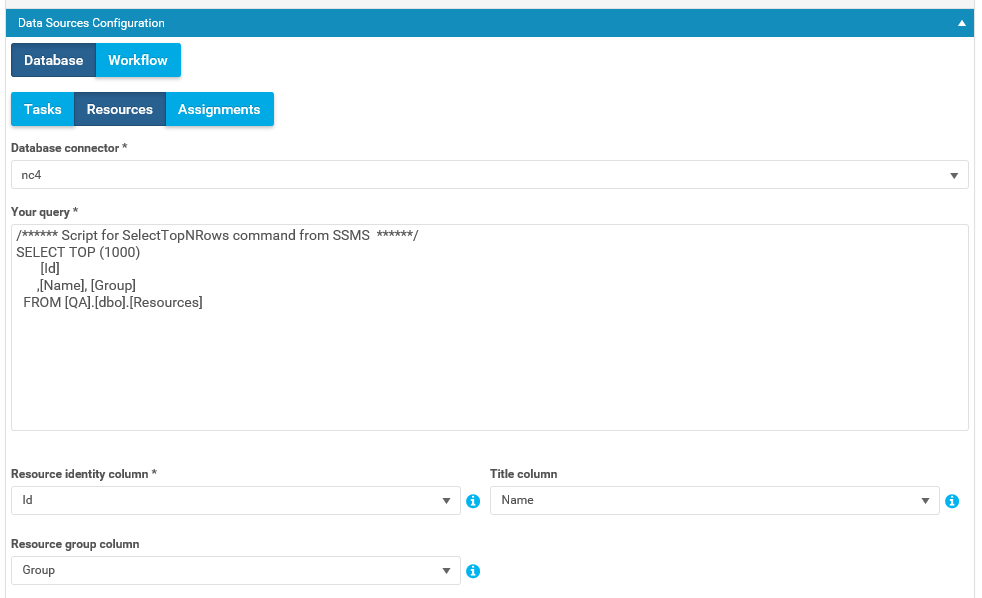
Assignments - an assignment must have a unique id and the configuration connects the resource id with the task id.
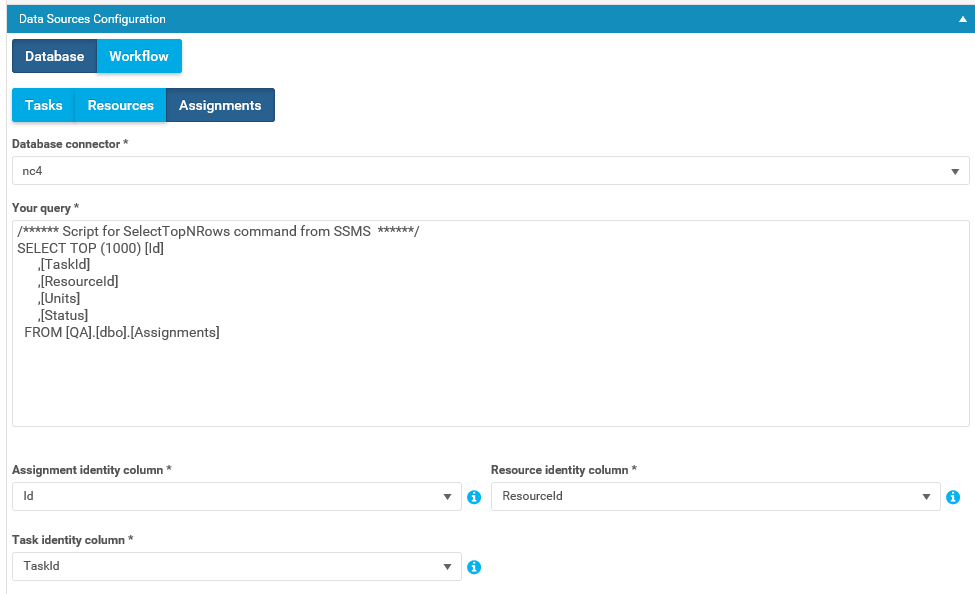
Flow Configuration
See Flow Configuration in Table Portlet.
Workflows:
Create Task - this workflow is to be able to create new tasks in the scheduler, the user clicks in a timeslot to run the workflow.
Drag and Drop - this workflow it to change or move tasks. A task can have the time period extended or decreased, moved in an earlier or later timeslot for the resource or moved to a different resource altogether.
Double Click - double click on a task to run a workflow.
Task Icon Configuration
It is possible to display icons on Scheduler tasks.
Default Icon - field where a default icon value can be added.
Icon rules - add a row here to enter icons with conditions. It is possible to enter multiple conditions. The first condition that an activity fulfills is the icon that will be displayed on the activity. Us the Add button to add rows, the X on row level to remove.
Task Coloring Configuration
The tasks for the Scheduler can be configures to be displayed in different colors. Select a default color or set up specfic color rules.
Color rule setup:
- First value - variable.
- Func - parameter to consider.
- Second Value - the value to be measured against the variable.
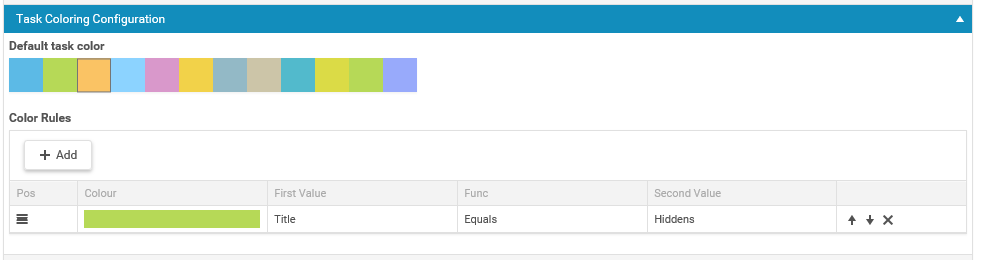
Task Tooltip Configuration
In tooltip configuration enter the text and the variables that are to be seen in the tool tip when the cursor hovers above a task.
Fields - add the columns where the data mapper is required, for example remove the time stamp when a date is displayed
Tooltip - add the text and variables, using {}, which are to be displayed
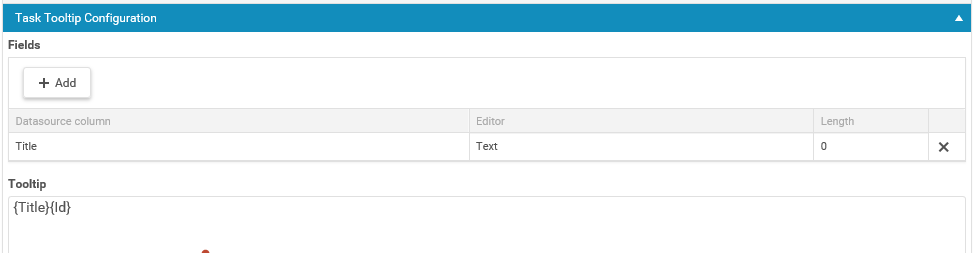
Usage in Client
Scheduler views
Settings in examples:
Week/Day view Start and End time = 07:00 - 17:00
Start and End workday = 08:00 - 16:00
Major tick = 240
Horizontal grouping unticked
Custom timeline column width = 50Day
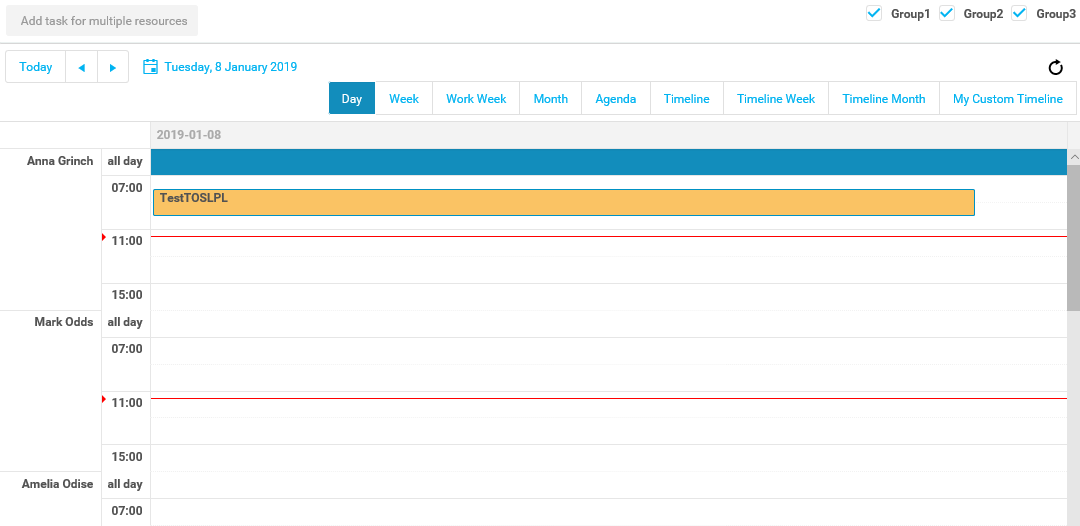
Week (shows 7 days, including Saturday and Sunday):
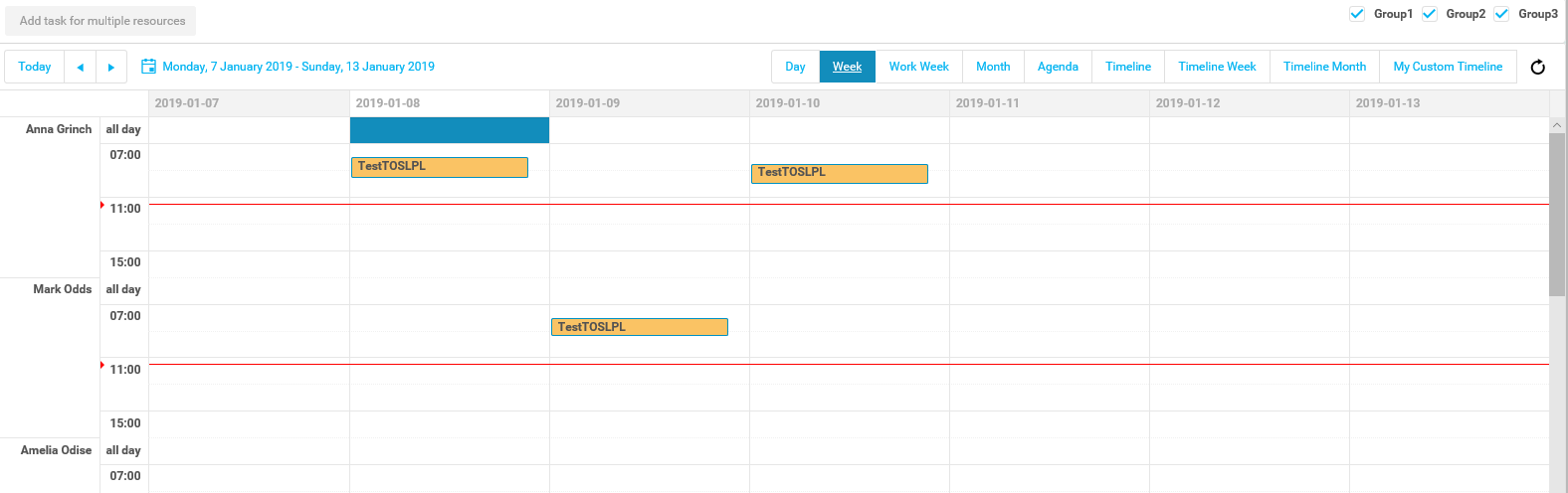
WorkWeek (shows 5 days, excluding Saturday and Sunday):
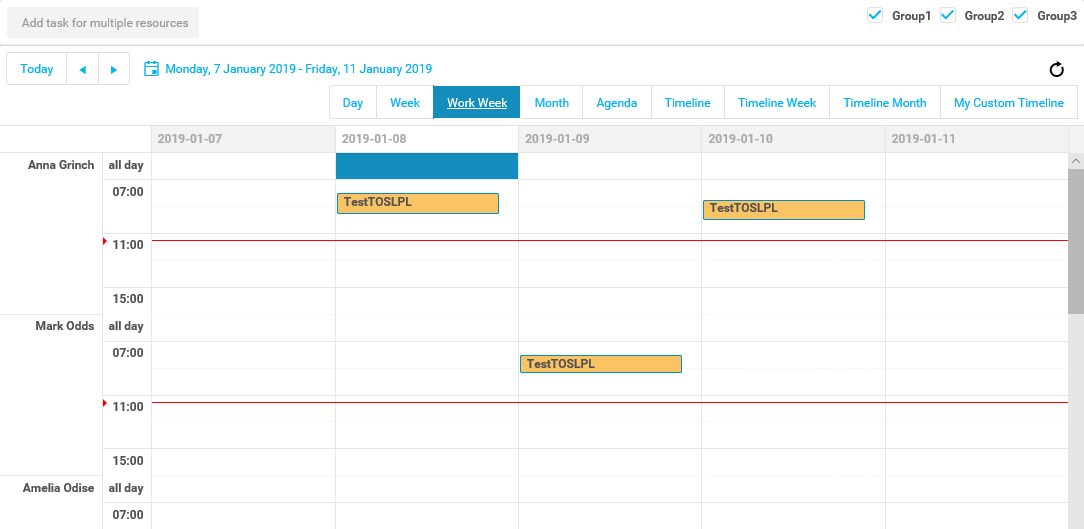
Month:
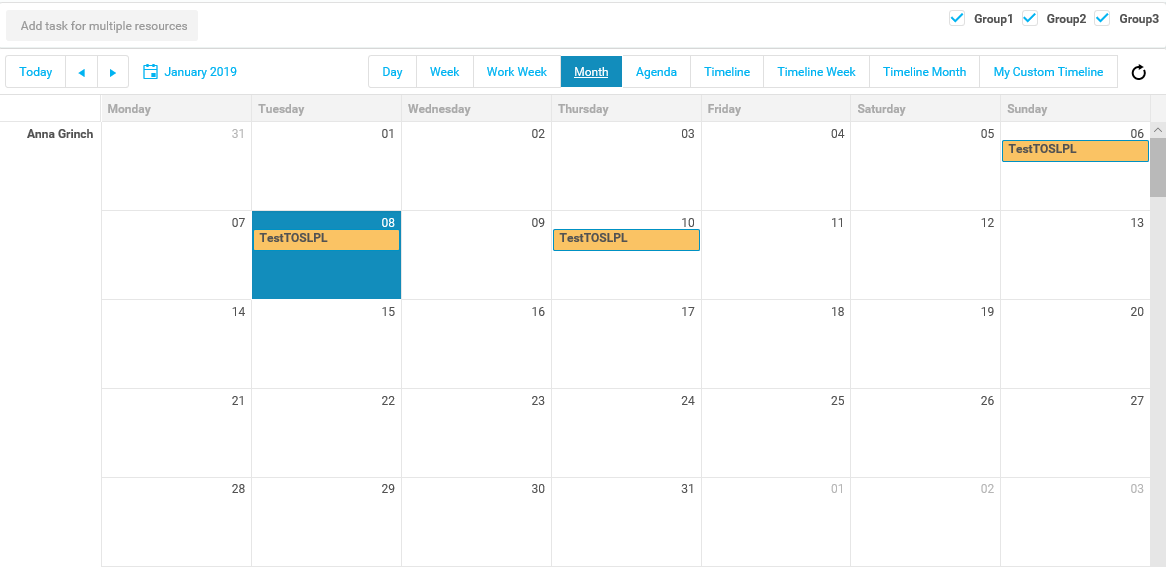
Agenda:
Timeline (shows one day):
TimelineWeek (shows timeline for one week, scrollbar available at the bottom of the portlet):
TimelineMonth (shows timeline for one month, scrollbar available at the bottom of the portlet):
CustomTimeline:
Filter Option - Group
The resources can be filtered by group, if a group has been mapped in the resource data source configuration. The groups are top right in the scheduler and by ticking and unticking the boxes the resources shown will be filtered. All groups shown:
Fetching data from databases with queries
When configuring the table portlet and want to fetch data from a database using a flow db connector follow these steps:
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute specified queries towards the chosen database connector.
- Database connector - Select which connector that the query will execute against.
- Your query - Text field where queries can be written
- Page Size - Amount of rows showed on each page
- Default Sort - List of columns of which the sorting should be done by default.
- Default column width - The default width that all columns will have in pixels.
- Database column window - Modify how the columns will be shown in the table portlet.
The Add and Map All Columns adds a column or all columns and their respective values to what is displayed in the portlet.
- Datasource Columns - A list of all columns fetched from the query.
- Column Name - Set the display name of that column.
- Width - How wide (in pixels) the column should be, leave blank to use default.
- Lov - List of values, only used when you created a list of values.
- Editor - Set what kind of data you can input into the column cells.
- Length - todo
- Editable - Checkbox if this column is editable or not.
- Hidden - Checkbox whether to show the column or not.
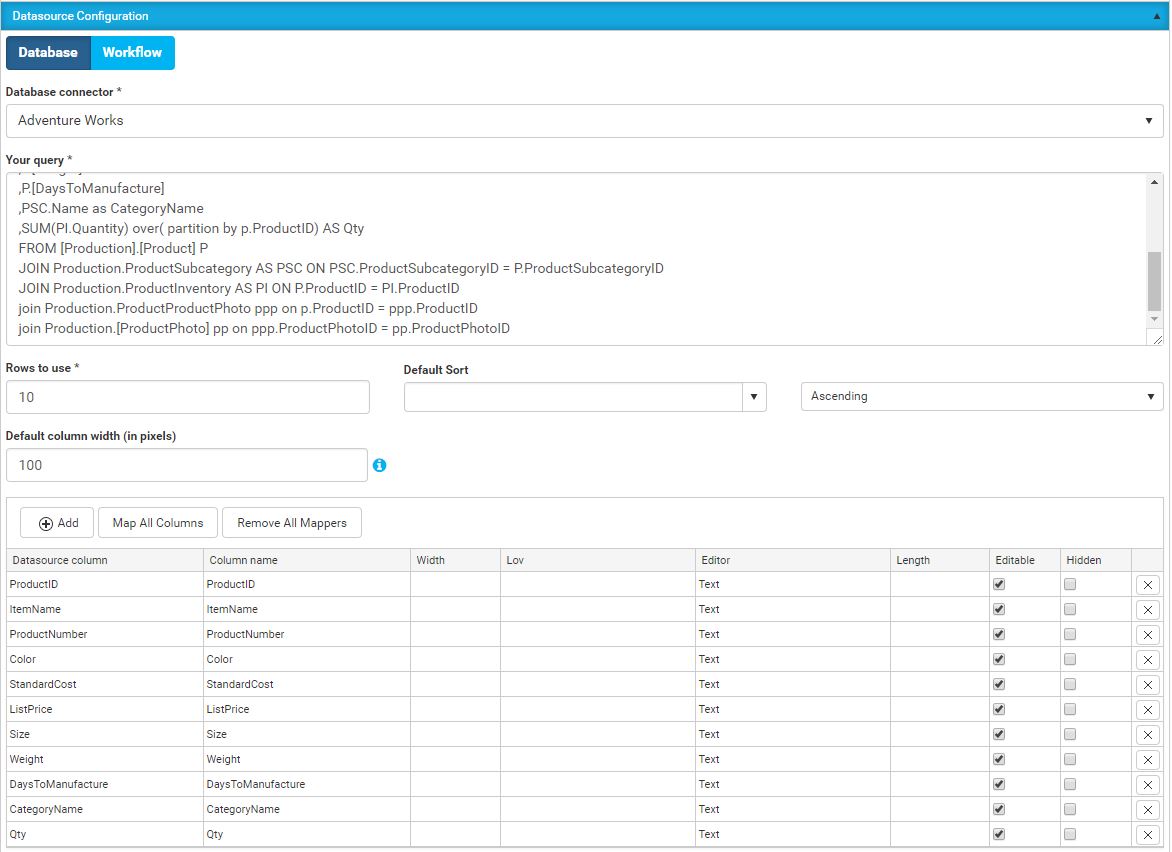
Fetching data from workflows
When configuring the table portlet and want to fetch data from workflows one needs to first configure the settings in the portal, then inside the workflow.
Setting up workflow to fetch data from
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute specified workflows to fetch data from the flow.
We introduce two types of data sources. Based on different use cases, they can be created in Studio or Portal using different machine workflow schemas.
Data source with Pagination and Filtering - this a workflow where features like Pagination, Sorting and Filtering are being used on the data fetched from database or API connectors, it can also be applied when using table operations connector.
Data source - this is a workflow which should return entire data set. For example all data from SQL table. Portal will automatically apply all parameters like pagination and filtering. This data source can additionally take Input parameter so data additionally can be filtered out (when a portlet is configured to listen to another portlet). When using Input parameter data is cached individually per user. If not, cached data is shared between multiple Portal users.
To be able to use workflows as data source one needs to: 1. Select a workflow from the list or add a new one on the add button. 2. Press open in Flow Studio
- Refresh - updates the list of workflows
- Open in Flow Studio - Opens the selected workflow in Flow Studio
- Add - Creates a new workflow, pop-up window for creating a workflow has Data source with filtering and data source without filtering, the workflow created will contain different preset input data and elements depending on which one is chosen.
Workflow Input Configuration
The input in the workflow will be automatically generated from the portal when creating a new workflow, what the input contains depends on what data is being sent and if its with filtering or not.
- Input - When communicating between two portlets this needs to be filled with the data/columns expected to be sent. Can be column names such as ID and Value.
- Query Settings - This contains necessary information for filtering, pagination, sorting(Only when using pagination and filtering).
These are added automatically when creating the workflow from the portal, what needs to be added on its own are the variables inside the Input table.
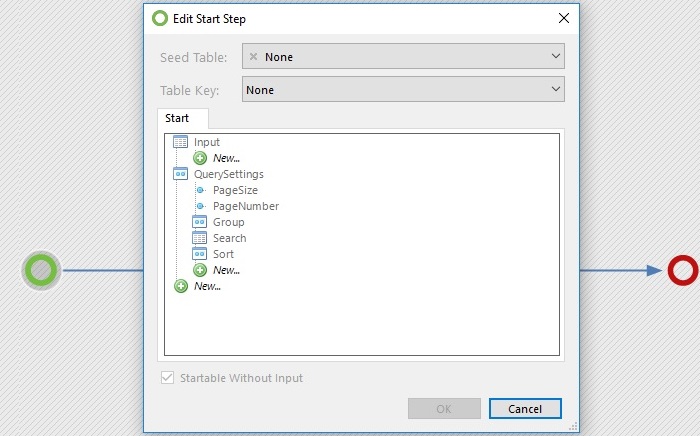
Workflow Data Source Configuration
After the input is configured machine steps fetching data can be added, all types of data sources are supported, both API connectors and database connectors.
Workflow Output Configuration
To send the data to the portlet the output data needs to be configured. The two important values that need to be sent are:
- TotalCount - the calculated total count(Only when using pagination and filtering).
- Single table variable - table variable with data that can be used by the portal.
E.g a page from sql table.
These are added by opening the end step, pressing edit output variables and checking each variable that is to be sent to the portal.
Setting layout and settings for table portlet in portal
The Add and Map All Columns adds a column or all columns and their respective values to what is displayed in the portlet.
- Datasource Columns - A list of all columns fetched from the query.
- Column Name - Set the display name of that column.
- Width - How wide (in pixels) the column should be, leave blank to use default.
- Lov - List of values, only used when you created a list of values.
- Editor - Set what kind of data you can input into the column cells.
- Length - todo
- Editable - Checkbox if this column is editable or not.
- Hidden - Checkbox whether to show the column or not.
Table Portlet
The table portlet can show data from databases as a table by executing SQL queries. It is possible to configure the columns in the table portlet editor to customize how the data is displayed. The portlet can export the table as a Microsoft excel file (.xls) and run machine and user workflows by pressing a preconfigured or customized button.
Basic Data
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique.
Checkbox options
- Read only - enable that data cannot be modified.
- Groupable - group data in table by selected column.
- Multi Select - enables hold SHIFT to select several rows.
- Reordarable - enables to adjust in which order the columns are ordered by drag and drop.
- Resizable - enables to adjust the width of the columns.
- Exportable - enables a button to export the data as a Microsoft Excel File (.xls).
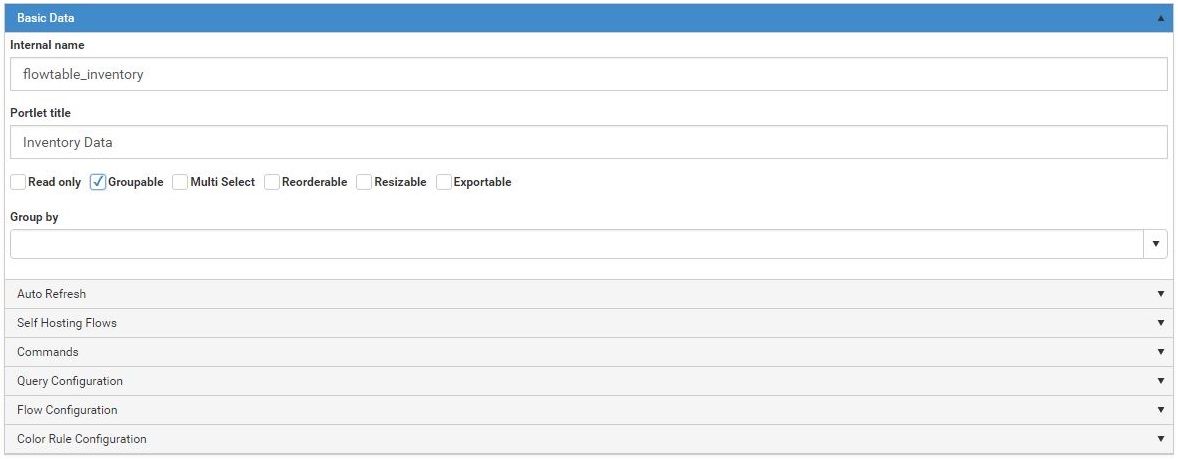
Auto Refresh
Auto Refresh - enables the portlet to refresh the data every SS:second. If data has changed in the columns the table wont refresh until the changes are saved or canceled.
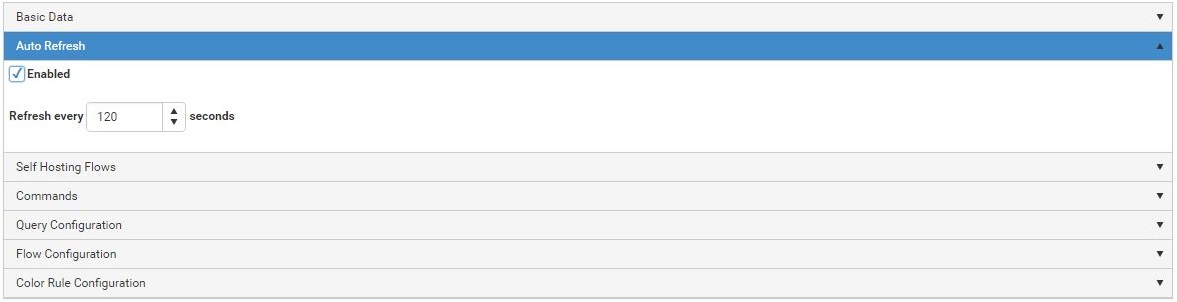
Self-Hosting Flows
Self-Hosting Flows - enables the portlet to continue running when the user reaches for another portlet.
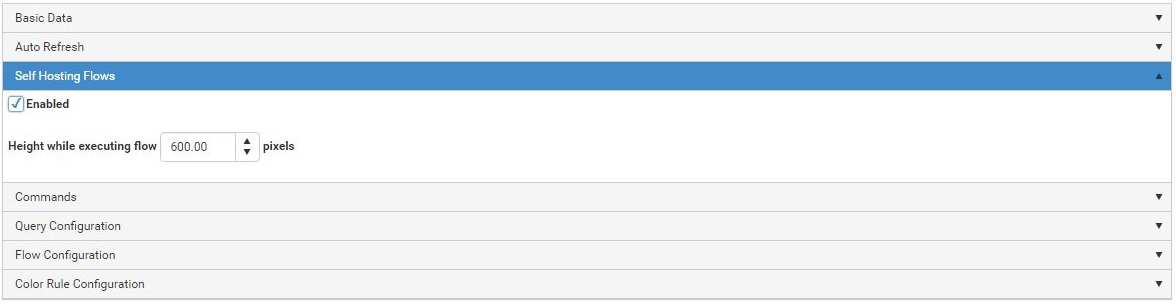
Commands
Commands enables the portlet to listen for events sent by other portlets to execute specified commands. The portlet will listen to the following commands
- onRowSelected
- onGenericTreeNodeSelected
- onRefresh
- onFilter
The portlet will listen to the following portlets Specify which portlet the commands above will trigger from. The portlets that appears will be shown with their unique internal name.
Show rows when onRowSelected empty - todo
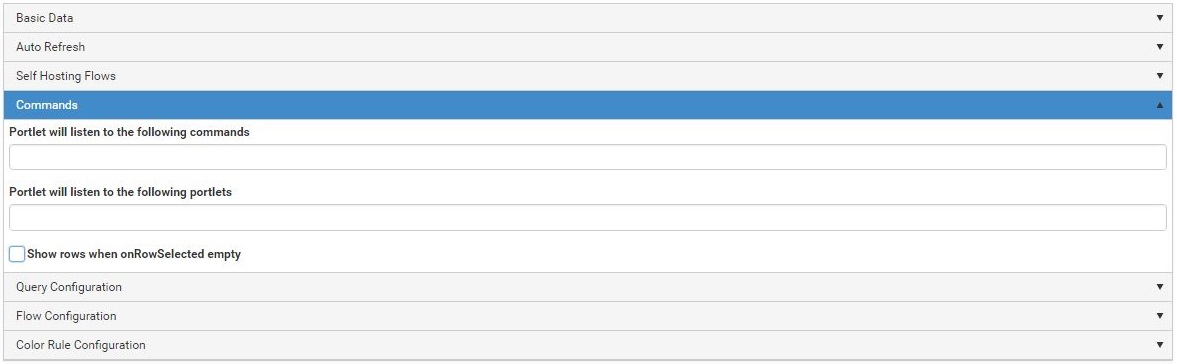
Data Source configuration
Data source configuration enables the portlet to execute specified queries towards the chosen database connector to fetch data, or fetch data from a workflow.
Database option queries a database through a flow db connector to retrieve data. Database source
Workflow option allows for any type of data table to be retrieved as data that the portlet can show. Workflow source
Flow Configuration
Flow Configuration enables the portlet to add machine and user workflows. The variables that are sent to the workflow that needs to be specified in start step are:
- Table with table name specified in output.
- All columns to be specified as variable inside the table
- Type variable which contains the text "update", "add", "delete"
There are three kinds of workflows that can be used in the Table portlet:
- CRUD Workflow - This option executes changes that have been made in the table (UPDATE, CREATE, DELETE) to an attached machine workflow.
- Double Click Workflow - This option enables a button that runs Machine Workflows, if User Actions is checked you can also choose User Workflows.
- Note when this option is checked, data will be sent as a table parameter named DblClickRow
- Custom Workflows - This option can be linked to a custom button attached to the table. Machine workflows cannot be used here.
- Note: Left Value can be values e.g. {VALUE IN COLUMN} from the sql query where Dataset is the specified column.
User Action checkbox enables the portlet to add user task workflows.
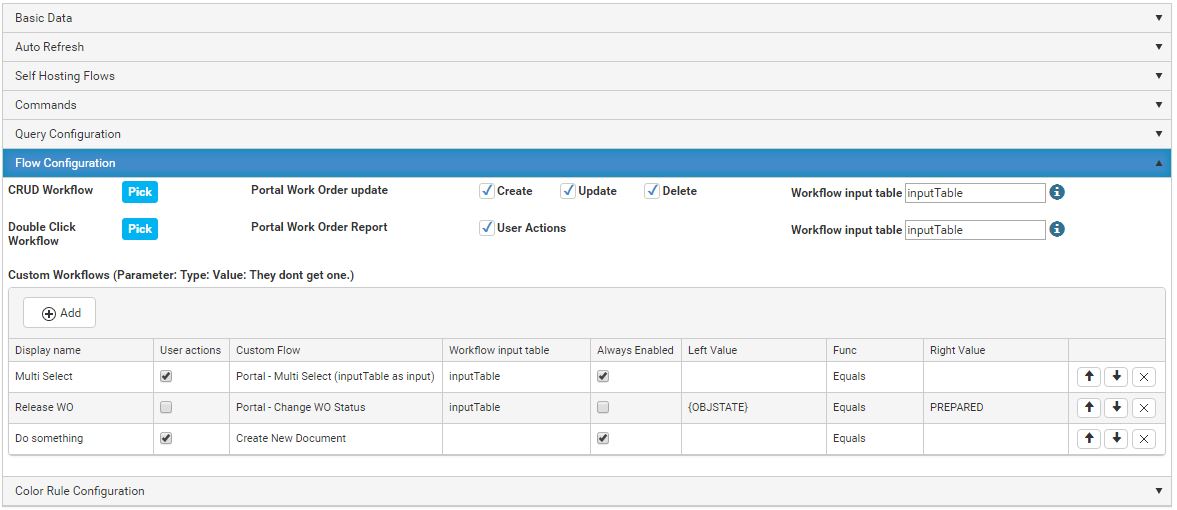
Color Rule Configuration
Configure coloring rules on the table rows.
Color rule setup
- First value - variable.
- Func - parameter to consider.
- Second Value - the value to be measured against the variable.
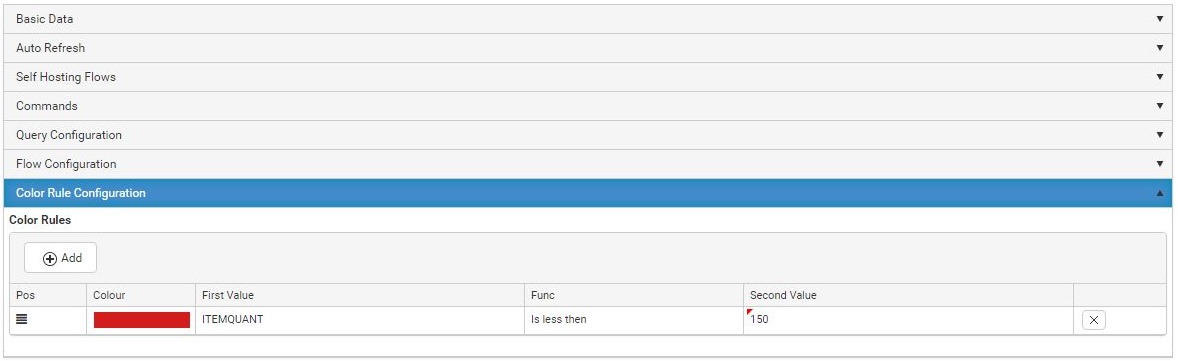
Text Portlet
The Text portlet contains a text editor where you can show text, links and images in the portlet container.

Text Options
Internal name - unique string to identify this portlet. Portlet title - title of the portlet, does not have to be unique. Content - Options to create links, images and format text.
Novacura Flow Portal Portlets
Portlets are applications that are added to portlet containers in the Flow Portal and can be configured to do a number of tasks.
The portal supports a large variety of portlets ranging from a dataset visualizer that supports editing to KPI indicators
Novacura Windows 10 client
Novacura Flow is an innovative, rule changing software with one sole purpose: to improve your critical business processes. With Novacura Flow, we put the business and the user in focus, allowing you to create intelligent and user friendly business applications in three simple steps: Design, Configure, Run.
System requirements
Computers, tablets and mobile phones running Windows 10.
Installation
To install the Novacura Flow UWP client:
- Download the client from Microsoft Store: Search for Novacura Flow 6 or use this https://www.microsoft.com/store/apps/9nx2hknlfm84
Connect and Log In
In order to be able to run your Novacura Flow applications, you first need to connect to the correct Flow environment.
When you first start the Novacura Flow app you will get to this screen:

Screen for connecting to your Flow Environment
There are three ways of connecting to your Flow environment:
- Scan Code: Scan the QR Code on the Server Page. The server address should be https://[your servername]/Novacura.flow.server.
- Enter Pin: Enter the Pin Code visible on the Server Page.
- Enter server address manually: Enter the server address above manually to connect.
When you have connected to your Novacura Flow environment, you should get to the login page where you can enter your Novacura Flow user name.

Depending on the set up, you will be prompted to enter one or many passwords. These passwords is either your Flow login password OR passwords for logging in to any connected system. The login can therefore be different for different users.
For User setup, see User configuration.
Get started
Open the Novacura Flow client and enter your Flow server address and press the arrow to the right. Enter your username and password then click on login. The main view is displayed with menus and it is related workflows. To reload the menu, change settings or log out use the menu on the top right corner.
Start a new workflow by tapping on the workflow you want to run under the menu which it is attached to. Pause a workflow with the arrow in the left corner and quit by using the cross in the right corner. A paused workflow is indicated by a play-button in the right corner of the workflow. Start a paused workflow by taping on it from the main view. To delete a paused workflow on a computer, right-click on the workflow and on mobile press and hold on the workflow to kill the ongoing execution (observe that all transaction that is done in the workflow will not be deleted).
Offline mode
When working with offline applications in the iOS Flow clients, all transactions that are produced by the workflow are put in a queue. This queue can be found in the Offline Data section, under MY WORK. The transactions are executed automatically in the background when the device have access to internet. Always download or update the offline data under Offline Data -> MY OFFLINE DATA, after that is done, then it will be possible to execute a workflow without internet connection.
Help request
Transactions that is done in offline applications will normally execute without any problems and then disappear from the queue. However, if a workflow transaction has failed, then is possible to send a Help Request to an Administrator, so that the problem can be fixed. The Administrator can then either correct the problem in the back-end system or correct the data in the workflow transaction. When the Administrator has sent back the transaction can the transaction be executed again, and if the problem is fixed will the transaction execute without any errors.
- If there is an error in a transaction a warning will show up next to the Offile data button.
- Workflow error details are registered in the MY WORK section under Offline data.
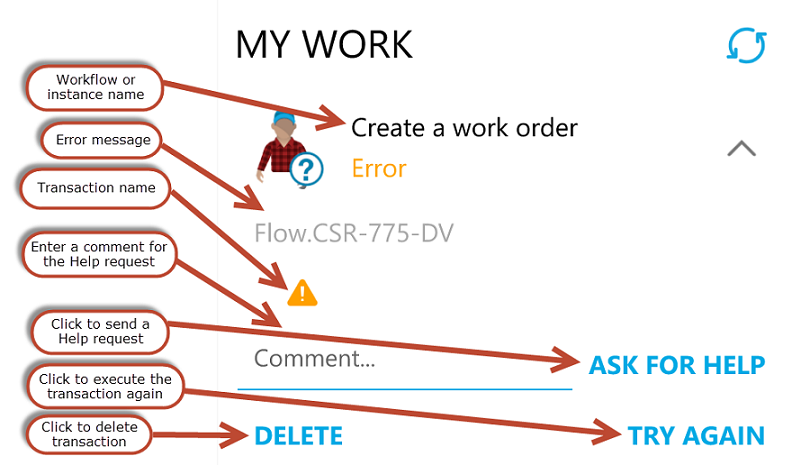
- To send a Help request for a transaction that has an error, fill in the optional Comment field and click on ASK FOR HELP, the Help request will be sent to an Administrator that will take care of the issue.
- When the Help request is sent, then will the status for the transaction change to Waiting for response.
- A notification will be sent when an Administrator has started to work with the Help request, and another notification will arrive when the Help request is sent back to be executed again.
- To execute the transaction again, go to MY WORK section under Offline data, find the transaction that is fixed and click in TRY AGAIN.
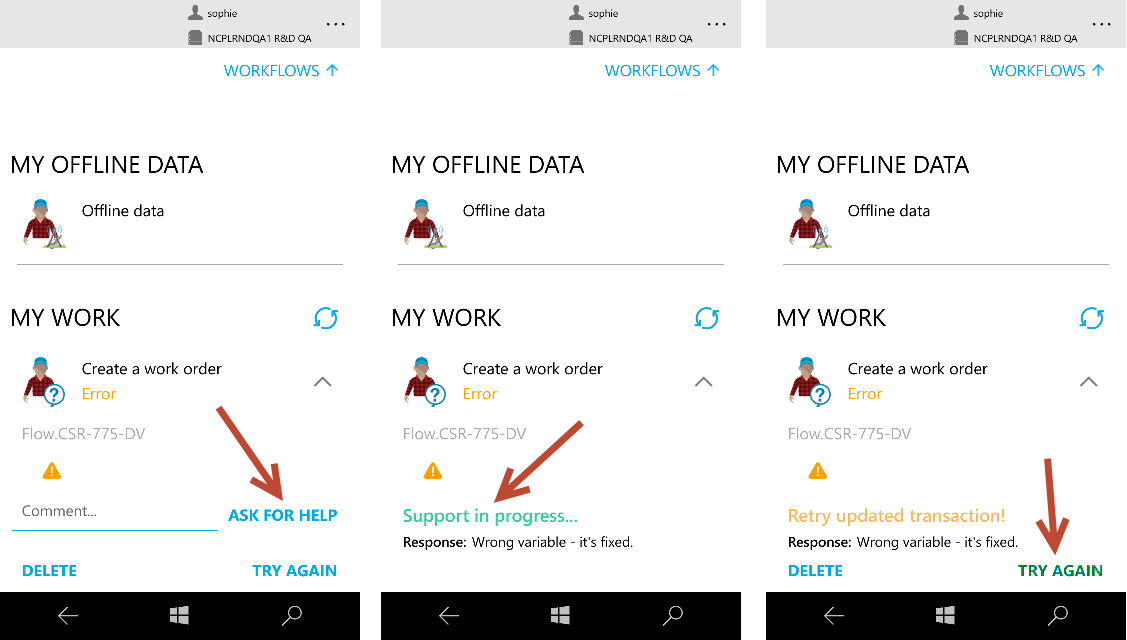
The User can use the following options:
- ASK FOR HELP: Send a Help request to and Administrator
- TRY AGAIN: Retry a transaction without asking for help
- DELETE: Delete the transaction (observe that all data for that transaction will be deleted)
Scanning
Novacura Flow Web client
System requirements
Installation
Get started
Novacura Flow WinCE client
System requirements
Windows CE Client requires version 5.0 or newer with .NET Compact Framework 3.5.
Installation
Go to http://community.novacuraflow.com/downloads/ to download the WinCE client.
There are two ways to do the installation either with the .Cab file or the manual way to move the unzipped folder Device to the scanner device.
Always install the client under the flash drive on the device, otherwise can the installation be lost when doing a reboot
Install with .cab file:
Move the file to the scanner and run the file on the device. After the installation is done, change the Novacura Flow server address in the setting.xml.
Manual installation:
Change the address to the Novacura Flow server address in the file setting.xml. Copy the Device folder with the changed settings.xml file to the scanner. Create a shortcut to the .exe file on the desktop.
Good to know
If the error message: An error message is available for this exception but cannot be displayed because these messages are optional and are not currently installed on this device. Please install 'NETCFv35.Messages.EN.wm.cab' for Mobile 5.0 and above or 'NETCFv35.Messages.EN.cab' for other platforms. Restart the application to see the message. appear, then download and install NETCFv35.Messages.EN.wm.cab and NETCFv35.Messages.EN.cab on the device, this will make the real error appear. Download here: https://home.novacuraflow.com/Downloads/CE-language.zip
To setup the device to, after a scan, automatically move forward in the workflow, go to the control panel and open "NID scanner" and go to tab "Misc2" and set the scanner prefixes and postfixes to semicolon. As in the picture to the right. This will make everything that is scanned automatically get a semicolon in front and the end of the scanned value.
Microsoft Active Directory Connector
The Microsoft Active Directory connector can be used to perform various Active Directory related operations.
Configuration
- LDAP Path: LDAP path to use (if any).
- Domain Name: Active Directory domain.
- LDAP User: User name this connector should use while accessing Active Directory.
- LDAP Password: Password for user.
Database Connector
The database connector is used to connect to various databases. Supported databases are Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, IBM DB2 iSeries, IBM DB2, MySql Server and IFS Applications.
Configuration
- Database Type: Type of database
- Database server. Address to database
- Global User ID: User to login to database with
- Global Password: Password for User
- Initialization Command: Optional command to execute immediately after successful login
- Cleanup Command: Optional command to execute on database after operation has completed.
- Command Timeout: Command timeout, in seconds, to use when executing a script or a query. If not set, default value for database type will be used (most likely 30 seconds). Please note that this is the timeout between Flow Server and database. It is possible that the communication between Flow Client and Flow Server will timeout prior to the command timeout. If the client experiences timeout, but the database command does not, the database command will still be executed completely.
- Connection Pooling: Sets whether connection pooling should be used (not supported by all database types)
Security
The database connects directly to the database using different kinds of authentication protocols according to what kind of database this is connected.
IFS Applications 10 API
The IFS Applications 10 API connector can be used to execute procedures (including New__, Modify__ and Remove__) and functions in IFS Applications 9.
Configuration
Server
Url to server, for instance http://host:portGlobal runtime User Id
If specified, the User to login to IFS with at runtime.Global runtime password
If specified, the password for the user to use at runtime.Design time User Id
The User to login to IFS with at at design time.Design time password
The password for the user to use at design time.Debug settings
In this section debug settings are configured. In order to get log files, Path where to write log files must be set to a valid path relative to the Flow Server. The log files are created by IFS Applications, not by Flow.
IFS Applications 9 API
The IFS Applications 9 API connector can be used to execute procedures (including New__, Modify__ and Remove__) and functions in IFS Applications 9.
Configuration
Server
Url to server, for instance http://host:portGlobal runtime User Id
If specified, the User to login to IFS with at runtime.Global runtime password
If specified, the password for the user to use at runtime.Design time User Id
The User to login to IFS with at at design time.Design time password
The password for the user to use at design time.Debug settings
In this section debug settings are configured. In order to get log files, Path where to write log files must be set to a valid path relative to the Flow Server. The log files are created by IFS Applications, not by Flow.
IFS Applications Connector
TODO
M3 Infor API Connector
The Infor M3 API Connector is used to integrate with Infor M3.
Configuration
- M3 Server Name
- Address or name of M3 Server. Required.
- Port Number
- Port to use when communicating with M3 Server. Required.
- CONO DIVI Parameter
- Global Username
- Username for connecting to M3 Server. Leave blank if username and password is to depend on Flow user.
- Global Password
- Password for Global Username when connecting to M3 Server.
- Advanced configuration
- Call SetLstMaxRec when getting metadata
- Sets whether a SetLstMaxRec should be called before getting programs and transactions. If SetLstMaxRec is not called, M3 will at most return 100 items.
- Argument to SetLstMaxRec
- Sets the argument to use with SetLstMaxRec. Setting it to 0 typically will return all available metadata, but this can be M3 version dependent.
- Sets the argument to use with SetLstMaxRec. Setting it to 0 typically will return all available metadata, but this can be M3 version dependent.
- Enable log
- Sets whether to write a log of certain events, such as opening and closing a connection, to the log file provided in Path to log file.
- Path to log file
- Path to the file where logs are written if Enable log is used. The file is created if it does not exist.
- Call SetLstMaxRec when getting metadata
Infor M3 REST Connector
The M3 Rest Connector is used to execute transactions in M3 via the M3-API-REST bulk API.
Configuration
Url
Required url to base address of REST API.Design time Authentication
In this section the authentication to be used when fetching metadata from the REST API is configured. User name (basic) and Password (basic) is used for Basic Authentication, as specified in RFC2617. The information in this section is only used while designing workflows in Flow Studio. It is never used in runtime. The user specified here must be allowed to run the transactions LstPrograms, LstTransactions and LstFields in the program MRS001MI.
In this section there is also the possibility to accept any certificate from server in an https session. This should only be used for test or development scenarios when no other option exists.Runtime Authentication
In this section the authentication to be used when executing machine tasks is configured. User name (basic) and Password (basic) is used for Basic Authentication, as specified in RFC2617.
In this section there is also the possibility to accept any certificate from server in an https session. This should only be used for test or development scenarios when no other option exists.Logging
In this section logging is configured. Either incoming or outgoing or both can be logged. If something goes wrong in the communication, an entry is added to the file errorLog.txt. In order to enable logging, a valid path relative to the Flow Server must also be provided. Note that the path must already exist, the connector will not create the path. Also note that the user that Flow Server is running as must have write access to the path.
Get started
Press Select operation to select which transaction to execute.
Input
The input will of course depend on the transaction to execute. There is one common parameter that always is available though, readtimeoutmillis. In this parameter you can specify the amount of time to wait for response from job.
Another common feature for all transactions is the possibility to use an iterator. If you select a iterator it means that the transaction will be executed once for each row in the table specified as iterator. Using a iterator will change the output of the cogwheel to a table with the same number of rows as the iterator table, each row in the table is corresponding result of transaction execution for row in iterator table. You can of course map columns in iterator to parameters of transaction. Simply select an iterator, and for a parameter select I Iterator in dropdown menu for parameter and then select the suitable column of iterator table.
Output
Record (or table of records if iterator is used).
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HttpStatusCode | The status code returned from REST API. Typically 200 if request (not necessarily transaction) was successful. 401 if not authorized etc. |
| ReasonPhrase | HTTP ReasonPhrase, if any |
| AllHeaders | Simple variable containing all headers (with line feed between each header) returned by REST API. |
| OK | A record containing result of transaction if it was successfully executed. Will be empty if transaction failed. - Program - Simple variable containing the program executed - Transaction - Simple variable containing the transaction executed - Records - A table containing the records (if any) returned by transaction. The columns of the table will of course depend on the transaction, but you can always choose not the request particular columns by unchecking the Included checkbox. By doing that, it will not be requested from the REST API, which could boost performance. You can also specify a row limit on Records (default 100). |
| Error | A record containing error information if transaction failed for some reason. Will be empty if transaction was successfully executed. |
Note that if HttpStatusCode is 200, either OK or Error (never both) contains data. This can be used to take different paths in your workflow. Simply add a 'Decision Step' and add a script rule like transactionResults.Error != nil to check for errors.
Maximo Generic Connector
Maximo Generic connector communicates with Maximo Web Services.
Configuration
First step is connector configuration in Flow Studio (see picture below)
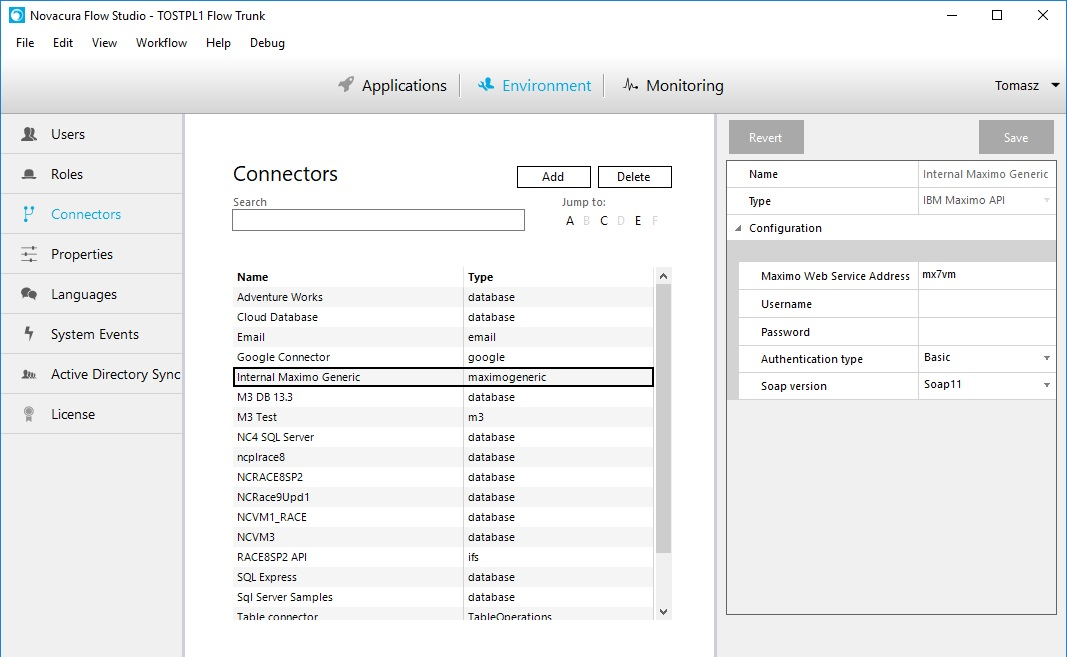
Communication with Web Services is always over the HTTP protocol.
The following parameters are configurable in the configuration:
- Maximo Web Service Address: The Maximo server name which hosts web services
- User name: user name (credential) used in authentication
- Password: password (credential) used in authentication
Authentication type: it decides how credentials are used when web service is called. The connector uses SoapHttpClientProtocol dotnet object to communicate with Maximo Web Services, but credentials can be used with two modes:
Basic: dotnet NetworkCredential objects is created and attached to Credentials property of SoapHttpClientProtocol object.
Base64: credentials are encoded with base-64 digits and put into soap request header
Soap version ? connector can communicate with web services in two SOAP versions: SOAP1.1 and SOAP 2.2
Get started
When connector is configured we can use it in machine steps. We have to do the following steps:
- Reload Maximo Web Services
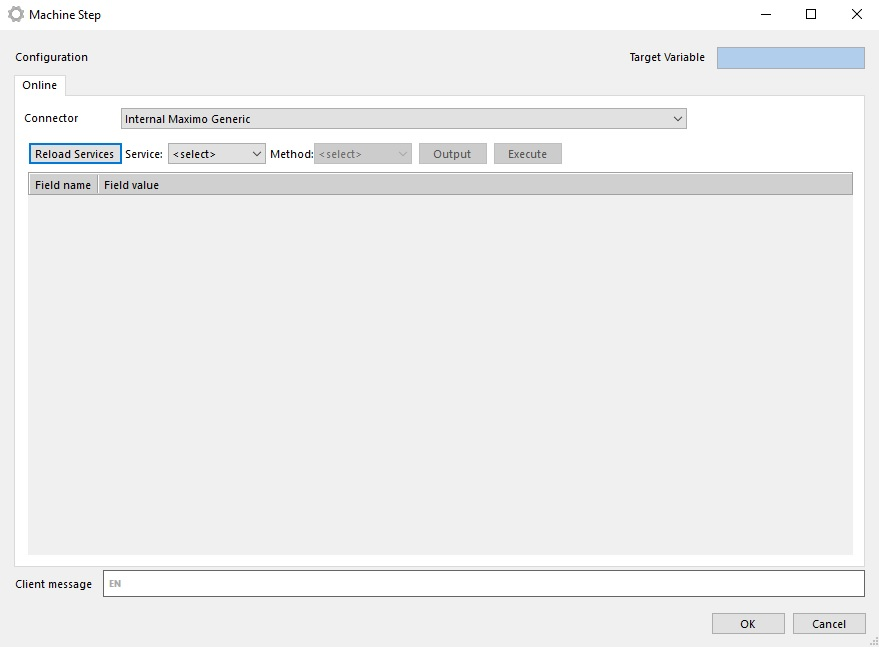
Connector reads WSDL from Maximo Main Web Services from MaximoWebServiceAddress (configuration):
for example: http://{MaximoWebServiceAddress}/meaweb/wsdl/MXWSREGISTRY.wsdl
After that it creates the web service dotnet client object and call Maximo Main Web Services.
Response from Maximo Main Web Service contains list with all available Maximo Web Services.
- Choose specific Maximo Web Service
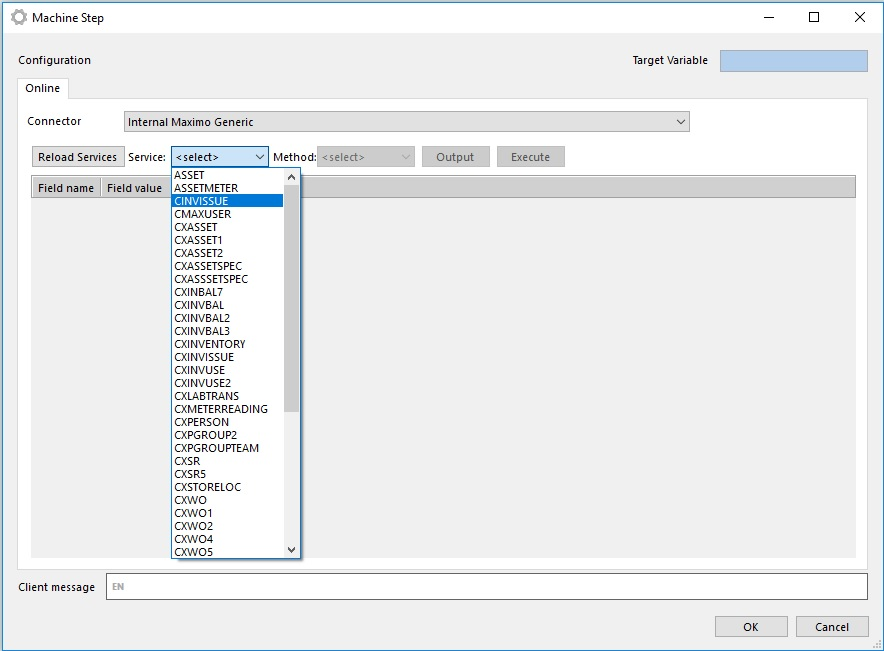
When specific web service is chosen the connector reads the WSDL for the SelectedWebService from MaximoWebServiceAddress (configuration):
for example: http://{MaximoWebServiceAddress}/meaweb/wsdl/{SelectedWebService}.wsdl
After that it creates web service dotnet client object and calls the selected Maximo Web Service.
Response from Selected Maximo Web Service contains list with all available methods and their parameters.
- Choose Method and fill method parameters
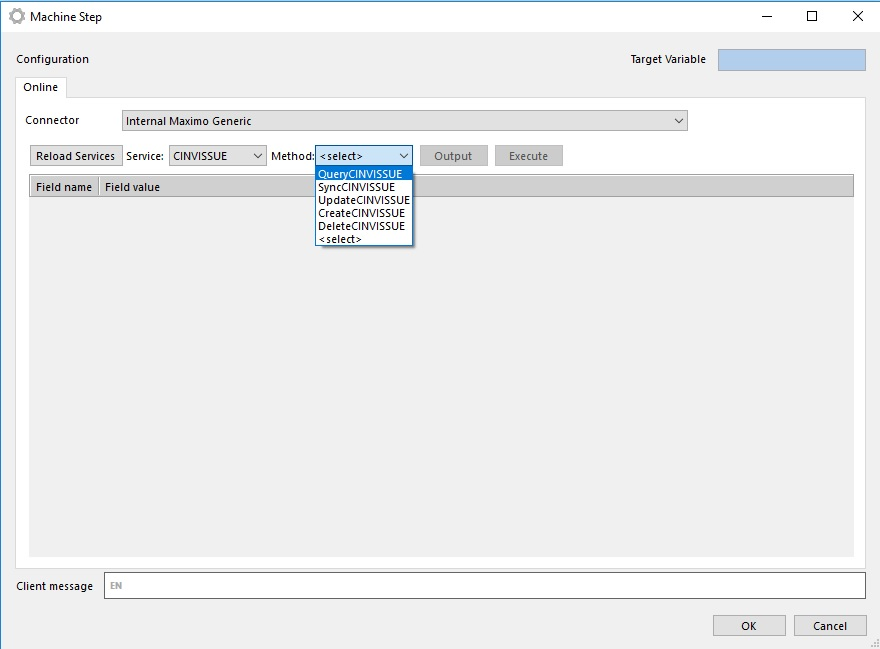
When specific web service method is chosen, the connector reads all input parameters from the method definition and displays it:
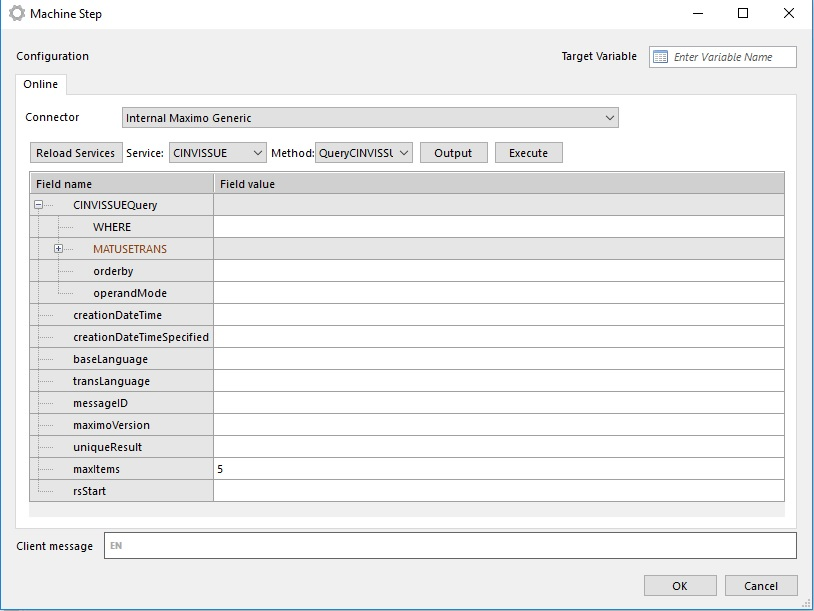
When all required parameters are set we can use connector (by running workflow or directly from Flow Studio to test it).
When Connector is executed it use web service dotnet client (created in point 2) and execute method and read response data.
Microsoft Dynamics AX Connector
The Dynamics AX Connector is used to interact with Microsoft Dynamics AX.
Configuration
- Dynamics AX Service Address:
- Username:
- Password:
- AX User Domain:
- Windows User Domain:
- Server Port:
Microsoft Dynamics CRM Connector
The Dynamics CRM Connector is used to interact with Microsoft Dynamics CRM.
Configuration
- Organization:
- MSCRM Web Service Address:
- Username:
- Password:
- Domain:
Oracle Primavera Connector
The Oracle Primavera Connector can be used to access Oracle Primavera P6.
Configuration
- Url:
- User name:
- Password:
Basic API
About the Novacura Flow Transporter Package
The Novacura Flow SAP connector will call a number of SAP BAPIs in order to retrieve the interface information. The following functions give the required information:
- ZNCFLOW_APPLICATION_COMPONENT: List BAPI application tree
- BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST: Returns a list of all available BAPI's in the SAP system.
- BAPI_INTERFACE_GETDOCU: Returns the help text documentation for a BAPI on different levels.
- RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE: Returns all parameters for a BAPI or function module in SAP.
- ZNCFLOW_DDIF_FIELDINFO_GET: Returns the data dictionary specification for parameter fields
BAPI: BAPI_INTERFACE_GETDOCU
With this BAPI you will get the documentation for the requested BAPI in the form of help text. This is useful for giving detailed descriptions of the BAPI on a general level or on the Method. If you give the Object you will get text on the object and if you give the object and the method you get details on the method. The fields in the input Is the same as the resulting table (BAPILIST) in the previous BAPI (BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST).
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJTYPE | Object type | I | CHAR10 | SFLIGHT |
| OBJNAME | Object name | I | CHAR32 | |
| METHOD | Method name of the object type | I | CHAR32 | GetDetail |
| PARAMETER | Name of parameter in method | I | CHAR32 | |
| FIELD | Field name in the parameter for F4 values | I | CHAR30 | |
| LANGUAGE | Language of the text to be displayed | I | LANG1 | |
| TEXTFORMAT | Format of the text to be displayed | I | CHAR3 | |
| LINKPATTERN | Convert SAPscript Hyperlinks to HTML | I | CHAR255 | |
| RETURN | Return messages | O | BAPIRET2 | |
| TEXT | Table for the text | T | BAPITGB |
Table: BAPITGB
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINE | Line in documentation text | CHAR255 |
BAPI: BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST
This BAPI returns information for BAPI's relating to the position in the BAPI application tree. Giving an * in the first input parameter will give a full list of all BAPI's.
The other parameters can be left blank thus letting the system using default values. It is possible to select BAPI's for a list of application nodes by sending in a table COMPONENTS2SELECT with rows of nodes in the field COMPONENT. This BAPI together with the first (ZNCFLOW_APPLICATION_COMPONENT) will give you enough information to draw the complete Application tree containing all BAPI's.
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OBJECTTYPE | Object type | I | CHAR10 | * (will result in full list) |
| SHOW_RELEASE | Release /Reference Release to Display | I | CHAR4 | Use default |
| BAPIS_POTENTIAL | Display Potential BAPIs | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| BAPIS_NEW | Display New BAPIs in Release | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| BAPIS_OLD | Display BAPIs from Previous Releases | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| RELEASED_BAPI | Release Status of BAPIs | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| RELEASED_FUNC | Release Status of Function Modules | I | CHAR1 | Use default |
| RETURN | Return messages | O | BAPIRET2 | |
| COMPONENTS2SELECT | Application Components/Areas to Select | T | BAPIMONCOM | |
| SYSTEMS2SELECT | Original System of BAPIs to Select | T | BAPISRCSYS | Use default |
| BAPILIST | List of Selected BAPIs | T | BAPIMONSTR |
Structure: BAPIRET2
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| TYPE | Message type: S Success, E Error, W Warning, I Info, A Abort | CHAR1 | |
| ID | Message Class | CHAR30 | |
| NUMBER | Message Number | NUMC3 | |
| MESSAGE | Message text | CHAR220 | |
| LOG_NO | Application log: log number | CHAR20 | |
| LOG_MSG_NO | Application log: Internal message serial number | NUMC6 | |
| MESSAGE_V1 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| MESSAGE_V2 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| MESSAGE_V3 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| MESSAGE_V4 | Message Variable | CHAR50 | |
| PARAMETER | Parameter Name | CHAR32 | |
| ROW | Lines in parameter | INT4 | |
| FIELD | Field in parameter | CHAR30 | |
| SYSTEM | Logical system from which message originates | CHAR10 |
Table: COMPONENTS2SELECT
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMPONENT | Application component ID | CHAR24 |
Table: BAPILIST
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| OBJECTTYPE | Object Type | CHAR10 | SFLIGHT |
| OBJECTNAME | Object name | CHAR32 | Flight |
| BAPINAME | Method name of BAPI | CHAR32 | GetDetail |
| ABAPNAME | Function module name | CHAR30 | BAPI_FLIGHT_GETDETAIL |
| COMP | Application component ID | CHAR24 | BC-DWB |
| CREA_REL | Release at Creation | CHAR4 | 610 |
| CREATOR | Author | CHAR12 | SAP |
| UDATE | Changed On | CHAR8 | 18.09.2001 |
| CHANGER | Last changed by | CHAR12 | SAP |
| SOURCESYS | Name of the SAP system | CHAR8 | SAP |
| BAPI_AG | Application area or BAPI work group responsible | CHAR5 | Basis |
| ISINTERFAC | Interface object type | CHAR1 | |
| BAPI_REL | Release status of BAPI method | CHAR1 | X |
| FUNC_REL | Release status of function module | CHAR1 | R |
| OBSOLETE | Release in which the status was set to obsolete | CHAR4 | |
| FM_DOCU | Documentation on function module exist | CHAR1 | |
| BO_DOCU | Documentation for business object exist | CHAR1 | |
| MESTYPE | Message type | CHAR30 | |
| VERB | Object type component | CHAR32 | GETLIST |
| BO_TEXT | Description | CHAR80 | Flight with connection data (SAP training) |
| BAPI_TEXT | Description | CHAR80 | Find list of flights |
BAPI: ZNCFLOW_DDIF_FIELDINFO_GET
This BAPI will return de definition of data dictionary objects. In this case the parameters for BAPI's or function modules returned from BAPI: RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE.
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TABNAME | Name of the Table (of the Type) for which Information is Required | I | CHAR30 | |
| FIELDNAME | Use Parameter LFIELDNAME Instead | I | CHAR30 | |
| LANGU | Language of the Texts | I | LANG1 | |
| LFIELDNAME | If Filled, only Field with this Long Name | I | CHAR132 | |
| ALL_TYPES | Take all Types into Consideration | I | CHAR1 | |
| GROUP_NAMES | Take Named Includes into Consideration | I | CHAR1 | |
| UCLEN | Unicode length with which runtime object was generated | I | RAW1 | |
| DO_NOT_WRITE | Write | I | CHAR1 | |
| X030L_WA | Nametab Header of the Table (of the Type) | E | CHAR30 | |
| DDOBJTYPE | Kind of Type | E | CHAR8 | |
| DFIES_WA | Single Information if Necessary | E | CHAR30 | |
| LINES_DESCR | Information about Other Referenced Types | E | DDTYPEDESC-TYPENAME (CHAR30)-TYPEKIND (CHAR4)-DFIES | |
| DFIES_TAB | Field List if Necessary | T | DFIES | |
| FIXED_VALUES | Description of Domain Fixed Values | T | DDFIXVALUES |
Table/Structure: DFIES_TAB
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| TABNAME | Table Name | CHAR30 | |
| FIELDNAME | Field Name | CHAR30 | |
| LANGU | Language Key | LANG1 | |
| POSITION | Position of the field in the table | NUMC4 | |
| OFFSET | Offset of a field | NUMC6 | |
| DOMNAME | Domain name | CHAR30 | |
| ROLLNAME | Data element (semantic domain) | CHAR30 | |
| CHECKTABLE | Table Name | CHAR30 | |
| LENG | Length (No. of Characters) | NUMC6 | |
| INTLEN | Internal Length in Bytes | NUMC6 | |
| OUTPUTLEN | Output Length | NUMC6 | |
| DECIMALS | Number of Decimal Places | NUMC6 | |
| DATATYPE | ABAP/4 Dictionary: Screen data type for Screen Painter | CHAR4 | |
| INTTYPE | ABAP data type (C,D,N,...) | CHAR1 | |
| REFTABLE | Table for reference field | CHAR30 | |
| REFFIELD | Reference field for currency and qty fields | CHAR30 | |
| PRECFIELD | Name of included table | CHAR30 | |
| AUTHORID | Authorization class | CHAR3 | |
| MEMORYID | Set/Get parameter ID | CHAR20 | |
| LOGFLAG | Indicator for writing change documents | CHAR1 | |
| MASK | Template (not used) | CHAR20 | |
| MASKLEN | Template length (not used) | NUMC4 | |
| CONVEXIT | Conversion Routine | CHAR5 | |
| HEADLEN | Maximum length of heading | NUMC2 | |
| SCRLEN1 | Max. length for short field label | NUMC2 | |
| SCRLEN2 | Max. length for medium field label | NUMC2 | |
| SCRLEN3 | Max. length for long field label | NUMC2 | |
| FIELDTEXT | Short Description of Repository Objects | CHAR60 | |
| REPTEXT | Heading | CHAR55 | |
| SCRTEXT_S | Short Field Label | CHAR10 | |
| SCRTEXT_M | Medium Field Label | CHAR20 | |
| SCRTEXT_L | Long Field Label | CHAR40 | |
| KEYFLAG | Identifies a key field of a table | CHAR1 | |
| LOWERCASE | Lowercase letters allowed/not allowed | CHAR1 | |
| MAC | Flag if search help is attached to the field | CHAR1 | |
| GENKEY | Flag (X or Blank) | CHAR1 | |
| NOFORKEY | Flag (X or Blank) | CHAR1 | |
| VALEXI | Existence of fixed values | CHAR1 | |
| NOAUTHCH | Flag (X or Blank) | CHAR1 | |
| SIGN | Flag for sign in numerical fields | CHAR1 | |
| DYNPFLD | Flag: field to be displayed on the screen | CHAR1 | |
| F4AVAILABL | Does the field have an input help | CHAR1 | |
| COMPTYPE | DD: Component Type | CHAR1 | |
| LFIELDNAME | Field name | CHAR132 | |
| LTRFLDDIS | Basic write direction has been defined LTR (left-to-right) | CHAR1 | |
| BIDICTRLC | DD: No Filtering of BIDI Formatting Characters | CHAR1 | |
| OUTPUTSTYLE | DD: Output Style (Output Style) for Decfloat Types | NUMC2 | |
| NOHISTORY | DD: Flag for Deactivating Input History in Screen Field | CHAR1 | |
| AMPMFORMAT | DD: Indicator whether AM/PM time format is required | CHAR1 |
Table: FIXED_VALUES
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOW | Values for Domains: Single Value / Upper Limit | CHAR10 | |
| HIGH | Values for domains: upper limit | CHAR10 | |
| OPTION | Option for domain fixed values | CHAR2 | |
| DDLANGUAGE | Language Key | LANG1 | |
| DDTEXT | Short Text for Fixed Values | CHAR60 |
BAPI: RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE
This BAPI will return all parameters and parameter attributes for a specific BAPI or function module. The function module name (FUNCNAME) is the same value that was returned for each BAPI in the call to BAPI_MONITOR_GETLIST (field ABAPNAME in table BAPILIST).
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUNCNAME | Name of the function module | I | CHAR30 | BAPI_FLIGHT_GETDETAIL |
| LANGUAGE | Language of the parameter text | I | LANG1 | |
| NONE_UNICODE_LENGTH | Length is also supplied in Unicode systems in non-Unicode format | I | CHAR1 | |
| REMOTE_BASXML_SUPPORTED | BasXML Protokoll | E | CHAR1 | |
| REMOTE_CALL | Function module can be called Remote-Function | E | CHAR1 | |
| UPDATE_TASK | Function module is in the update | E | CHAR1 | |
| PARAMS | Parameter of function module | T | RFC_FUNINT | |
| RESUMABLE_EXCEPTIONS | Resumable Exceptions | T | RSEXC |
Table: PARAMS
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| PARAMCLASS | Parameter type | CHAR1 | I |
| PARAMETER | Parameter name | CHAR30 | AIRLINEID |
| TABNAME | Table Name | CHAR30 | BAPISFLKEY |
| FIELDNAME | Field Name | CHAR30 | AIRLINEID |
| EXID | ABAP Data Type | CHAR1 | C |
| POSITION | Position of field in structure (from 1) | CHAR10 | 1 |
| OFFSET | Field offset from beginning of structure (from 0) | INT10 | 0 |
| INTLENGTH | Internal length of field | INT10 | 6 |
| DECIMALS | Number of decimal places | INT10 | 0 |
| DEFAULT | Default value for import parameter | CHAR21 | |
| PARAMTEXT | Short text | CHAR79 | Airline Code |
| OPTIONAL | Optional parameters | CHAR1 |
BAPI: ZNCFLOW_APPLICATION_COMPONENT
This BAPI returns the BAPI application tree. The resulting table contains all nodes in the BAPI tree indicating what level the node is on and what the superior node is. The input parameter can list all nodes (giving only a *) or a specific component. Ending with an * can give all nodes starting with a specific name. For example AP-MD* will give all nodes starting with AP-MD. I.e all nodes below that node.
| Field | Description | Type | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMP | Application Component | I | CHAR24 | * (will result in full list) |
Table: COMPONENTS
| Field | Description | Spec | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| COMP | Application component ID | CHAR24 | AP-MD-BF |
| NAME | Short text | CHAR60 | Master data |
| LEVEL | Numc3, internal use | NUMC3 | 002 |
| SUPERIOR | Application component ID | CHAR220 | AP-MD |
SAP BAPI
The SAP BAPI Connector can be used to execute any published BAPI (standard or custom) in an SAP ABAP system, including HANA-based systems. Resulting table(s) are available as Flow variables.
The SAP BAPI connector require Microsoft C++ Runtime DLLs version 10.0 (contained in the Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Redistributables). MSI installers for these runtimes can be obtained from here.
This must be installed on the machine running Flow Server.
Configuration
Go to the Environment/Connectors section in Flow Studio and Add a new connector. For parameter details, see below.
- Name: Your own name of the connector. For easy connector identification in design time, include the name of the target SAP system.
- Type: Choose SAP BAPI
- Application server address: URL or IP address of the target SAP system
- System number: Enter system or installation number of target SAP system
- System ID: Enter the System ID.
- Client: Configured user will log in to specified client
- Language: Configured user will log in with specified language. Note that BAPIs called from Novacura Flow must be enabled for the language specified.
- Global runtime user: If specified, this username will be used every time Flow connects with the target SAP system. For license audit, traceability and security reasons, Novacura recommends that Global users are only used with caution and only in automated scenarios, i.e. without user interaction, for instance when using Flow as an integration engine, together with a SAP service or system account designated for the specific scenario.
- Global runtime password: Password of global user.
- Design time user name: Design-time user which is only used in Flow studio when developing the Flow.
- Design time password: Password of design time user
- Logging path: If specified, any logs produced by the connector will be written to the specified path. Please note that this path is relative to Flow Server and that the user that Flow Server is running as must have write access to the path.
- Advanced configuration: Depending on your environment, you may need to add additional details, such as specific network or security settings.
Personal user configuration
If Global runtime user is not specified, SAP username must be configured on the Flow user. For general information on Flow users, see here.
- Username: Enter username of the SAP user
- Password: Enter password of the SAP user. If SAP password is not supplied, the Flow login dialogue will ask for the SAP password to use for the session.
Authorization requirements for SAP users connecting from Flow
Authorization object S_RFC containing the following : - Activity 16 (Execute) - RFC_NAME: SYST, RFCPING, RFC1, RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE, RFCH, RFC_GET_UNICODE_STRUCTURE - RFC_TYPE: FUGR and FUNC
On top of this, the S_RFC authorization must also contain the function group and the function module being called, as well as any authorization needed to pass authorization checks in any of the called programs, including authorization for the applicable organization level (for example purchasing organization).
Security considerations
The SAP BAPI Connector is using the standard SAP authorization concept. The connector always logs in to the SAP system through RFC with a user that is set-up and active in the SAP system as a dialog, system or service user. Any authorization object checks will be performed the same way it would be done if the user logged in using SAP GUI.
For more information on RFC security, see SAP?s official RFC security guide.
Using the SAP Connector for creating workflows
For details on design-time usage of the SAP connector, see here.
Getting started
There are a couple of things that needs to be done before you can start using the SAP connector.
In short, these four steps needs to be done prior to creating workflows with the SAP connector (assuming that you of course already have installed the Flow Server):
- Install the SAP GUI for Windows on the Flow server. This is necessary for Flow to be able to connect to SAP.
- Verify that the connection between the Flow Server and SAP works, using the SAP Logon Pad.
- Install the Novacura Flow Transporter package in the SAP environment you want to connect to. The Transporter package will install a couple of BAPIs that the connector need to generate an API tree in the Flow Studio. Download Transporter package here.
- Make sure you have a license for the SAP Connector, read more; here.
- Configure the SAP Connector in the Flow Studio, read more; here.
Steps 3 to 5 are described below.
Designing a SAP workflow
If you want an example of a SAP workflow, you can find a simple workflow here, using the ABAP workbench BAPIs for Flight Booking: http://community.novacuraflow.com/product/sap-flight-booking-example/
Make sure you have these BAPI in your SAP environment before you use this workflow.
When in the Flow Studio, adding a Machine Step to your workflow will let you create a connection to SAP. After selecting the SAP connector you have defined in Environment/Connectors, you will be able to configure a method call to SAP with the following steps.
Get the list of BAPIs: When selecting youe SAP connector in the list of available connectors, press the button with the three dots. This will connect to your SAP environment and generate the entire BAPI tree in the connector. So whatever BAPIs you have in your installatione of SAP will be accessible directly from Flow.

Select a BAPI: After the generation of the BAPI tree is done, you will see all BAPIs arranged in a folder structure. You can find the BAPI you need by either browse through the structure or by searching for the BAPI using the Filter option.

Configure the BAPI call (Input):
There are three tabs that can be used for configuration of the BAPI all:
- Import: input data do the BAPI
- Export: output data from the BAPI
- Tables: both input and output. One or many tables can be used here.
First, define the input. You can either set fixed data by just typing the value you need or by using existing (single) variables in the workflow. Note that Input can be set both on the Import and Tables tabs.
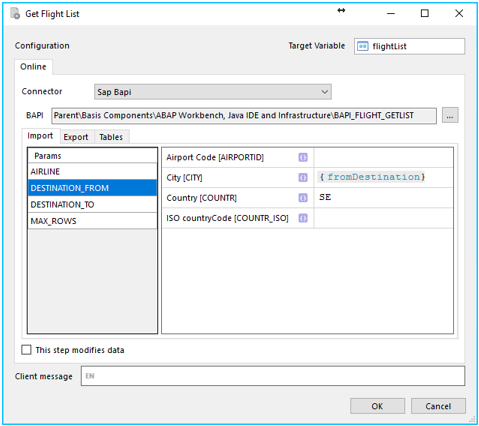
Configure the BAPI call (Output): All data coming out from the called BAPI will end up in the Target Variable, so the Target Variable must be set (as in all Machine Steps returning data). There are two tabs for output; Export and Tables. Export are singe variables returned from the BAPI. Tables are table variables returned from the BAPI. Depending on the BAPI, Export and Tables will look and function differently.

Configuring Commit step
Selecting check box This step modifies data will ensure that a BAPI commit step is executed. Check this box for any BAPI that updates or inserts data in the ECC system. For a BAPI that only reads data it can be left unchecked.
When you have configure the BAPI call, you can test it using the Play button on the top right of the Application Window in the Studio.

Error handling
SAP returns errors as output from the BAPI. This means that you will need to handle errors from SAP in the workflow. Like this:
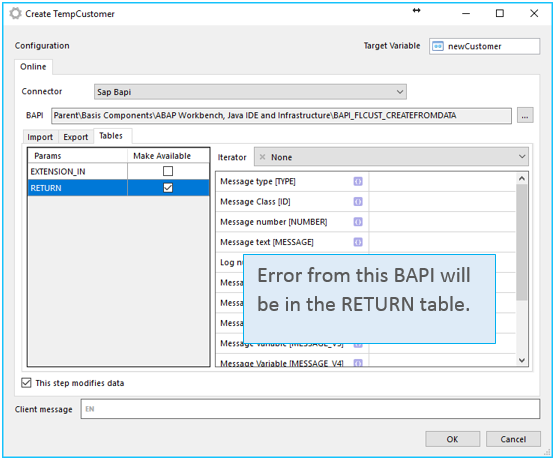
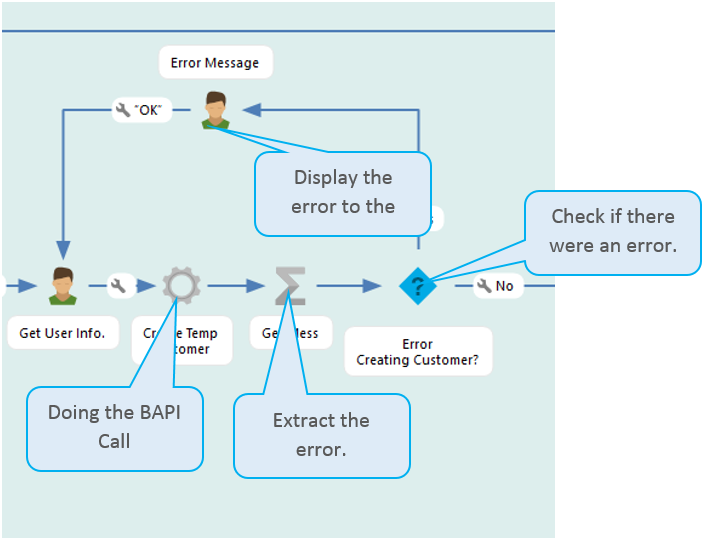
So, now you can create any app directly on top of your SAP environment!
Add attached file (from bytes)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Source bytes | Table (consisting of bytes) to read from |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from file system)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Local filename | Full path to file to upload. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have access to the file. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from stream)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Filename | Remote filename |
| Source stream | Simple variable containg a stream |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete all attached files
Delete all attachments on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete attached file
Delete an attachment on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
| 1000005 | File not found. |
List attached files
Lists all files attached to specified item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete item
Deletes item with given ID.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get items by query
Gets information about items by provided CAML Query
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| CAML Query | The query to send to SharePoint |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- StaticName
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List all items
Lists all items in Custom List app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Row limit | Limit on how many items to list. A value of -1 indicates no limit |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- StaticName
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List fields of items
Lists the fields that are available for items in Custom List app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Create new item
Creates a new item in a Custom List app. Returns the ID of created item in Results.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item name | Title of new item |
| Folder url | Url to folder to create item in. Leave empty for root folder. Example if adding item to folder 'folder1' in Custom List 'clist' in subsite 'subsite1': '/subsite1/Lists/clist/folder1' |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Create new item, with field values
Creates a new item in a Custom List app. Returns the ID of created item in Results.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item name | Title of new item |
| Field values | Table consisting of field values. Note that StaticName of fields needs to be provided, not Title |
| Folder url | Url to folder to create item in. Leave empty for root folder. Example if adding item to folder 'folder1' in Custom List 'clist' in subsite 'subsite1': '/subsite1/Lists/clist/folder1' |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Update item field
Updates a field of a given item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Custom List app name | Name of Custom List app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Item ID | ID of item |
| Field | Name of field/column (StaticName, not Title) |
| Value | New value of property |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Check in file
Checks in a file to SharePoint that the user has checked out
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Comment | Comment, must not exceed 1023 characters |
| Checkin type | Specifies check in type |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000002 | User has not checked out the file. |
Check out file
Checks out a file to the SharePoint user the connector is running as.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000003 | File already checked out. |
Discard check out
Undo a check out of a file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000002 | User has not checked out the file. |
Copy file
Copies a file from a Document Library to another (or the same) Document Library at the same SharePoint site.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Document Library Name | Name of source Document Library in SharePoint to copy file from |
| Source filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" to move |
| Destination Document Library Name | Name of target Document Library in SharePoint to copy file to |
| Destination filename | Name of file in destination Document Library |
| Overwrite | Specifies whether to overwrite destination file if it already exists |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Delete file
Deletes a file in the Document Library. If the file does not exist, the operation is considered succesful.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" to move |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Get file information
Gets information about a file provided as a releative url, example: '/subsite1/Shared Documents/file.doc'
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List files
Lists all files at the root of a Document Library
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Populate user members | Specifies whether to populate members that relates to SharePoint users, e.g. Author. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Move file
Moves a file from a Document Library to another (or the same) Document Library at the same SharePoint site.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Document Library Name | Name of source Document Library in SharePoint to move file from |
| Source filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" to move |
| Destination Document Library Name | Name of target Document Library in SharePoint to move file to |
| Destination filename | Name of file in destination Document Library |
| Move operations | Specifies move options. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Update file property
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder/file.txt". |
| Field name | Name of field or column |
| New value | The new value to set on field |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Create subfolder
Creates a new folder beneth specfied folder. If the folder already exists, the operations is considered succesful
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Parent folder | Name of folder to create sub folders in. E.g. "folder1" or "folder1/subfolder2" |
| Name of sub folder | Name of folder to create |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Delete folder
Deletes a folder by its relative url.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url of folder | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List files in folder
Lists all files in a specified folder.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Folder | Remote folder in Document Library, can include sub folders if applicable. E.g. "subfolder1/subfolder2" |
| Populate user properties | Specifies whether to populate members that relates to SharePoint users, e.g. Author |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List files in folder by relative url
Lists all files in a folder specified by relative url. Useful for instance if you got a Record containg folder information including its relative url and want to list those files.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder". |
| Populate user properties | Specifies whether to populate members that relates to SharePoint users, e.g. Author |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
- Id
- LoginName
- Title
- IsSiteAdmin
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List folders in root of Document Library
Lists all folders in the root of the Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List subfolders of folder
Lists all subfolders of specified folder.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Folder | Name of folder to list sub folders of. E.g. "subfolder1/subfolder2" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Get subfolders by relative url
Lists all subfolders of specified folder provided by relative url. Useful for instance if you got a Record containg folder information including its relative url and want to list the sub folders of that folder.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file by url to file system
Downloads a single file by server relative url to file system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder/file.txt". |
| Local filename | Full path where to download file. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have write access to the file. If the file already exists, it is overwritten. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file by url to stream
Downloads a single file by server relative url to a simple variable (stream).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Server relative url | An url relative to server, e.g. "/subsite/doclib/folder/file.txt". |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file to file system
Downloads a single file from Document Library by path to file system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Remote filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Local filename | Full path where to download file. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have write access to the file. If the file already exists, it is overwritten. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Download file to stream
Downloads a single file to a simple variable (stream).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Upload file from bytes
Uploads a single file from a Table of bytes to a SharePoint Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source bytes | Table (consisting of bytes) to read from |
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename to use in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Overwrite if exists | Specifies whether to overwrite remote file if it already exists or abort |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Upload file from local file system
Uploads a single file from file system to a SharePoint Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | Full path to file to upload. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have access to the file. |
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Remote filename | Remote filename to use in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Overwrite if exists | Specifies whether to overwrite remote file if it already exists or abort |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Upload file from stream
Uploads a single file from a stream to a SharePoint Document Library.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source stream | Simple variable containg a stream |
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| Filename | Remote filename to use in Document Library, including any extensions or folders if applicable. E.g. "file.txt" or "subfolder1/subfolder2/file.txt" |
| Overwrite if exists | Specifies whether to overwrite remote file if it already exists or abort |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Set description
Set a new description on a Document Library
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| New description | New description to set on Document Library |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Set name
Set a new title on a Document Library
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Document Library Name | Name of Document Library in SharePoint (not id) |
| New title | The new title |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Add attached file (from bytes)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Source bytes | Table (consisting of bytes) to read from |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from file system)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Remote filename | Remote filename |
| Local filename | Full path to file to upload. Note that the user the application pool running Flow Server must have access to the file. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Add attached file (from stream)
Upload a file as an attachment to task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Filename | Remote filename |
| Source stream | Simple variable containg a stream |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete all attached files
Delete all attachments on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete attached file
Delete an attachment on provided task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Filename | Remote filename |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
| 1000005 | File not found. |
List attached files
Lists all files attached to specified task item.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get task information by ID
Get information such as start date, due date etc about a task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get task information by name
Get information such as start date, due date etc about all tasks with given name.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task name | Name of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Get task information by query
Gets information about tasks by provided CAML Query. Example to get all tasks that are 50% or more completed:
<View>
<Query>
<Where>
<Geq>
<FieldRef Name='PercentComplete' />
<Value Type='Number'>0.50</Value>
</Geq>
</Where>
</Query>
</View>
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| CAML Query | The query to send to SharePoint. |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Get task property value
Gets the value of a field of a given task. This is an advanced operation that require deeper knowledge on how SharePoint works. The Property parameter is the identifier of a field, which might not be the same as is displayed in SharePoint. E.g use 'Body' as Property to update 'Description'.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Property | Name of property |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
List tasks
Lists all tasks.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Row limit | Limit on how many tasks to list. A value of -1 indicates no limit |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List fields of tasks
Lists the fields that are available for tasks in Task app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Include read only fields | Specifies whether to include fields that can only be read in the results of the operation |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List tasks assigned to current user
Lists all tasks assigned to current user. Optionally including finished tasks.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Include already finshed tasks | Specifies whether to also include completed tasks |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
List tasks assigned to specific user
Lists all tasks assigned to specified user. Optionally including finished tasks.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| User ID | ID of user |
| Include already finshed tasks | Specifies whether to also include completed tasks |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
Results- UserID
- Value
- TaskID
- Value
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Add predecessor
Adds an existing task as a predecessor to provided task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Predecessor task id | ID of predecessor task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Get predecessors
Gets all predecessors of given task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Remove all predecessor
Removes all predecessor of provided task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Remove predecessor
Removes a predecessor of provided task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Predecessor task id | ID of predecessor task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Assign task to user (by username)
Assign a task to given SharePoint user (by username).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Username | Username of user to assign task to |
| Remove other assignees | Specfies whether to remove other assignees. Default true |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Delete task
Deletes task with given ID.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Set task as finished
Sets the percent complete to 100%.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Update task progress
Updates the progress of a given task.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| New progress | New progress in % |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Update task property
Updates a field of a given task. This is an advanced operation that requires deeper knowledge on how SharePoint works. The Property parameter is the identifier of a field, which might not be the same as is displayed in SharePoint. E.g use 'Body' as Property to update 'Description'.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task ID | ID of task |
| Property | Name of property |
| Value | New value of property |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
| 1000004 | Item with given id does not exist. |
Create new subtask
Creates a new subtask in a Task app.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Parent Task ID | ID of parent task |
| Task name | Name of new subtask |
| Start date | When task is to be started |
| Due date | When task is to be finished |
| Percent complete | How much of task that is finished. Default 0 |
| Description | Description of task |
| Priority | Priority of task |
| Status | Status of task |
| Assigned to (user ID(s)) | User ID to assign task to, if any |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Create new task
Creates a new task in a Task app. Returns the ID of created task in Results.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Task app name | Name of Task app in SharePoint (not id) |
| Task name | Name of new task |
| Start date | When task is to be started |
| Due date | When task is to be finished |
| Percent complete | How much of task that is finished. Default 0 |
| Description | Description of task |
| Priority | Priority of task |
| Status | Status of task |
| Assigned to (user ID(s)) | User ID to assign task to, if any |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| Results | Simple variable containing the results of operation |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | User is not authorized to perform operation. |
Assign user to group
Assigns a user to a group
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Group id | Id of group |
| Login name | Login name of user, not id |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Detach user from group
Detaches the user from the group
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Group id | Id of group |
| Login name | Login name of user, not id |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List site groups
Gets and list all site groups
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List users by group id
List all users assigned to a group.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Group id | Id of group |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Get user by ID
Get information about a SharePoint user.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| User ID | ID of user |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Get user by Login name
Get information about a SharePoint user.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Login name | Login name of user, not id |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Record variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
List users
Get list of all users at site.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not. If succesful, result of operation is stored in Results member
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
| Results | Table variable containing the results of operation |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Microsoft SharePoint 2013
The SharePoint 2013 connector can be used to integrate with various apps in SharePoint 2013.
Configuration
- Url: Url to SharePoint site. Note that subsite must be specified in the url if applicable. E.g. http://servername/subsite
- Domain: Domain any user that connectors to SharePoint is a member of
- Global runtime user: If specified, this is the user any Flow that uses this connector will connect to SharePoint with. Leave empty for per-user usage
- Global runtime password: If specified, this is the password related to Global runtime user
Business systems
Under business systems, all third party system connectors are listed, with information about configuration to setup the connector and how to use it.
Email Connector
User the email connector to send email in your workflow. It is possible to use Flow script in the email connector to make the email more informative.
TODO
Create directory
Creates a directory at the FTP server. It is not possible to create several levels of directories in one step. If you want to create the directory "./dirA/dirB", the directory "./dirA" must exist. Otherwise you have to do it in two steps; first creates directory "./dirA" and the second one created "./dirA/dirB".
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to the directory to create. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete empty directory
Deletes specified empty directory. Note if directory contain a file it will return an error.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to directory to delete |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Directory operations
Check if directory exists
Determains whether directory at specified path exists.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to check. |
Output: Simple value,'True' if directory exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since: 6.3
Create directory
Creates a directory at the FTP server. It is not possible to create several levels of directories in one step. If you want to create the directory ./dirA/dirB", the directory ./dirA* must exist. Otherwise you have to do it in two steps; first creates directory ./dirA and the second one created ./dirA/dirB.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to the directory to create. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Delete empty directory
Deletes specified empty directory. Note if directory contain a file it will return an error.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to directory to delete |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
List directory
Lists all files and directories in a specified path.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
| Mask | Mask to use when filtering items in directory. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B" |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Include files | Specifies whether to include files in the listing. |
| Include directories | Specifies whether to include directories in the listing. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also search in subdirectories. |
Output: A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file or directory. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since: 6.3
See also
List directory
Lists all files and directories in a specified path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
| Mask | Mask to use when filtering items in directory. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B" |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Include files | Specifies whether to include files in the listing. |
| Include directories | Specifies whether to include directories in the listing. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also search in subdirectories. |
Output
A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file or directory. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since
6.3
See also
Download single file
Downloads a file from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded file. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download multiple files
Downloads multiple files from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to downloaded files from. |
| Remote mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded files. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| File copy mode | Specifies what to do with the file after download has been completed. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to download files from sub directories recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download Operations
Download multiple files
Downloads multiple files from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to downloaded files from. |
| Remote mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example *.txt. Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].** to list all files starting with A or B. |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded files. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| File copy mode | Specifies what to do with the file after download has been completed. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to download files from sub directories recursivly. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Download single file
Downloads a file from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded file. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Download stream
Downloads a file from FTP server and store it as Flow variable.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
Output: Simple value (binary stream).
Since: 6.3
See also
Delete file
Delete a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to file to delete. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete files
Delete multiple remote files based on mask.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path where to delete files. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to delete files recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
File Operations
Check if file exists
Checks if a remote file exists.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to check. |
Output: Simple value,'True' if file exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since: 6.3
Delete file
Delete a remote file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to file to delete. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Delete files
Delete multiple remote files based on mask.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path where to delete files. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to delete files recursivly. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Get size of file
Gets the size, in bytes, of remote file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | File of interest. |
Output: Simple value, numeric.
Since: 6.3
Rename file
Renames a remote file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Old path | Current name of file. |
| New path | New name of file. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Get file time
Get a remote file time.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
Output: Simple value, Date.
Since: 6.3
Set file time
Changes a remote file time.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
| New time | New time for the file. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Get list of files
Get list of files in a directory.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
Output: A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since: 6.3
Get file time
Get a remote file time.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
Output
Simple value, Date.
Since
6.3
See also
Get list of files
Get list of files in a directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
Output
A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since
6.3
See also
Get size of file
Gets the size, in bytes, of remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | File of interest. |
Output
Simple value, numeric.
Since
6.3
See also
Rename file
Renames a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Old path | Current name of file. |
| New path | New name of file. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Set file time
Changes a remote file time.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
| New time | New time for the file. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Clear Command Channel
Clears command channel encryption state, turning off SSL/TLS encryption.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Graceful SSL Closure | Send closure notification to the server. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Get Server System
Get server system operating system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output
Single value, text.
Since
6.3
See also
Server Operations
Send Command
Sends a command to the FTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Send Command | Command to send. Send NOOP for a dummy message. |
Output
Single value, text. Returns a error code.
Since
6.3
Clear Command Channel
Clears command channel encryption state, turning off SSL/TLS encryption.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Graceful SSL Closure | Send closure notification to the server. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
Get Server System
Get server system operating system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output
Single value, text.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload single file
Uploads a single file from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | File to upload. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the file. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload multiple files
Uploads multiple files from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local path | Path where to upload files from. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to upload. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Remote path | Path where to upload the files. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also upload from subdirectories. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload operations
Upload multiple files
Uploads multiple files from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local path | Path where to upload files from. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to upload. Example *.txt. Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with regex:, example regex:[A|B].* to list all files starting with A or B. |
| Remote path | Path where to upload the files. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also upload from subdirectories. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Upload single file
Uploads a single file from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | File to upload. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the file. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Upload stream
Uploads the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream. This can for instance be used to upload data from a camera input.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local stream | Stream to read data from. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the data. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
See also
Directory operations
Check if directory exists
Determains whether directory at specified path exists.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to check. |
Output: Simple value,True if directory exists. False otherwise.
Since: 6.3
Create directory
Creates a directory at the FTP server. It is not possible to create several levels of directories in one step. If you want to create the directory ./dirA/dirB, the directory ./dirA must exist. Otherwise you have to do it in two steps; first creates directory ./dirA and the second one created ./dirA/dirB.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to the directory to create. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Delete empty directory
Deletes specified empty directory. Note if directory contain a file it will return an error.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to directory to delete |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
List directory
Lists all files and directories in a specified path.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
| Mask | Mask to use when filtering items in directory. Example *.txt. Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with regex:, example regex:[A|B].* to list all files starting with A or B |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Include files | Specifies whether to include files in the listing. |
| Include directories | Specifies whether to include directories in the listing. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also search in subdirectories. |
Output: A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file or directory. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since: 6.3
See also
Download Operations
Download multiple files
Downloads multiple files from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to downloaded files from. |
| Remote mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with regex:, example regex:[A|B]." to list all files starting with A or B. |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded files. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| File copy mode | Specifies what to do with the file after download has been completed. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to download files from sub directories recursivly. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Download single file
Downloads a file from the FTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded file. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Download stream
Downloads a file from FTP server and store it as Flow variable.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
Output: Simple value (binary stream).
Since: 6.3
File Operations
Check if file exists
Checks if a remote file exists.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to check. |
Output: Simple value,True if file exists. False otherwise.
Since: 6.3
Delete file
Delete a remote file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to file to delete. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Delete files
Delete multiple remote files based on mask.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path where to delete files. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example *.txt. Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with regex:, example regex:[A|B].* to list all files starting with A or B. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to delete files recursivly. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Get size of file
Gets the size, in bytes, of remote file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | File of interest. |
Output: Simple value, numeric.
Since: 6.3
Rename file
Renames a remote file.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Old path | Current name of file. |
| New path | New name of file. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Get file time
Get a remote file time.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
Output: Simple value, Date.
Since: 6.3
Set file time
Changes a remote file time.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | File of interest. |
| New time | New time for the file. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Get list of files
Get list of files in a directory.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
Output: A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
Since: 6.3
FTP
The FTP Connector is used to upload and download files from an FTP server. It can also perform other operations such as creating remote directories and list files and directories on the FTP server.
Configuration
- Address. Address to FTP server.
- Port. Port to use, usually 21.
- Username. Username for a user on the FTP server.
- Password. Password for a user on FTP server.
- Communication settings
- Transfer type. ASCII or Binary (recommended), default is Binary.
- Concurrent connections.
- Concurrent connections.
- SSL / TSL settings
- Use SSL / TLS. To enable a secure connection between client and server. Enabled is recommended.
- Encrypt data channel. If enabled the data transfer will be encrypted, otherwise only command channel will be encrypted.
- SSL Mode.
- Implicit the connection is performed to the dedicated port (usually 990), and immediately starts SSL negotiation (without sending AUTH command).
- Explicit the client connects to the generic FTP port (21), and then sends AUTH command.
- ExplicitManual mode
- Client certificate patch. Path to the clients certification.
- Auth command. Specifies an authorization command that should be sent to server to request an explicit SSL session. Different servers support different commands, so in most cases it is a good idea to set this to Auto.
- Auto. Try to specify command supported by server automatically.
- AuthTLS. Use AUTH TLS command.
- AuthSSL. Use AUTH SSL command.
- AuthTLSP. Use AUTH TLS-P command (protected data channel).
- AuthTLSC. Use AUTH TLS-C command (clear data channel).
- Validate server. If enabled the client validates server.
- Server certificate path. Path to the server certification.
- FTP Version. The secure version of SSL or TLS. Default SSL Version 3 and TLS Version 1.0. -Validation options.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of FTP Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the FTP Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
Operations
| Directory operations |
|---|
| Check if directory exists |
| Create directory |
| Delete empty directory |
| List directory |
| Download operations |
|---|
| Download multiple files |
| Download single file |
| Download stream |
| File operations |
|---|
| Check if file exists |
| Delete file |
| Delete files |
| Get size of file |
| Rename file |
| Set file time |
| Get time of file |
| Get list of files |
| Upload operations |
|---|
| Upload multiple files |
| Upload file |
| Upload stream |
| Server operations |
|---|
| Send Command |
| Clear Command Channel |
| Get Server System |
Server Operations
Send Command
Sends a command to the FTP Server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Send Command | Command to send. Send NOOP for a dummy message. |
Output: Single value, text. Returns a error code.
Since: 6.3
Clear Command Channel
Clears command channel encryption state, turning off SSL/TLS encryption.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Graceful SSL Closure | Send closure notification to the server. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Get Server System
Get server system operating system.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|
Output: Single value, text.
Since: 6.3
See also
Upload operations
Upload multiple files
Uploads multiple files from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local path | Path where to upload files from. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to upload. Example *.txt. Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with regex:, example regex:[A|B].* to list all files starting with A or B. |
| Remote path | Path where to upload the files. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also upload from subdirectories. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Upload single file
Uploads a single file from the Flow Server to the FTP Server.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | File to upload. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the file. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
Upload stream
Uploads the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream. This can for instance be used to upload data from a camera input.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local stream | Stream to read data from. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the data. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output: No output.
Since: 6.3
See also
Modbus
The Modbus Connector is a communications protocol for PLC systems.
Configuration
- Address. Address to Modbus device.
- Port. Port to use, usually 502.
- SerialPort settings
- Enable Serial Port. If you are using Serial port insted of TCP.
- Serial Port. RTU connection. Example ,COM1, COM2 etc.
- Baudrate. Symbols per seconds. ex 4800, 9600.
- StopBits. How many bits it should stop after transmisson, None, One, Two, OnePointFive(1.5).
- Parity. A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code to ensure that the total number of 1-bits in the string is none ,even, odd, mark or space.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of Modbus Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the Modbus Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
Get Started
All commands can be sent in synchronous or asynchronous mode. If a value is accessed in synchronous mode the program will stop and wait for slave to response. If the slave didn't answer within a specified time a timeout exception is called. The class uses multi threading for both synchronous and asynchronous access. For the communication two lines are created. This is necessary because the synchronous thread has to wait for a previous command to finish.
Operations
| Read operations |
|---|
| Read Coils Inputs |
| Read Digital Inputs |
| Read Holding Register |
| Read Inputs Register |
| Write operations |
|---|
| Read Write Multiple Holding Register |
| Write Multiple Coils |
| Write Multiple Holding Register |
| Write Single Coil |
| Write Single Holding Register |
Read Coils
Reads Coils
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values, true or false.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Digital Inputs
Read Digital Inputs
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values, true or false.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Holding Register
Read Holding Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Input Register
Read Input Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
Returns a table with values.
Since
6.4
See also
Read Write Multiple Holding Register
Read Write Multiple Holding Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be read | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
| First address to be written | Length of data. |
| Holding register inputs to be written | Contains the register information. |
Output
Return table with values.
Since
6.4
See also
Write Coil
Write Coil
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Length of data. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
Write Single Register
Write Single Register
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data written begins. |
| Holding register input to be written. | Value to write on the address. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
Write Multiple Coils
Write Multiple Coils
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data written begins. |
| Number of addresses to be set. | Values to be set. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
Write Multiple Registers
Write Multiple Registers
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| First Address to be written | Address from where the data read begins. |
| Number of addresses to be read | Values to write. |
| Slave Address / Unit identifier | Unit identifier (previously slave address). In asynchonous mode this unit is given to the callback function. |
Output
No return!
Since
6.4
See also
External Oauth 2.0 provider
The External OAuth 2.0 provider can be used to acquire acess tokens from OAuth 2.0 providers to be consumed in eg the REST connector.
Configuration
- Uri: The uri to the access token provider eg https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token for Google
Header Properties: A key/value table to specify the HTTP headers to provided when making the call to acquire the access token. The header typically consists of two parts: the type of the token, which is JWT, and the hashing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA.
Body Properties: Values to be sent in the body of the http token request call, in addition to the encoded assertion specified by the values in the JWT heading described below, if any.
JWT: Values used to encode the assertion of your token request. Assertion property: the name of the key corresponding to the assertion value in the payload, usually just assertion. Certificate file path: the location to a .p12 file or corresponding certificate file, which holds the public key to be used when encoding the assertion. These are usually issued by the token provider. Make sure you store this file in a location actually accessible by the server. Certificate password: the password for the certificate specified above. Valid in minutes: how long you would like the token to last after it was issued. May or may not last as long depending on the provider.
Claims: items used when encoding the assertion, usually values that tells something about the user the token is to be issued for and what kind of permissions the token should be able to access. The three most common values are: iss: identity of issuer, eg id of the app to issue the token for which the certificate was created for aud: the endpoint to issue the token. Usually similar as that of the uri value exp: expiration time, no need to specify this since the value of Valid in minutes will substitute this. scope: access scopes requested for the token, eg read the mails of a user of a group in google. Not part of the JWT standard but the providers do not seem to care.
More can be read about the claim on the specification for JWT: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519#section-4.1
Get Started
There are no settings, only choose what variable you would like to output the token to. This variable can be used in conjuction the REST connector to access Oauth 2.0 authenticated resources, like azure graph api
Authorization schemes
Authorization schemes can be applied to operations to set what kind of authorizations are required to use the operation. When there are schemes defined they can be applied to operations simply by clicking the "ADD" button:
You can also apply an authorization on all children of a given container by selecting the container and then right clicking on it and selecting "Authorization->Apply authorization to all children".
But first you have to define the schemes. There are three kinds of schemes that can be used.
OAuth2
OAuth2 is currently mainly for documentation purposes. There is no requirement to configure this at the moment (6.7). If you import a swagger specification, that specification can contain this information, and it is good to keep track of. It certainly does not hurt to specify OAuth2.
API Key
REST API:s often require an API key. Typically it is sent either via a query parameter or as a header. You can specify this yourself on the operation, adding the query parameter or header manually. There certainly are cases when this is a good idea. One example is when you want the api key to be associated with the Flow user. You can then set the api key per flow user and in machine step do like this:

You can also set the parameter as a 'Constant', effectively hiding it from the workflow designer. But then the key is hard coded in the connector, which of course could be problematic.
If you want the API key to be configurable in connector configuration you have to apply an API key scheme on applicable operations. Start by creating a new API key:
Provide a Name for the API Key. This is how you want to identify the key. You can provide description for documentation purposes, but that is not required. "API key name" is required and is what the REST API expects the parameter name to be. Finally you have to define whether the key is sent as a query parameter or as a header.

Once the API key has been defined it can be applied to operations as described above.
Finally, after creating the connector, API keys can be set in connector config.
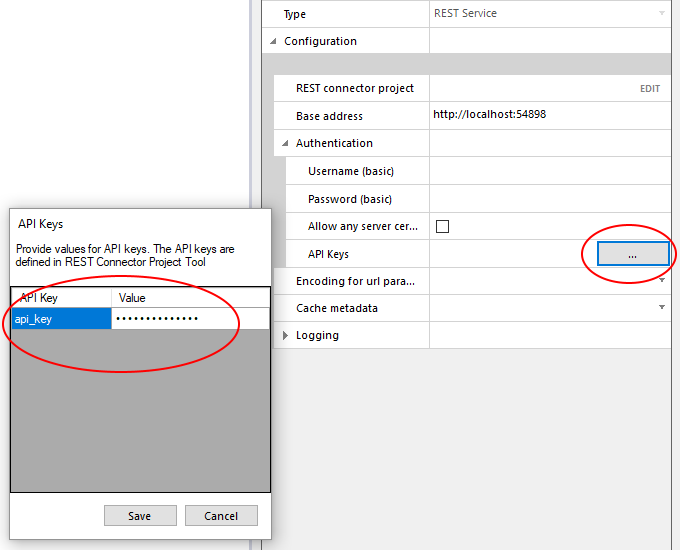
The key will then be applied to all operations that uses the scheme in runtime.
Basic authorization
Another common way for an API to authorize requests is by the use of The 'Basic' Authentication Scheme.
If the API requires this you must add that scheme to the project and apply it to all operations that should use it. There is nothing more to configure in REST Project Tool, all configuration is done in Flow Studio.
Either you set the username and password in the connector config:

Or you can leave it empty and define it per Flow user:
REST Service
The REST Service Connector can be used to consume REST services. The configuration for a REST Connector is mainly done in the tool "Novacura REST Connector Project" which is access by pressing the 'EDIT' button in 'REST connector project' section.
Configuration
REST connector project
Contains the connector project, press 'EDIT' to edit the project. See REST Project Tool for more information.Base address
Required url to base address of REST service.Authentication
In this section the authentication to be used while communicating with REST service can be configured. "Username (basic)" and "Password (basic)" can be used for Basic Authentication, as specified in RFC2617. If the connector has been configured to send Authorization headers, that will be used, otherwise the values set in this section will be used (or per Flow user if no Username setup in this section).
In this section there is also the option to accept any certificate from server in an https session. This should only be used for test or development scenarios when no other option exists.Encoding for url parameters
The encoding to use when parameters are sent as part of the url (query parameters). If not set, UTF-8 will be used.Cache metadata In this section you can specify whether the machine step should cache metadata information or not. It is useful to set this to 'No' while developing the REST connector, and then to 'Yes' once it's stable.
Logging
In this section logging is configured. Either incoming or outgoing or both can be logged. If something goes wrong in the communication, an entry is added to the file errorLog.txt. In order to enable logging, a valid path relative to the Flow Server must also be provided. Note that the path must already exist, the connector will not create the path. Also note that the user that Flow Server is running as must have write access to the path..
Custom model member
With the custom data type on a model member you can specify external (from the perspective of the REST project tool) data types. You use Custom specification the specify the type.
Currently the only available custom data types are types originating from the .NET Base Class Library (BCL). To use a type from BCL you prefix the full name of that type with 'bcl:', for instance 'bcl:System.TimeSpan'. Note that certainly not all types will work, and most of them will make no sense. You can consider this feature as an advanced one with limited support available. It is however powerful and useful in many scenarios and can save you a lot of development time and need of custom connectors by using it properly. Since it can reduce the need for custom connectors it also simplifies deployment and reduces maintenance.
So, after this warning, let's walk through an example of how it can be used.
Consider this scenario:
* You want to fetch pdf documents from a REST API.
* The REST API returns the pdf documents as base64 encoded strings.
* You want to store these documents in the filesystem, of course not as base 64 encoded string but as the actual binary data.
This is how the json looks like when returned from the server:
{
Data: "JVBERi...base64 encode data...PDj8OT==",
Name: "4cdda37a-fa71-1065-a761-141a4ebaf7d3",
Extension: ".pdf",
InvoiceId: "401757"
}Since this is what the API will return, we need a model for it. This is quickly done with 'NEW FROM JSON' in the Model part of the REST Project Tool. See Models for more information on how to to that.
Once we've created the model it will look like this:

We now need a model that contains not the base 64 encoded string, but instead an instance of System.IO.Stream.
Since this model will look almost the same as the 'Invoice' model, we can use the 'Clone model' feature. This is accessed by selecting the tree node for the model and right clicking: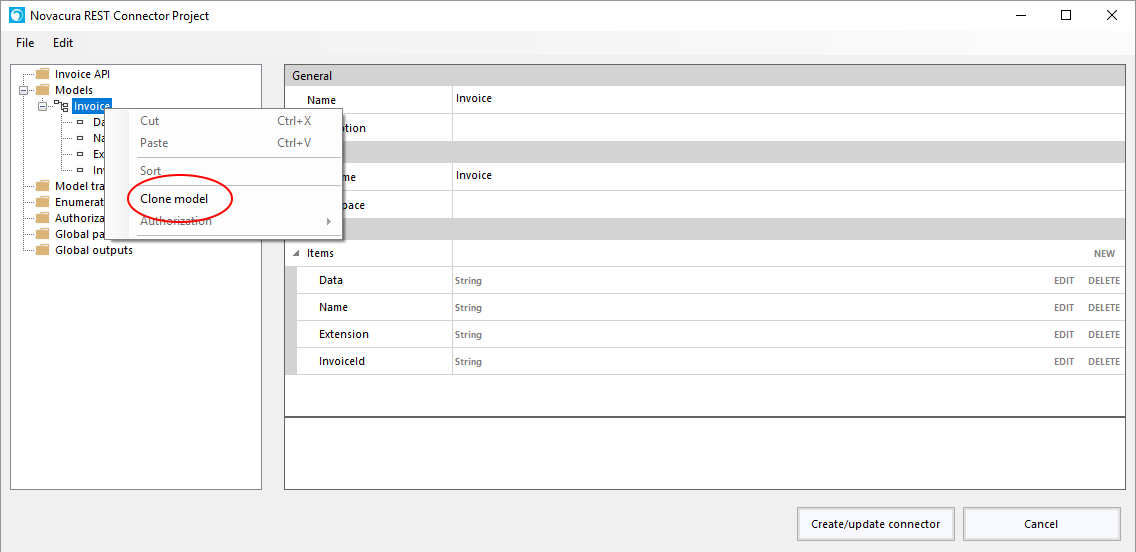
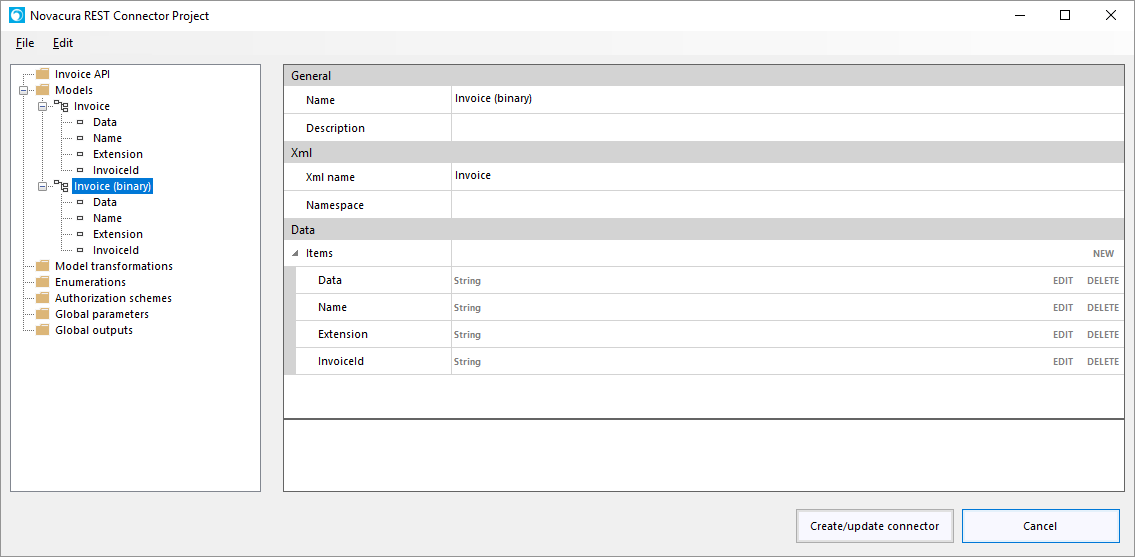
Next step is to change the data type of 'Data' in 'Invoice (binary)'. Select the 'Data' member and change 'Type' to 'Custom' and set 'Custom specification' to 'bcl:System.IO.Stream'.

Next step is to create a model transformation between the two models.
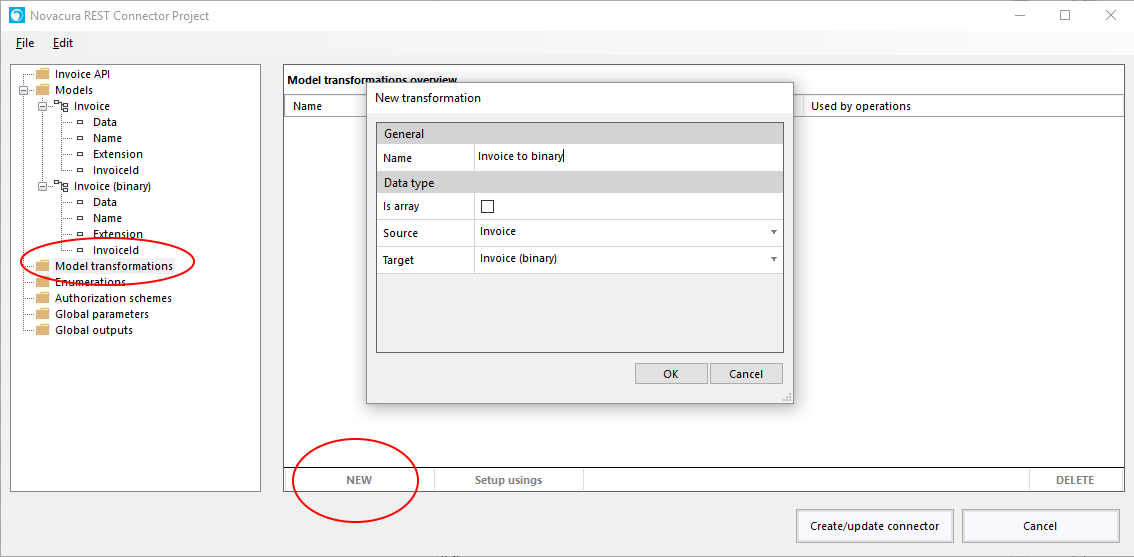
The code could look something like this:
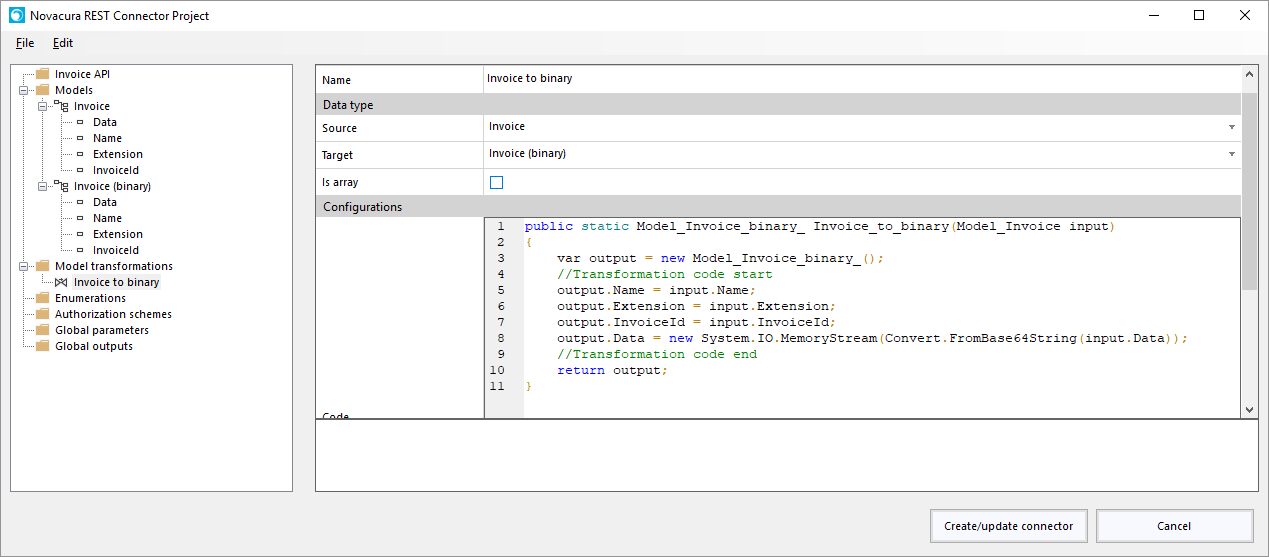
Now this transformation can be applied to a GET operation

Finally the workflow could look something like this:
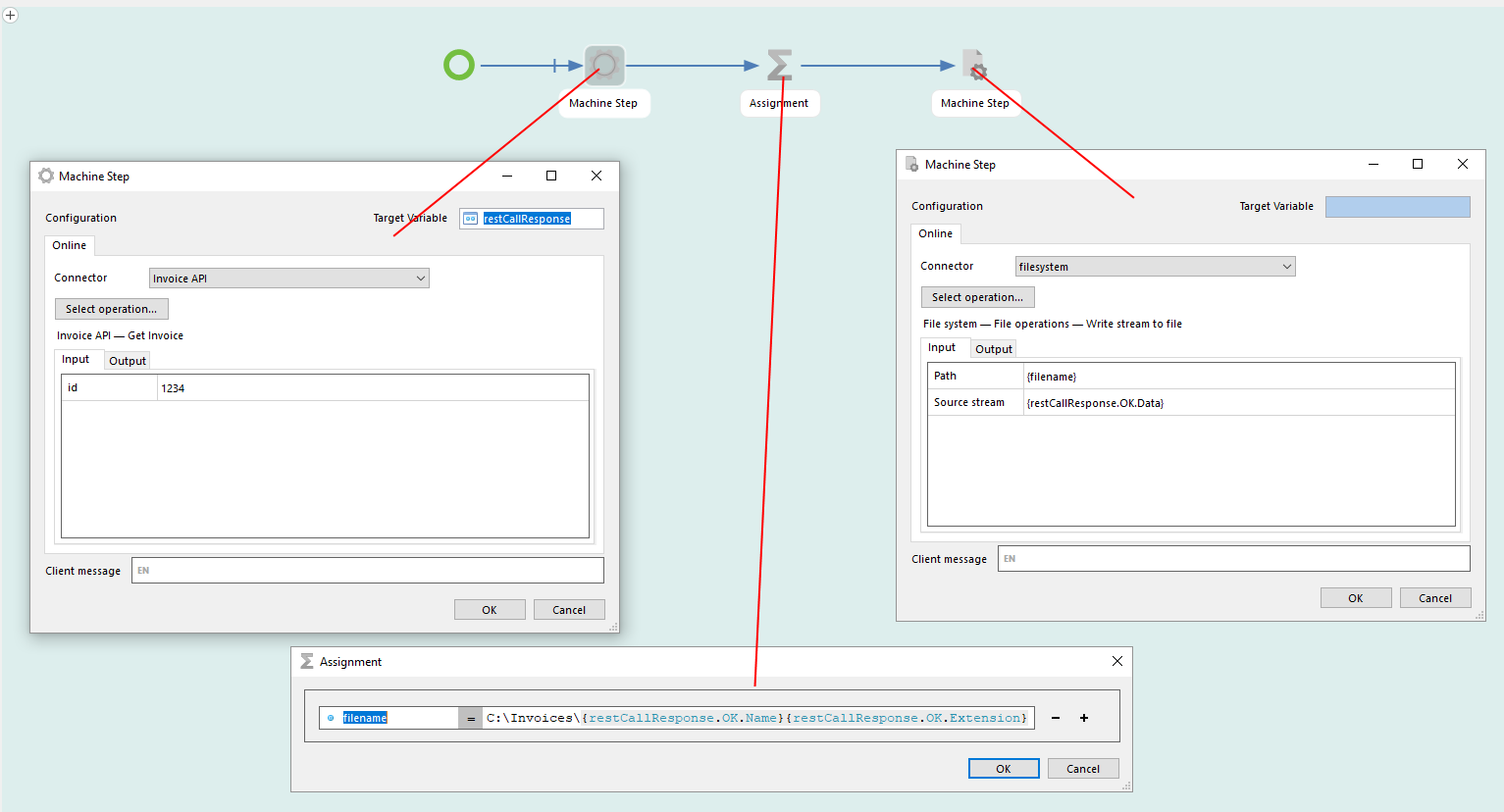
Enumerations
Enumerations can be used in models to limit the possible values a workflow designer can assign to a member of a model.
Consider for instance an API for 'orders' in a 'store'. We got the operations 'Add new order', 'Update order' and 'Delete order'. Let's look at the 'Order' model:

'status' is of type 'Enum':
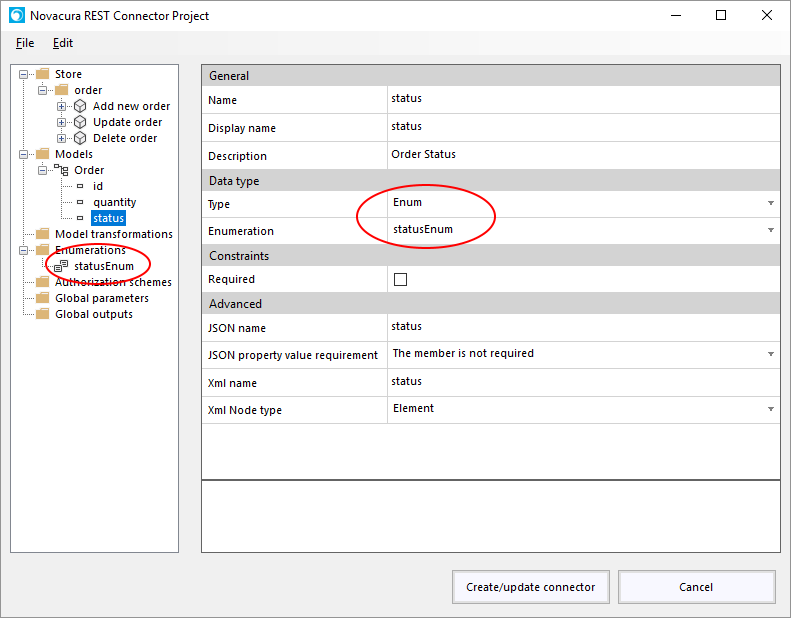
And if we look at that enum you can see what possible values that member can have:
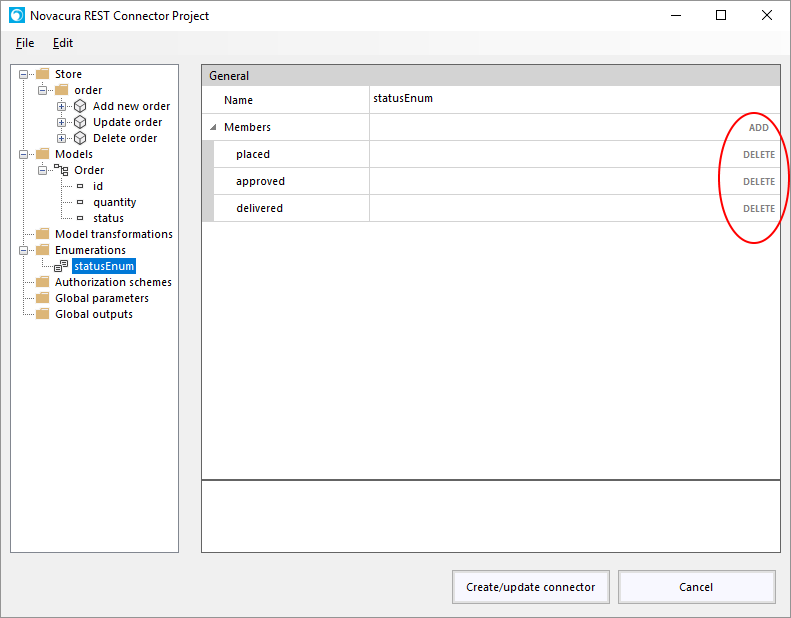
Members of the enum can be added and deleted as needed (circled area above).
Let's look at an operation using the 'Order' model, 'Update order'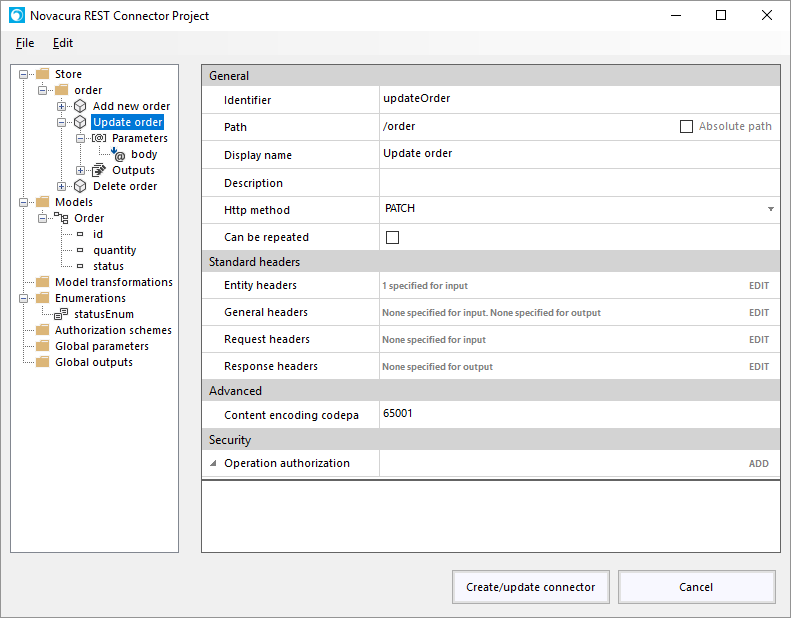

It uses 'PATCH' to only update certain members, accepting a body of model 'Order'.
Let's look how this will look in Flow Studio: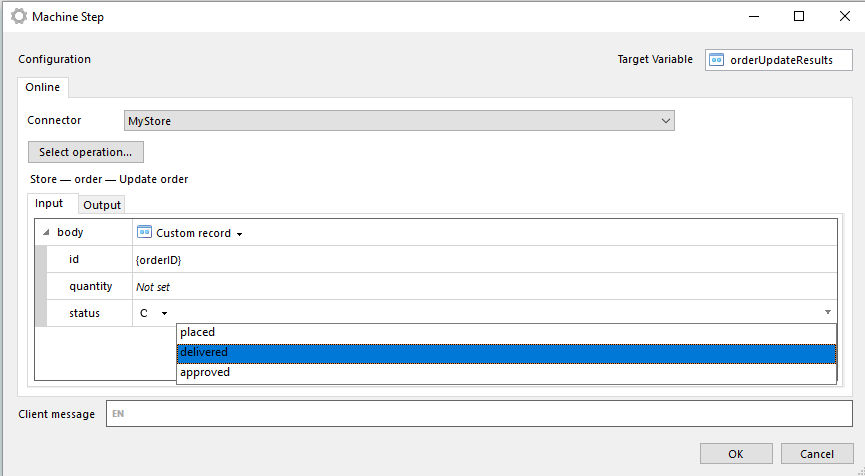
When using 'Constant' as mapping to 'status' only the members of the enum are available. You can still mess it up by selecting 'Variable' as mapping and providing an invalid value in the passed variable. But with the usage of enums you can at least guide the person using the connector in Flow Studio in what kind of values are expected.
Getting started
To create a REST connector you go to Environment -> Connectors -> Add and select Type "REST Service".
Provide a 'Name' and click on "EDIT" to get started. You will also be required to provide a base address before you can save the connector.

When you click on "EDIT" you will open a tool where you'll define the connector.

Let's walk through all the properties.
General
- Connector name
This is just what you want to call the connector. - Connector description
A description of the connector. For documentation purposes. - Base path
If set, all paths are prepended with the value of 'Base path'. If for example the base address of the connector (set not in the tool but in connector configuration) is 'https://www.googleapis.com' and 'Base path' is set to '/drive/v3' and you define the operation 'about' with 'Path' '/about' the url called in runtime will be 'https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/about' - Connector version
For documentation purposes.
Containers
The main purpose of containers are to help you organize the operations in a logical way. You do not need to specify any containers, but it usually make senses to use them. Containers can contain operations and other containers. They can also define 'Standard headers' that can be applied to all sub-containers and operations. Containers can also define a 'Path' which is appended to the 'Base path' (described above). The final 'Path' of an operation is the concatenation of all parent containers 'Path' (can be overridden).
Operations
In the 'Operations' section you can add and delete operations of the connector. This is most likely the first thing you will do when starting a new REST Connector project.
Standard headers
In this section you can specify entity, general, request and response headers that should be applied to all operations of connector. You can for instance set that all operations must send 'Content-Type: application/json'. Sub-containers and operations can always override the header.
Advanced
In this section you can specify advanced features that you usually do not need to worry about.
Global output
'Global outputs' is used to define output parameters that can be reused on multiple operations.
A typical use case is when an API returns some kind of error that is always of the same format. The API might return some data depending on the operation with http status code 200. But in case of error it could still return http status code 200, but a different model, containing information about the error. Although each operation has different models in case of success, in the case of failure could be the same.

Note that priority has been set to a number higher than '1' (in this case '10'). The REST connector will try all defined outputs of given http status code until it succeeds, in the order of 'Priority', starting with the one with highest priority (lowest number). Assuming the operation will be successful more often than not, it makes sense to assign a lower priority on the error output.
You can also define a "NEW DEFAULT OUTPUT", which is just like normal "DEFAULT OUTPUT", that is an output for all http status codes not defined by other outputs.
Once you have defined a global output you can add it to any operation.
Just select "Outputs" on operation and press the 'ADD GLOBAL' button.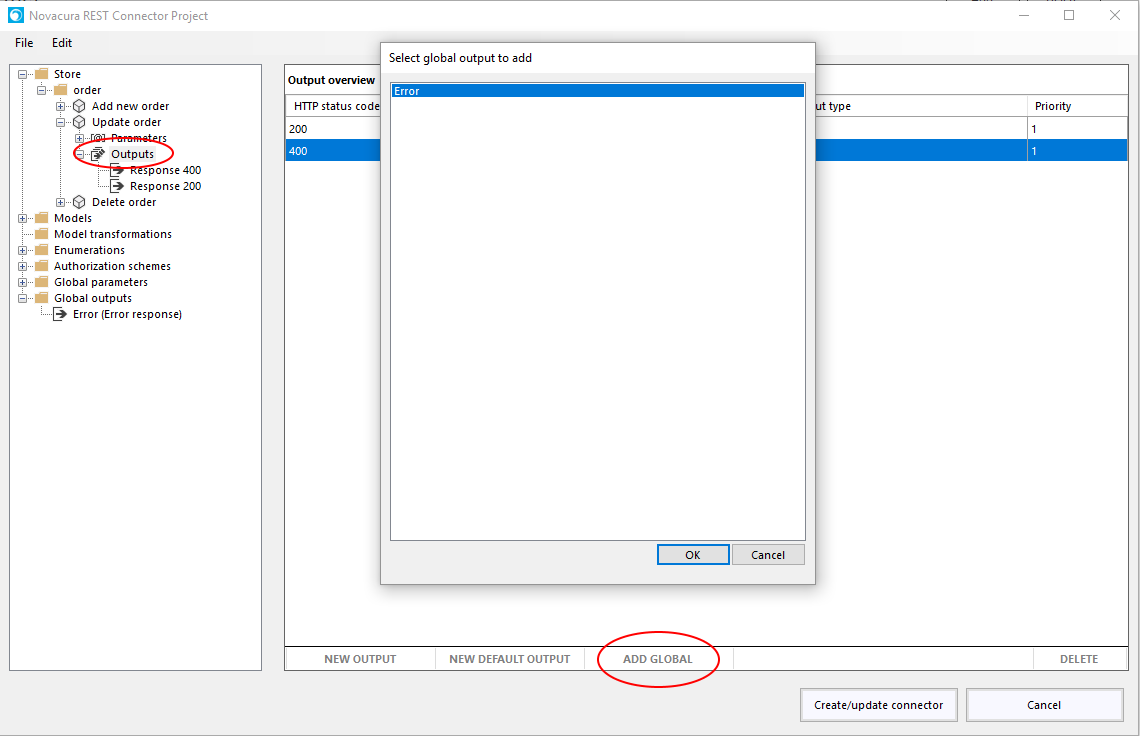
Select output of interest and press 'OK'. You will then be given the option to include the output as a copy or as reference. If added as copy, a new output that looks exactly like the global one will be added to the operation, but there is no connection between the two. So if the global output is changed in any way, the added copy is not affected. If you add it as a reference any changes to the global output will affect the output you added to the operation (it is the same output).
Global parameters
'Global parameters' is used to define parameters that can be reused on multiple operations. You can define query, form, body, header and matrix parameters.

A global parameter is defined like a 'normal' one except that you have to give it a unique identifier once you have defined it. This is to enable you to have multiple global parameters with the same parameter 'Name'. You can of course still only apply one global parameter of given 'Name' to an operation, but this way you can build up a library of useful parameters.
Once you have defined a global parameter you can add it to any operation (as long as that operation not already has a parameter with the same 'Name').
Just select parameters on operation and press the 'ADD GLOBAL' button.
Select parameter of interest and press 'OK'. You will then be given the option to include the parameter as a copy or as reference. If added as copy, a new parameter that looks exactly like the global one will be added to the operation, but there is no connection between the two. So if the global parameter is changed in any way, the added copy is not affected. If you add it as a reference any changes to the global parameter will affect the parameter you added to the operation (it is the same parameter). So if you for instance change the 'Name' of the global parameter, this means that the operation now sends a parameter with a different 'Name'. This can create conflicts. Let's say for instance that you add the global parameter 'q1' to an operation as a reference. You then add the parameter 'q2' to the operation. If you then change the 'Name' of the global parameter to 'q2' the operation will have two parameters with the same 'Name'. This is not allowed, but will not raise any warnings until you try to "Create/update connector".
Internal parameters
In the 'Global parameters' section you can create parameters of kind 'Internal'. This kind of parameters can only be add to operations as a reference, never a copy. The purpose of internal parameters are to be able to send in parameters to an operation that can be used in model transformations. They are not sent to the remote API. Internal parameters will always be set to a nullable type. So when you use it in a model transformation this must be considered. Let's say for instance that you have a global internal parameter called 'Remove empty entries' of type 'Boolean', the usage of that parameter could look like this:
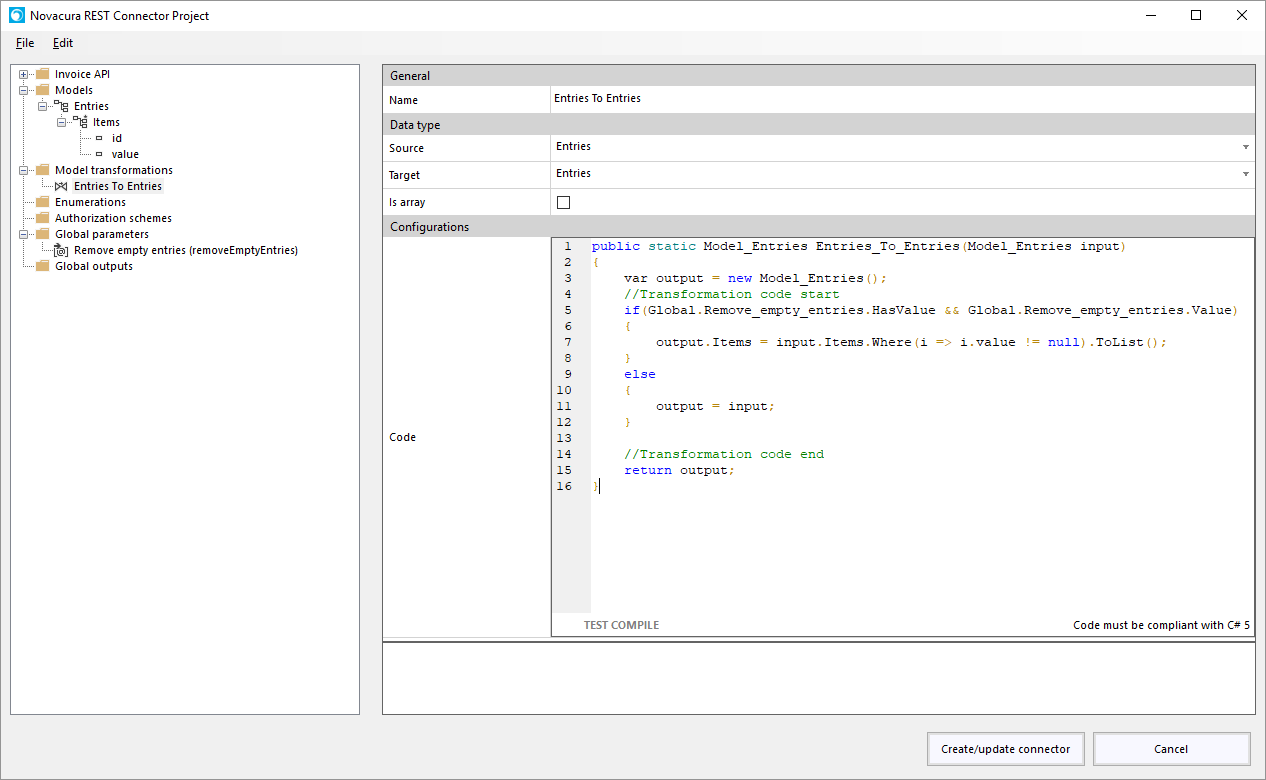
Models
Models are a central concept when creating a REST connector. They are use both for posting object data to an API and also when receiving object data from an API.
Models are managed from the "Model" node in the connector tree.
Below the grid you can create new models. You can create an empty model by pressing the "NEW" button, or you can create a new model based on JSON (sample or Schema Draft 4) or XML sample.
Let's start with creating an empty model.

- Name
A unique name for the model. - Description Currently purely a documentation feature for you as a REST connector designer. Provide a description of the model if it makes sense.
- Base model Used to set a base model that the new model should be based on. All members of base model is added to the new model. Base models are described in detail in its own section below.
- Namespace Used when model is sent or received as xml. If no Namespace is provided and the model is sent as xml, no namespace is assumed.
- Xml name Name of xml element when model is sent or received as xml. If no Xml name is provided, Name is assumed to be the xml elements name.
After the model has been created it is empty and pretty much useless. Press "NEW" on "Items" to create members of model
This will bring up a dialog where you can specify details about the member of the model.
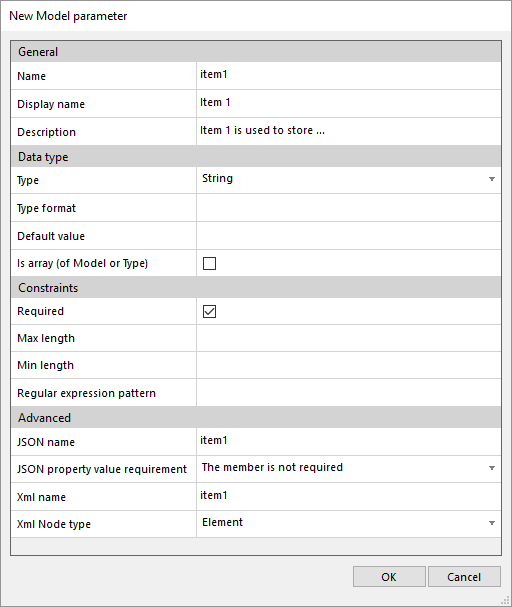
- Name
The name of this member of the model, must be unique in the scope of the model. - Display name
A more human readable version name of the member. If model is used as input to an operation this is what the workflow designer will see as name of member. The actual name of the member is still Name though, and if you want to create a record to use as input (as opposed to a 'Custom record') you must specify Name in that record. - Description
Currently purely a documentation feature for you as a REST connector designer. - Type
Here you select what type of member this is.
- Boolean - true or false.
- Integer - Type format is available. As Type format you can set int64 for big integers (default is int32)
- Number - Type format is available. As Type format you can set float or double (larger, and default if not set)
- Object - Used when the member is of a Model.
- Object (embedded) - Used when the member is a Model, but the Model is only used once, so creating an independent Model is inefficient. More information about embedded models can be found below.
- String - Type format is available. As Type format you can set date-time to indicate that the member is actually datetime.
- Enum - used to set that this member is of an enum. See Enum for more information.
- Custom - Custom specification is available. With the Custom specification you can set the type for special use cases. See Custom model member for more information.
- Boolean - true or false.
- Is array (of Model or Type)
Available for all Type except Enum. Set this if the member is a collection of Type - Constraints
Constraints section depends on Type and it's members are at the moment more of a documentation nature than actual impact on usage of connector. This may change in a future version. - Advanced
This section is used to specify if member has another name in JSON or xml than it's Name. If JSON you can also specify how to handle missing value of this member. Default is to ignore missing members. In the case of xml you can also specify whether the member is an attribute or a element of parent xml element.
You can manually create as many members of the model as needed. You can of course also delete and edit members when needed. At the moment there is no way to rearrange the order of the members. The order does not matter in runtime, but for clarity it could have been good to be able to rearrange them.
While creating the model manually is easy, it is even easier if you already got a JSON or xml representation of it.
Here is an example of a model from JSON (sample):
Types are assumed based of the example data, for instance "Prop3" is assumed to be of type Boolean since the example value of it is 'true'. This feature works for most cases, but there are cases where you need to manually specify exactly the type you need (setting an Integer to have Type Format int64 is one example). You can set all data types to 'large ones' by checking 'Use large data types'. Note that all members of type Integer will then have int64 format.
You can also create models from JSON Schema (draft 4), this is much more accurate than from sample but is not as commonly used as JSON samples.
Here is an example of a model from JSON Schema:
As you might notice, id is specified as int64 already in the schema, and this will be stored in the Model. JSON Schema (draft 4) is superior to JSON Sample in almost every way but, as stated above, unfortunately not as commonly used to document REST APIs as JSON samples.
Another way to get an external representation of a Model into the REST Project is by xml. Currently only sample xml is supported, not from any schema (such as xsd).
Here is an example of a model from xml sample:
Embedded models
When creating models from JSON or XML sample, inner structures of the model are created as 'embedded models'. This is new in version 6.8 of Flow, in earlier versions independent models were created. If a model is used only once it makes little sense to have an independent model. Chances are that you will end up with lots of models and the project will be hard to manage. When using an embedded model all the members of the model is located directly under the model member. This is perhaps best illustrated with an example:
Consider this structure:
{
"property1":"string",
"property2":"string",
"property3":
{
"innerProperty1" : "string",
"innerProperty2" : "string",
"innerProperty3" : "string"
},
"property4":
{
"innerProperty1" : "string",
"innerProperty2" : "string",
}
}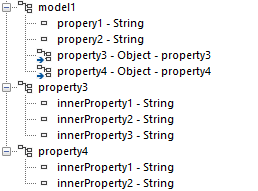
This is not wrong, it will work just fine, but as project grows larger the number of models will be problematic. With the use of embedded models you would end up with model like this:
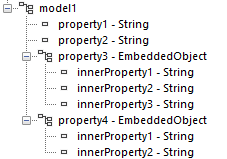
The two extra models that was referenced by 'model1' are now embedded in the model. This of course means that the model 'property3' cannot be used by another model, but in the situations where that will not happen, this is a better solution.
Referring to an embedded model in model transformation
If you want to create an instance of an embedded model in a model transformation you refer to it as 'Model_NAMEOFMODEL.Embedded.NAMEOFPROPERTY'. An example with the 'model1' above:
public static Model_model1 modeltransform(Model_model1 input)
{
var output = new Model_model1();
//Transformation code start
output.property3 = new Model_model1.Embedded.property3();
output.property3.innerProperty1 = "a value";
//Transformation code end
return output;
}Converting between embedded and independent models
By default all inner structures are interpreted as embedded models (possibly with the exception of JSON schemas). You can convert between embedded models and independent models in the tool after they've been created by right-clicking on their usage in the tree view and select 'Convert to independent model' (or 'Convert to embedded model' if already independent). If you convert to an embedded model, the related independent model will not be removed. If the rest project tool detects that the model is not used anywhere you will be prompted with the option to delete it though.
Base models
In version 6.8 of Flow the support for base models were added. Basically a model can use another model as a base, meaning that all members of the base model are available also in the new model.
Here is an example where 'Model2' has 'Model1' as base model and 'Model3' has 'Model2' as base model. All members of both 'Model1' and 'Model2' are available in 'Model3'.
Model transform
Model transform is a feature where you as REST connector developer can manipulate the response from a REST API before returning it to the workflow. You can also use it to manipulate an outgoing object (body parameter).
Transforming incoming models
Typical use case is when an API returns data like this:
{
properties : [
{
property: "Property1",
value : "Value1"
},
{
property: "Property2",
value : "Value2"
},
{
property: "Property3",
value : "Value3"
},
]
}When used as an output model in REST connector you would end up with an output looking like this in Flow:
This can be managed with Flow Script, but it can be more convenient and efficient to do the transformation inside the connector. Especially if the connector is used in multiple workflows.
The output of the remote operation is of course still the data above, so we have to define a model to represent that data:
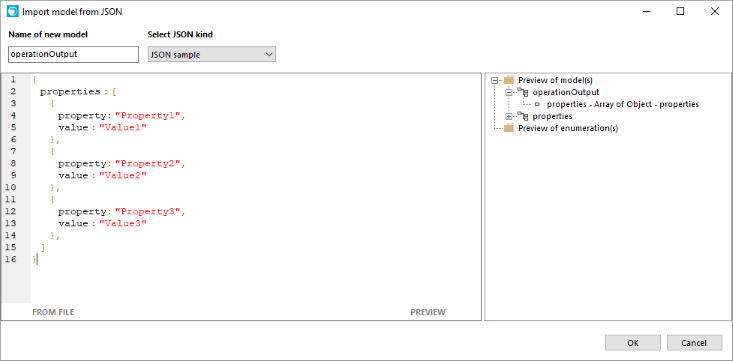
But we can also define the model that we want to expose to the workflow. Something like this:
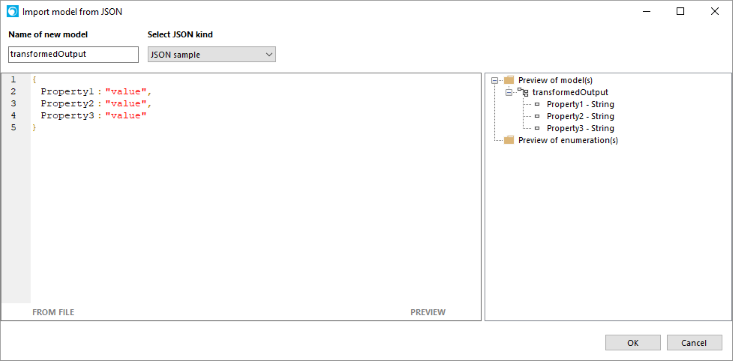
Let's add the transformation.
Select "Model transformations" in connector tree and press the "NEW" button
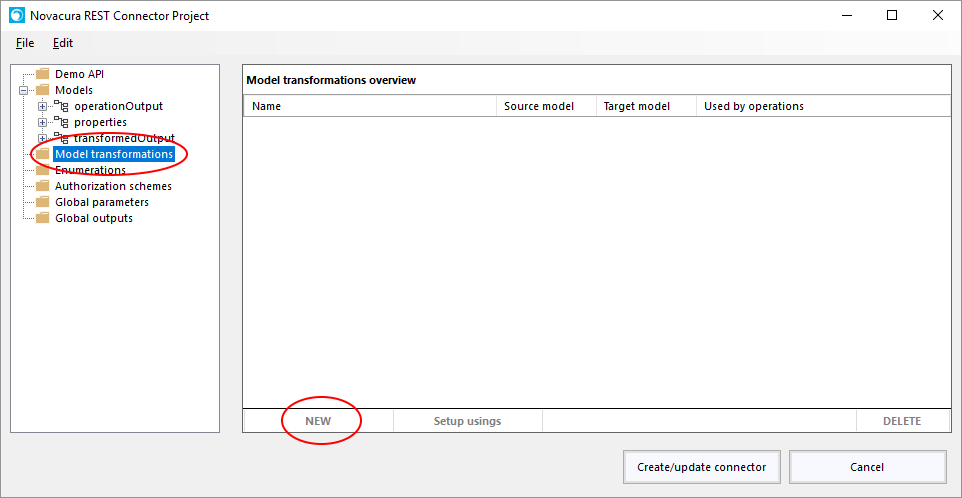
Give the transformation a descriptive name and select source model and target model
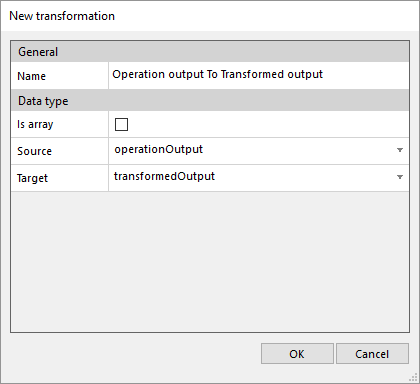
Double click on the newly created transformation in the list, or select it from the connector tree. Something like this should be loaded:
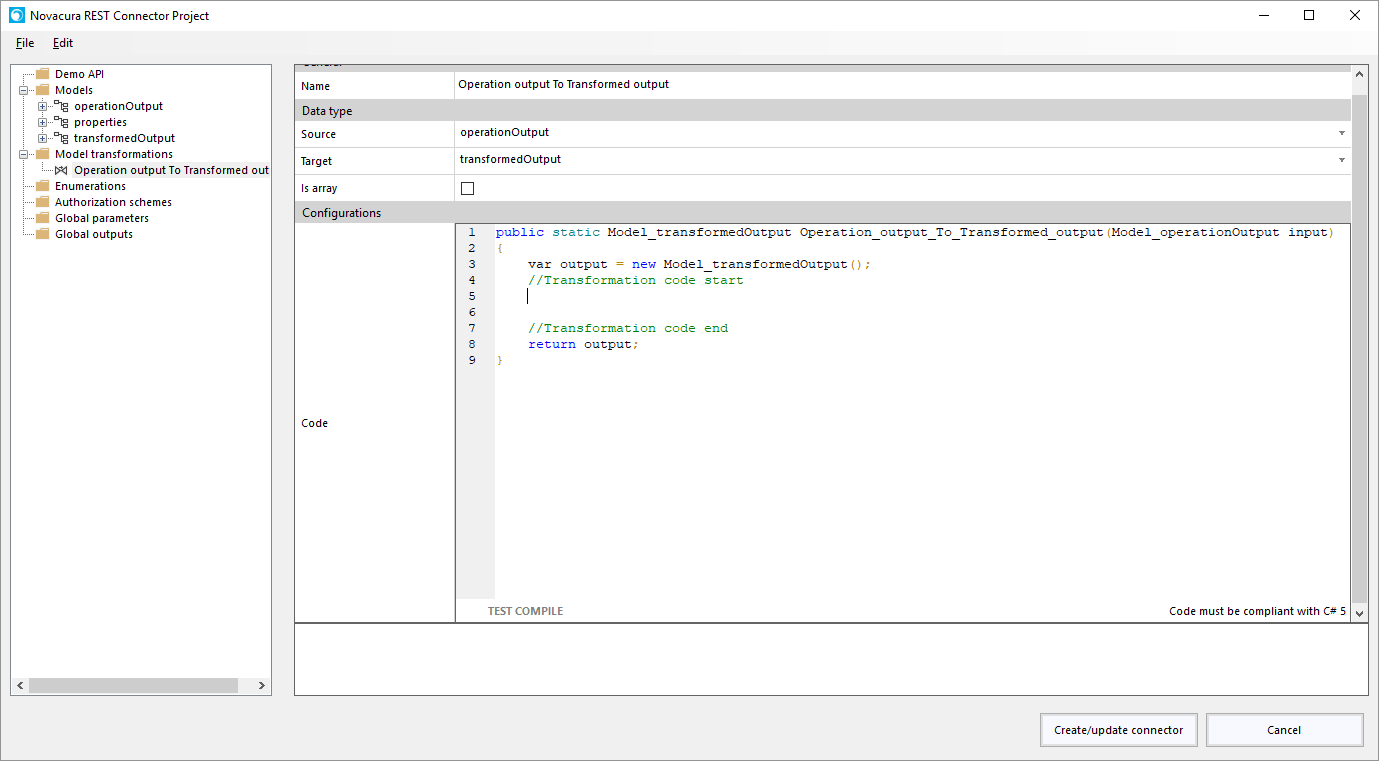
So the actual transformation is done with c# code that you provide. Do not enter any code above //Transformation code start or below //Transformation code end
This is a very powerful feature. You are, however, limited to provide code that is compliant with c# 5.0. You are also limited to only use types from the following assemblies:
System
System.ComponentModel
System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations
System.Core
System.Data
System.Drawing
System.Net.Http
System.Runtime
System.Runtime.Serialization
System.ServiceModel
System.ServiceModel.Web
System.Web
System.Xml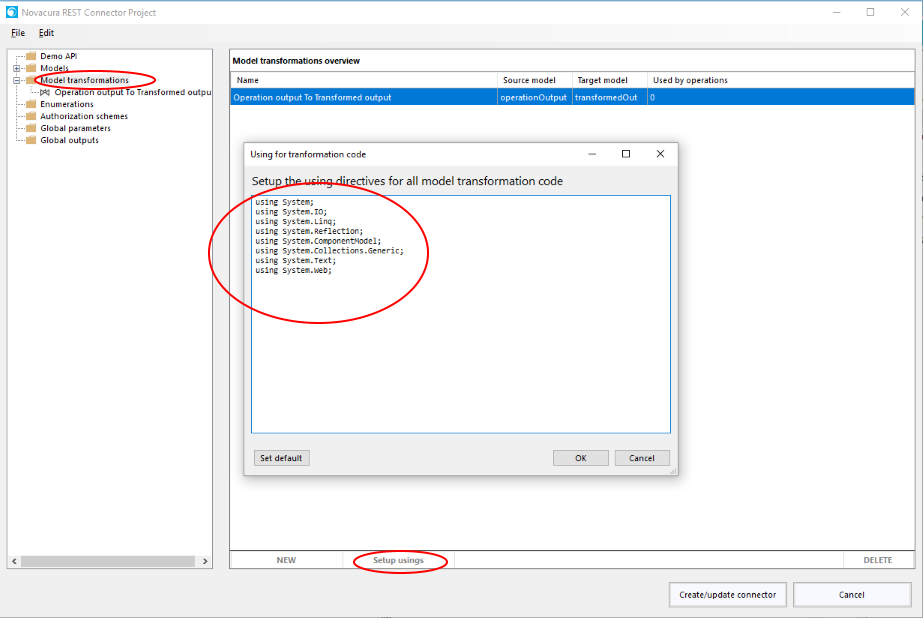
An example of transformation code for this situation could be:
public static Model_transformedOutput Operation_output_To_Transformed_output(Model_operationOutput input)
{
var output = new Model_transformedOutput();
//Transformation code start
output.Property1 = input.properties.First(p => p.property == "Property1").value;
output.Property2 = input.properties.First(p => p.property == "Property2").value;
output.Property3 = input.properties.First(p => p.property == "Property3").value;
//Transformation code end
return output;
} Note that models are called 'Model_' followed by the name of the model.
All that is left to do now is to apply the transformation to the operation of interest:
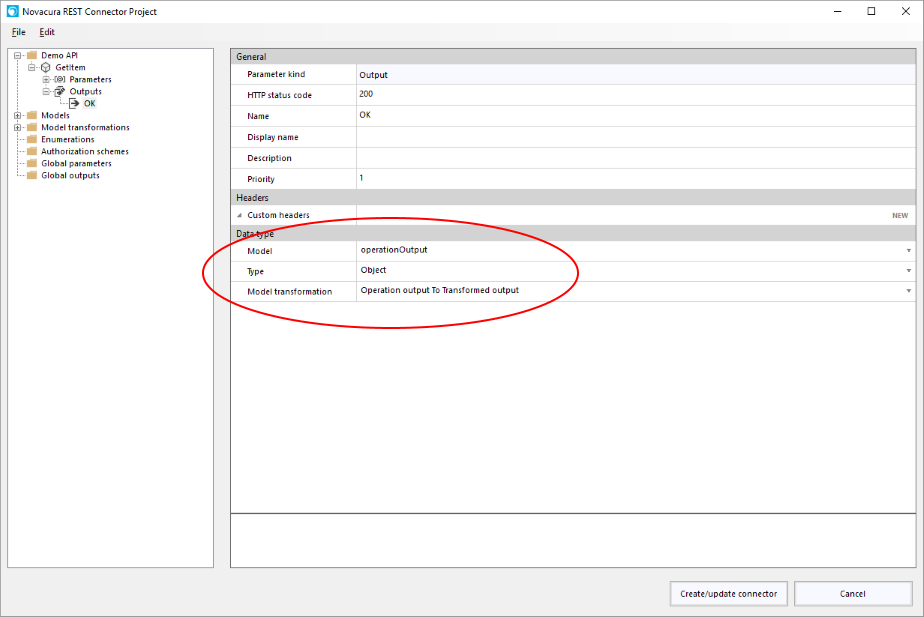
Now when the connector is used in a workflow the output from the operation will look like this:
Which is easier to work with as a workflow designer.
There are a lot more scenarios that this feature enables. You could for instance add new output members (composed of values from other members for instance) or hide members that are not of interest to the workflow designer.
The code will run with limited permissions. It is for instance not allowed to access the file system, so code such as
System.IO.File.AppendAllText(@"C:\logs\values.txt", input.Property1);will not work and you will get an error in runtime.
Transforming outgoing models
Like incoming models there are scenarios where it makes sense to transform the outgoing models before it is sent to remote API. Let's assume the same data structures as above are in action here as well. The transformation now needs to be from the model 'transformedOutput' to model 'operationOutput'. Names now becomes a bit off, since we are not dealing with output, but I'm sure you get the picture.
Then the transformation code could look something like this:
public static Model_operationOutput Transformed_to_real_output(Model_transformedOutput input)
{
var output = new Model_operationOutput();
//Transformation code start
output.properties = new System.Collections.Generic.List<Model_properties>();
output.properties.Add(new Model_properties() { property = "Property1", value = input.Property1});
output.properties.Add(new Model_properties() { property = "Property2", value = input.Property2});
output.properties.Add(new Model_properties() { property = "Property3", value = input.Property3});
//Transformation code end
return output;
}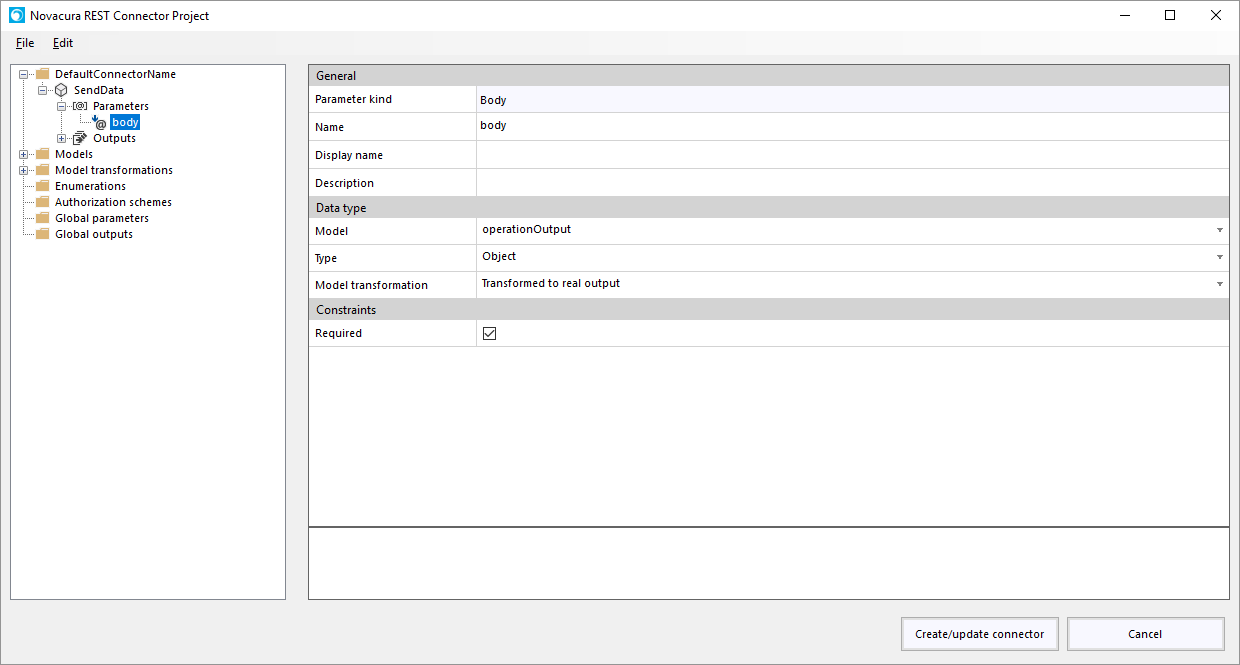
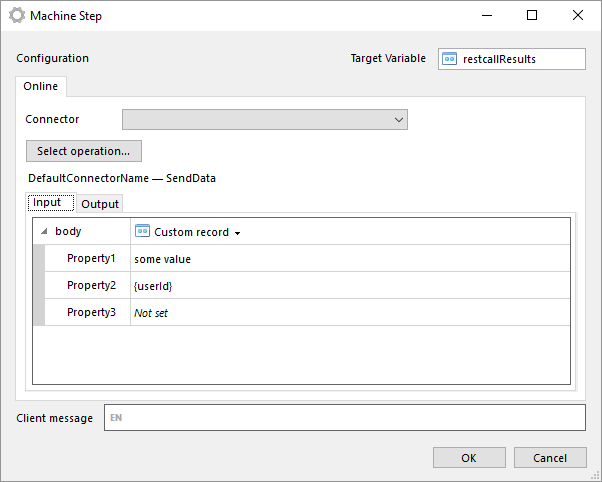
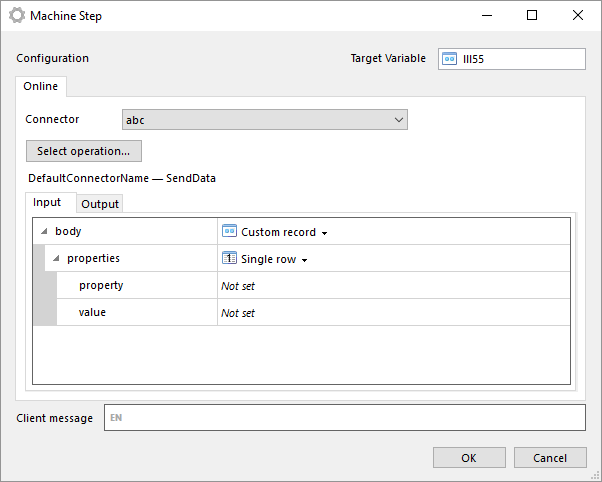
There certainly are situations where the later is preferred, maybe there is already a table with property+values available and so forth. With the transformation feature you can control what best suites your scenario.
For a more advanced example of model transformation see Custom model member
Operations
New operations are added to the project or container by pressing the 'ADD' button.
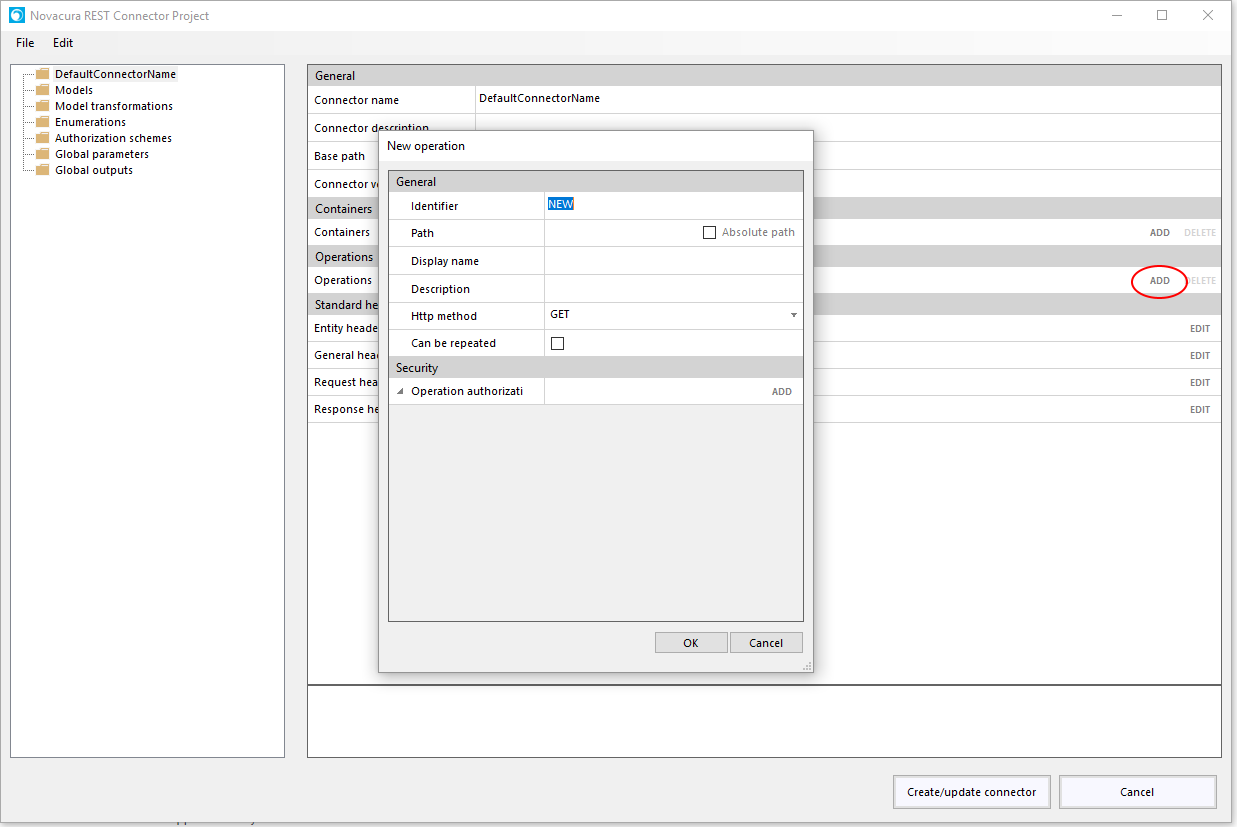
There are a couple or properties that can or must be defined for each operation.
General
- Identifier
A unique (in the context of the container this operation belongs to) identifier for the operation. Must start with a character and can only contain characters and numbers. - Path
Required. The path to call for this operation. Sometimes referred to as resource or simply url. You can add 'path parameters' like this: '/resource/{id}' where 'id' is a path parameter. You also have to option to check 'Absolute path'. If you do, the 'Path' will not depend on any containers (just on the 'Base address' set in connector configuration). - Display name
Friendly name of operation. If specified, this is what will be displayed when selecting operation in machine step. If not specified, 'Identifier' will be used. - Description
Mainly for documentation purposes. It will also appear as a tool tip when selection operation in machine step. - Http method
Required. Specify which http method to use for this operation, such as GET, POST or DELETE. - Can be repeated
Here you can specify if this operation is to be repeatable in a workflow. Typically a 'GET'-operation can be repeated while a 'DELETE' or 'POST' should not be repeated. But it is up to you to set this. Nothing is assumed.
Security
You specify operation authorization if you have created any in Authorization schemes. This can always be added later, so there is no requirement to set this upfront.
Press OK to create the operation. Once the operation has been created you can specify input and output of the operation.
Learn more here:
Parameters
Outputs
Outputs
The output of an operation needs to be defined so Flow can use it. If you do not need any output, it is safe to define no output. The machine step will still return a record, consisting only of 'HttpStatusCode', 'ReasonPhrase' and 'AllHeaders'.
But typically you want to define the possible outputs of an operation. When you create a new operation one output is added by default. This output is for http status code '200'. If the operation does not ever return 200 you can delete it.
You can define multiple outputs for an operation, for example you might want one for http status code '200' another for '400', yet another for '500' etc. You might even need several outputs per http status code. An API can for instance always return '200', but in case of an error return an object describing the error instead of expected object. The REST Connector will try to parse the response from the API until it is successful. To control the order the connector tries to parse the response, use 'Priority' - where the output with highest priority (lower number) will be tried first. If two outputs has the same 'Priority', it's undefined which output is tried first.
To define a new output you press 'NEW OUTPUT'.

- Parameter kind
Always output
- Http status code Specify for what Http status code that output is valid for.
- Name
A unique name for the output
- Display name
A more human readable name for the output (not required)
- Description
Currently purely a documentation feature for you as a REST connector designer.
- Priority
Applicable if there are more than one output on a given http status code.
- Data type
Here you specify the kind of output - None - Array - Boolean - Integer - Number - Object - String - File
- Override content-type
Here you can specify that REST connector should always consider the returned content to be of a specific content-type, regardless of what the actual response states. Applicable values are "application/json" and "application/xml". This is to mitigate situations where a remote API for instance states content-type "text/plain" even though it actually is "application/json".
See Parameters for more information about these types. Note that 'File' will translate to a 'Stream' in Flow. So if you download a file from a REST API (output is of type 'File') you can then use for instance the 'File System Connector' to write the stream to disk. Or another connector that can handle streams, such as SFTP, FTP or the Database connector. If the output is 'Object', you can also select an transformation (if there are any transformations available based on the selected model. See Model transform for more information.
You can also add one (and only one) 'DEFAULT OUTPUT'. The purpose of this output is to capture all http status codes not defined by another output.
Example
Let's look at an example with multiple outputs.
We got two outputs for http status code 200 defined.

Which leads to that when the operation is later used in Flow, it will have two records, one called 'OK' and one called 'Error'. At most one of the two will have a value after the REST call has been made.

This can be used for better error handling, for instance like this:
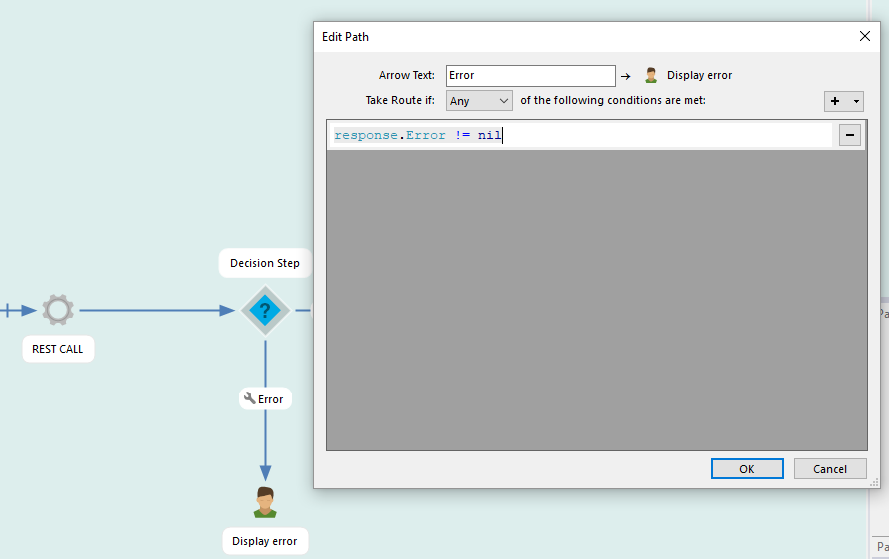
Parameters
Most operations will have parameters of some kind. To define them you simple click on 'Parameters' beneath the operation.
In this example a 'Path parameter' (id) was specified so that is added to the parameters automatically. Path parameters are added and removed directly in the 'Path' by declaring them there. Example: '/{resource}/{id}' where both 'resource' and 'id' are path parameters.
Query parameters
Query parameters are very commonly used by REST APIs. They are added at the end of the 'Path', after a '?' and separated by a '&'. But you do not have to worry about any of that, just add query parameters by clicking the 'NEW QUERY' button and the connector will take care of all the details. If you want add multiple parameters at once there is a convenient shortcut accessible by right clicking on 'Parameters' and selecting 'Add multiple query parameters'. You can then enter as many (within reason) parameters as you like. Choose how they are separated (comma, semicolon or new line) and what type they should all be (typically string). You can also decide whether the parameters are required or not.
The parameters in the example above were all of type 'String', which probably is the most common type you'll use. There are however multiple types available, more information about the different types can be found later in this page.
Query parameters can be set to be an 'Empty value parameter'. This means that if set to "true" the parameter will be included in the query but without a value. If for instance parameters 'x' and 'y' are defined and set to 'true' the url called by REST connector could look something like this:
http://theurl?otherParameter=someValue&x&yForm parameters
Form parameters are added to your operation by clicking the 'NEW FORM' button. Form parameters requires you to also set a 'Content-Type' header on the operation - 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' for GET or 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' or 'multipart/form-data' for POST. If you are sending a file (binary data) you must use 'multipart/form-data'. If you do not set any header, the tool will force you to do so when clicking the 'Create/update connector' button. Form parameters cannot be used at the same time as body parameters.
Body parameters
Body parameters can be used with POST, PUT and PATCH operations. Typically they are used to send object data to an API. Objects are defined as models, see Models for more information. You can use model transformations on the model before it is sent to remote API, see Model transform for more information. Body parameters cannot be used at the same time as form parameters, and you can have only one body parameter in an operation.
Header parameters
Header parameters, or custom headers, are parameters that are sent as http headers to the API. One common use case is to send API keys in a header. If the API you are creating a connector for requires this, there are however other options available than creating a custom header, read more in the section 'API Keys' in Authorization schemes for more information.
Matrix parameters
Matrix parameters are parameters that are added to the 'Path' before any query parameters. They are separated by a ';'. If you for example has an operation 'op1' with two matrix parameters defined, 'm1' and 'm2' and one query parameter 'q1' which at runtime have the values 'm1Value', 'm2Value' and 'q1Value' the 'Path' (url) would look something like: 'https://site/api/op1;m1=m1Value;m2=m2Value?q1=q1Value'.
Parameter types
String
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Strings is a very common parameter type. Default to this if you do not know the type. String supports 'Type formats'. Currently only 'date-time' will have an impact on runtime - causing the parameter to be treated as a datetime. The 'Required' constraint is used to force the Flow designer to provide a value, but the other constraints ('Max length' etc) are currently only for documentation purposes. This can change in future version of Flow.
Integer
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Integer supports 'Type formats'. Currently only 'int64' will have an impact on runtime - causing the parameter to be treated as a 64-bit integer (instead of a 32-bit integer). The 'Required' constraint is used to force the Flow designer to provide a value, but the other constraints ('Is exclusive maximum' etc) are currently only for documentation purposes. This can change in future version of Flow.
Number
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Number is a used to support floating-point values. Number supports 'Type formats'. Currently only 'float' will have an impact on runtime - causing the parameter to be treated as a 32-bit floating-point value (instead of 64 bit one). The 'Required' constraint is used to force the Flow designer to provide a value, but the other constraints ('Is exclusive minimum' etc) are currently only for documentation purposes. This can change in future version of Flow.
Boolean
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Simple type which allows true or false as value. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value.
Object
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x |
Used to send objects (instances of models) to an API. The header 'Content-Type' must be set, typically to 'application/xml' or 'application/json'. See Models for more information. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value.
File
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x |
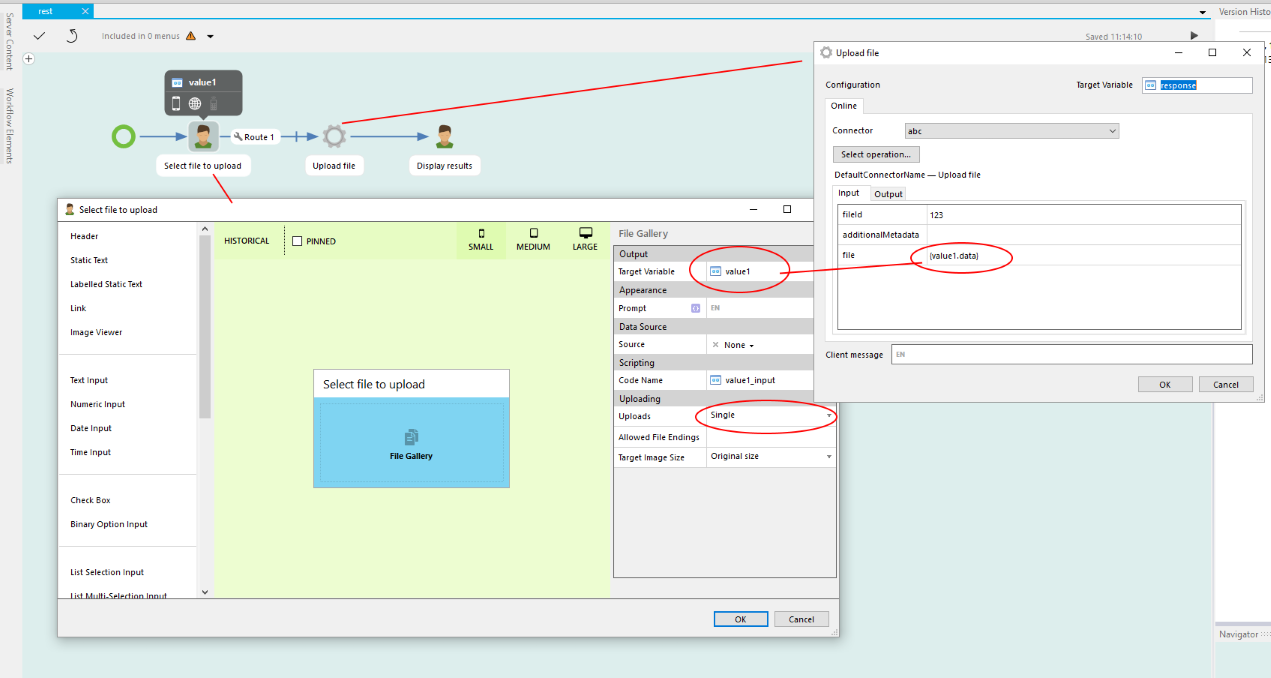
Stream
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x |
Used to send binary data to API. Similar to the 'File' parameter type, but for body parameters. From a workflow perspective used in the same way. The header 'Content-Type' must be set to 'application/octet-stream'. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value.
Array
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Arrays are supported by all parameters, but will behave a bit differently depending on the parameter type. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value. 'Unique items' constraint is only for documentation purposes at the moment, but this can change in a future release of Flow.
At it's core arrays are of course collections of something. But you must define what the collection consist of.
For query, form, header and matrix parameters the 'inner type' can be 'String', 'Integer', 'Number', 'Boolean' or 'Array'. You define how the different items of the array are separated by selecting one of the following:
- Csv. Comma separated, example: param=item1,item2,item3
- Ssv. Space separated, example: param=item1 item2 item3
- Tsv. Tab separated (''), example: param=item123
- Pipes. Separated by '|' char, example param=item1|item2|item3
- Multi. The parameter is repeated multiple times. Example for query parameter: param=item1¶m=item2¶m=item3. Multi is not supported for Path parameters.
For body you can use 'String', 'Integer', 'Number', 'Boolean' and 'Array' as well. But also 'Object'. When set to 'Object' the separation format has no effect.
When the 'inner type' is string you have the option to specify 'Available options'. The use of this is best described with an example:
Consider the operation 'GetOrdersByStatus'. As a parameter you can set the parameter 'status' with what statuses you are interested in. Available statuses are 'Pending payment', 'Processing', 'Approved' and 'Shipped'. To do this the API uses a query parameter array with csv separation. An example call would look like: 'https://store/api/GetOrdersByStatus?status=Approved,Shipped' to get all orders that are either 'Approved' or 'Shipped'. You can of course just specify a query parameter of type array with inner type string and csv separation and that is fine. You will then end up in Flow with something like this:

Either the Flow designer uses 'Single row' and provides one value or defines a table earlier in the workflow with multiple values. Either way, the Flow designer has to know which values are valid and the risk that something is misspelled etc is not neglectable.
A better way is to use 'Available options'.
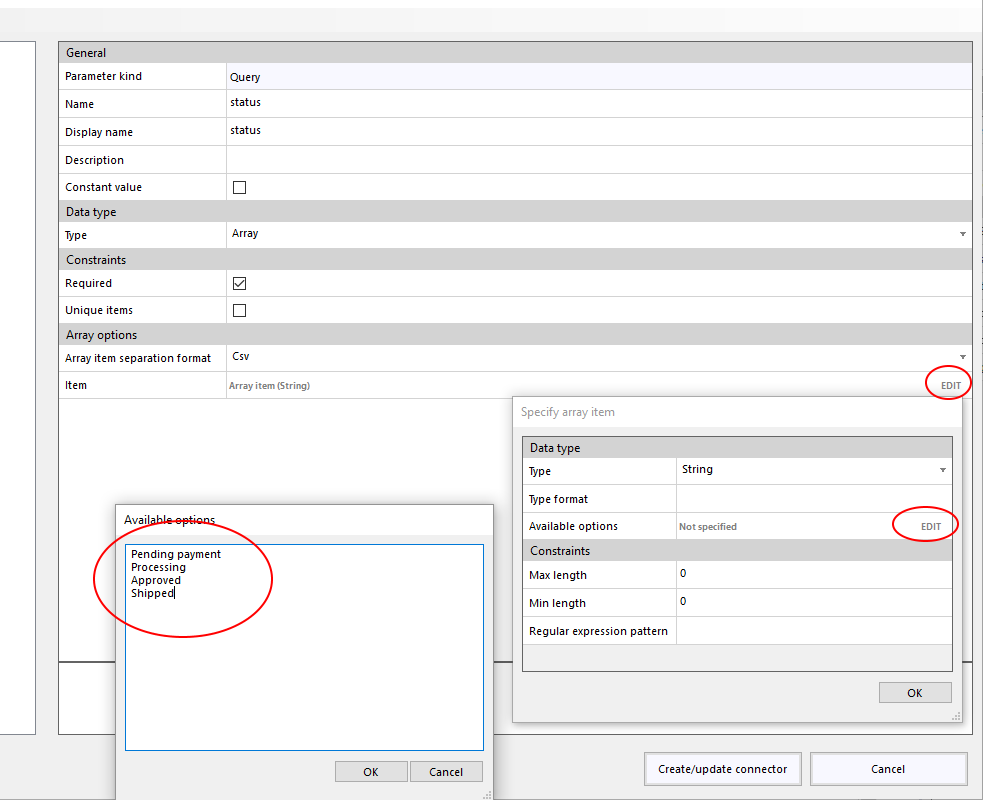
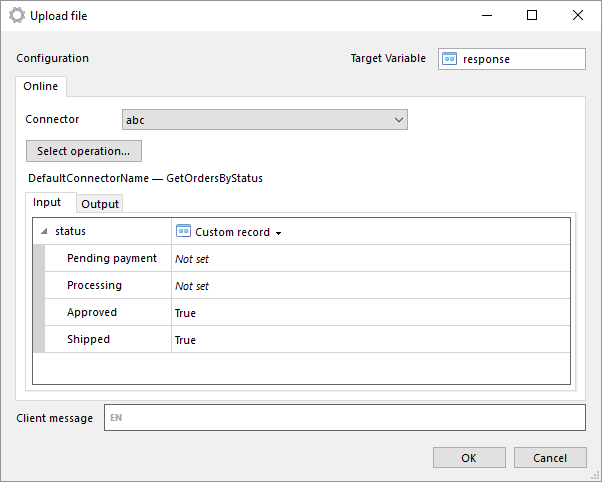
The options are identified as 'c1', 'c2', 'c3' etc, so if you want to setup the record outside of the machine step you can use those names. Example:
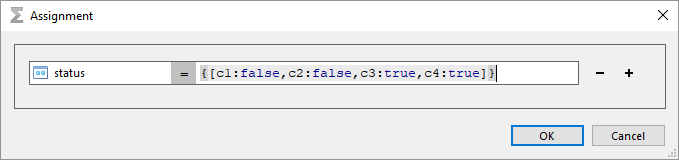
REST Project Tool
The REST Project Tool is used to define how your REST connector is going to integrate with a REST API.
The tool looks something like this:
This is a REST connector for Google Drive V3.
On the left side there is a 'Connector tree', where you get an overview over the different parts of the connector. The first node ('Google Drive V3' in the picture above) is all the operations and containers of the connector. This is what will be available in the machine step once the connector has been created. Below the first node there are different sections where you can define different features that the operations can use, such as models. Each feature is described in its own section.
Getting started
Operations
Model
Enumeration
Model transformations
Authorization schemes
Global parameters
Global outputs
In the menu you will find a couple of important features as well.
- New
Creates a new, empty, project. - Import
Lets you import an exported REST Project. You can import an entire project (optionally replacing your current project) or only parts of another project. - Export
Allows you to export parts or all of your project to file which can later be imported, for instance on another Flow Server. - Import OpenAPI (swagger) specification
OpenAPI specifications can be imported (commonly referred to as Swagger 2.0). OpenAPI 3 is not supported. Imported specifications are added to your current project.
When you are done configuring the connector, press 'Create/update connector'-button. If the connector is successfully created, the 'REST Connector Project'-window will close down and you will be back in connector configuration in Flow Studio. Do not forget to press 'SAVE' in connector configuration to save your changes to the connector.
Create directory
Creates a directory at the SFTP server. It is not possible to create several levels of directories in one step. If you want to create the directory "./dirA/dirB", the directory "./dirA" must exist. Otherwise you have to do it in two steps; first creates directory "./dirA" and the second one created "./dirA/dirB".
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to the directory to create. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete directory
Deletes specified directory. Note that the directory must be empty unless Recursive is set to true.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to directory to delete |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also delete all files and subdirectories. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if directory exists
Determains whether directory at specified path exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if directory exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
List directory
Lists all files and directories in a specified path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to list. |
| Mask | Mask to use when filtering items in directory. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B" |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Include files | Specifies whether to include files in the listing. |
| Include directories | Specifies whether to include directories in the listing. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also search in subdirectories. |
Output
A table consisting of records with the following structure:
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the file or directory. |
| IsDirectory | True if the item is a directory, false if it is a file. |
| Size | The size, in bytes, of the item. |
| LastAccessTime | Last time item was accessed. |
| LastModifiedTime | Last time the item was modified. |
| CreationTime | Time of item creation. |
Since
6.3
See also
Download single file
Downloads a file from the SFTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
| Local filename | Filename of where on Flow Server to store the downloaded file. |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download multiple files
Downloads multiple files from the SFTP server to the machine where Flow Server is running.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to downloaded files from. |
| Remote mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| File tranfer mode | Specifies how to handle if file already exists. |
| File copy mode | Specifies what to do with the file after download has been completed. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to download files from sub directories recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Download stream
Downloads a file from SFTP server and store it as Flow variable.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote filename | The name of the file to be downloaded |
Output
Simple value (binary stream).
Since
6.3
See also
Copy remote file
Copies a remote file into the selected destination.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote source path | Path where to copy from. |
| Remote destination path | Path where to copy to. |
| Overwrite if already exists | True or false. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete file
Delete a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to file to delete. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Delete files
Delete multiple remote files based on mask.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path where to delete files. |
| Mask | Mask used to filter which files to download. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Case sensitive | Specifies if mask is case sensitive (not applicable if regex is used). |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to delete files recursivly. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if file exists
Checks if a remote file exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | Path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if file exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Get size of file
Gets the size, in bytes, of remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Remote path | File of interest. |
Output
Simple value, numeric.
Since
6.3
See also
Rename file
Renames a remote file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Old path | Current name of file. |
| New path | New name of file. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload single file
Uploads a single file from the Flow Server to the SFTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local filename | File to upload. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the file. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload multiple files
Uploads multiple files from the Flow Server to the SFTP Server.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local path | Path where to upload files from. |
| Local mask | Mask used to filter which files to upload. Example "*.txt". Regular expressions can also be used by prefixing with "regex:", example "regex:[A|B].*" to list all files starting with "A" or "B". |
| Remote path | Path where to upload the files. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Case sensitive | Specifies whether to ignore casing or not. |
| Recursive | Specifies whether to also upload from subdirectories. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
Upload stream
Uploads the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream. This can for instance be used to upload data from a camera input.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Local stream | Stream to read data from. |
| Remote filename | Where to upload the data. |
| File transfer mode | Specifies what to do if the file already exists. |
| Restart position | Can be used to resume a broken transfer operation. If set to a non-zero positive value, the file being transferred is read starting from that position and is written also starting from provided position. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.3
See also
SFTP
The SFTP Connector is used to upload and download files from an SFTP server. It can also perform other operations such as creating remote directories and list files and directories on the SFTP server.
Configuration
- Address. Address to SFTP server.
- Port. Port to use, usually 22.
- Server validation. Select what kind of validation of the server that is to be used. Public key is strongly recommended.
- Authentication
- Username.
- Password.
- Client private key path. Path to file containing client private key. Note that this is relative to the Flow Server, not Flow Studio.
- Password to private key file.
- Keyboard-interactive. Use this to setup responses to challanges from the server (if this authentication method is used)
- Communication settings
- SFTP Version. Set which SFTP version to use. Default is version 3.
- Auto adjust transfer settings. Set this to instruct the connector to try to auto adjust download and upload block size and pipeline length for optimal performance.
- Pipeline length. The number of concurrent pipelines the client is allowed to use. Only valid if Auto adjust transfer settings is not set.
- Download block size. The block size to use when downloading files. Only valid if Auto adjust transfer settings is not set.
- Upload block size. The block size to use when uploading files. Only valid if Auto adjust transfer settings is not set.
- Request compression. If set, the client will explicitly require compression.
- Transfer type. ASCII or Binary (recommended), default is Binary.
- Adjust file times. If set, the original date and time values (such as last modification time and creation time) of a file will be retained after upload or download. If not set, time values will be set to when file transfer occured.
- Incoming traffic limit. This can be used to limit the bandwidth used when downloading files. Setting it to zero indicates no limit.
- Outgoing traffic limit. This can be used to limit the bandwidth used when uploading files. Setting it to zero indicates no limit.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of SFTP Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the SFTP Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
Operations
| Directory operations |
|---|
| Check if directory exists |
| Create directory |
| Delete directory |
| List directory |
| Download operations |
|---|
| Download multiple files |
| Download single file |
| Download stream |
| File operations |
|---|
| Check if file exists |
| Copy remote file |
| Delete file |
| Delete files |
| Get size of file |
| Rename file |
| Upload operations |
|---|
| Upload multiple files |
| Upload file |
| Upload stream |
Siox
Before using the Siox connector download the Siox driver from the Siox website.
The Siox Connector is used to communicate with Siox terminals. Read more on Siox website., and download Siox SDK for the documentations for all the opertations.
Configuration
- BaudRate. Symbols per seconds. ex 4800, 9600 etc.
- Serial Port. RTU connection. Example ,COM1, COM2 etc.
- Network Connection settings
- Use network connections. If you are using Serial port insted of TCP.
- IP Address. IP Address to the siox bus.
- Connection timeout(ms). The time before the connection should timeout if it cannot connect.
- StopBits. How many bits it should stop after transmisson, None, One, Two, OnePointFive(1.5).
- Port. Port to the siox bus.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of Siox Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the Siox Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
Webservice example: Connector to Microsoft Dynamics AX
This is an example of how the Web Service connector can be used to consume Microsoft Dynamics AX AIF services.
How to set up any AIF service, such as a document service, in Microsoft Dynamics AX is beyond the scope of this example, but once that has been done the Web Service connector can be used to consume it. From AX, get the URI to the WSDL of the service.
Step1
Copy the URI from AX.
Create connector of type Web Service.
Provide a name for the connector and paste in the URI. Make sure server address is correct and press "Create/update"-button
Step2
Wait for the connector to be created
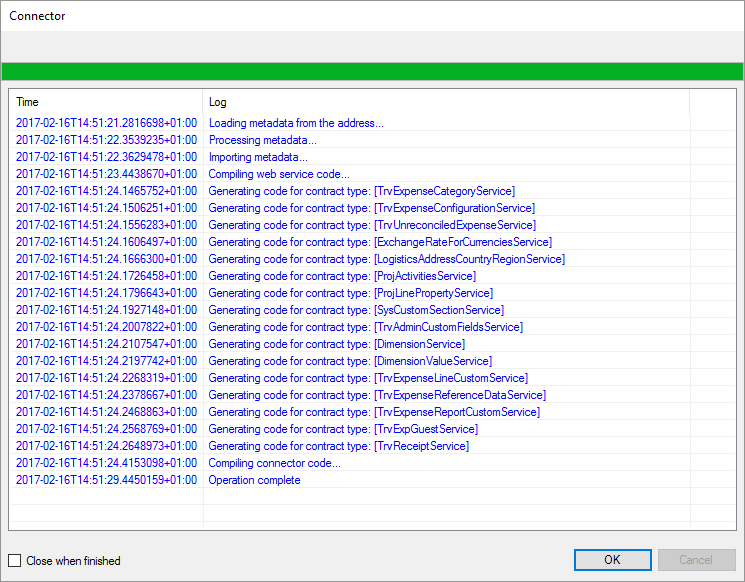
Step3
Examine the configuration. Might be a good idea to increase maxRecievedMessageSize.
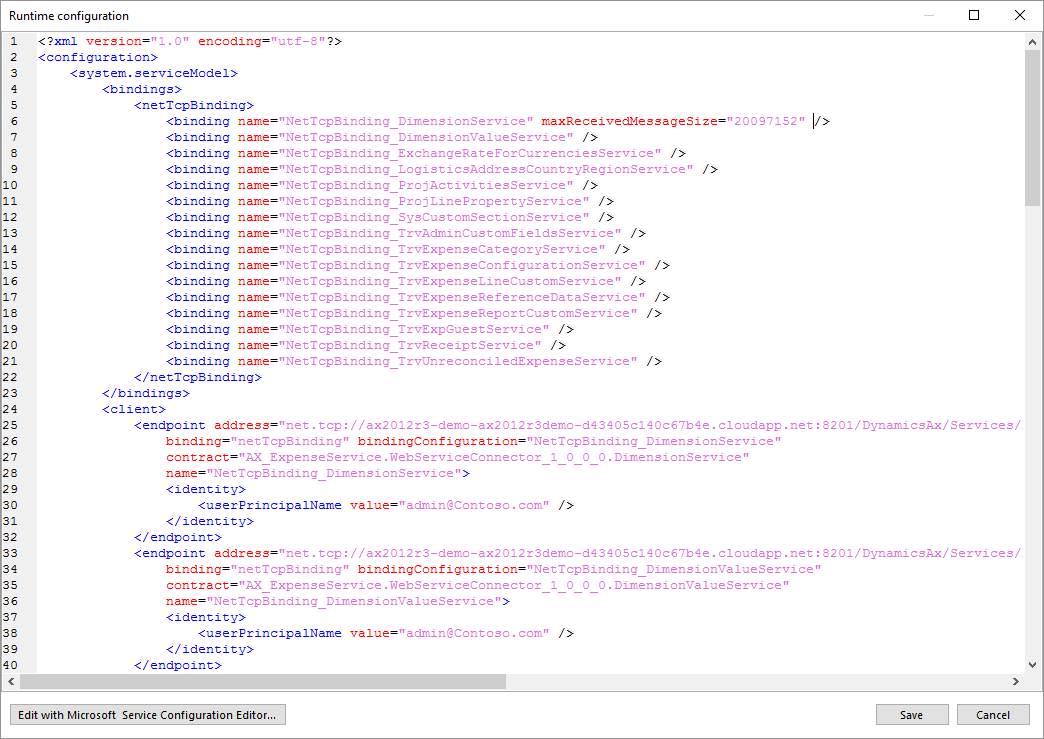
Step4
Setup Client credentials by expanding Client credentials -> Windows and enter UserName and Password and, if required, domain and impersonation level.
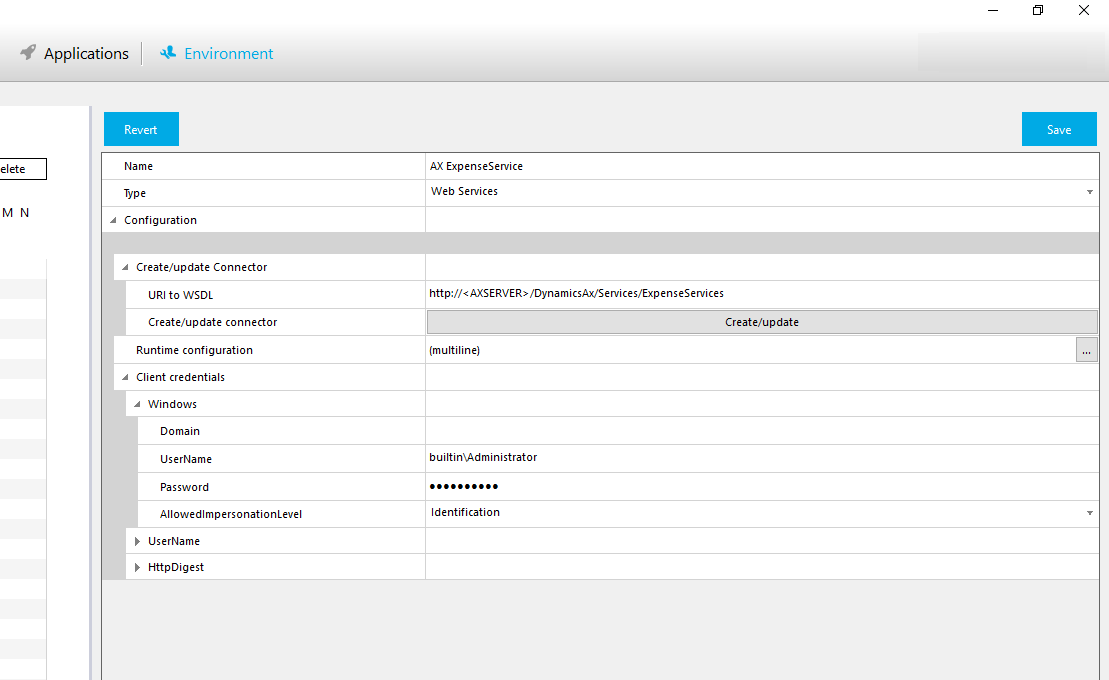
Step5
Save the configuration
The connector should now be available to be used in a Machine Step.
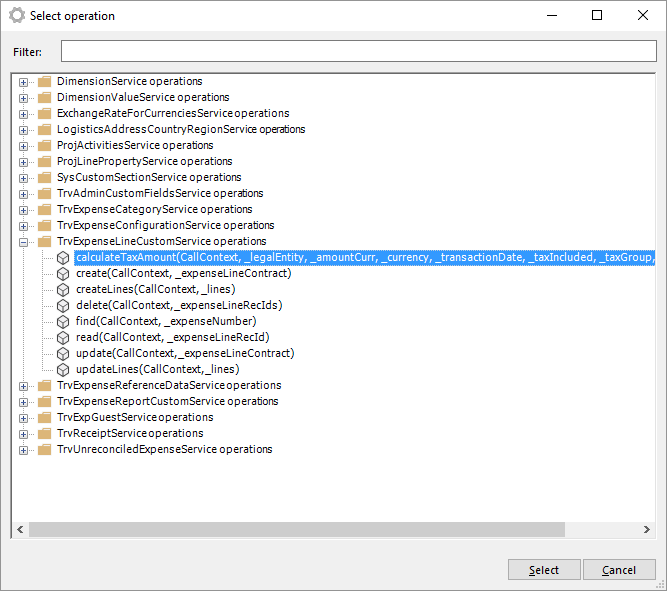
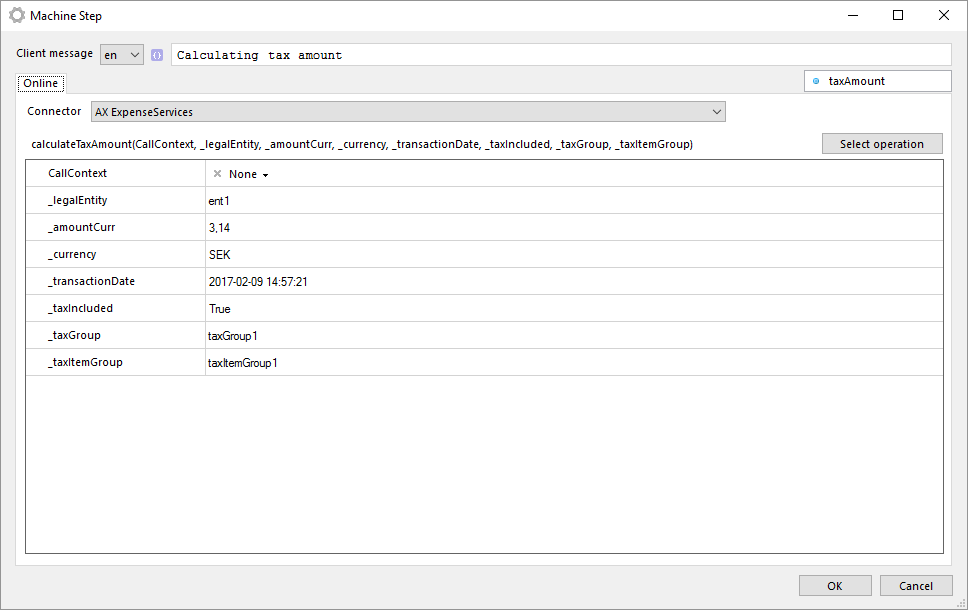
Web Service
The Web Service Connector can be used to consume SOAP based web services. It can also be used to consume WCF services that are not based on SOAP, such as net.pipe and net.tcp bindings.
Configuration
- Create/update Connector
In this section the WSDL that describes the web service is specified and there is also a button for creating the actual connector. Before a connector can be created it must have a Name specified. You must provide a valid URI to a WSDL and start Create/update before the connector configuration can be saved.
The URI can refer to a file if there are no external references in the WSDL. Note that the file path is relative to Flow Server.
If the URI refers to an http endpoint (typically it is) you can, if needed, provide user and password (and optionally domain) before starting Create/update.
Do not update the connector unless the remote service has changed. Runtime configuration
After the connector has been created a basic configuration is stored in this section.Client credentials
Setups the client credentials to use when communicating with remote service.
Example
Web Page Submit
The Web Page Submit Connector can be used to send HTTP POST and GET requests to a given url. At least one parameter must be sent.
Configuration
- Authenication URL
- User name
- Password
- HTTP Headers
- Encoding
Communication
Under communication, all connectors related to generic communication protocols are listed, with information about configuration to setup the connector and how to use it.
BarTender 2016
The BarTender connector can be used to integrate with BarTender 2016 R8, typically to print BarTender documents.
32-bit version of BarTender 2016 R8 Automation Edition or Enterprise Automation Edition needs to be installed on the same machine as Flow Server.
Configuration
Path to look for .btw files in
Specifies where to find BarTender documents. Required in order to print documents (unless using BTXML). Must be a path that is accessible for the user specified in 'Design time identity' while developing workflows and accessible for the runtime user (either set per Flow user or in 'Global runtime identity') when executing the workflow. If no identity is provided, the identity of the application pool running Flow Server is used.Default printer
Name of printer to use. Leave empty to use the printer set on BarTender document. The printer can also be overridden in print operations.Global runtime identity
Identity of user to run BarTender operations as. If any Domain is specified here it will be applied also on identity specified on Flow user. If no runtime identity is provided, the identity of the application pool running Flow Server will be used.Design time identity
Identity of user to use while designing workflows. Never used in runtime. If left empty (i.e User not specified) and Global runtime identity is provided, Global runtime identity will be used also while designing workflows. If no runtime identity is provided, not design nor runtime, the identity of the application pool running Flow Server will be used.Cache metadata
Specifies whether the connector should cache any metadata regarding what BarTender documents there are and what parameters they have.
Example of usage, embedded data
This is a an example of printing the label "Caterpillar\Master label.btw" which can be found among the example labels installed with BarTender.
The label looks like this in BarTender:
It can be configured with embedded data, 1L, 3S, 4S and so on.
If you select this BarTender document in Flow Studio it will look like this:
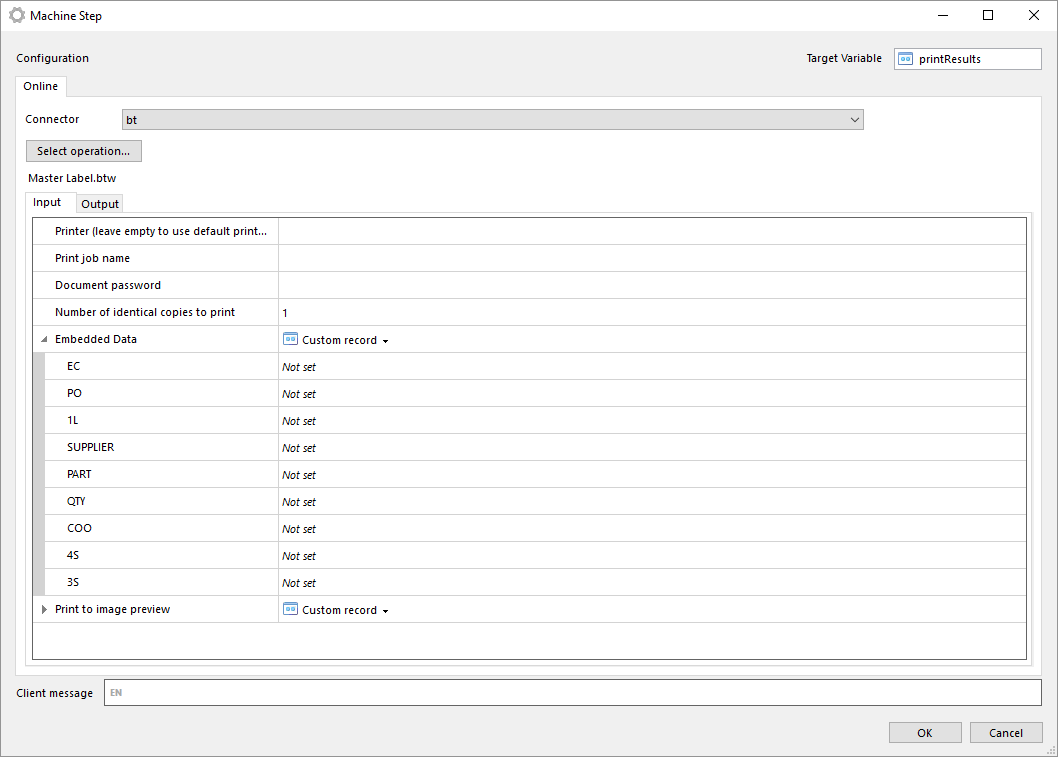
As you can see, the Embedded data is set to Custom record, and this is where you can control the data input to the BarTender document.
If we provide it with some random data:
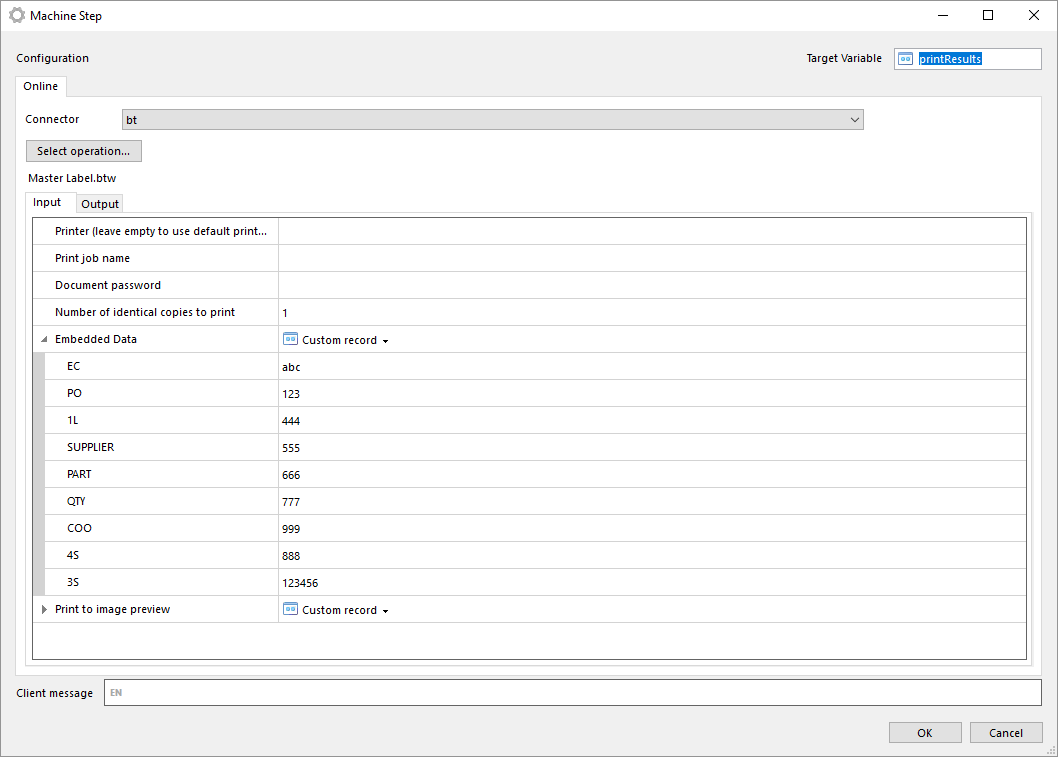
And then print the labels, in this case to an image preview, the output will look like this:
Example of usage, text database
This is a an example of printing the label "EU Energy Labels\EU Energy Television A 2010-1062-2011.btw" which can be found among the example labels installed with BarTender.
The label looks like this in BarTender:
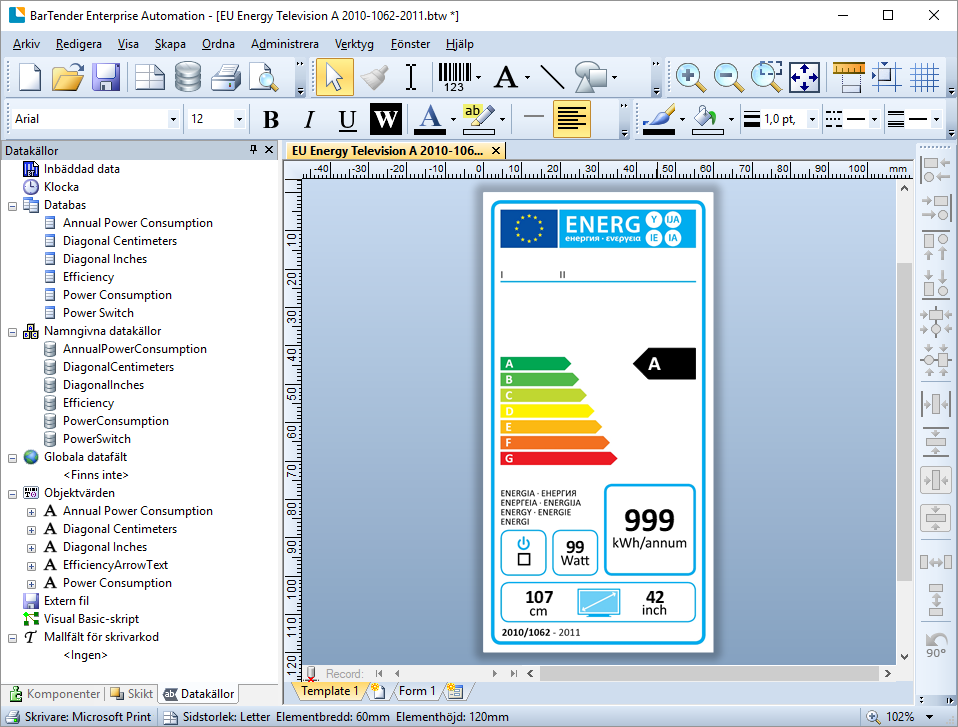
It takes a text file as data input. Example file looks like this:
Efficiency;Annual Power Consumption;Power Consumption;Power Switch;Diagonal Inches;Diagonal Centimeters
0.28;10000;80;1;32;81
0.40;22222;120;0;32;81
0.50;23456;140;0;27;69
0.70;90009;160;0;27;69
0.85;90809;30;1;42;107
0.95;90909;40;1;42;107
1.10;99999;50;0;20;51So seven (one per line) labels will be printed.
If you select this BarTender document in Flow Studio it will look like this:
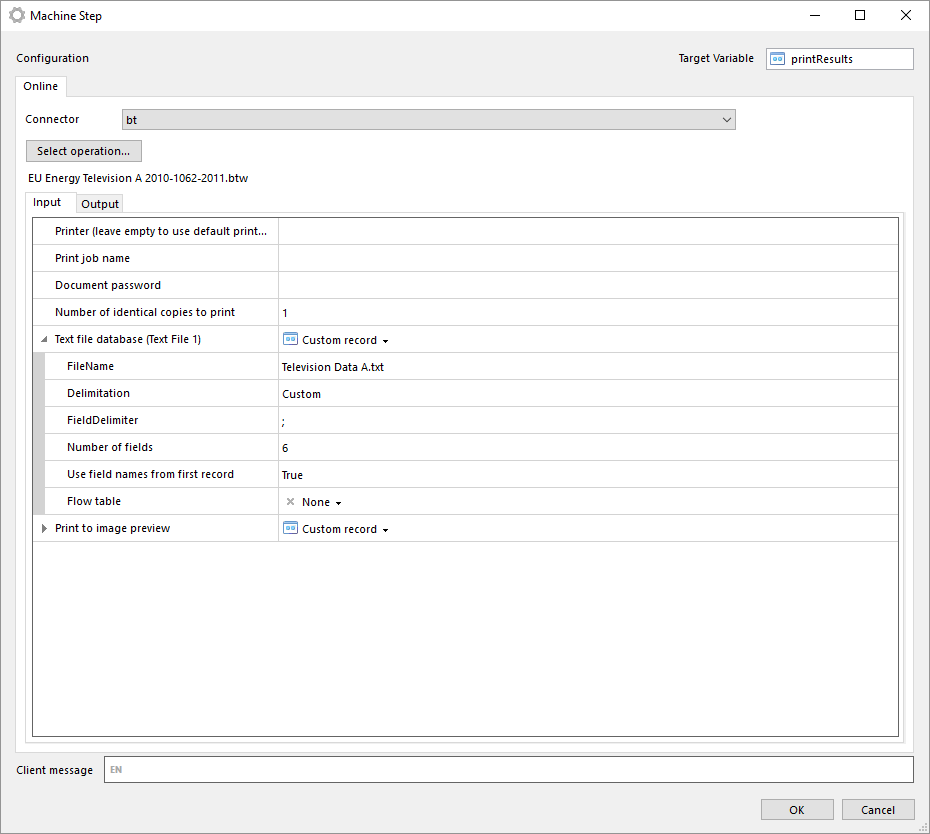
As you can see, the Text file database (Text file 1) is expanded, and this is where you can control the data input to the BarTender document. You can for instance select another text file than 'Television Data A.txt'.
You can also map data from a Flow table to the document. Let's do that. Consider the following flow table:
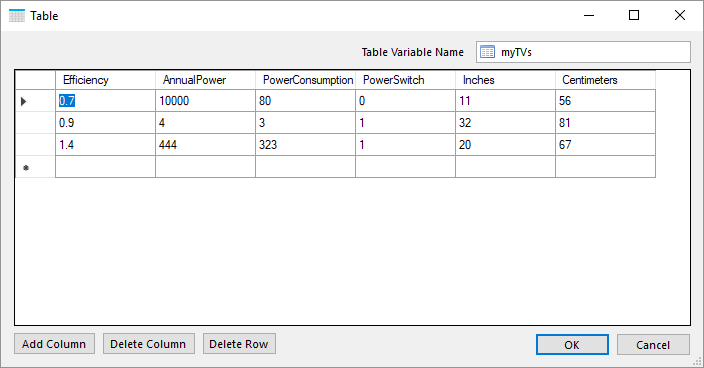
So mapping this to the BarTender document can be done like this:
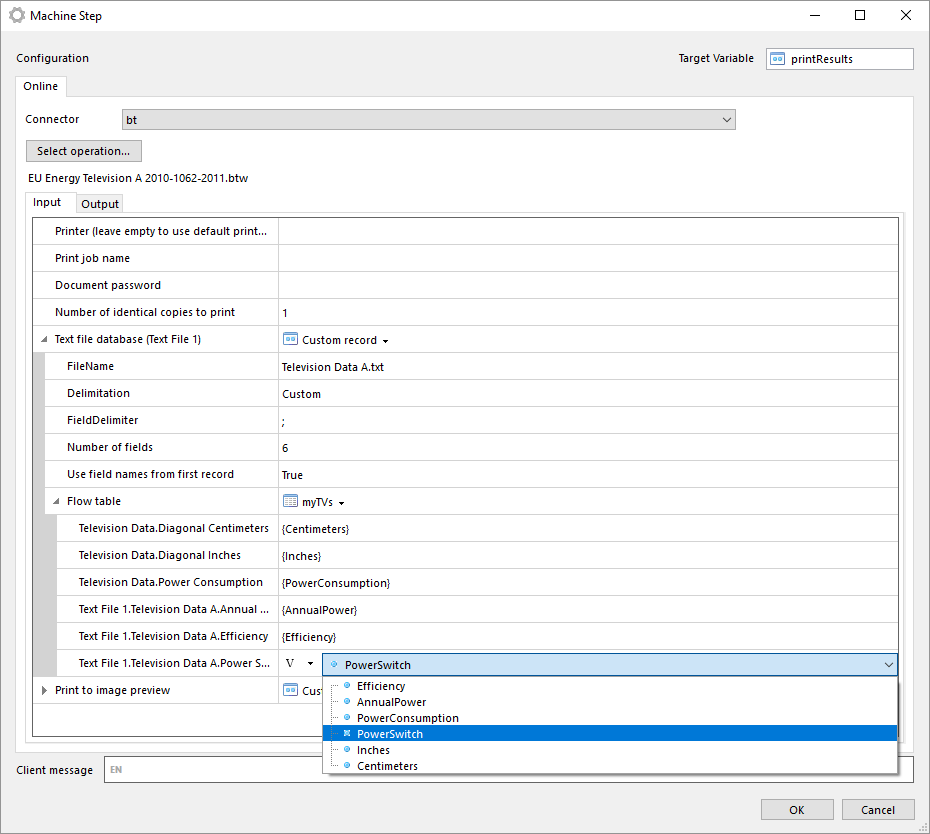
It is important that the data types matches, for instance will sending in a text to any of these members generate an error. You can see the data type in BarTender. Unfortunately there is no way to know the types from Flow Studio. If you choose to map to a Flow Table, the file ('Television Data A.txt' in this case) will be ignored.
If you then print the labels, in this case to an image preview, the output will look like this:
The values does of course not make sense, but hopefully this has given you an idea how to map your data to BarTender documents.
List printers
Lists all printers available.
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a table with information about printers |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Structure of Results
ResultsErrors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Manually select BarTender document
With this operation you can manually select a BarTender document from your local file system.
The file is stored in the machine step and is not in any way synchronized with the file in your local file system. Once the file has been selected you can export the file by clicking on Export file....
Note that if you select another operation in the machine step the document will be lost and has to be selected from the file system again.
The same input and outputs as 'Print' applies, see Print for more information.
Print BarTender Document
Prints a BarTender document to specified printer or to an image (printing to image requires Enterprise Automation Edition).
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Printer | Printer to print to, leave empty to use default printer |
| Print job name | Name of print job, can be omitted |
| Document password | If applicable, the password to use in order to print the document |
| Number of identical copies to print | If supported, specifies how many identical copies to print |
| Embedded data | Values to embedded data can be provided here |
| Text file database | If the document reads data from a text file, this section can be used to configure it |
| Database connection | If the document reads data from a database, this section can be used to configure it |
| Print to image preview | This section can be used to configure that the document should be printed to an image instead of a printer. Requires Enterprise Automation Edition of BarTender |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a message from BarTender, typically information about the printing |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
| 1000001 | Failed to print. |
| 1000002 | Failed due to timeout. |
Print from BTXML script (from file)
Sends a BTXML Script to BarTender.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Filename | Full path to file containing BTXML Script |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a record with the xml response from BarTender and a table with messages from BarTender |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Structure of Results
Results- Text
- ID
- Severity
- Category
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Print from BTXML script (from string)
Sends a BTXML Script to BarTender.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Script value | String containing the BTXML Script |
Output
Record with information about whether operation failed or not.
| Member | Description |
|---|---|
| Results | Contains a record with the xml response from BarTender and a table with messages from BarTender |
| HasFailed | Whether operation has failed or not |
| ErrorMessage | A description of the failure, if any |
| ErrorCode | An error code related to operation failure. Is 0 if no failure occured |
Structure of Results
Results- Text
- ID
- Severity
- Category
Errors
| Error code | Description |
|---|---|
| 1000 | Unspecified error. |
Html to PDF Connector
Use the PDF connector to create PDF files in your workflow. The connector uses Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) to define the layout of your PDF pages and fully supports using FlowScript.
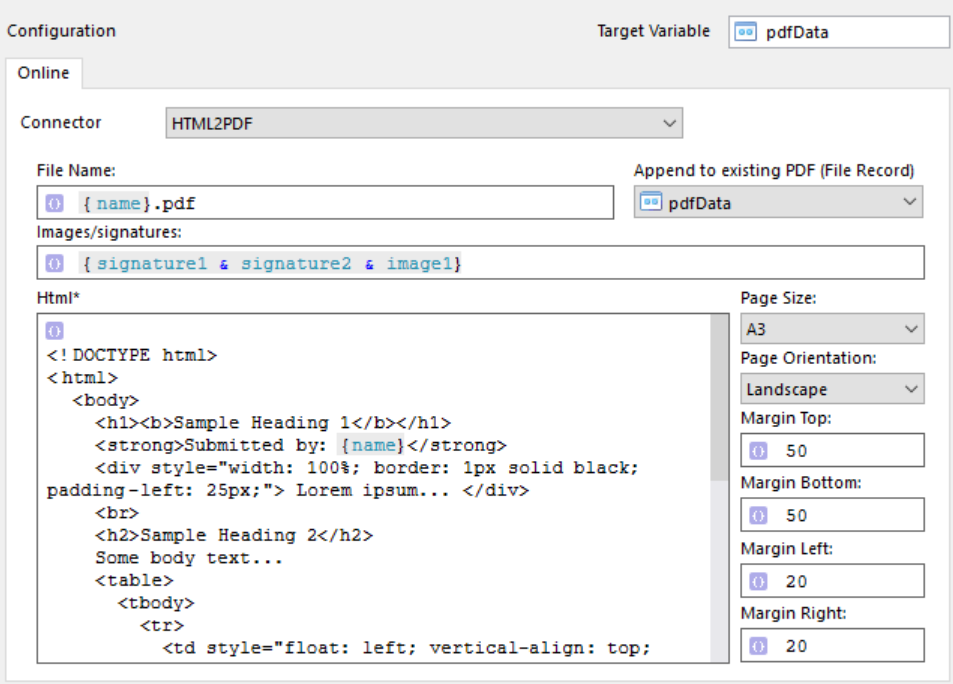
Connector Output
The output from the connector is a standard file record: [filename:the_file_name, data:binary_pdf_data].
General Tips & Tricks
In most use cases, you want to take control over the page breaks in your document. In order to achieve this, you need to specify a maximum length for all dynamic data in your workflow and specify the height of the elements which contains the dynamic data using the HTML DOM Style height property. If you do not to this, the document will grow with its content and you might get undesirable page breaks.
Tip: Create a simple workflow with a PDF connector and a user step. In the user step, add a file gallery with the generated PDF document(s)
and use the workflow for designing and debugging your page layouts.
Another good practice is to use one machine step per page and then supply the previous PDF document (file record) as input parameter for the next PDF task (see Append a new page to an existing PDF below).
Settings
This chapter describes the available settings in the PDF connector.
File Name
This string defines the filename-key value of the target file record (see Connector Output).

Append new page to an existing PDF
The connector optionally takes a file record containing a PDF file as an input variable. If suppied, the new page(s) created in the current machine step will be appended to the existing PDF file. The target variable will contain the merged PDF file as a standard file record.
To keep the file name from the previous PDF step, just re-use the filename value from the previous PDF file record:

Margins
The margin size in points (one inch = 72 points).

Page Size
Page Orientation
Choose between Portrait and Landscape orientation. The default orientation is Portrait.
Images / Signatures
If you need to display images or signatures in your PDF pages, you need to make sure to have them available in your flow as file records. Signatures from the signature input provider is by default a file record with some extra fields and are supported by the PDF connector. The Images / Signatures field takes either a file record or a table of file records. The image below gives an example of two signature records being passed to the PDF connector.
In order to be able to differentiate between the images/signatures in the HTML code, you might need to override the filename
component of the file records and give them unique and identifiable file names prior to passing them to the PDF connector. The image below shows a file name being overriden in an assignment step.
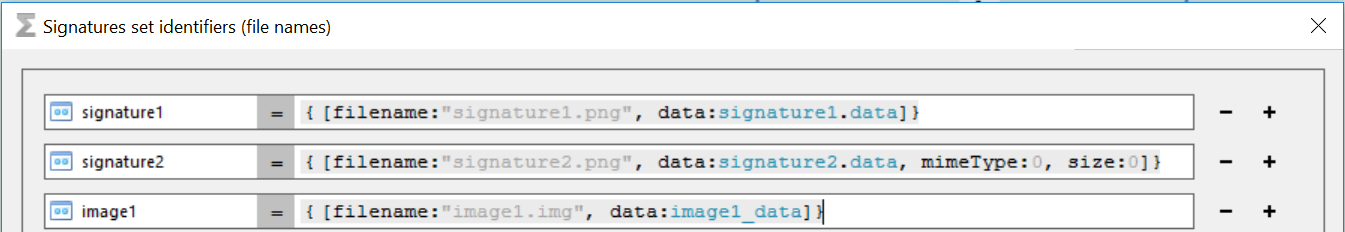
To position your image/signature in the document, the HTML IMG tag is used. I.e. <img src=your_file_name.jpg
height=40
>. See the image under the HTML headline below.
HTML
The document layout is defined using HTML. It's recommended to keep the code as simple as possible and build the layout using a bottom-up approach. If you are new to HTML, visit https://wordhtml.com/. However if you use the generated code directly you will get disappointed as there are some important aspects to keep in mind. Most importantly, you need to use percentages instead of absolute values for width. Keep the total width of your columns at about 95%.
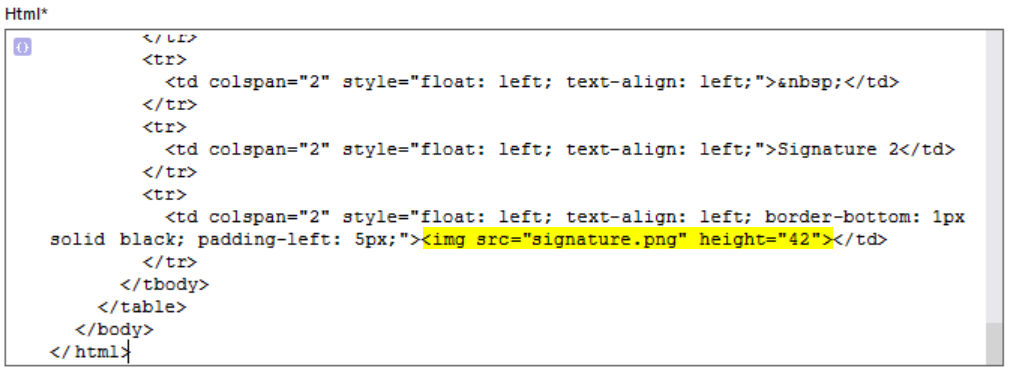
NiceLabel Connector
Configuration
Set up of NiceLabel Automation to accept Flow request.
- Start NiceLabel Automation Builder and create new configuration:
- Select TCP/IP Server Trigger:
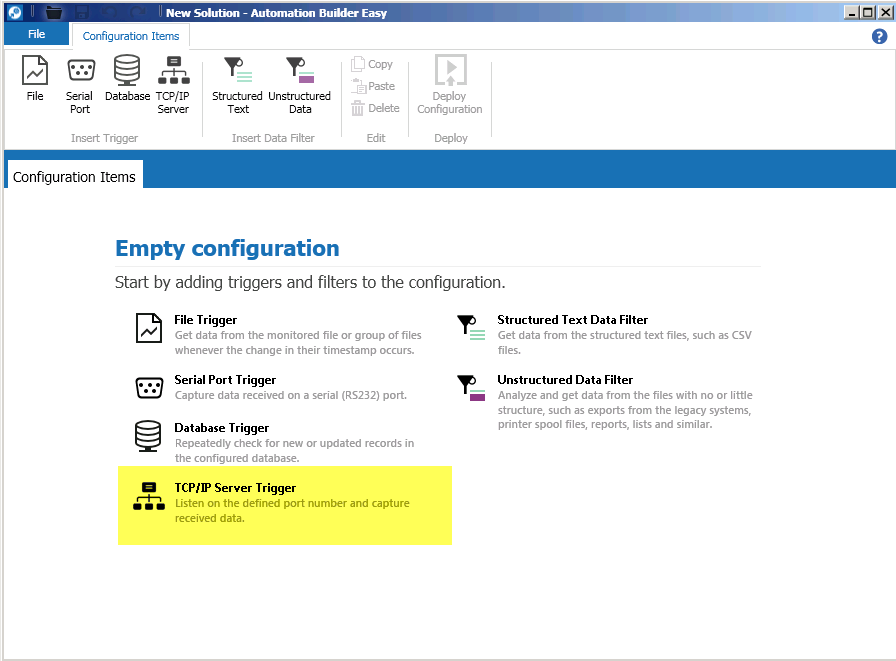
- Note Port number (will be used in Flow configuration):
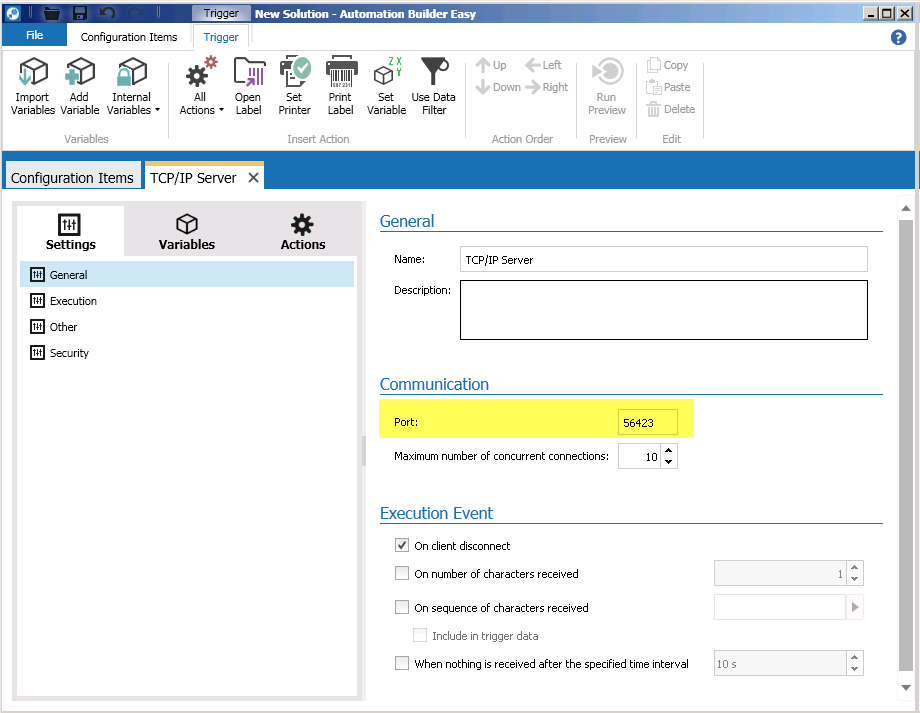
- Go to Variable tab on TCP/IP Server:
- Select DataFileName from Internal Variables:
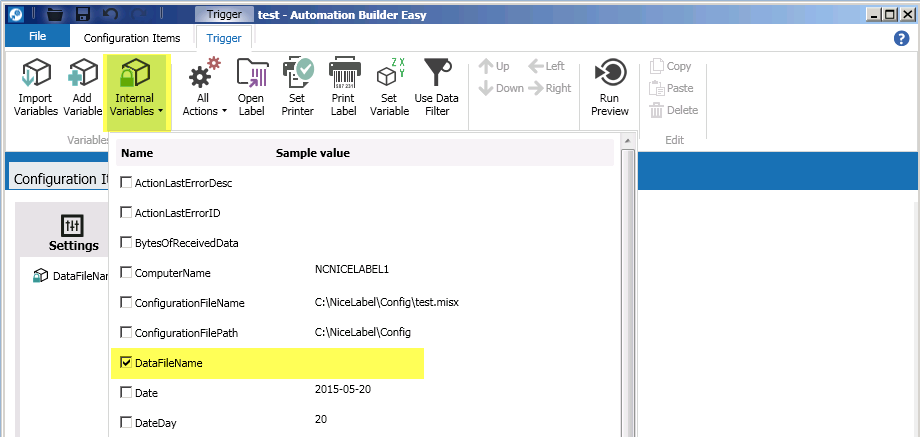
- Go to Action tab on TCP/IP Server:
- From All Action - select Run Command File:
- Select variable DataFileName as File name. Make sure that File Type is XML File:
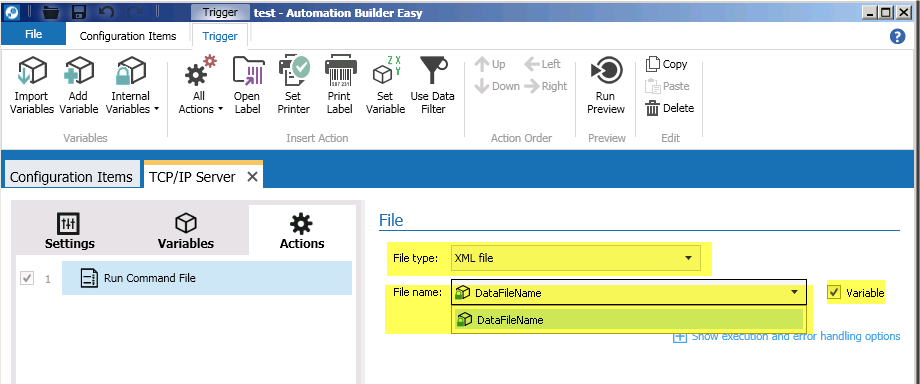
- Save configuration to some suitable folder.
- Start Automation Manager and select saves configuration:
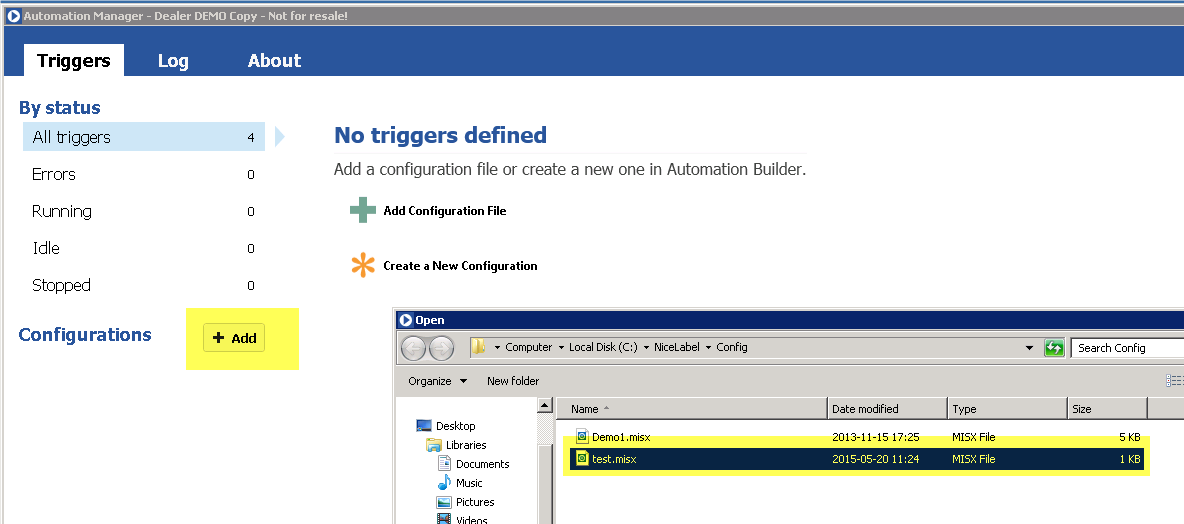
- Start configuration process:
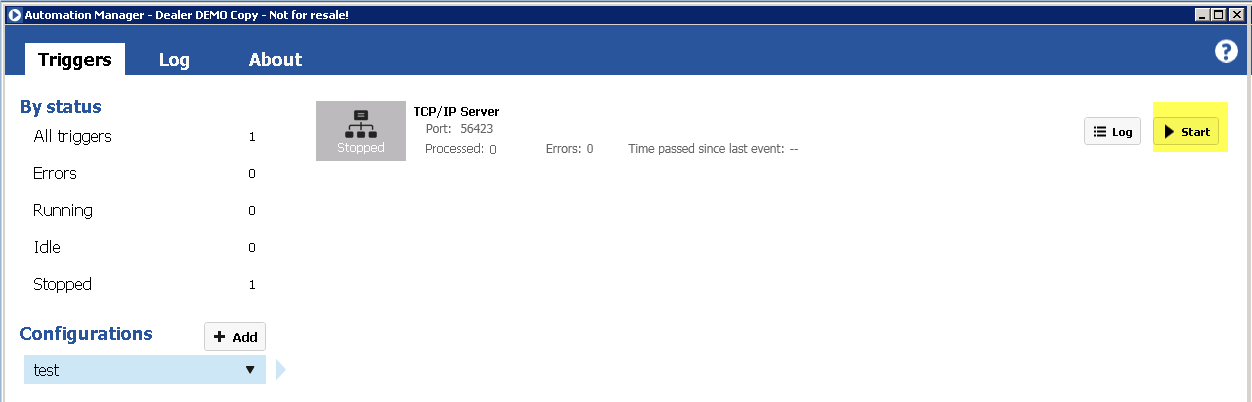
- Configure NiceLabel connector in Flow. Use TCPIP port number from step 3:
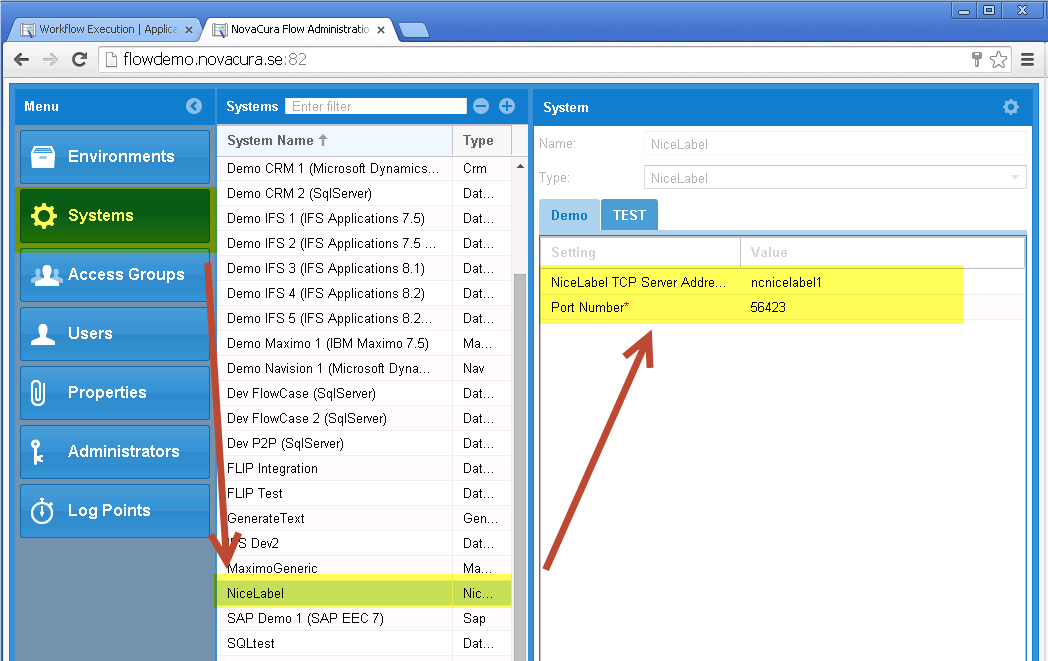
- When request is send from Flow, trigger will execute it and status will be changed:
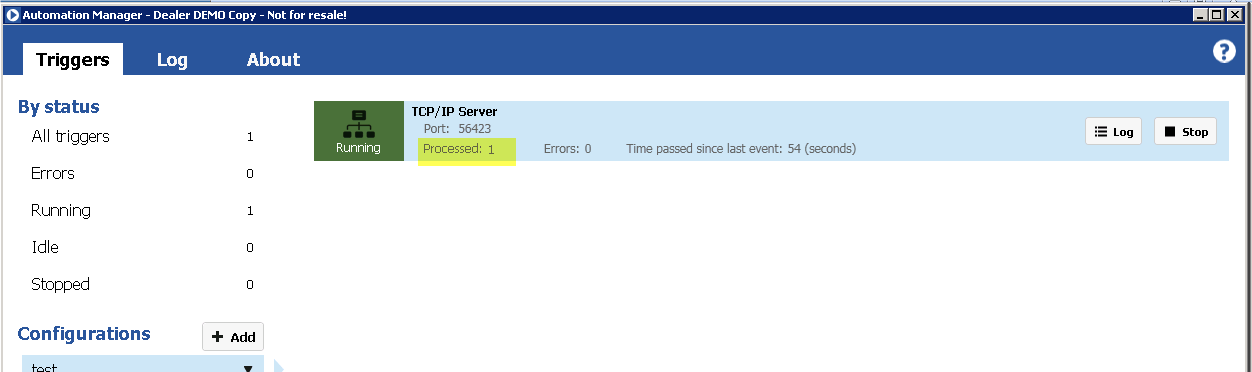
- Example flow looks like this:
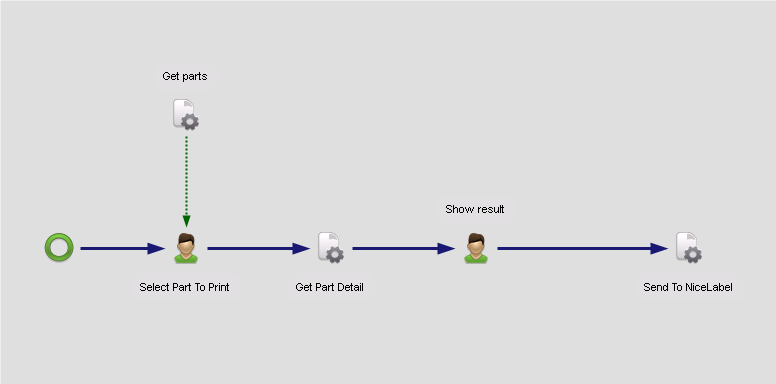
- Send To Nice Label task is set up like this:
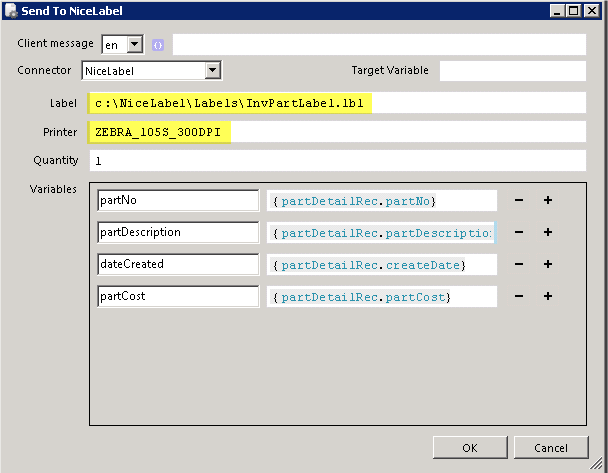
Label file and printer need to be available on the NiceLabel server.
Use the NiceLabel connector
This instruction assumes that following programs/components are installed:
- NiceLabel Automation
- NiceLabel DesignPro (configured label printers is recommended)
- Novacura Flow5 with configured NiceLabel connector
- Start NiceLabel DesignerPro and select to create new label. Select the printer and label size you are using in the Wizard that opens automatically.
- Add variables; It is important to set correct size for variables, if you send data that exceed the defined size, NiceLabel will fail to print the label.
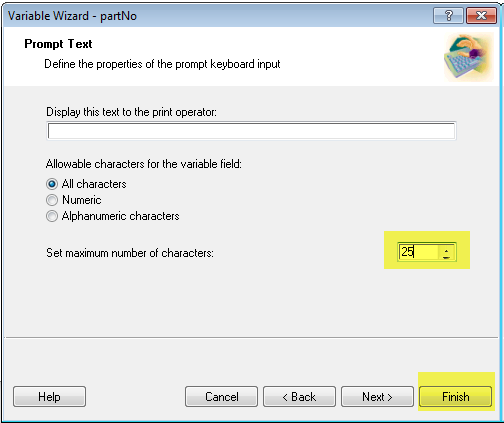
- Note names of all variables:
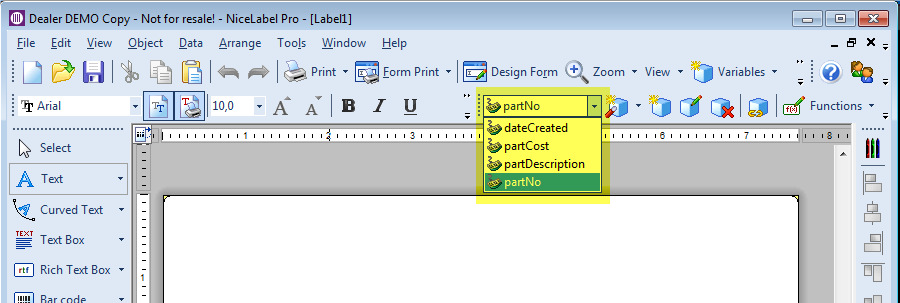
- Design the label layout using created variables.
- To add a barcode do as follow:
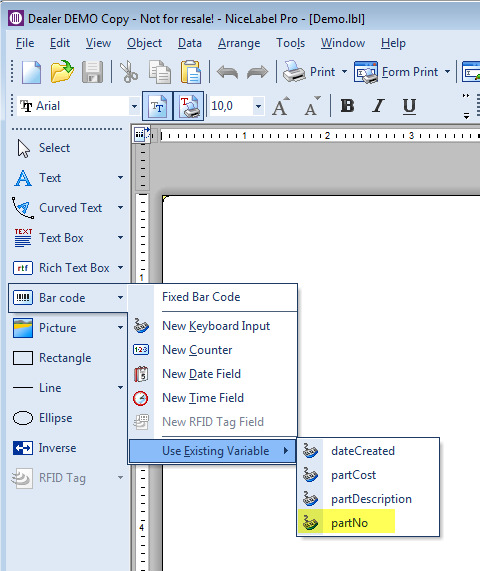
- To add a text box do as follow:
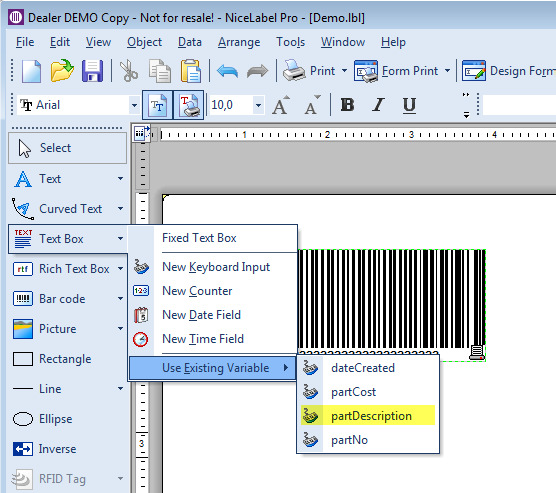
- Save the label file to folder on server that runs NiceLabel Automation.
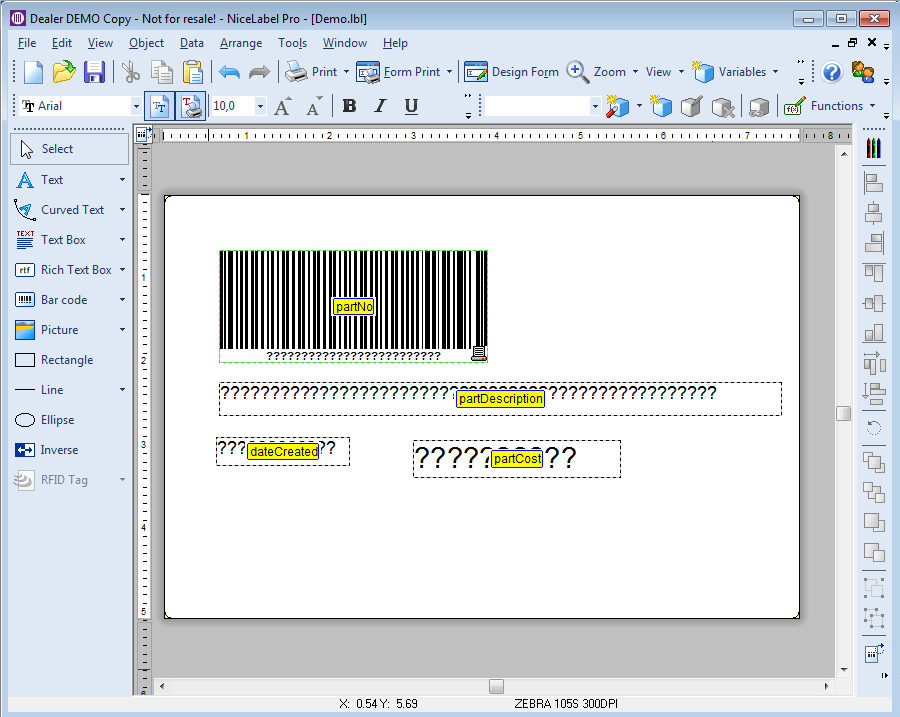
- Add Flow machine task and configure it as NiceLabel connector.
- Bind variables from the label to local variables in the flow. Variable name in NiceLabel are case sensitive. Label path is relative to NiceLabel automation server (local map on that server).
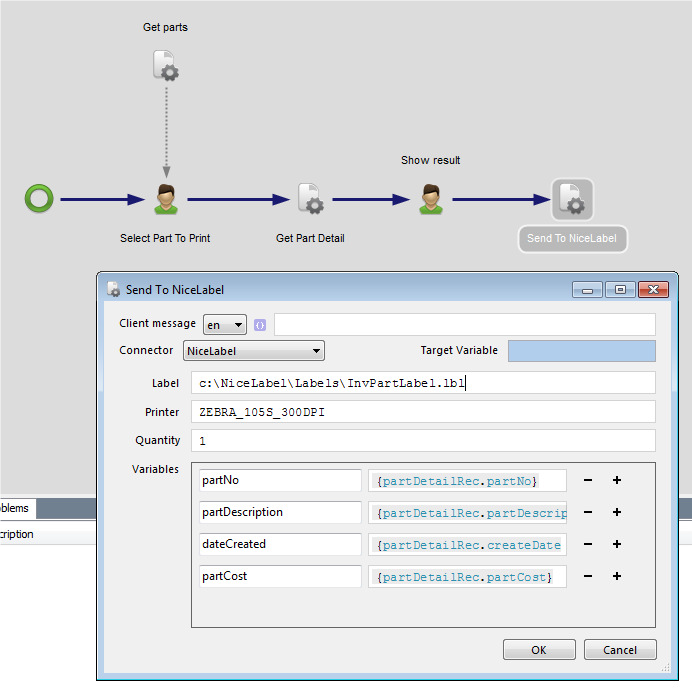
- Save flow and execute. Check status on NiceLabel Automation server.
Printing
Under printing, all connectors related to printing are listed, with information about configuration to setup the connector and how to use it.
Custom Connector
Flow has support for using third party .net assemblies. All public static methods with primitive types as arguments can be executed from a machine step in any type of workflows.
Follow these steps to setup a custom connector:
- Run NovaCura.Flow.Connector.Wrapper.exe from your command line console.
- It is located in Flow Designer program folder.
- First argument is output connector dll name, example: CustomConnector.dll
- Second argument is input assembly path.
- If input assembly has dependencies to other assemblies those can be entered as arguments. For example: NovaCura.Flow.Connector.Wrapper.exe CustomConnector.dll CustomAssembly.dll CustomUtil.dll
Copy output dll to the current studio version (%appdata%\{{version}}) and to bin/CustomConnectors* folder located in Server installation folder.
Add a connector element to CustomConnectors.xml located in bin/CustomConnectors folder in Server installation folder.
<!-- Change 'species' to a unique technical name --> <!-- Change 'displayName' to a suitable display name --> <!-- Change 'assemblyname' to the name of the output dll exluding .dll, in the example below the file is named CustomConnector.dll --> <connector species="custom_connector_name" displayName="DotNet API Custom Connector" assemblyname="CustomConnector" type="NovaCura.Flow.Connector.Wrapper.ConnectorWrapper" uitype="NovaCura.Flow.ApiConnector.UI.ApiConnectorUI" uiassemblyname="NovaCura.Flow.ApiConnector.UI" />Start Flow Designer and verify that a new connector type with the previous specified display name exists in Connectors page under Environments when adding a new connector.
Add the new connector and enter a suitable name.
The new connector should now exist in all machine step configurations.
Read/Write to Flow Environment
The Flow Environment Connector can be used to read information from the flow 6 database, it can also write new data to said database.
The Flow Environment Connector can be used to read information from the flow 6 database, it can also write new data to said database.
Configuration
- Url: Flow server url (example: http://flowserver/novacura.flow.server/)
- User: Flow username that can read and write in the environment.
- Password: Username password in the flow environment.
- Storage Service Url: Flow storage service url (example: http://flowserver/NovaCura.Flow.Storage.Service)

Operations
These are the functions that the connector supports, the flow connector can fetch data and write/update data to the flow 6 database. All operations either returns a table, row or a true/false boolean depending on if the operation was successful or not.
Connector
- Get connector name and species - Fetches a table of each connector with its type (species) and name.
Language
- Get Languages - Fetches a table of all languages set in the environment.
- Add or update language - Set a new language with two parameters/use record with parameters in it:
Code: Language code e.g "SV"Name: Name of the language e.g "Swedish"
- Delete Language - Delete an existing language set in the environment/use record with parameter in it:
Code: Language code e.g "SV"
Properties
- Get properties - Fetches all properties.
- Get user properties - Fetches all properties their types and values connected to the user ID provided:
User ID: The Flow User you wish to get property information from.
- Get user type properties - Fetches the name of all properties that are not global.
- Get global type properties - Fetches the name of all properties that are global
- Add property - Adds a new property:
Name: the name of the propertyType: table or textColumn only used in table: name of the column/sScope: global or userValue only used in global scope: static value
- Get property types - Returns what types of properties that are present in the environment.
- Get property scopes - Return what property scopes that are present in the environment.
- Delete property - Deletes a property using the property name:
Name: the name of the property that is to be deleted
- Set value of global property - Sets the value of a global property:
Name of property: the name of the property that the value is added toNew value: the value of the property
Roles
- Add or update/delete Role Group - Adds/deletes or update an existing role group:
Group ID: Id of the role groupGroup Name: Display name of the role groupInherit Children: true/false if the role group will inherit children
- Add roles to Role Group/Delete roles from role group - Adds/deletes roles to a role group:
Group ID: id of the role group the roles will belong toRoles: a table containing the columns "Path" and "DisplayName"Path points towards the Rolegroup/Role e.g "Administrators/ITadmins" where Administrators is the rolegroup and the ITadmins is the role. Displayname is the displayname of the role
- Get Role group by group ID - Returns a row containing Name, DisplayName, Inheritchildren and a table containing all role paths.
- Get role groups - Returns a table containing Name, DisplayName, Inheritchildren and a table containing all role paths.
- Add/delete roles to user - Assigns/deletes a role to a user:
User ID: User ID that is to receive the roleA table containing: Path - path to the role in the format "RolegroupID/Role" DisplayName - The displayname of the role
- Get assigned user roles - Returns a table with Path and DisplayName columns.
Users
- Add or update user/from record - Adds or updates a user:
Name: mame of the userActive: true/false if the user is activeUser ID: the User ID of the userAccess level: sets the access level of the user e.g "Work"Group: assigns the user to a groupType: assigns the user to a user-type e.g "FullUser"Password: sets a password for the userEmail: sets the email for the userLanguage: sets the language of the user by using lang codes e.g "SV"
- Delete user - Deletes a user in the environment:
User ID: which User ID that is to be deleted
- Get user by User ID - Returns a row with all user values.
- Get access levels - Returns a table with all access levels.
- Get types - Returns a table with all types.
- Get users - Returns a table of all users.
- Get user groups - Returns a table with all user groups.
- Set value of property on user - Sets the value of a property on a user:
User ID: the user to receive the property valueProperty Name: the name of the propertyValue: the value that is to be added (tables are not supported yet)
- Get value of property on user - Returns the value of a property:
User ID: the user to fetch the property fromThe property name to fetch the value from
- Set connector properties for user - sets the login/password for the connector:
User ID: the user id that will get the connector login/password addedConnector Name: the connector that is getting values addedConnector Username: the username for the connectorConnector Password: the password for the connector
Create directory
Creates all the directories at specified path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to create. Allow subdirectories on path will also be created if they do not exist. |
| Allow Everyone to have full control over directory | If set to True, all users have full control over directory. If set to False, only the user the Connector is running as can access the directory. Default True. |
Output
Simple value containing the path to the newly created directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Delete directory
Deletes directory at provided path. Directory must be empty unless 'Also delete all subdirectories (and files)' is true.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to delete. |
| Also delete all subdirectories (and files) | If set to True, all files and subdirectories will be deleted. If set to False, the directory must be empty in order to delete it. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if directory was successfully deleted. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Delete files in directory
Deletes all files in directory matching specified pattern.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to the directory to delete files from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match files against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. Default value "*". |
Output
Simple value, number of files deleted.
Since
6.3
See also
Check if directory exists
Determains whether directory at specified path exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to check. |
Output
Simple value,'True' if directory exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Get directory modification times
Gets a record containing directory modification times.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get modification times from. |
| As UTC | True to get the modification times in UTC |
Output
Record with members 'CreationTime', 'LastWriteTime' and 'LastAccessTime'.
Since
6.0
See also
Get all subdirectories of directory (full path)
Gets the full path of all subdirectories of given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get file names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match directories against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. Default value "*". |
| Also get directories in subdirectories | Specifies whether to also include directories in subdirectories of Path. Default value False. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is a full path to directory in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Get name of all subdirectories of directory
Gets the names of all directories in given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get directory names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match directories against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is the name of a directory in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Get name of files in directory
Gets the names (including extension) of all files in given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get file names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match files against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is the name of a file in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Get files in directory (full path)
Gets the full path of all files in given directory.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get file names from. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Search pattern | Pattern to match files against. Supports wildcards * and ? but not regular expressions. Default value "*". |
| Also get files in subdirectories | Specifies whether to also include files in subdirectories of Path. Default value False. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is a full path to file in given directory.
Since
6.0
See also
Move directory
Moves a directory to a new location.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source path | The path to directory to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Destination path | The path to directory to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Overwrite destination directory if it exists | If set to True and destination path already exists, it is overwritten. If set to false and destination path already exists, no move operation is done. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if directory was successfully moved. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Appends all lines to file
Appends all provided lines to a file. If the file does not exist, it is created.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to append lines to. |
| Lines | Lines to append. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the lines in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Appends all text to file
Appends all provided text to a file. If the file does not exist, it is created.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to append text to. |
| Text to append | Text. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the text in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Copy file
Copies a file to a new location.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source | The file to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Destination | The location of the file. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Overwrite if destination file exists | If set to True and destination file already exists, it is overwritten. If set to false and file already exists, no copy operation is done. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file was successfully copied. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Delete file
Deletes file at provided path.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to file to delete. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file was successfully deleted. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Check if file exists
Determains whether file at specified path exists.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to the file to check. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file exists. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Get files modification times
Gets a record containing files modification times.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | The path to get modification times from. |
| As UTC | True to get the modification times in UTC. |
Output
Record with members 'CreationTime', 'LastWriteTime' and 'LastAccessTime'
Since
6.0
See also
Move file
Moves a file to a new location.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Source | The file to move. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Destination | The location of the file. Path can be UNC path or local file path. |
| Overwrite destination file if it exists | If set to True and destination file already exists, it is overwritten. If set to false and file already exists, no move operation is done. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if file was successfully moved. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.0
See also
Read all bytes from file
Reads all bytes from a file and puts it a Table variable. Reading too large files can cause performance issues.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to source file to read lines from. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is one byte from source file.
Since
6.0
See also
Read all lines from file
Reads all lines from a file and puts it a Table variable. Reading too large files can cause performance issues.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to source file to read lines from. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to read the file in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
Table with column 'value' where each row is one line in source file.
Since
6.0
See also
Read all text from file
Reads all text from a file and puts it a simple value variable. Reading too large files can cause performance issues.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to source file to read text from. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to read the file in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
Simple value variable (string), with all content of file in it.
Since
6.0
See also
Write all bytes to file
Writes all provided bytes to a file. If the file already exist, it is overwritten.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to append text to. |
| Bytes | A Table containing one column, value, with numeric values (byte, 0-255). |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Write all lines to file
Writes all provided lines to a file. If the file already exist, it is overwritten..
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to write lines to. |
| Lines | Lines to write. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the lines in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.0
See also
Write all text to file
Writes all provided text to a file. If the file already exist, it is overwritten.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to write text to. |
| Text to write | Text. |
| Code page | Specifies which code page to write the text in. Default 65001 (UTF-8 with BOM). Use 0 for UTF-8 without BOM. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.1.6
See also
Write stream to file
Writes the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream to a file. This can for instance be used to write data from a camera input to the file system.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to file to write stream to. |
| Source stream | Stream to write. Must be a Flow variable. |
Output
No output.
Since
6.2
See also
Add single file to zip
Compresses a single file and adds it to a zip file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| File | File to add to archive. |
| Path to zip file | Zip file to add file to. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
| Replace mode | Specifies what to do if a specific file already exists in the archive. |
| Compression level | Specifies the level of compression, valid values are 1-9 where 9 indicates highest level of compression (and slowest). Default value is 6. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Add stream to zip
Compresses the content of a Flow variable that contains a binary stream. This can for instance be used to compress data from a camera input.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Stream | Stream to read data from. |
| Filename for stream in zip file | The name of the file in the archive the content of the stream should be written to. |
| Path to zip file | Zip file to add stream content to. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
| Replace mode | Specifies what to do if a specific file already exists in the archive. |
| Compression level | Specifies the level of compression, valid values are 1-9 where 9 indicates highest level of compression (and slowest). Default value is 6. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Extract files from zip
Extracts all files from a zip file which matches provided mask.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path to zip file | Zip file to extract from. |
| Destination path | Path where to extract files to. If file or directory already exists at destination path, it is skipped (not overwritten). The directory should exist before this operation is called. |
| Filter | Filet to use when filtering items in archive. Example "*.txt". |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
Extract file to stream
Extracts a single file to a stream. The entire file will be loaded into memory, so do not use this operation with large files.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path to zip file | Zip file to extract from. |
| Filename | The name of the file in the archive to extract. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
Output
Simple value, read-only binary stream trinket.
Since
6.3
See also
Add folder to zip file
Zips all files and subfolders in a folder into a zip file.
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Path to read files and folders from. |
| Path to zip file | Zip file to add folder content to. |
| Password | Optional password to the zip file. |
| Replace mode | Specifies what to do if a specific file already exists in the archive. |
| Compression level | Specifies the level of compression, valid values are 1-9 where 9 indicates highest level of compression (and slowest). Default value is 6. |
Output
Simple value, 'True' if operation was successfully. 'False' otherwise.
Since
6.3
See also
File System
The File System connector can be used to perform directory and file operations on any file system which the Flow Server can access.
Configuration
File System connector should be configured to run as a specific user. If not configured, it will run as the same user as the Flow Server is running as.
- Domain. Domain name or leave empty to use a local user.
- User. User to run file system connector operations as.
- Password. Password for user.
- Logon Type. Typically use Interactive.
Operations
| Zip operations |
|---|
| Add folder to zip file |
| Add single file to zip |
| Add stream to file |
| Extract file to stream |
| Append all text to file |
Generate Text Connector
The Generate Text Connector can be used to output text either to a file or over the network via HTTP or TCP. Flow variables can be used to compose the text to write.
Configuration
No configuration is required.
Google API
The Google API Connector can be used to access Googles public APIs. Currently only URL Shortener API is supported.
Configuration
The Google Connector currently does not use any API that requires authentication, so no configuration is required.
Table Operations
Configuration
Generate Xml Data
The Generate Xml Data Connector can be used to write Flow variables to an xml file.
Configuration
No configuration needed.
Utility
Under utility, all utility related connectors are listed, with information about configuration to setup the connector and how to use it.
Connectors
Branding
Branding is only available in the Enterprise version of Flow.
Logotype
Change the logotype shown in the left corner of the Flow clients. Click in the up load icon and choose a new logotype.

Color theme
With Color Themes is it possible to change colors on the client banner, workflow buttons and the header text.
Add a new theme by clicking on Add and enter a name of the theme, change the colors and save theme. Activate the theme that should be used by Flow.

Create your own color palette and use as backgrund colors for the workflows.

With the color picker is it possible to change the colors. Click on the color that should be changed and either enter RGB, hex code or choose a color from the color palette.
The workflow colors will apply in the palette where to choose workflow color from.

BarTender 2016
The BarTender connector can be used to integrate with BarTender 2016 R8, typically to print BarTender documents.
32-bit version of BarTender 2016 R8 Automation Edition or Enterprise Automation Edition needs to be installed on the same machine as Flow Server.
Configuration
Path to look for .btw files in
Specifies where to find BarTender documents. Required in order to print documents (unless using BTXML). Must be a path that is accessible for the user specified in 'Design time identity' while developing workflows and accessible for the runtime user (either set per Flow user or in 'Global runtime identity') when executing the workflow. If no identity is provided, the identity of the application pool running Flow Server is used.Default printer
Name of printer to use. Leave empty to use the printer set on BarTender document. The printer can also be overridden in print operations.Global runtime identity
Identity of user to run BarTender operations as. If any Domain is specified here it will be applied also on identity specified on Flow user. If no runtime identity is provided, the identity of the application pool running Flow Server will be used.Design time identity
Identity of user to use while designing workflows. Never used in runtime. If left empty (i.e User not specified) and Global runtime identity is provided, Global runtime identity will be used also while designing workflows. If no runtime identity is provided, not design nor runtime, the identity of the application pool running Flow Server will be used.Cache metadata
Specifies whether the connector should cache any metadata regarding what BarTender documents there are and what parameters they have.
Example of usage, embedded data
This is a an example of printing the label "Caterpillar\Master label.btw" which can be found among the example labels installed with BarTender.
The label looks like this in BarTender:
It can be configured with embedded data, 1L, 3S, 4S and so on.
If you select this BarTender document in Flow Studio it will look like this:

As you can see, the Embedded data is set to Custom record, and this is where you can control the data input to the BarTender document.
If we provide it with some random data:
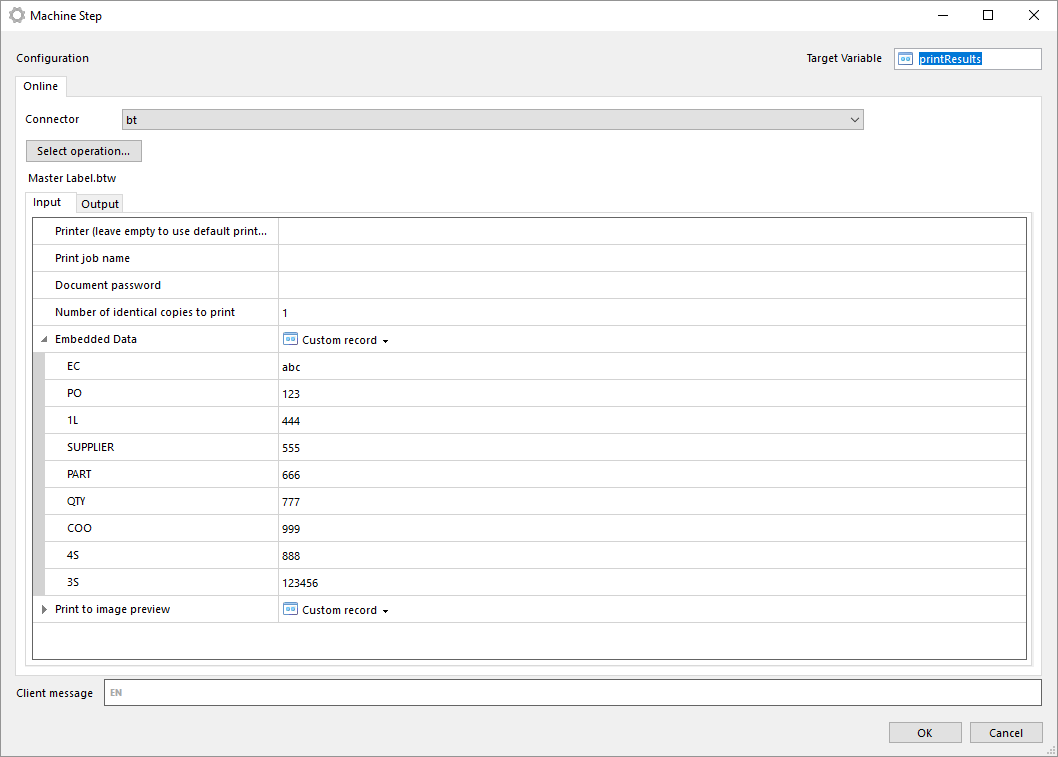
And then print the labels, in this case to an image preview, the output will look like this:
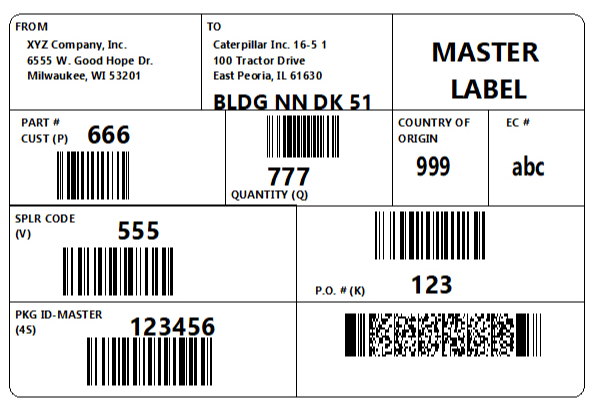
Example of usage, text database
This is a an example of printing the label "EU Energy Labels\EU Energy Television A 2010-1062-2011.btw" which can be found among the example labels installed with BarTender.
The label looks like this in BarTender:
It takes a text file as data input. Example file looks like this:
Efficiency;Annual Power Consumption;Power Consumption;Power Switch;Diagonal Inches;Diagonal Centimeters
0.28;10000;80;1;32;81
0.40;22222;120;0;32;81
0.50;23456;140;0;27;69
0.70;90009;160;0;27;69
0.85;90809;30;1;42;107
0.95;90909;40;1;42;107
1.10;99999;50;0;20;51So seven (one per line) labels will be printed.
If you select this BarTender document in Flow Studio it will look like this:
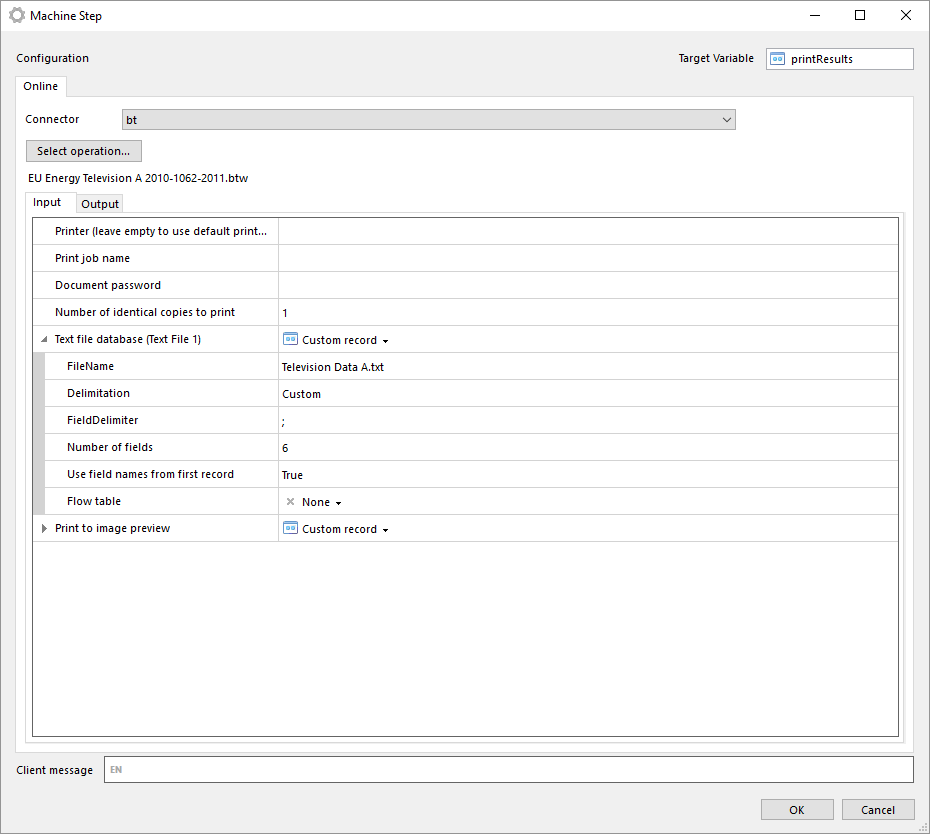
As you can see, the Text file database (Text file 1) is expanded, and this is where you can control the data input to the BarTender document. You can for instance select another text file than 'Television Data A.txt'.
You can also map data from a Flow table to the document. Let's do that. Consider the following flow table:

So mapping this to the BarTender document can be done like this:
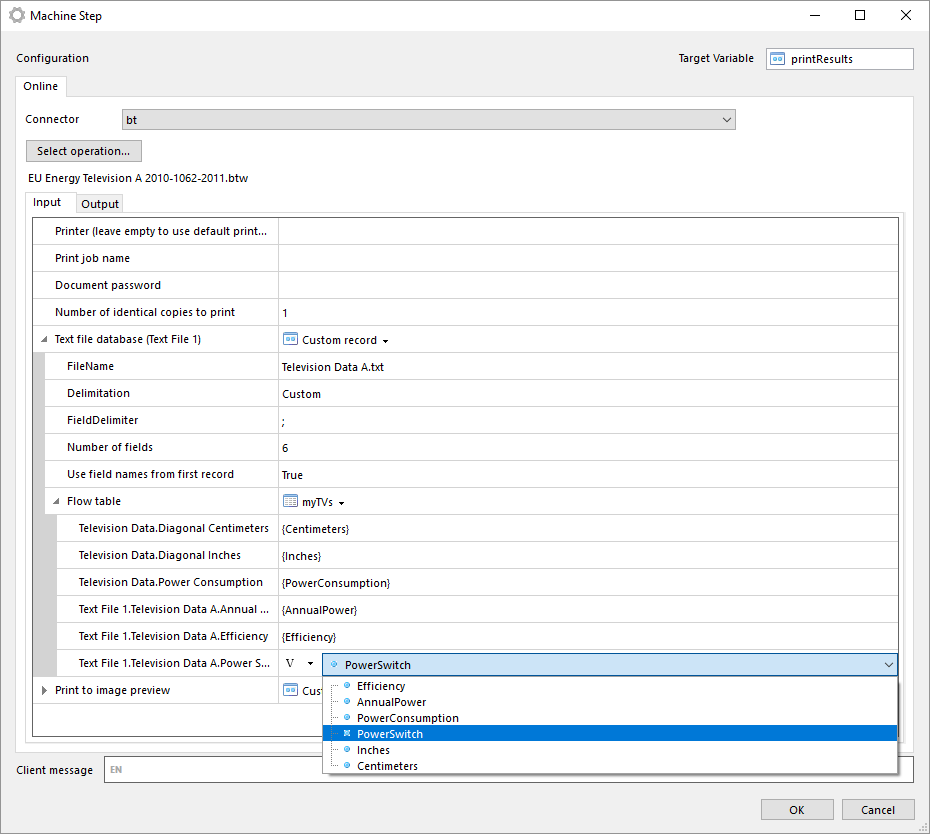
It is important that the data types matches, for instance will sending in a text to any of these members generate an error. You can see the data type in BarTender. Unfortunately there is no way to know the types from Flow Studio. If you choose to map to a Flow Table, the file ('Television Data A.txt' in this case) will be ignored.
If you then print the labels, in this case to an image preview, the output will look like this:
The values does of course not make sense, but hopefully this has given you an idea how to map your data to BarTender documents.
Microsoft Active Directory
The Microsoft Active Directory connector can be used to perform various Active Directory related operations.
Configuration
- LDAP Path. LDAP path to use, if any.
- Domain Name. Active Directory domain.
- LDAP User. Username this connector should use while accessing Active Directory
- LDAP Password. Password for user.
Business systems
Database
The database connector is used to connect to various databases. Supported databases are Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, IBM DB2 iSeries, IBM DB2, MySql Server and IFS Applications.
Configuration
- Database Type : Type of database
- Database server. Address to database
- Global User ID: User to login to database with
- Global Password: Password for User
- Initialization Command: Optional command to execute immediately after successful login
- Cleanup Command: Optional command to execute on database after operation has completed.
- Command Timeout: Command timeout, in seconds, to use when executing a script or a query. If not set, default value for database type will be used (most likely 30 seconds). Please note that this is the timeout between Flow Server and database. It is possible that the communication between Flow Client and Flow Server will timeout prior to the command timeout. If the client experiences timeout, but the database command does not, the database command will still be executed completely.
- Connection Pooling: Sets whether connection pooling should be used (not supported by all database types)
Security
The database connects directly to the database using different kinds of authentication protocols according to what kind of database you connect to.
Microsoft Dynamics CRM
The Dynamics CRM Connector is used to interact with Microsoft Dynamics CRM.
Configuration
- Organization
- MSCRM Web Service Address
- Username
- Password
- Domain
Google API
The Google API Connector can be used to access Googles public APIs. Currently only URL Shortener API is supported.
Configuration
The Google Connector currently does not use any API that requires authentication, so no configuration is required.
IFS Applications 10 API
The IFS Applications 10 API connector can be used to execute procedures (including New__, Modify__ and Remove__) and functions in IFS Applications 9.
Configuration
Server
Url to server, for instance http://host:portGlobal runtime User Id
If specified, the User to login to IFS with at runtime.Global runtime password
If specified, the password for the user to use at runtime.Design time User Id
The User to login to IFS with at at design time.Design time password
The password for the user to use at design time.Debug settings
In this section debug settings are configured. In order to get log files, Path where to write log files must be set to a valid path relative to the Flow Server. The log files are created by IFS Applications, not by Flow.
IFS Applications 9 API
The IFS Applications 9 API connector can be used to execute procedures (including New__, Modify__ and Remove__) and functions in IFS Applications 9.
Configuration
Server
Url to server, for instance http://host:portGlobal runtime User Id
If specified, the User to login to IFS with at runtime.Global runtime password
If specified, the password for the user to use at runtime.Design time User Id
The User to login to IFS with at at design time.Design time password
The password for the user to use at design time.Debug settings
In this section debug settings are configured. In order to get log files, Path where to write log files must be set to a valid path relative to the Flow Server. The log files are created by IFS Applications, not by Flow.
Infor M3 REST API
The Infor M3 REST API Connector can be used to consume M3-API-REST bulk API.
Configuration
Url
Required url to base address of REST API.Design time Authentication
In this section the authentication to be used when fetching metadata from the REST API is configured. Username (basic) and Password (basic) is used for Basic Authentication, as specified in RFC2617. The information in this section is only used while designing workflows in Flow Studio. It is never used in runtime. The user specified here must be allowed to run the transactions LstPrograms, LstTransactions and LstFields in the program MRS001MI.
In this section there is also the possiblity to accept any certificate from server in an https session. This should only be used for test or development scenarios when no other option exists.Runtime Authentication
In this section the authentication to be used when executing machine tasks is configured. Username (basic) and Password (basic) is used for Basic Authentication, as specified in RFC2617.
In this section there is also the possiblity to accept any certificate from server in an https session. This should only be used for test or development scenarios when no other option exists.Logging
In this section logging is configured. Either incoming or outgoing or both can be logged. If something goes wrong in the communication, an entry is added to the file errorLog.txt. In order to enable logging, a valid path releative to the Flow Server must also be provided. Note that the path must already exist, the connector will not create the path. Also note that the user that Flow Server is running as must have write access to the path.
Infor M3 API
The Infor M3 API Connector is used to integrate with Infor M3.
Configuration
- M3 Server Name
- Address or name of M3 Server. Required.
- Port Number
- Port to use when communicating with M3 Server. Required.
- CONO DIVI Parameter
- Global Username
- Username for connecting to M3 Server. Leave blank if username and password is to depend on Flow user.
- Global Password
- Password for Global Username when connecting to M3 Server.
- Advanced configuration
- Call SetLstMaxRec when getting metadata
- Sets whether a SetLstMaxRec should be called before getting programs and transactions. If SetLstMaxRec is not called, M3 will at most return 100 items.
- Argument to SetLstMaxRec
- Sets the argument to use with SetLstMaxRec. Setting it to 0 typically will return all available metadata, but this can be M3 version dependent.
- Sets the argument to use with SetLstMaxRec. Setting it to 0 typically will return all available metadata, but this can be M3 version dependent.
- Enable log
- Sets whether to write a log of certain events, such as opening and closing a connection, to the log file provided in Path to log file.
- Path to log file
- Path to the file where logs are written if Enable log is used. The file is created if it does not exist.
- Call SetLstMaxRec when getting metadata
Configuring Maximo Connector
First step is connector configuration in Flow Studio (see picture below)
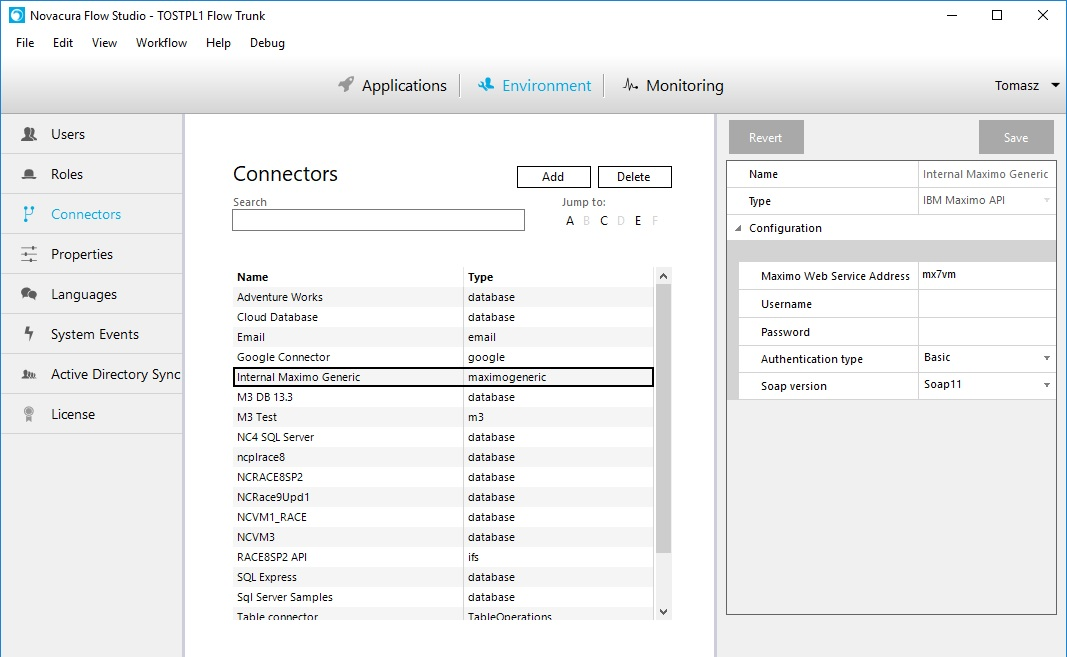
Communication with Web Services is always over the HTTP protocol.
The following parameters are configurable in the configuration:
- Maximo Web Service Address: The Maximo server name which hosts web services
- User name: user name (credential) used in authentication
- Password: password (credential) used in authentication
Authentication type: it decides how credentials are used when web service is called. The connector uses SoapHttpClientProtocol dotnet object to communicate with Maximo Web Services, but credentials can be used with two modes:
Basic: dotnet NetworkCredential objects is created and attached to Credentials property of SoapHttpClientProtocol object.
Base64: credentials are encoded with base-64 digits and put into soap request header
Soap version - connector can communicate with web services in two SOAP versions: SOAP1.1 and SOAP 2.2
IBM Maximo (old)
The IBM Maximo (old) Connector can be used to access IBM Maximo. This connector is obselete. Use IBM Maximo API instead.
Configuration
- Maximo Web Service Address
Oracle Primavera
The Oracle Primavera Connector can be used to access an Oracle Primavera P6.
Configuration
- Username
- Password
- Url
SAP BAPI
The SAP BAPI Connector can be used to execute any published BAPI (standard or custom) in an SAP ABAP system, including HANA-based systems. Resulting table(s) are available as Flow variables.
The SAP BAPI connector require Microsoft C++ Runtime DLLs version 10.0 (contained in the Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Redistributables). MSI installers for these runtimes can be obtained from here. This must be installed on the machine running Flow Server.
Configuration
Go to the Environment/Connectors section in Flow Studio and Add a new connector. For parameter details, see below.
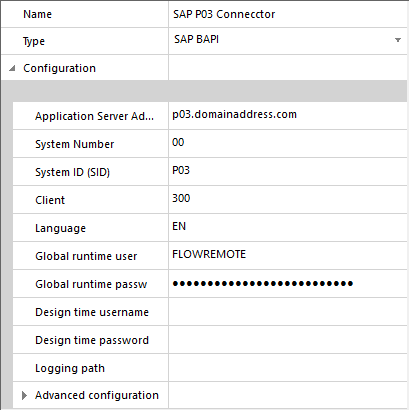
- Name: Your own name of the connector. For easy connector identification in design time, include the name of the target SAP system.
- Type: Choose "SAP BAPI"
- Application server address: URL or IP address of the target SAP system
- System number: Enter system or installation number of target SAP system
- System ID: Enter the System ID.
- Client: Configured user will log in to specified client
- Language: Configured user will log in with specified language. Note that BAPIs called from Novacura Flow must be enabled for the language specified.
- Global runtime user: If specified, this username will be used every time Flow connects with the target SAP system. For license audit, traceability and security reasons, Novacura recommends that Global users are only used with caution and only in automated scenarios, i.e. without user interaction, for instance when using Flow as an integration engine, together with a SAP service or system account designated for the specific scenario.
- Global runtime password: Password of global user.
- Design time user name: Design-time user which is only used in Flow studio when developing the Flow.
- Design time password: Password of design time user
- Logging path: If specified, any logs produced by the connector will be written to the specified path. Please note that this path is relative to Flow Server and that the user that Flow Server is running as must have write access to the path.
- Advanced configuration: Depending on your environment, you may need to add additional details, such as specific network or security settings.
Personal user configuration
If Global runtime user is not specified, SAP username must be configured on the Flow user. For general information on Flow users, see here.

- Username: Enter username of the SAP user
- Password: Enter password of the SAP user. If SAP password is not supplied, the Flow login dialogue will ask for the SAP password to use for the session.
Authorization requirements for SAP users connecting from Flow
Authorization object S_RFC containing the following : - Activity 16 (Execute) - RFC_NAME: SYST, RFCPING, RFC1, RFC_GET_FUNCTION_INTERFACE, RFCH, RFC_GET_UNICODE_STRUCTURE - RFC_TYPE: FUGR and FUNC
On top of this, the S_RFC authorization must also contain the function group and the function module being called, as well as any authorization needed to pass authorization checks in any of the called programs, including authorization for the applicable organization level (for example purchasing organization).
Security considerations
The SAP BAPI Connector is using the standard SAP authorization concept. The connector always logs in to the SAP system through RFC with a user that is set-up and active in the SAP system as a dialog, system or service user. Any authorization object checks will be performed the same way it would be done if the user logged in using SAP GUI.
For more information on RFC security, see SAP's official RFC security guide.
Using the SAP Connector for creating workflows
For details on design-time usage of the SAP connector, see here.
Microsoft SharePoint
The Microsoft SharePoint Connector can be used to interact with a SharePoint installation.
Configuration
- Url
Url to SharePoint site. Note that subsite must be specified in the url if applicable. E.g. http://servername/subsite - Domain
Domain any user that connectors to SharePoint is a member of. - Global runtime user
If specified, this is the user any Flow that uses this connector will connect to SharePoint with. Leave empty for per-user usage - Global runtime password
If specified, this is the password related to Global runtime user - Design time user User to login to SharePoint with during creation of workflow.
- Design time password Password for design time user.
Authorization schemes
Authorization schemes can be applied to operations to set what kind of authorizations are required to use the operation. When there are schemes defined they can be applied to operations simply by clicking the "ADD" button:
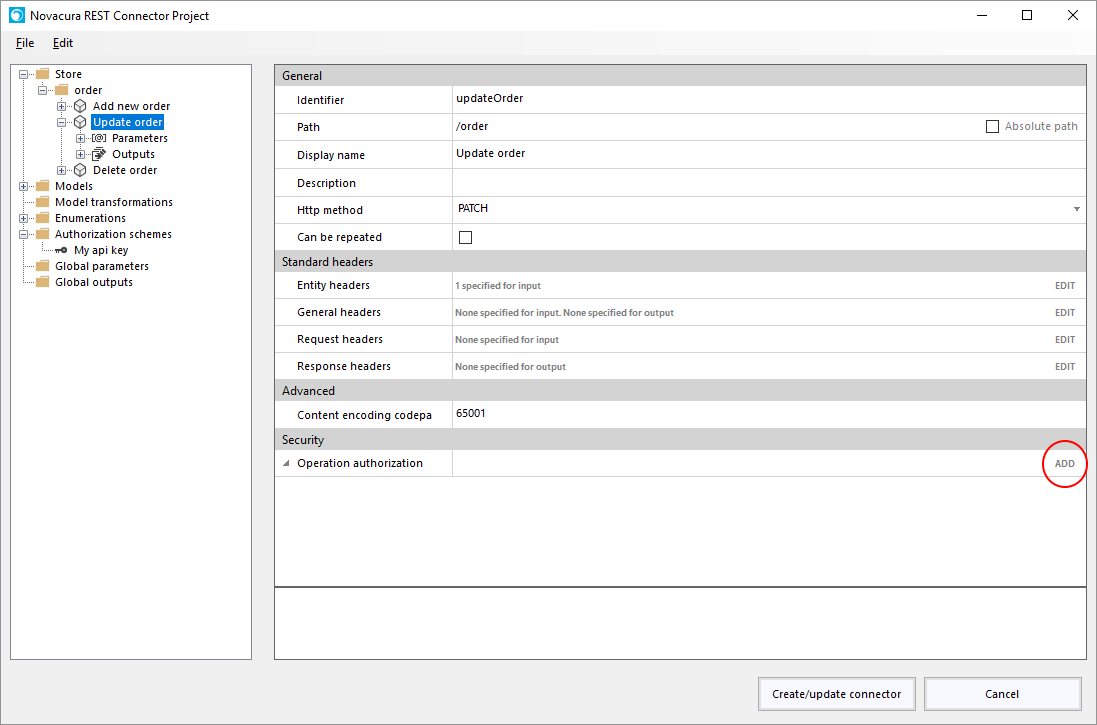
You can also apply an authorization on all children of a given container by selecting the container and then right clicking on it and selecting "Authorization->Apply authorization to all children".
But first you have to define the schemes. There are three kinds of schemes that can be used.
OAuth2
OAuth2 is currently mainly for documentation purposes. There is no requirement to configure this at the moment (6.7). If you import a swagger specification, that specification can contain this information, and it is good to keep track of. It certainly does not hurt to specify OAuth2.
API Key
REST API:s often require an API key. Typically it is sent either via a query parameter or as a header. You can specify this yourself on the operation, adding the query parameter or header manually. There certainly are cases when this is a good idea. One example is when you want the api key to be associated with the Flow user. You can then set the api key per flow user and in machine step do like this:
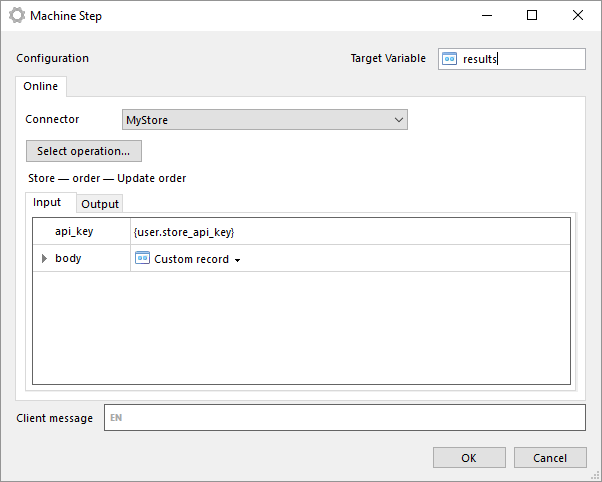
You can also set the parameter as a 'Constant', effectively hiding it from the workflow designer. But then the key is hard coded in the connector, which of course could be problematic.
If you want the API key to be configurable in connector configuration you have to apply an API key scheme on applicable operations. Start by creating a new API key:

Provide a Name for the API Key. This is how you want to identify the key. You can provide description for documentation purposes, but that is not required. "API key name" is required and is what the REST API expects the parameter name to be. Finally you have to define whether the key is sent as a query parameter or as a header.
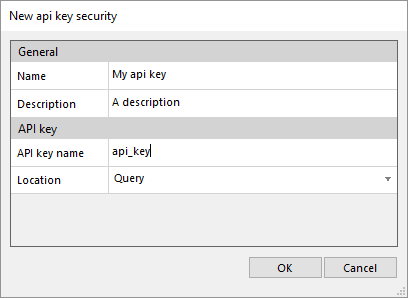
Once the API key has been defined it can be applied to operations as described above.
Finally, after creating the connector, API keys can be set in connector config.

The key will then be applied to all operations that uses the scheme in runtime.
Basic authorization
Another common way for an API to authorize requests is by the use of The 'Basic' Authentication Scheme.
If the API requires this you must add that scheme to the project and apply it to all operations that should use it. There is nothing more to configure in REST Project Tool, all configuration is done in Flow Studio.
Either you set the username and password in the connector config:
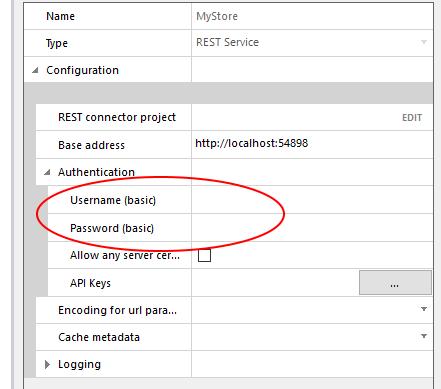
Or you can leave it empty and define it per Flow user:
Enumerations
Enumerations can be used in models to limit the possible values a workflow designer can assign to a member of a model.
Consider for instance an API for 'orders' in a 'store'. We got the operations 'Add new order', 'Update order' and 'Delete order'. Let's look at the 'Order' model:

'status' is of type 'Enum':

And if we look at that enum you can see what possible values that member can have:

Members of the enum can be added and deleted as needed (circled area above).
Let's look at an operation using the 'Order' model, 'Update order'

It uses 'PATCH' to only update certain members, accepting a body of model 'Order'.
Let's look how this will look in Flow Studio: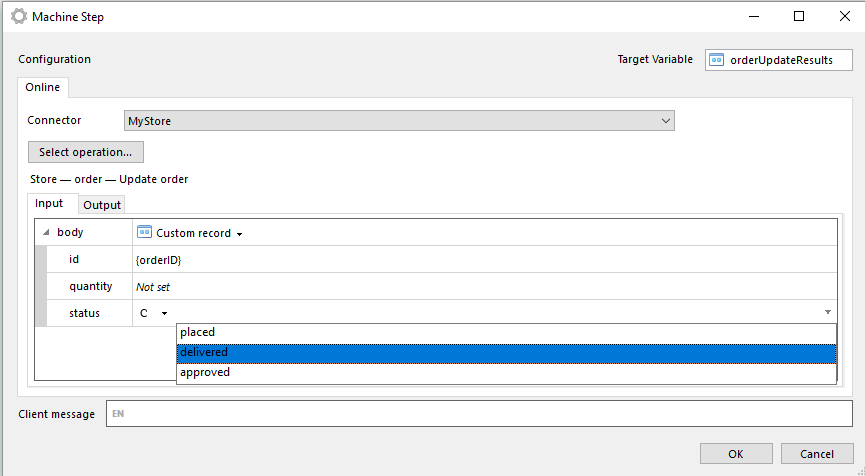
When using 'Constant' as mapping to 'status' only the members of the enum are available. You can still mess it up by selecting 'Variable' as mapping and providing an invalid value in the passed variable. But with the usage of enums you can at least guide the person using the connector in Flow Studio in what kind of values are expected.
Getting started
To create a REST connector you go to Environment -> Connectors -> Add and select Type "REST Service".
Provide a 'Name' and click on "EDIT" to get started. You will also be required to provide a base address before you can save the connector.

When you click on "EDIT" you will open a tool where you'll define the connector.
Let's walk through all the properties.
General
- Connector name
This is just what you want to call the connector. - Connector description
A description of the connector. For documentation purposes. - Base path
If set, all paths are prepended with the value of 'Base path'. If for example the base address of the connector (set not in the tool but in connector configuration) is 'https://www.googleapis.com' and 'Base path' is set to '/drive/v3' and you define the operation 'about' with 'Path' '/about' the url called in runtime will be 'https://www.googleapis.com/drive/v3/about' - Connector version
For documentation purposes.
Containers
The main purpose of containers are to help you organize the operations in a logical way. You do not need to specify any containers, but it usually make senses to use them. Containers can contain operations and other containers. They can also define 'Standard headers' that can be applied to all sub-containers and operations. Containers can also define a 'Path' which is appended to the 'Base path' (described above). The final 'Path' of an operation is the concatenation of all parent containers 'Path' (can be overridden).
Operations
In the 'Operations' section you can add and delete operations of the connector. This is most likely the first thing you will do when starting a new REST Connector project.
Standard headers
In this section you can specify entity, general, request and response headers that should be applied to all operations of connector. You can for instance set that all operations must send 'Content-Type: application/json'. Sub-containers and operations can always override the header.
Global output
'Global outputs' is used to define output parameters that can be reused on multiple operations.
A typical use case is when an API returns some kind of error that is always of the same format. The API might return some data depending on the operation with http status code 200. But in case of error it could still return http status code 200, but a different model, containing information about the error. Although each operation has different models in case of success, in the case of failure could be the same.

Note that priority has been set to a number higher than '1' (in this case '10'). The REST connector will try all defined outputs of given http status code until it succeeds, in the order of 'Priority', starting with the one with highest priority (lowest number). Assuming the operation will be successful more often than not, it makes sense to assign a lower priority on the error output.
You can also define a "NEW DEFAULT OUTPUT", which is just like normal "DEFAULT OUTPUT", that is an output for all http status codes not defined by other outputs.
Once you have defined a global output you can add it to any operation.
Just select "Outputs" on operation and press the 'ADD GLOBAL' button.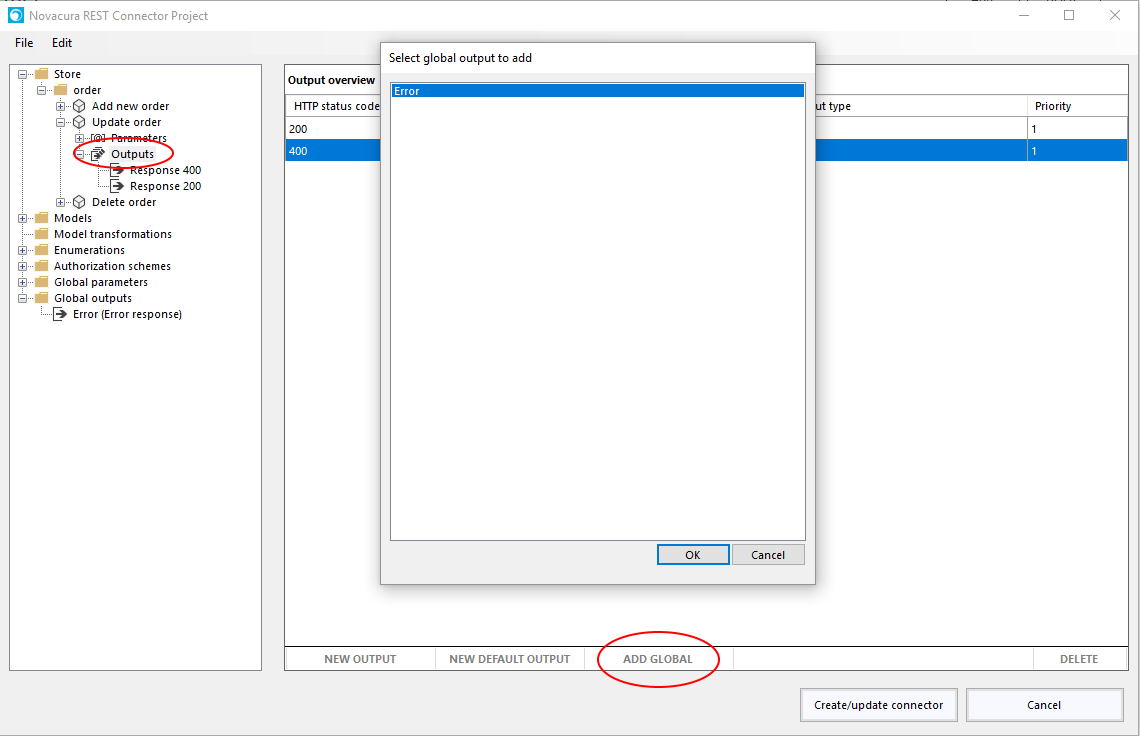
Select output of interest and press 'OK'. You will then be given the option to include the output as a copy or as reference. If added as copy, a new output that looks exactly like the global one will be added to the operation, but there is no connection between the two. So if the global output is changed in any way, the added copy is not affected. If you add it as a reference any changes to the global output will affect the output you added to the operation (it is the same output).
Global parameters
'Global parameters' is used to define parameters that can be reused on multiple operations. You can define query, form, body, header and matrix parameters.
A global parameter is defined like a 'normal' one except that you have to give it a unique identifier once you have defined it. This is to enable you to have multiple global parameters with the same parameter 'Name'. You can of course still only apply one global parameter of given 'Name' to an operation, but this way you can build up a library of useful parameters.
Once you have defined a global parameter you can add it to any operation (as long as that operation not already has a parameter with the same 'Name').
Just select parameters on operation and press the 'ADD GLOBAL' button.
Select parameter of interest and press 'OK'. You will then be given the option to include the parameter as a copy or as reference. If added as copy, a new parameter that looks exactly like the global one will be added to the operation, but there is no connection between the two. So if the global parameter is changed in any way, the added copy is not affected. If you add it as a reference any changes to the global parameter will affect the parameter you added to the operation (it is the same parameter). So if you for instance change the 'Name' of the global parameter, this means that the operation now sends a parameter with a different 'Name'. This can create conflicts. Let's say for instance that you add the global parameter 'q1' to an operation as a reference. You then add the parameter 'q2' to the operation. If you then change the 'Name' of the global parameter to 'q2' the operation will have two parameters with the same 'Name'. This is not allowed, but will not raise any warnings until you try to "Create/update connector".
Internal parameters
In the 'Global parameters' section you can create parameters of kind 'Internal'. This kind of parameters can only be add to operations as a reference, never a copy. The purpose of internal parameters are to be able to send in parameters to an operation that can be used in model transformations. They are not sent to the remote API. Internal parameters will always be set to a nullable type. So when you use it in a model transformation this must be considered. Let's say for instance that you have a global internal parameter called 'Remove empty entries' of type 'Boolean', the usage of that parameter could look like this:

Models
Models are a central concept when creating a REST connector. They are use both for posting object data to an API and also when receiving object data from an API.
Models are managed from the "Model" node in the connector tree.
Below the grid you can create new models. You can create an empty model by pressing the "NEW" button, or you can create a new model based on JSON (sample or Schema Draft 4) or XML sample.
Let's start with creating an empty model.
- Name
A unique name for the model. - Description Currently purely a documentation feature for you as a REST connector designer. Provide a description of the model if it makes sense.
- Base model Used to set a base model that the new model should be based on. All members of base model is added to the new model. Base models are described in detail in its own section below.
- Namespace Used when model is sent or received as xml. If no Namespace is provided and the model is sent as xml, no namespace is assumed.
- Xml name Name of xml element when model is sent or received as xml. If no Xml name is provided, Name is assumed to be the xml elements name.
After the model has been created it is empty and pretty much useless. Press "NEW" on "Items" to create members of model
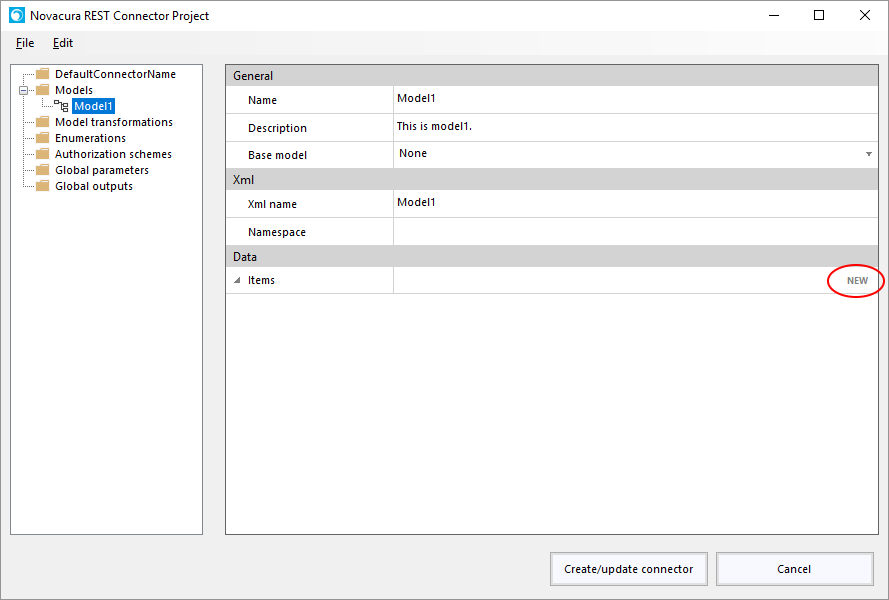
This will bring up a dialog where you can specify details about the member of the model.
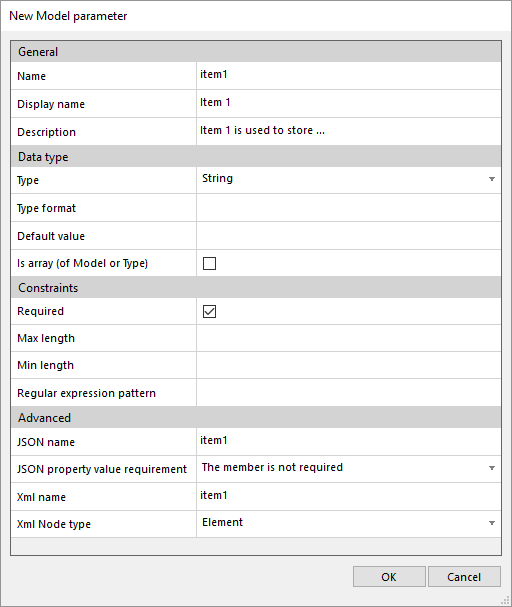
- Name
The name of this member of the model, must be unique in the scope of the model. - Display name
A more human readable version name of the member. If model is used as input to an operation this is what the workflow designer will see as name of member. The actual name of the member is still Name though, and if you want to create a record to use as input (as opposed to a 'Custom record') you must specify Name in that record. - Description
Currently purely a documentation feature for you as a REST connector designer. - Type
Here you select what type of member this is.
- Boolean - true or false.
- Integer - Type format is available. As Type format you can set int64 for big integers (default is int32)
- Number - Type format is available. As Type format you can set float or double (larger, and default if not set)
- Object - Used when the member is of a Model.
- Object (embedded) - Used when the member is a Model, but the Model is only used once, so creating an independent Model is inefficient. More information about embedded models can be found below.
- String - Type format is available. As Type format you can set date-time to indicate that the member is actually datetime.
- Enum - used to set that this member is of an enum. See Enum for more information.
- Custom - Custom specification is available. With the Custom specification you can set the type for special use cases. See Custom model member for more information.
- Boolean - true or false.
- Is array (of Model or Type)
Available for all Type except Enum. Set this if the member is a collection of Type - Constraints
Constraints section depends on Type and it's members are at the moment more of a documentation nature than actual impact on usage of connector. This may change in a future version. - Advanced
This section is used to specify if member has another name in JSON or xml than it's Name. If JSON you can also specify how to handle missing value of this member. Default is to ignore missing members. In the case of xml you can also specify whether the member is an attribute or a element of parent xml element.
You can manually create as many members of the model as needed. You can of course also delete and edit members when needed. At the moment there is no way to rearrange the order of the members. The order does not matter in runtime, but for clarity it could have been good to be able to rearrange them.
While creating the model manually is easy, it is even easier if you already got a JSON or xml representation of it.
Here is an example of a model from JSON (sample):
Types are assumed based of the example data, for instance "Prop3" is assumed to be of type Boolean since the example value of it is 'true'. This feature works for most cases, but there are cases where you need to manually specify exactly the type you need (setting an Integer to have Type Format int64 is one example). You can set all data types to 'large ones' by checking 'Use large data types'. Note that all members of type Integer will then have int64 format.
You can also create models from JSON Schema (draft 4), this is much more accurate than from sample but is not as commonly used as JSON samples.
Here is an example of a model from JSON Schema:
As you might notice, id is specified as int64 already in the schema, and this will be stored in the Model. JSON Schema (draft 4) is superior to JSON Sample in almost every way but, as stated above, unfortunately not as commonly used to document REST APIs as JSON samples.
Another way to get an external representation of a Model into the REST Project is by xml. Currently only sample xml is supported, not from any schema (such as xsd).
Here is an example of a model from xml sample: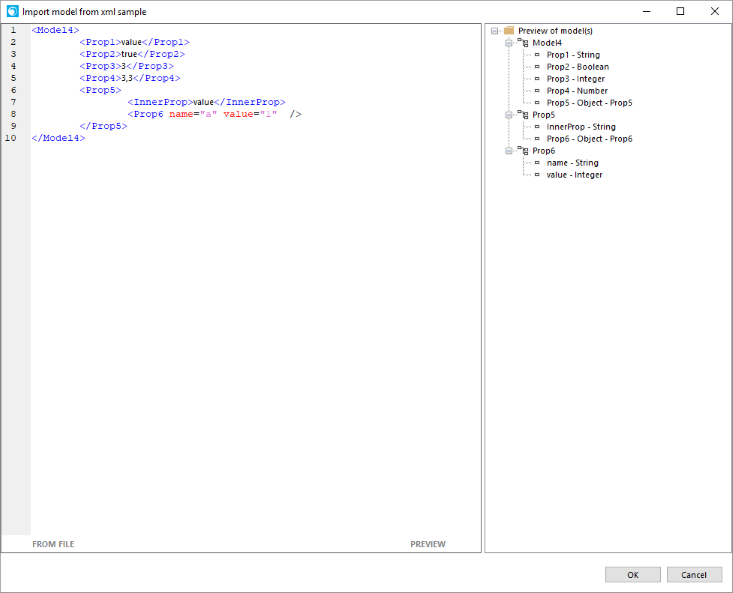
Embedded models
When creating models from JSON or XML sample, inner structures of the model are created as 'embedded models'. This is new in version 6.8 of Flow, in earlier versions independent models were created. If a model is used only once it makes little sense to have an independent model. Chances are that you will end up with lots of models and the project will be hard to manage. When using an embedded model all the members of the model is located directly under the model member. This is perhaps best illustrated with an example:
Consider this structure:
{
"property1":"string",
"property2":"string",
"property3":
{
"innerProperty1" : "string",
"innerProperty2" : "string",
"innerProperty3" : "string"
},
"property4":
{
"innerProperty1" : "string",
"innerProperty2" : "string",
}
}
This is not wrong, it will work just fine, but as project grows larger the number of models will be problematic. With the use of embedded models you would end up with model like this:

The two extra models that was referenced by 'model1' are now embedded in the model. This of course means that the model 'property3' cannot be used by another model, but in the situations where that will not happen, this is a better solution.
Referring to an embedded model in model transformation
If you want to create an instance of an embedded model in a model transformation you refer to it as 'Model_NAMEOFMODEL.Embedded.NAMEOFPROPERTY'. An example with the 'model1' above:
public static Model_model1 modeltransform(Model_model1 input)
{
var output = new Model_model1();
//Transformation code start
output.property3 = new Model_model1.Embedded.property3();
output.property3.innerProperty1 = "a value";
//Transformation code end
return output;
}Converting between embedded and independent models
By default all inner structures are interpreted as embedded models (possibly with the exception of JSON schemas). You can convert between embedded models and independent models in the tool after they've been created by right-clicking on their usage in the tree view and select 'Convert to independent model' (or 'Convert to embedded model' if already independent). If you convert to an embedded model, the related independent model will not be removed. If the rest project tool detects that the model is not used anywhere you will be prompted with the option to delete it though.
Base models
In version 6.8 of Flow the support for base models were added. Basically a model can use another model as a base, meaning that all members of the base model are available also in the new model.
Here is an example where 'Model2' has 'Model1' as base model and 'Model3' has 'Model2' as base model. All members of both 'Model1' and 'Model2' are available in 'Model3'.
Model transform
Model transform is a feature where you as REST connector developer can manipulate the response from a REST API before returning it to the workflow. You can also use it to manipulate an outgoing object (body parameter).
Transforming incoming models
Typical use case is when an API returns data like this:
{
properties : [
{
property: "Property1",
value : "Value1"
},
{
property: "Property2",
value : "Value2"
},
{
property: "Property3",
value : "Value3"
},
]
}When used as an output model in REST connector you would end up with an output looking like this in Flow:
This can be managed with Flow Script, but it can be more convenient and efficient to do the transformation inside the connector. Especially if the connector is used in multiple workflows.
The output of the remote operation is of course still the data above, so we have to define a model to represent that data:
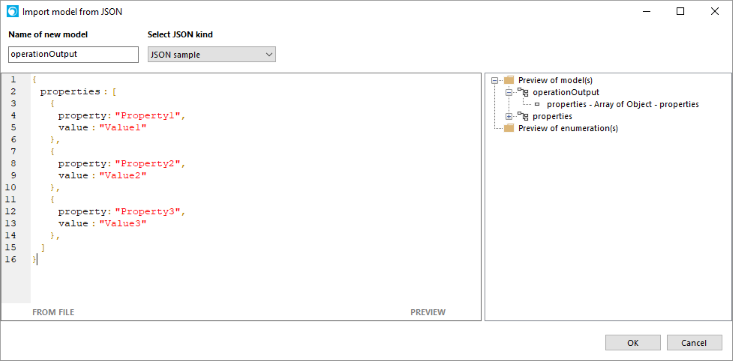
But we can also define the model that we want to expose to the workflow. Something like this:
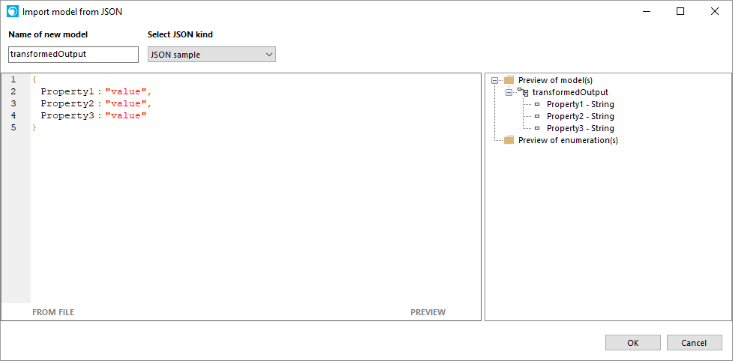
Let's add the transformation.
Select "Model transformations" in connector tree and press the "NEW" button
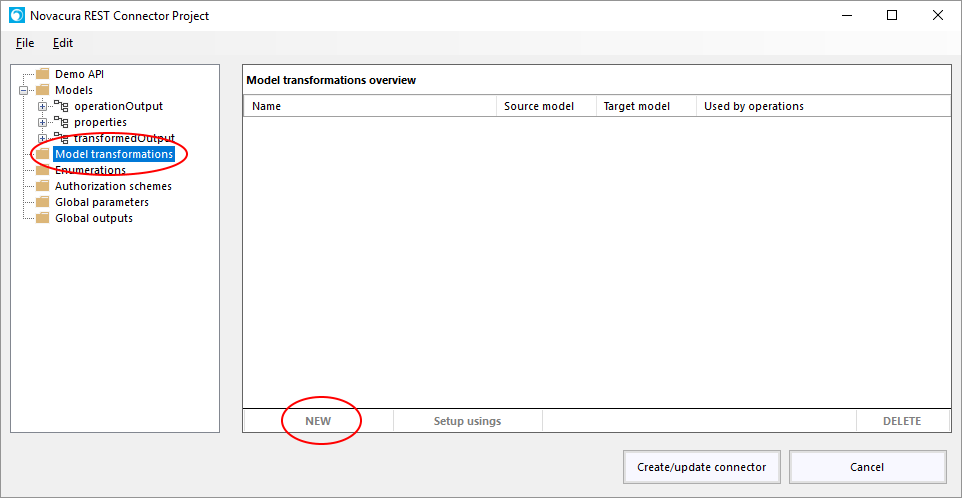
Give the transformation a descriptive name and select source model and target model
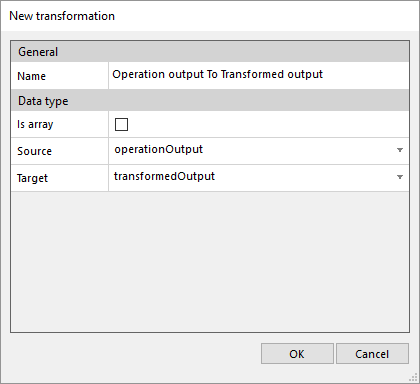
Double click on the newly created transformation in the list, or select it from the connector tree. Something like this should be loaded:
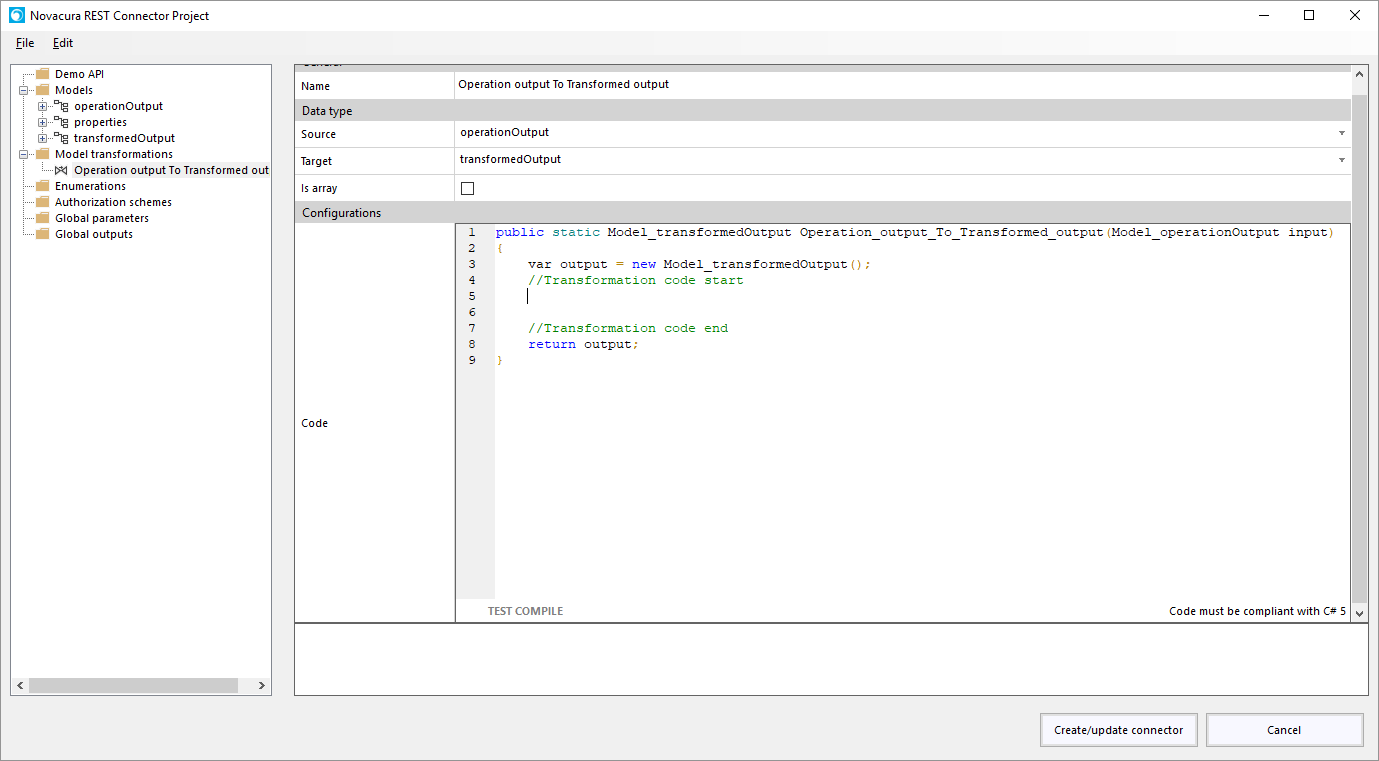
So the actual transformation is done with c# code that you provide. Do not enter any code above //Transformation code start or below //Transformation code end
This is a very powerful feature. You are, however, limited to provide code that is compliant with c# 5.0. You are also limited to only use types from the following assemblies:
System
System.ComponentModel
System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations
System.Core
System.Data
System.Drawing
System.Net.Http
System.Runtime
System.Runtime.Serialization
System.ServiceModel
System.ServiceModel.Web
System.Web
System.Xml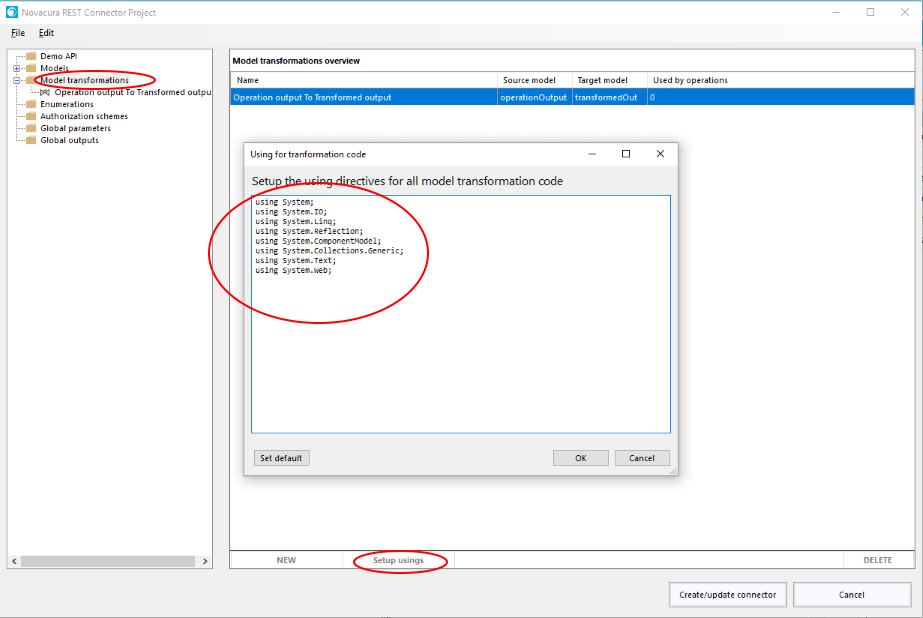
An example of transformation code for this situation could be:
public static Model_transformedOutput Operation_output_To_Transformed_output(Model_operationOutput input)
{
var output = new Model_transformedOutput();
//Transformation code start
output.Property1 = input.properties.First(p => p.property == "Property1").value;
output.Property2 = input.properties.First(p => p.property == "Property2").value;
output.Property3 = input.properties.First(p => p.property == "Property3").value;
//Transformation code end
return output;
} Note that models are called 'Model_' followed by the name of the model.
All that is left to do now is to apply the transformation to the operation of interest:
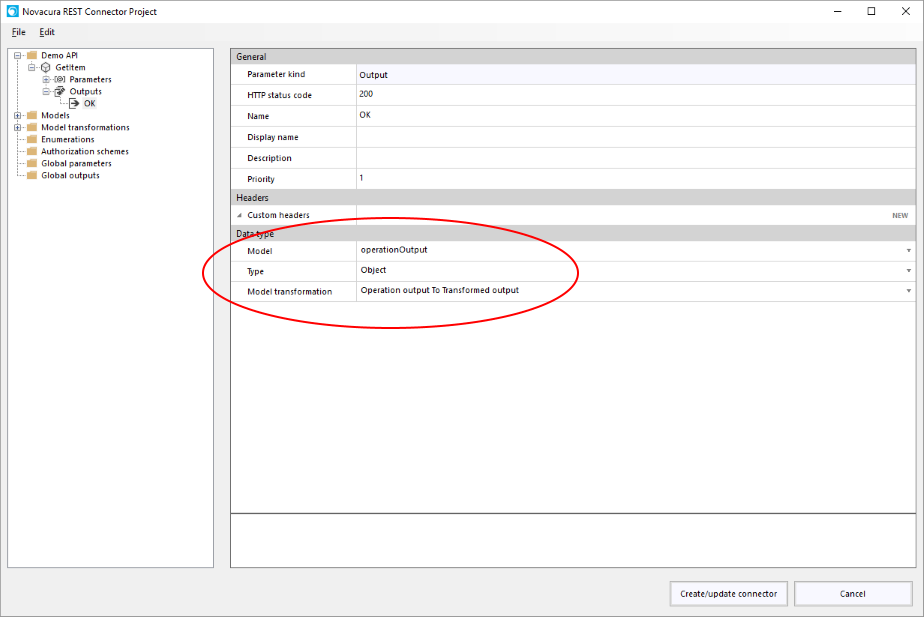
Now when the connector is used in a workflow the output from the operation will look like this:
Which is easier to work with as a workflow designer.
There are a lot more scenarios that this feature enables. You could for instance add new output members (composed of values from other members for instance) or hide members that are not of interest to the workflow designer.
You can of course provide code that has little with transformation to do, such as
System.IO.File.AppendAllText(@"C:\logs\values.txt", input.Property1);This is not recommended. Use this feature only to provide transformation code.
Transforming outgoing models
Like incoming models there are scenarios where it makes sense to transform the outgoing models before it is sent to remote API. Let's assume the same data structures as above are in action here as well. The transformation now needs to be from the model 'transformedOutput' to model 'operationOutput'. Names now becomes a bit off, since we are not dealing with output, but I'm sure you get the picture.
Then the transformation code could look something like this:
public static Model_operationOutput Transformed_to_real_output(Model_transformedOutput input)
{
var output = new Model_operationOutput();
//Transformation code start
output.properties = new System.Collections.Generic.List<Model_properties>();
output.properties.Add(new Model_properties() { property = "Property1", value = input.Property1});
output.properties.Add(new Model_properties() { property = "Property2", value = input.Property2});
output.properties.Add(new Model_properties() { property = "Property3", value = input.Property3});
//Transformation code end
return output;
}


There certainly are situations where the later is preferred, maybe there is already a table with property+values available and so forth. With the transformation feature you can control what best suites your scenario.
For a more advanced example of model transformation see Custom model member
Operations
New operations are added to the project or container by pressing the 'ADD' button.

There are a couple or properties that can or must be defined for each operation.
General
- Identifier
A unique (in the context of the container this operation belongs to) identifier for the operation. Must start with a character and can only contain characters and numbers. - Path
Required. The path to call for this operation. Sometimes referred to as resource or simply url. You can add 'path parameters' like this: '/resource/{id}' where 'id' is a path parameter. You also have to option to check 'Absolute path'. If you do, the 'Path' will not depend on any containers (just on the 'Base address' set in connector configuration). - Display name
Friendly name of operation. If specified, this is what will be displayed when selecting operation in machine step. If not specified, 'Identifier' will be used. - Description
Mainly for documentation purposes. It will also appear as a tool tip when selection operation in machine step. - Http method
Required. Specify which http method to use for this operation, such as GET, POST or DELETE. - Can be repeated
Here you can specify if this operation is to be repeatable in a workflow. Typically a 'GET'-operation can be repeated while a 'DELETE' or 'POST' should not be repeated. But it is up to you to set this. Nothing is assumed.
Security
You specify operation authorization if you have created any in Authorization schemes. This can always be added later, so there is no requirement to set this upfront.
Press OK to create the operation. Once the operation has been created you can specify input and output of the operation.
Learn more here:
Parameters
Outputs
Outputs
The output of an operation needs to be defined so Flow can use it. If you do not need any output, it is safe to define no output. The machine step will still return a record, consisting only of 'HttpStatusCode', 'ReasonPhrase' and 'AllHeaders'.
But typically you want to define the possible outputs of an operation. When you create a new operation one output is added by default. This output is for http status code '200'. If the operation does not ever return 200 you can delete it.
You can define multiple outputs for an operation, for example you might want one for http status code '200' another for '400', yet another for '500' etc. You might even need several outputs per http status code. An API can for instance always return '200', but in case of an error return an object describing the error instead of expected object. The REST Connector will try to parse the response from the API until it is successful. To control the order the connector tries to parse the response, use 'Priority' - where the output with highest priority (lower number) will be tried first. If two outputs has the same 'Priority', it's undefined which output is tried first.
To define a new output you press 'NEW OUTPUT'.

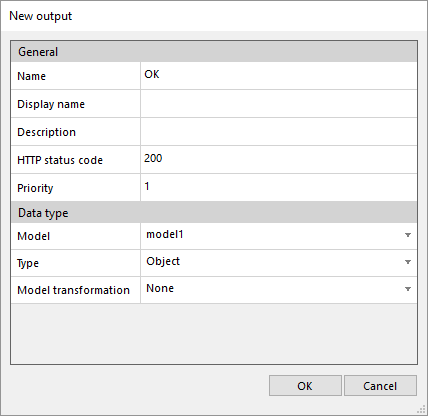
- Name
A unique name for the output
- Display name
A more human readable name for the output (not required)
- Description Currently purely a documentation feature for you as a REST connector designer.
- Http status code Specify for what Http status code that output is valid for.
- Priority Applicable if there are more than one output on a given http status code.
- Data type Here you specify the kind of output - Array - Boolean - Integer - Number - Object - String - File
See Parameters for more information about these types. Note that 'File' will translate to a 'Stream' in Flow. So if you download a file from a REST API (output is of type 'File') you can then use for instance the 'File System Connector' to write the stream to disk. Or another connector that can handle streams, such as SFTP, FTP or the Database connector. If the output is 'Object', you can also select an transformation (if there are any transformations available based on the selected model. See Model transform for more information.
You can also add one (and only one) 'DEFAULT OUTPUT'. The purpose of this output is to capture all http status codes not defined by another output.
Example
Let's look at an example with multiple outputs.
We got two outputs for http status code 200 defined.
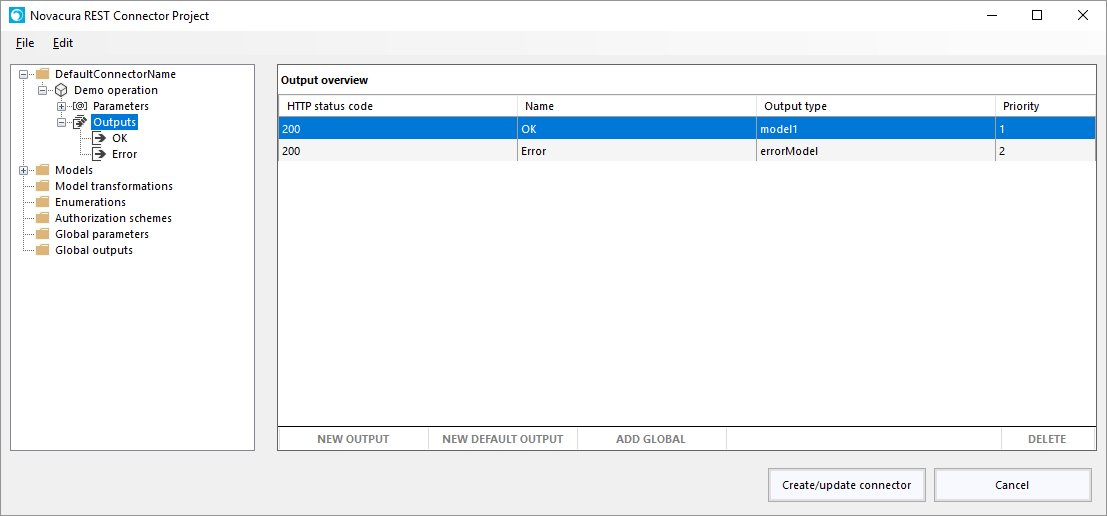
Which leads to that when the operation is later used in Flow, it will have two records, one called 'OK' and one called 'Error'. At most one of the two will have a value after the REST call has been made.
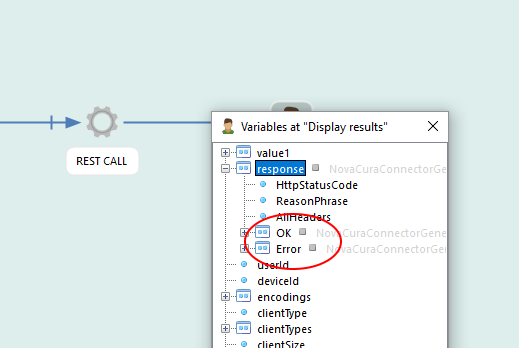
This can be used for better error handling, for instance like this:
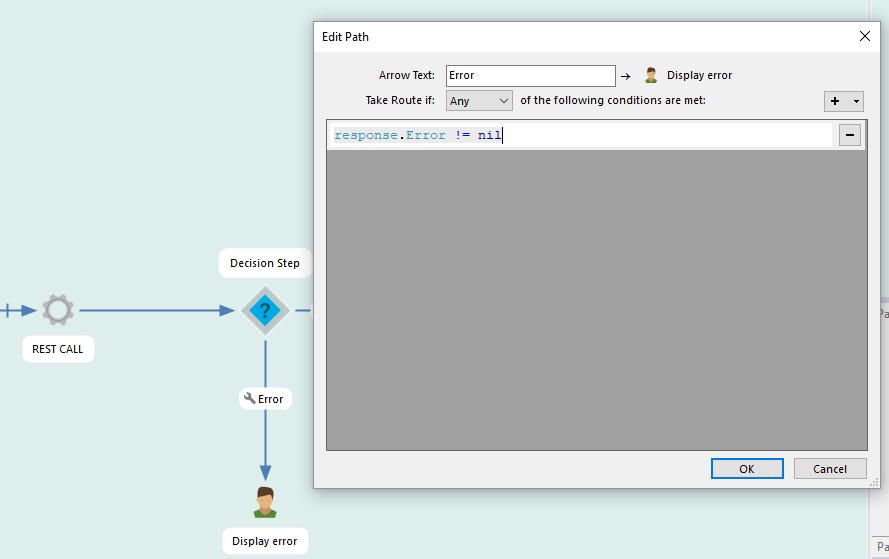
Parameters
Most operations will have parameters of some kind. To define them you simple click on 'Parameters' beneath the operation.
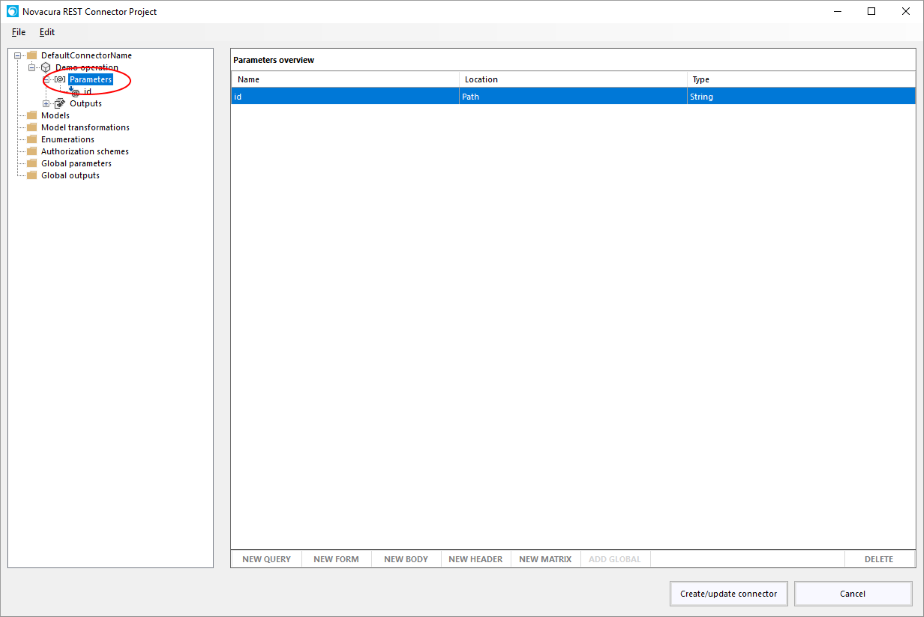
In this example a 'Path parameter' (id) was specified so that is added to the parameters automatically. Path parameters are added and removed directly in the 'Path' by declaring them there. Example: '/{resource}/{id}' where both 'resource' and 'id' are path parameters.
Query parameters
Query parameters are very commonly used by REST APIs. They are added at the end of the 'Path', after a '?' and separated by a '&'. But you do not have to worry about any of that, just add query parameters by clicking the 'NEW QUERY' button and the connector will take care of all the details. If you want add multiple parameters at once there is a convenient shortcut accessible by right clicking on 'Parameters' and selecting 'Add multiple query parameters'. You can then enter as many (within reason) parameters as you like. Choose how they are separated (comma, semicolon or new line) and what type they should all be (typically string). You can also decide whether the parameters are required or not.
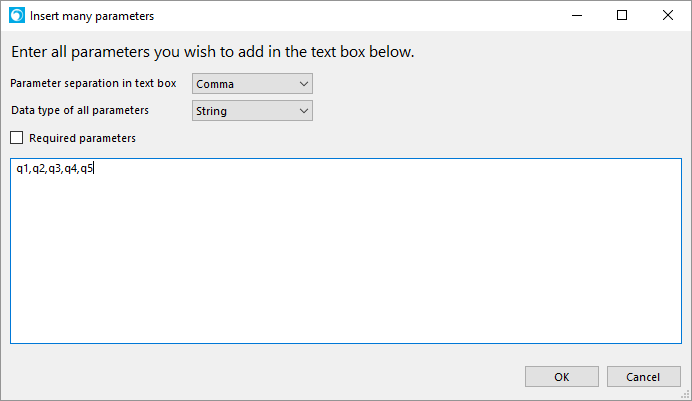
The parameters in the example above were all of type 'String', which probably is the most common type you'll use. There are however multiple types available, more information about the different types can be found later in this page.
Query parameters can be set to be an 'Empty value parameter'. This means that if set to "true" the parameter will be included in the query but without a value. If for instance parameters 'x' and 'y' are defined and set to 'true' the url called by REST connector could look something like this:
http://theurl?otherParameter=someValue&x&yForm parameters
Form parameters are added to your operation by clicking the 'NEW FORM' button. Form parameters requires you to also set a 'Content-Type' header on the operation - 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' for GET or 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' or 'multipart/form-data' for POST. If you are sending a file (binary data) you must use 'multipart/form-data'. If you do not set any header, the tool will force you to do so when clicking the 'Create/update connector' button. Form parameters cannot be used at the same time as body parameters.
Body parameters
Body parameters can be used with POST, PUT and PATCH operations. Typically they are used to send object data to an API. Objects are defined as models, see Models for more information. You can use model transformations on the model before it is sent to remote API, see Model transform for more information. Body parameters cannot be used at the same time as form parameters, and you can have only one body parameter in an operation.
Header parameters
Header parameters, or custom headers, are parameters that are sent as http headers to the API. One common use case is to send API keys in a header. If the API you are creating a connector for requires this, there are however other options available than creating a custom header, read more in the section 'API Keys' in Authorization schemes for more information.
Matrix parameters
Matrix parameters are parameters that are added to the 'Path' before any query parameters. They are separated by a ';'. If you for example has an operation 'op1' with two matrix parameters defined, 'm1' and 'm2' and one query parameter 'q1' which at runtime have the values 'm1Value', 'm2Value' and 'q1Value' the 'Path' (url) would look something like: 'https://site/api/op1;m1=m1Value;m2=m2Value?q1=q1Value'.
Parameter types
String
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Strings is a very common parameter type. Default to this if you do not know the type. String supports 'Type formats'. Currently only 'date-time' will have an impact on runtime - causing the parameter to be treated as a datetime. The 'Required' constraint is used to force the Flow designer to provide a value, but the other constraints ('Max length' etc) are currently only for documentation purposes. This can change in future version of Flow.
Integer
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Integer supports 'Type formats'. Currently only 'int64' will have an impact on runtime - causing the parameter to be treated as a 64-bit integer (instead of a 32-bit integer). The 'Required' constraint is used to force the Flow designer to provide a value, but the other constraints ('Is exclusive maximum' etc) are currently only for documentation purposes. This can change in future version of Flow.
Number
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Number is a used to support floating-point values. Number supports 'Type formats'. Currently only 'float' will have an impact on runtime - causing the parameter to be treated as a 32-bit floating-point value (instead of 64 bit one). The 'Required' constraint is used to force the Flow designer to provide a value, but the other constraints ('Is exclusive minimum' etc) are currently only for documentation purposes. This can change in future version of Flow.
Boolean
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Simple type which allows true or false as value. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value.
Object
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x |
Used to send objects (instances of models) to an API. The header 'Content-Type' must be set, typically to 'application/xml' or 'application/json'. See Models for more information. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value.
File
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x |
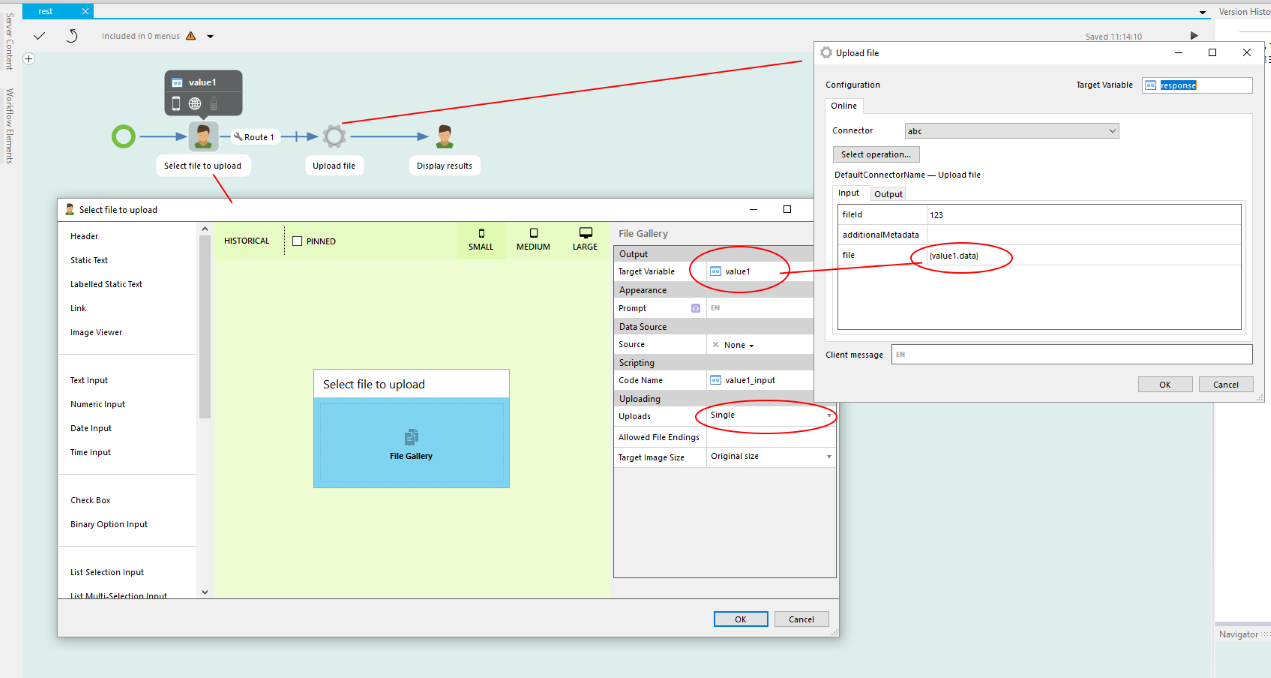
Stream
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x |
Used to send binary data to API. Similar to the 'File' parameter type, but for body parameters. From a workflow perspective used in the same way. The header 'Content-Type' must be set to 'application/octet-stream'. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value.
Array
| Path | Query | Form | Body | Header | Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | x | x | x | x | x |
Arrays are supported by all parameters, but will behave a bit differently depending on the parameter type. Can be set to 'Required', forcing the Flow designer to provide a value. 'Unique items' constraint is only for documentation purposes at the moment, but this can change in a future release of Flow.
At it's core arrays are of course collections of something. But you must define what the collection consist of.
For query, form, header and matrix parameters the 'inner type' can be 'String', 'Integer', 'Number', 'Boolean' or 'Array'. You define how the different items of the array are separated by selecting one of the following:
- Csv. Comma separated, example: param=item1,item2,item3
- Ssv. Space separated, example: param=item1 item2 item3
- Tsv. Tab separated (''), example: param=item123
- Pipes. Separated by '|' char, example param=item1|item2|item3
- Multi. The parameter is repeated multiple times. Example for query parameter: param=item1¶m=item2¶m=item3. Multi is not supported for Path parameters.
For body you can use 'String', 'Integer', 'Number', 'Boolean' and 'Array' as well. But also 'Object'. When set to 'Object' the separation format has no effect.
When the 'inner type' is string you have the option to specify 'Available options'. The use of this is best described with an example:
Consider the operation 'GetOrdersByStatus'. As a parameter you can set the parameter 'status' with what statuses you are interested in. Available statuses are 'Pending payment', 'Processing', 'Approved' and 'Shipped'. To do this the API uses a query parameter array with csv separation. An example call would look like: 'https://store/api/GetOrdersByStatus?status=Approved,Shipped' to get all orders that are either 'Approved' or 'Shipped'. You can of course just specify a query parameter of type array with inner type string and csv separation and that is fine. You will then end up in Flow with something like this:

Either the Flow designer uses 'Single row' and provides one value or defines a table earlier in the workflow with multiple values. Either way, the Flow designer has to know which values are valid and the risk that something is misspelled etc is not neglectable.
A better way is to use 'Available options'.
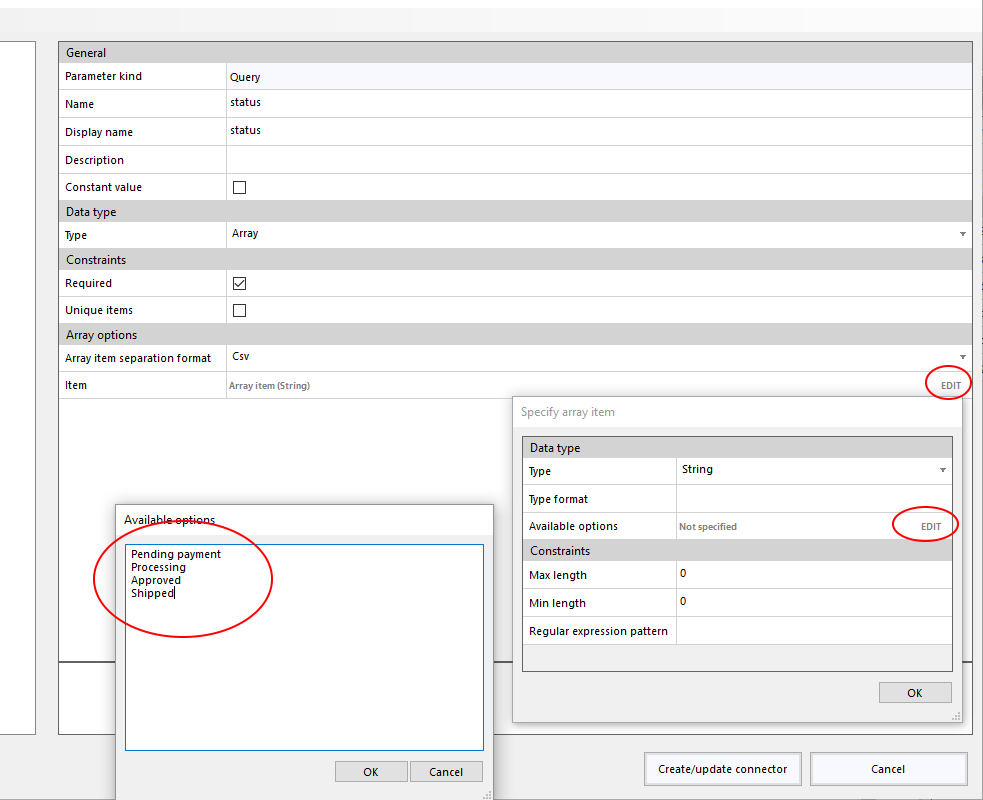
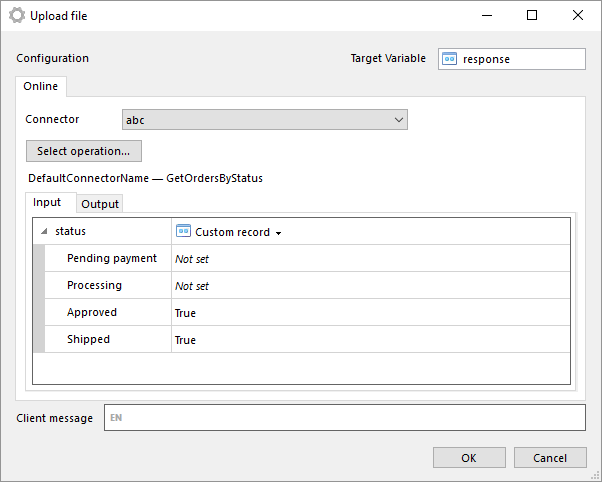
The options are identified as 'c1', 'c2', 'c3' etc, so if you want to setup the record outside of the machine step you can use those names. Example:

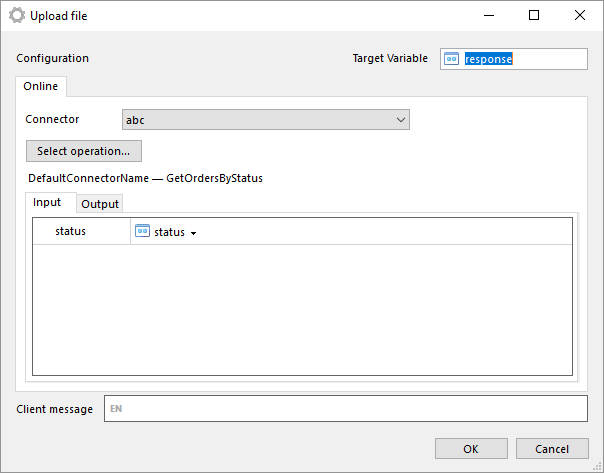
REST Project Tool
The REST Project Tool is used to define how your REST connector is going to integrate with a REST API.
The tool looks something like this:
This is a REST connector for Google Drive V3.
On the left side there is a 'Connector tree', where you get an overview over the different parts of the connector. The first node ('Google Drive V3' in the picture above) is all the operations and containers of the connector. This is what will be available in the machine step once the connector has been created. Below the first node there are different sections where you can define different features that the operations can use, such as models. Each feature is described in its own section.
Getting started
Model
Model transformations
Enumeration
Authorization schemes
Global parameters
Global outputs
In the menu you will find a couple of important features as well.
- New
Creates a new, empty, project. - Import
Lets you import an exported REST Project. You can import an entire project (optionally replacing your current project) or only parts of another project. - Export
Allows you to export parts or all of your project to file which can later be imported, for instance on another Flow Server. - Import OpenAPI (swagger) specification
OpenAPI specifications can be imported (commonly referred to as Swagger 2.0). OpenAPI 3 is not supported. Imported specifications are added to your current project.
When you are done configuring the connector, press 'Create/update connector'-button. If the connector is successfully created, the 'REST Connector Project'-window will close down and you will be back in connector configuration in Flow Studio. Do not forget to press 'SAVE' in connector configuration to save your changes to the connector.
Webservice example: Connector to Microsoft Dynamics AX
This is an example of how the Web Service connector can be used to consume Microsoft Dynamics AX AIF services.
How to set up any AIF service, such as a document service, in Microsoft Dynamics AX is beyond the scope of this example, but once that has been done the Web Service connector can be used to consume it. From AX, get the URI to the WSDL of the service.
Step1
Copy the URI from AX.
Create connector of type Web Service.
Provide a name for the connector and paste in the URI. Make sure server address is correct and press "Create/update"-button
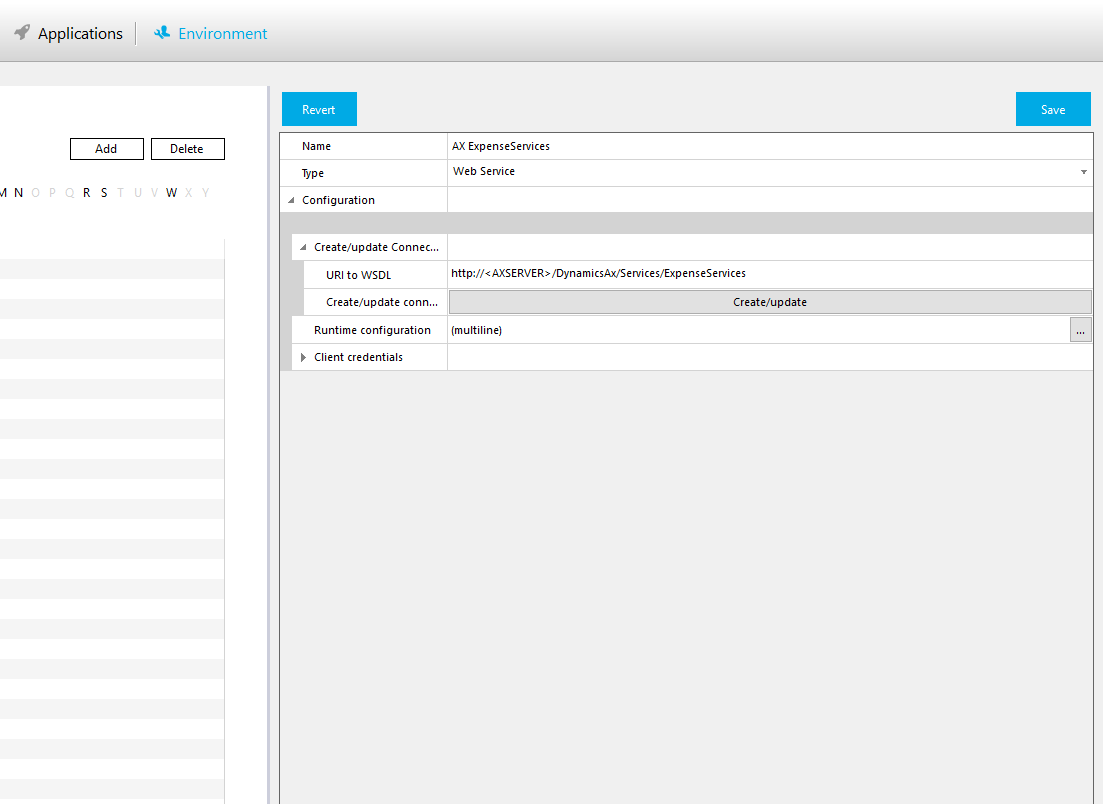
Step2
Wait for the connector to be created
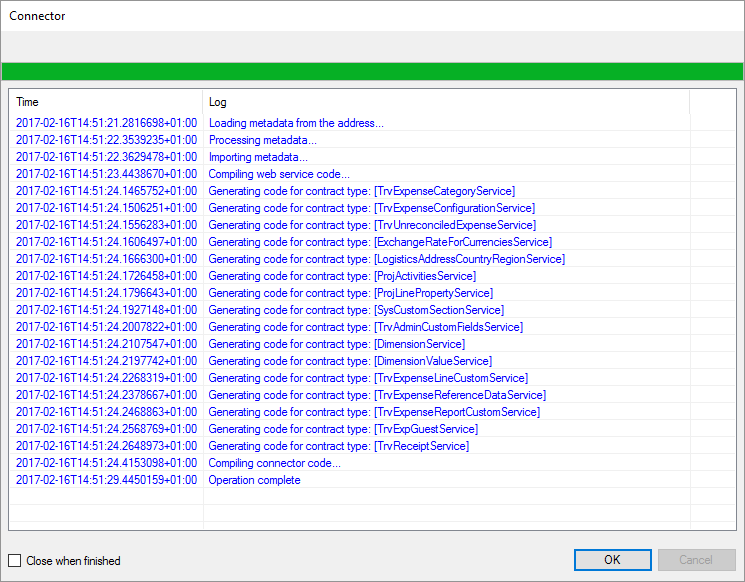
Step3
Examine the configuration. Might be a good idea to increase maxRecievedMessageSize.
Step4
Setup Client credentials by expanding Client credentials -> Windows and enter UserName and Password and, if required, domain and impersonation level.
Step5
Save the configuration
The connector should now be available to be used in a Machine Step.
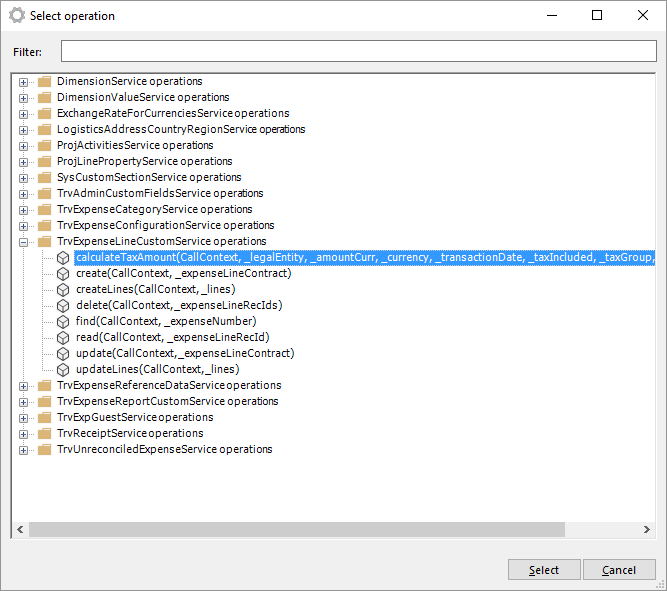
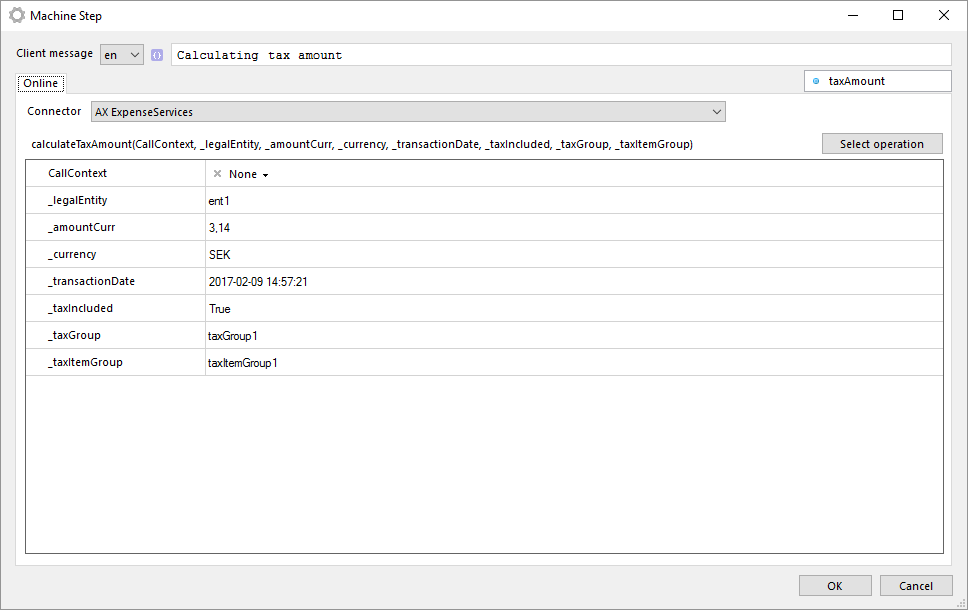
Web Service
The Web Service Connector can be used to consume SOAP based web services. It can also be used to consume WCF services that are not based on SOAP, such as net.pipe and net.tcp bindings.
Configuration
- Create/update Connector
In this section the WSDL that describes the web service is specified and there is also a button for creating the actual connector. Before a connector can be created it must have a Name specified. You must provide a valid URI to a WSDL and start Create/update before the connector configuration can be saved.
The URI can refer to a file if there are no external references in the WSDL. Note that the file path is relative to Flow Server.
If the URI refers to an http endpoint (typically it is) you can, if needed, provide user and password (and optionally domain) before starting Create/update.
Do not update the connector unless the remote service has changed. Runtime configuration
After the connector has been created a basic configuration is stored in this section.Client credentials
Setups the client credentials to use when communicating with remote service.
Example
Communication
Send E-mail
The E-mail Connector can be used to send e-mail via SMTP. Flow variables can be used to compose the message.
Configuration
- SMTP Server
- Port Number
- From Address
- Use Secure Transport
- Use Authentication
- Authentication User ID
- Authentication Password
External OAuth 2.0 Provider
The External OAuth 2.0 provider can be used to acquire acess tokens from OAuth 2.0 providers to be consumed in eg the REST connector.
Configuration
- Uri: The uri to the access token provider eg https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token for Google
Header Properties: A key/value table to specify the HTTP headers to provided when making the call to acquire the access token. The header typically consists of two parts: the type of the token, which is JWT, and the hashing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA.
Body Properties: Values to be sent in the body of the http token request call, in addition to the encoded assertion specified by the values in the JWT heading described below, if any.
JWT: Values used to encode the assertion of your token request. Assertion property: the name of the key corresponding to the assertion value in the payload, usually just assertion. Certificate file path: the location to a .p12 file or corresponding certificate file, which holds the public key to be used when encoding the assertion. These are usually issued by the token provider. Make sure you store this file in a location actually accessible by the server. Certificate password: the password for the certificate specified above. Valid in minutes: how long you would like the token to last after it was issued. May or may not last as long depending on the provider.
Claims: items used when encoding the assertion, usually values that tells something about the user the token is to be issued for and what kind of permissions the token should be able to access. The three most common values are: iss: identity of issuer, eg id of the app to issue the token for which the certificate was created for aud: the endpoint to issue the token. Usually similar as that of the uri value exp: expiration time, no need to specify this since the value of Valid in minutes will substitute this. scope: access scopes requested for the token, eg read the mails of a user of a group in google. Not part of the JWT standard but the providers do not seem to care.
More can be read about the claim on the specification for JWT: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519#section-4.1
FTP
The FTP Connector is primarily used to upload and download files to/from an FTP server.
Configuration
- Address. Address to FTP server.
- Port. Port to use, usually 21.
- Username. Username for a user on the FTP server.
- Password. Password for a user on FTP server.
- Communication settings
- Transfer type. ASCII or Binary (recommended), default is Binary.
- Concurrent connections.
- Concurrent connections.
- SSL / TSL settings
- Use SSL / TLS. To enable a secure connection between client and server. Enabled is recommended.
- Encrypt data channel. If enabled the data transfer will be encrypted, otherwise only command channel will be encrypted.
- SSL Mode.
- Implicit the connection is performed to the dedicated port (usually 990), and immediately starts SSL negotiation (without sending AUTH command).
- Explicit the client connects to the generic FTP port (21), and then sends AUTH command.
- ExplicitManual mode
- Client certificate patch. Path to the clients certification.
- Auth command. Specifies an authorization command that should be sent to server to request an explicit SSL session. Different servers support different commands, so in most cases it is a good idea to set this to Auto.
- Auto. Try to specify command supported by server automatically.
- AuthTLS. Use AUTH TLS command.
- AuthSSL. Use AUTH SSL command.
- AuthTLSP. Use AUTH TLS-P command (protected data channel).
- AuthTLSC. Use AUTH TLS-C command (clear data channel).
- Validate server. If enabled the client validates server.
- Server certificate path. Path to the server certification.
- FTP Version. The secure version of SSL or TLS. Default SSL Version 3 and TLS Version 1.0. -Validation options.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of FTP Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the FTP Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
Modbus
The Modbus Connector is a communications protocol for PLC systems.
Configuration
- Address. Address to Modbus device.
- Port. Port to use, usually 502.
- SerialPort settings
- Enable Serial Port. If you are using Serial port insted of TCP.
- Serial Port. RTU connection. Example ,COM1, COM2 etc.
- Baudrate. Symbols per seconds. ex 4800, 9600.
- StopBits. How many bits it should stop after transmisson, None, One, Two, OnePointFive(1.5).
- Parity. A parity bit, or check bit, is a bit added to a string of binary code to ensure that the total number of 1-bits in the string is none ,even, odd, mark or space.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of Modbus Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the Modbus Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
REST Service
The REST Service Connector can be used to consume REST services. The configuration for a REST Connector is mainly done in the tool "Novacura REST Connector Project" which is access by pressing the 'EDIT' button in 'REST connector project' section.
Configuration
REST connector project
Contains the connector project, press 'EDIT' to edit the project. See REST Project Tool for more information.Base address
Required url to base address of REST service.Authentication
In this section the authentication to be used while communicating with REST service can be configured. "Username (basic)" and "Password (basic)" can be used for Basic Authentication, as specified in RFC2617. If the connector has been configured to send Authorization headers, that will be used, otherwise the values set in this section will be used (or per Flow user if no Username setup in this section).
In this section there is also the option to accept any certificate from server in an https session. This should only be used for test or development scenarios when no other option exists.Encoding for url parameters
The encoding to use when parameters are sent as part of the url (query parameters). If not set, UTF-8 will be used.Cache metadata In this section you can specify whether the machine step should cache metadata information or not. It is useful to set this to 'No' while developing the REST connector, and then to 'Yes' once it's stable.
Logging
In this section logging is configured. Either incoming or outgoing or both can be logged. If something goes wrong in the communication, an entry is added to the file errorLog.txt. In order to enable logging, a valid path relative to the Flow Server must also be provided. Note that the path must already exist, the connector will not create the path. Also note that the user that Flow Server is running as must have write access to the path..
SFTP
The SFTP Connector is primarily used to upload and download files to/from an SFTP server.
Configuration
- Address. Address to SFTP server.
- Port. Port to use, usually 22.
- Server validation. Select what kind of validation of the server that is to be used. Public key is strongly recommended.
- Authentication
- Username.
- Password.
- Client private key path. Path to file containing client private key. Note that this is relative to the Flow Server, not Flow Studio.
- Password to private key file.
- Keyboard-interactive. Use this to setup responses to challanges from the server (if this authentication method is used)
- Communication settings
- SFTP Version. Set which SFTP version to use. Default is version 3.
- Auto adjust transfer settings. Set this to instruct the connector to try to auto adjust download and upload block size and pipeline length for optimal performance.
- Pipeline length. The number of concurrent pipelines the client is allowed to use. Only valid if Auto adjust transfer settings is not set.
- Download block size. The block size to use when downloading files. Only valid if Auto adjust transfer settings is not set.
- Upload block size. The block size to use when uploading files. Only valid if Auto adjust transfer settings is not set.
- Request compression. If set, the client will explicitly require compression.
- Transfer type. ASCII or Binary (recommended), default is Binary.
- Adjust file times. If set, the original date and time values (such as last modification time and creation time) of a file will be retained after upload or download. If not set, time values will be set to when file transfer occured.
- Incoming traffic limit. This can be used to limit the bandwidth used when downloading files. Setting it to zero indicates no limit.
- Outgoing traffic limit. This can be used to limit the bandwidth used when uploading files. Setting it to zero indicates no limit.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of SFTP Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the SFTP Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
Siox
Before using the Siox Connector download the siox driver from the Siox website.
The Siox Connector is used to communicate with Siox terminals. On Siox website. you can read more about it and download Siox SDK for the documentations for all the opertations.
Configuration
- BaudRate. Symbols per seconds. ex 4800, 9600 etc.
- Serial Port. RTU connection. Example ,COM1, COM2 etc.
- Network Connection settings
- Use network connections. If you are using Serial port insted of TCP.
- IP Address. IP Address to the siox bus.
- Connection timeout(ms). The time before the connection should timeout if it cannot connect.
- StopBits. How many bits it should stop after transmisson, None, One, Two, OnePointFive(1.5).
- Port. Port to the siox bus.
- Logging
- Enable log. Set this to enable logging of Siox Connector.
- Path to logfile. The file where the Siox Connector appends logs.
- Max size of logfile. Maximum size of logfile (in kilo bytes). Setting this to zero indicates no limit.
- Log level. Controls at what level logs will be written.
Web Service
The Web Service Connector can be used to consume SOAP based web services.
Configuration
URI to WSDL Specifies where to find information about web service. Can be a file if the file does not contain any external references.
Runtime configuration This is an advanced feature which should not be used unless explicit need for it exists.
Endpoint name This specifies what endpoint in Runtime configuration to use.
Client credentials Setups the client credentials to use when communicating with web service.
Web Page Submit
The Web Page Submit Connector can be used to send HTTP POST and GET requests to a given url. At least one parameter must be sent.
Configuration
- Authenication URL
- User name
- Password
- HTTP Headers
- Encoding
NiceLabel Connector
Configuration
Set up of NiceLabel Automation to accept Flow request.
- Start NiceLabel Automation Builder and create new configuration:
- Select TCP/IP Server Trigger:
- Note Port number (will be used in Flow configuration):
- Go to Variable tab on TCP/IP Server:
- Select DataFileName from Internal Variables:
- Go to Action tab on TCP/IP Server:
- From All Action - select Run Command File:
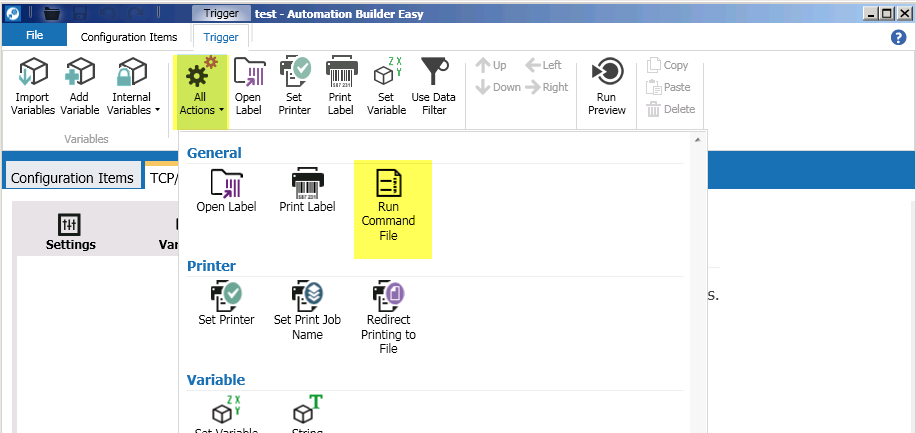
- Select variable DataFileName as File name. Make sure that File Type is XML File:
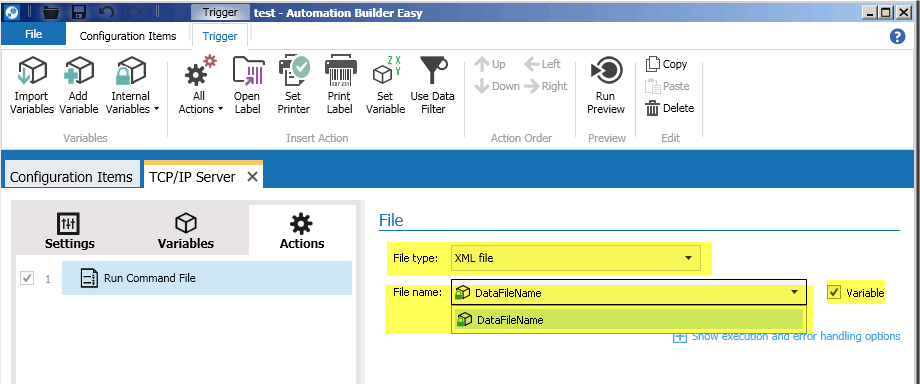
- Save configuration to some suitable folder.
- Start Automation Manager and select saves configuration:
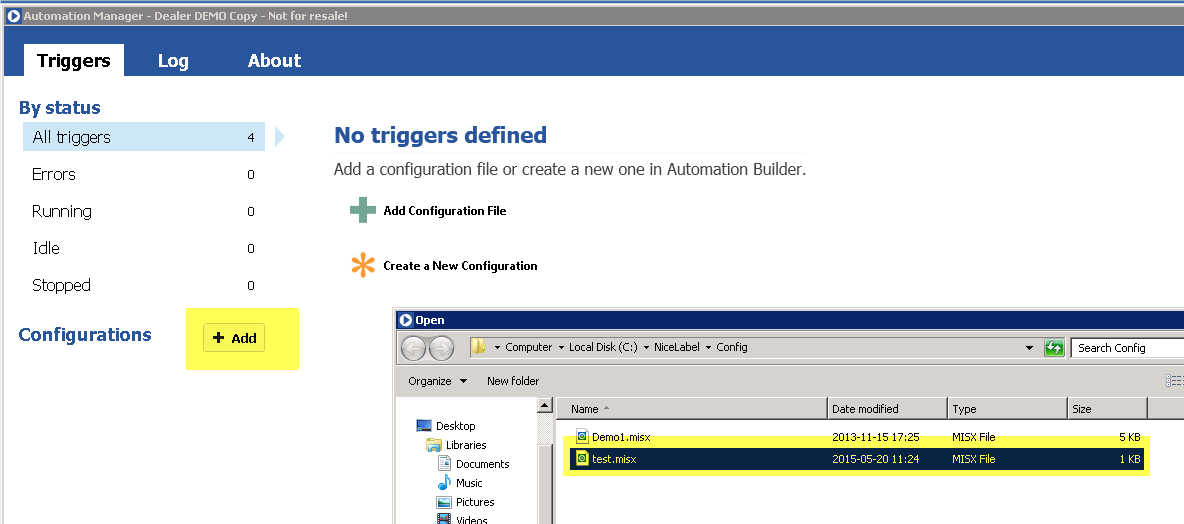
- Start configuration process:
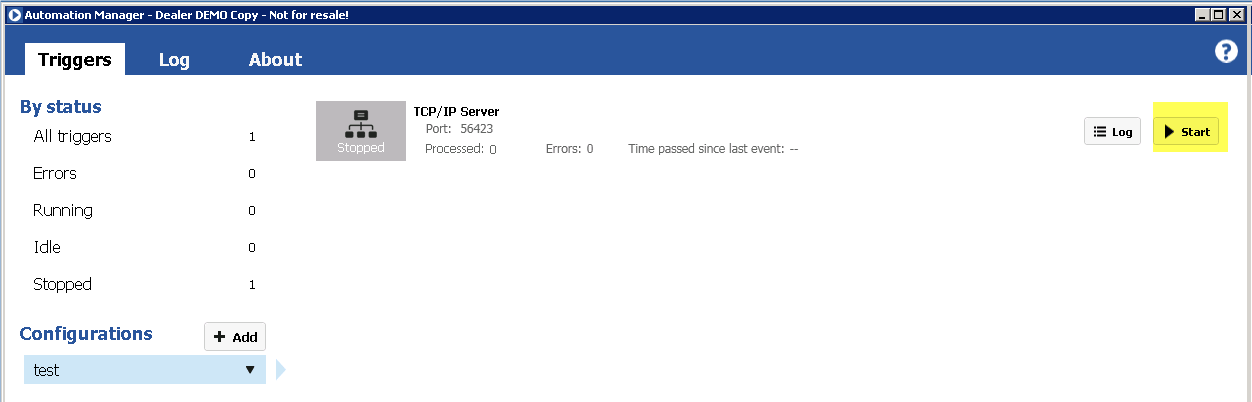
- Configure NiceLabel connector in Flow. Use TCPIP port number from step 3:
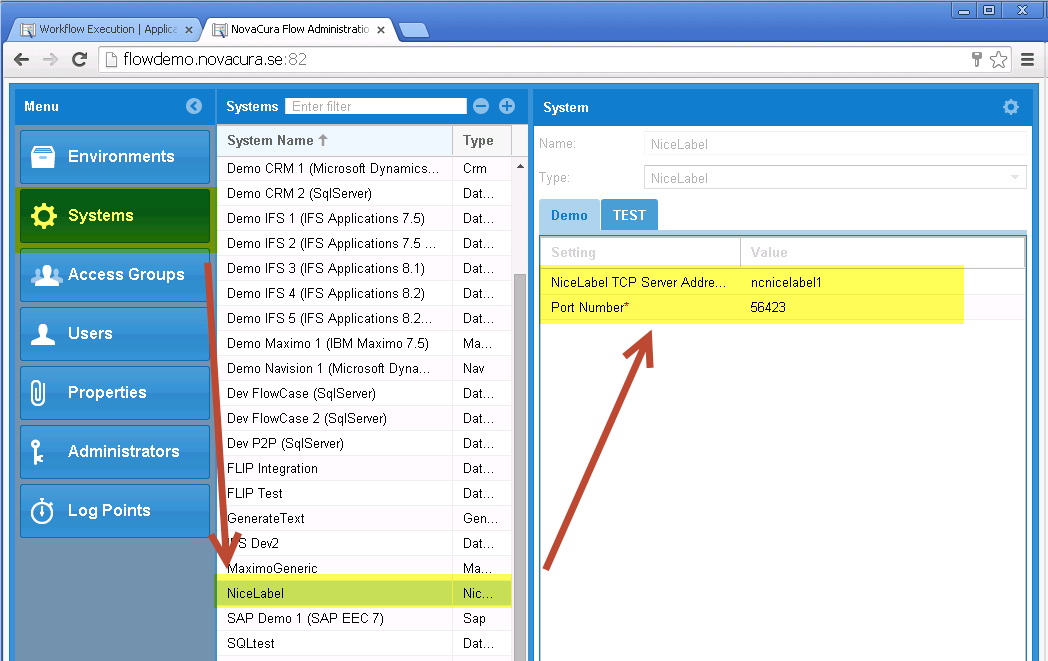
- When request is send from Flow, trigger will execute it and status will be changed:
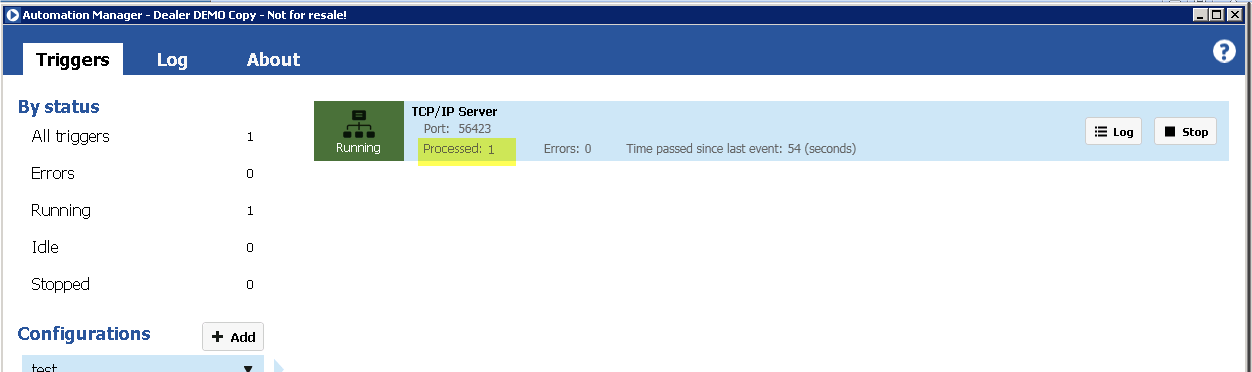
- Example flow looks like this:
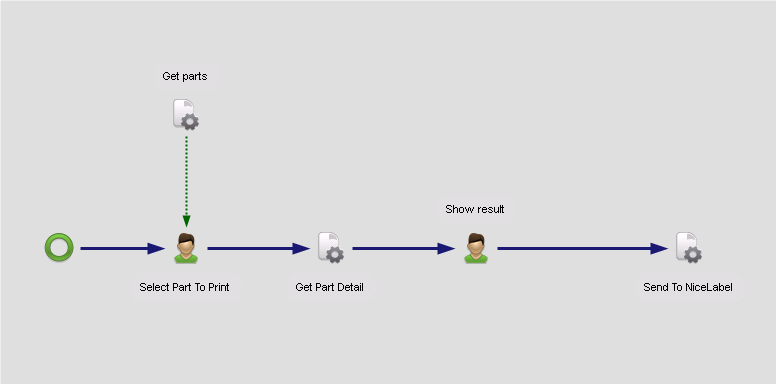
- Send To Nice Label task is set up like this:
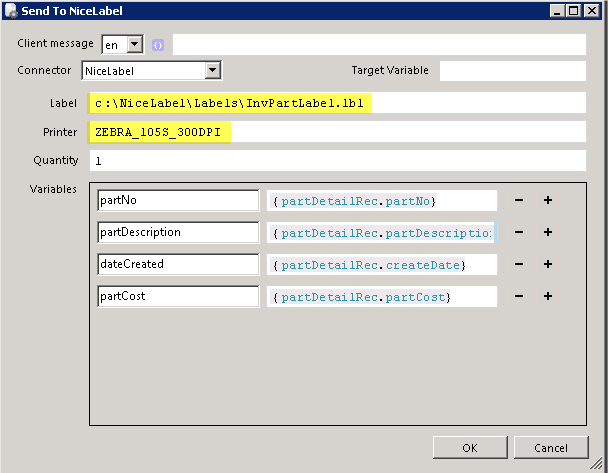
Label file and printer need to be available on the NiceLabel server.
Use the NiceLabel connector
This instruction assumes that following programs/components are installed:
- NiceLabel Automation
- NiceLabel DesignPro (configured label printers is recommended)
- Novacura Flow5 with configured NiceLabel connector
- Start NiceLabel DesignerPro and select to create new label. Select the printer and label size you are using in the Wizard that opens automatically.
- Add variables; It is important to set correct size for variables, if you send data that exceed the defined size, NiceLabel will fail to print the label.
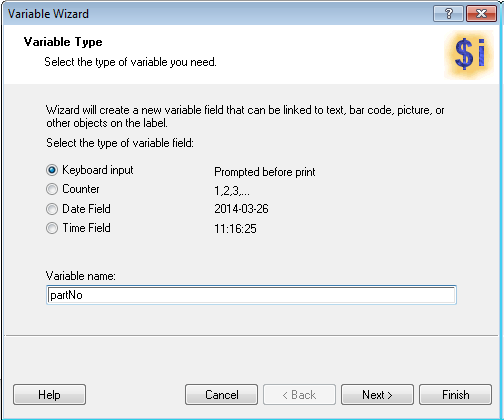
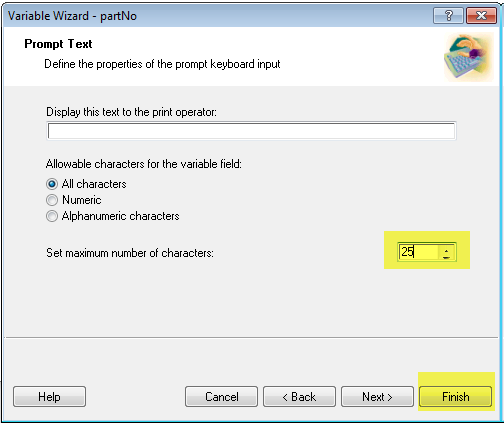
- Note names of all variables:
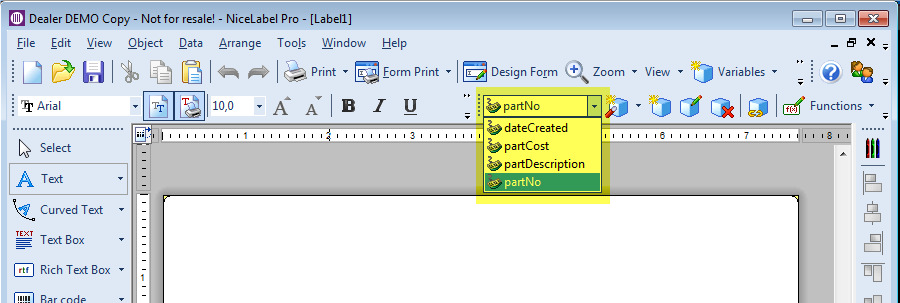
- Design the label layout using created variables.
- To add a barcode do as follow:
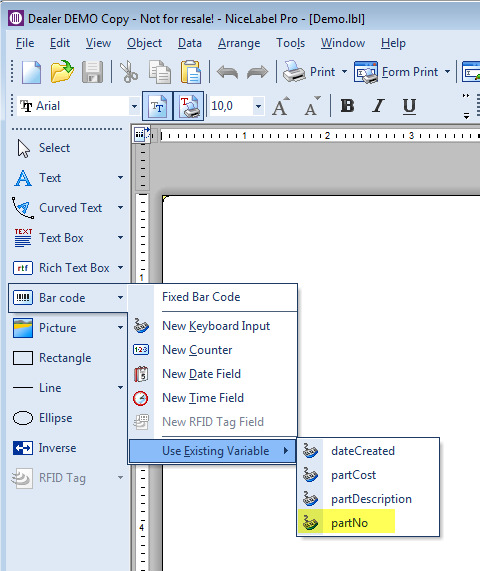
- To add a text box do as follow:
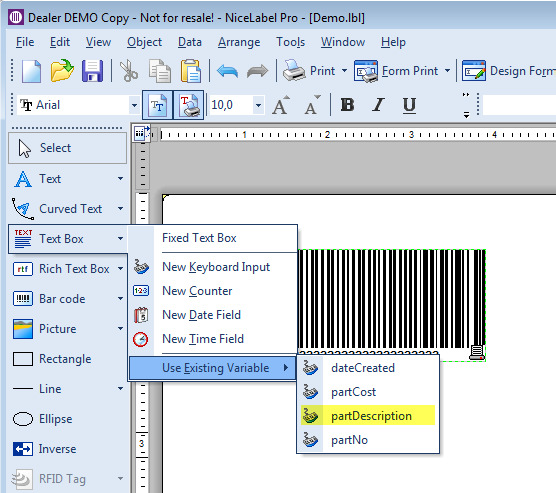
- Save the label file to folder on server that runs NiceLabel Automation.
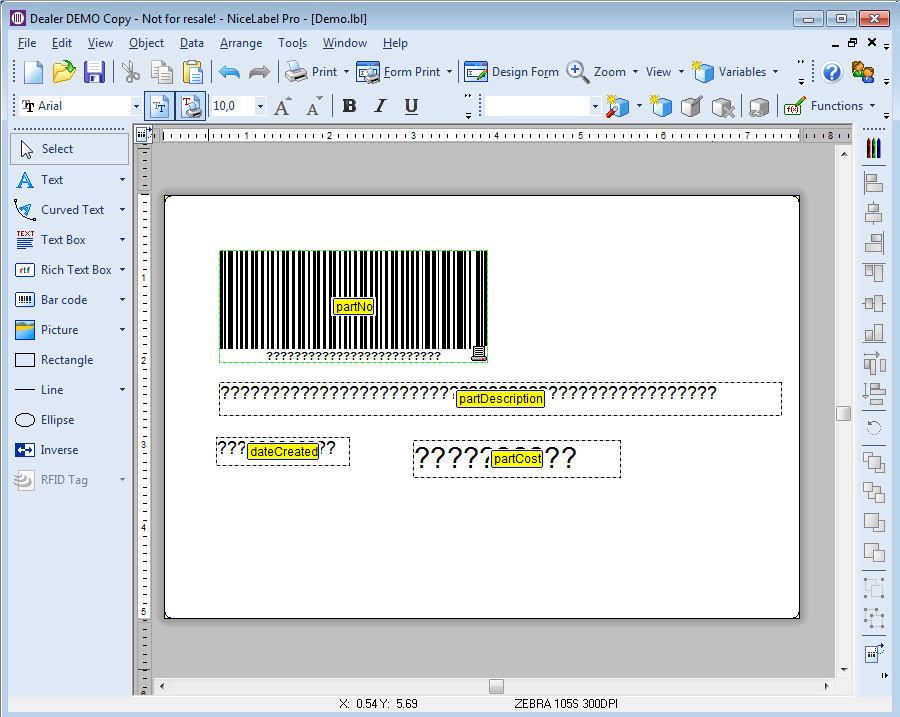
- Add Flow machine task and configure it as NiceLabel connector.
- Bind variables from the label to local variables in the flow. Variable name in NiceLabel are case sensitive. Label path is relative to NiceLabel automation server (local map on that server).
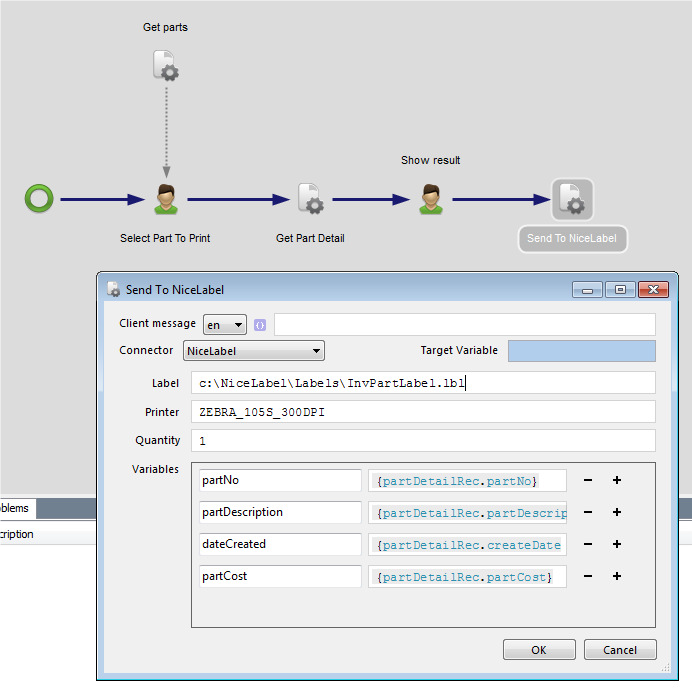
- Save flow and execute. Check status on NiceLabel Automation server.
BarTender 2016
The BarTender connector can be used to integrate with BarTender 2016 R6, typically to print BarTender documents.
32-bit version of BarTender 2016 R6 Automation Edition or Enterprise Automation Edition needs to be installed on the same machine as Flow Server
Configuration
Path to look for .btw files in Specifies where to find BarTender documents.
Default printer Name of printer to use. Leave empty to use the printer set on BarTender document. The printer can also be overriden in print operations.
Global runtime identity Identity of user to run BarTender operations as. If any Domain is specified here it will be applied also on identity specified on Flow user.
Design time identity Identity of user to use while designing workflows. Never used in runtime. If left empty (i.e User not specified) and Global runtime identity is provided, Global runtime identity will be used also while designing workflows.
Cache metadata Specifies whether to connector should cache any metadata regarding what BarTender documents there are and what parameters they have.
NiceLabel Connector
Configuration
Printing
Custom model member
With the custom data type on a model member you can specify external (from the perspective of the REST project tool) data types. You use Custom specification the specify the type.
Currently the only available custom data types are types originating from the .NET Base Class Library (BCL). To use a type from BCL you prefix the full name of that type with 'bcl:', for instance 'bcl:System.TimeSpan'. Note that certainly not all types will work, and most of them will make no sense. You can consider this feature as an advanced one with limited support available. It is however powerful and useful in many scenarios and can save you a lot of development time and need of custom connectors by using it properly. Since it can reduce the need for custom connectors it also simplifies deployment and reduces maintenance.
So, after this warning, let's walk through an example of how it can be used.
Consider this scenario:
* You want to fetch pdf documents from a REST API.
* The REST API returns the pdf documents as base64 encoded strings.
* You want to store these documents in the filesystem, of course not as base 64 encoded string but as the actual binary data.
This is how the json looks like when returned from the server:
{
Data: "JVBERi...base64 encode data...PDj8OT==",
Name: "4cdda37a-fa71-1065-a761-141a4ebaf7d3",
Extension: ".pdf",
InvoiceId: "401757"
}Since this is what the API will return, we need a model for it. This is quickly done with 'NEW FROM JSON' in the Model part of the REST Project Tool. See Models for more information on how to to that.
Once we've created the model it will look like this:
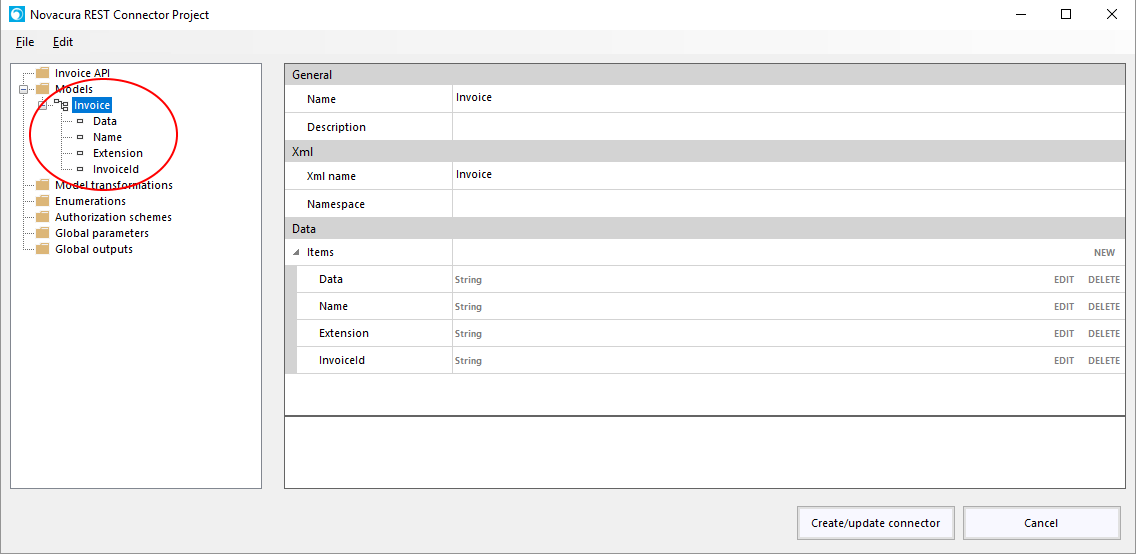
We now need a model that contains not the base 64 encoded string, but instead an instance of System.IO.Stream.
Since this model will look almost the same as the 'Invoice' model, we can use the 'Clone model' feature. This is accessed by selecting the tree node for the model and right clicking: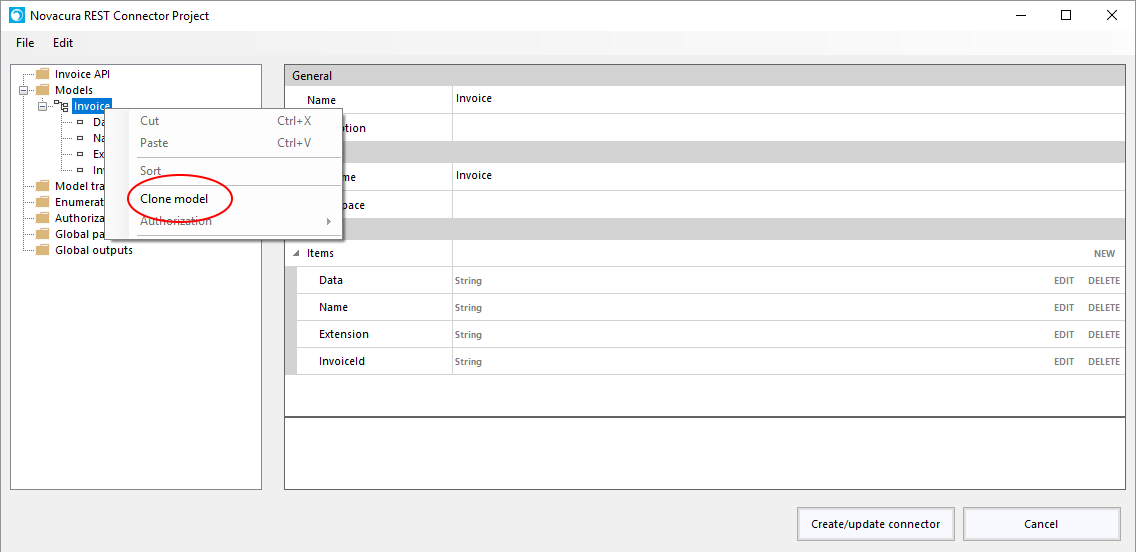

Next step is to change the data type of 'Data' in 'Invoice (binary)'. Select the 'Data' member and change 'Type' to 'Custom' and set 'Custom specification' to 'bcl:System.IO.Stream'.
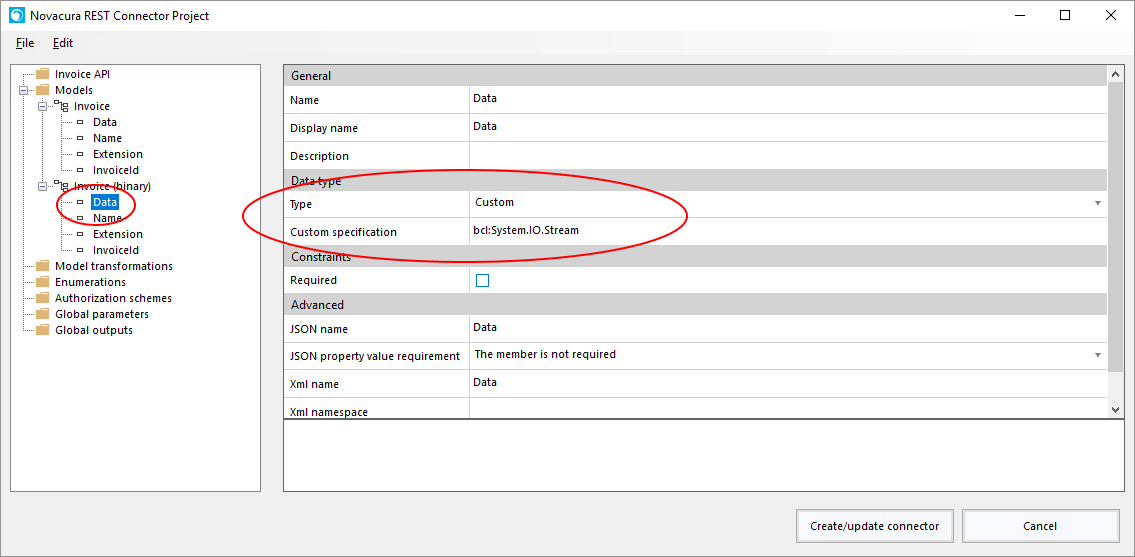
Next step is to create a model transformation between the two models.

The code could look something like this:
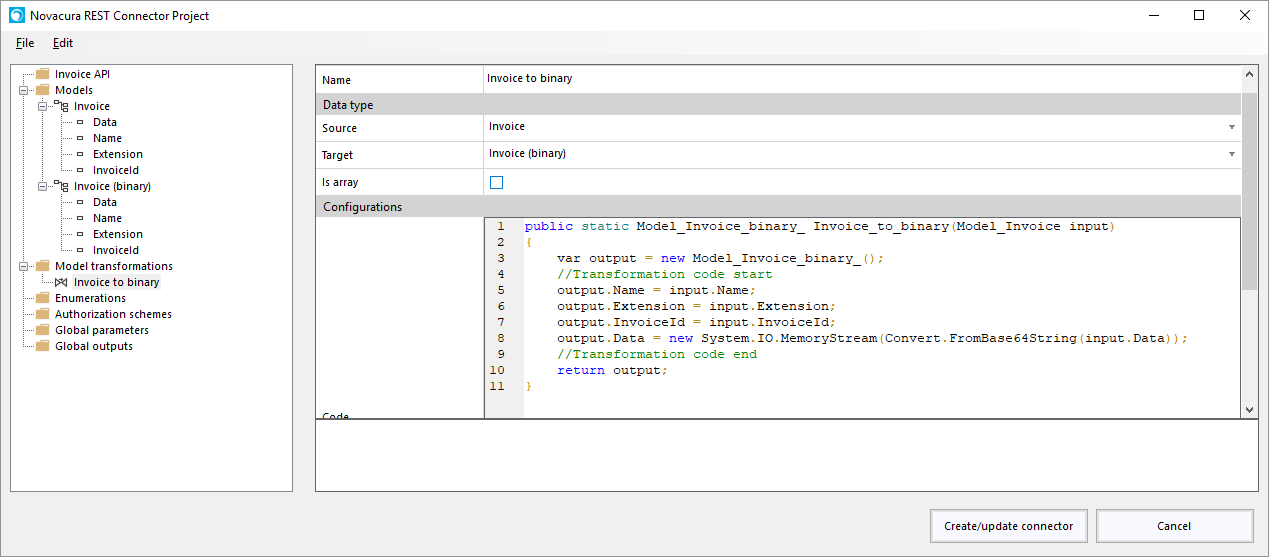
Now this transformation can be applied to a GET operation

Finally the workflow could look something like this:

Custom Connector
Flow has support for using third party .net assemblies. All public static methods with primitive types as arguments can be executed from a machine step in any type of workflows.
Follow these steps to setup a custom connector:
- Run NovaCura.Flow.Connector.Wrapper.exe from your command line console.
- It is located in Flow Designer program folder.
- First argument is output connector dll name, example: CustomConnector.dll
- Second argument is input assembly path.
- If input assembly has dependencies to other assemblies those can be entered as arguments. For example: NovaCura.Flow.Connector.Wrapper.exe CustomConnector.dll CustomAssembly.dll CustomUtil.dll
Copy output dll to the current studio version (%appdata%\{{version}}) and to bin/CustomConnectors* folder located in Server installation folder.
Add a connector element to CustomConnectors.xml located in bin/CustomConnectors folder in Server installation folder.
<!-- Change 'species' to a unique technical name --> <!-- Change 'displayName' to a suitable display name --> <!-- Change 'assemblyname' to the name of the output dll exluding .dll, in the example below the file is named CustomConnector.dll --> <connector species="custom_connector_name" displayName="DotNet API Custom Connector" assemblyname="CustomConnector" type="NovaCura.Flow.Connector.Wrapper.ConnectorWrapper" uitype="NovaCura.Flow.ApiConnector.UI.ApiConnectorUI" uiassemblyname="NovaCura.Flow.ApiConnector.UI" />Start Flow Designer and verify that a new connector type with the previous specified display name exists in Connectors page under Environments when adding a new connector.
Add the new connector and enter a suitable name.
The new connector should now exist in all machine step configurations.
File System
File System Connector can be used to perform basic file and directory operations on a Windows operating system which the Flow Server can access.
Configuration
File System connector should be configured to run as a specific user. If not configured, it will run as the same user as the Flow Server is running as.
- Domain. Domain name or leave empty to use a local user.
- User. User to run file system connector operations as.
- Password. Password for user.
- Logon Type. Typically use Interactive.
Read/Write to Flow Environment
The Flow Environment Connector can be used to read information from the flow 6 database, it can also write new data to said database.
Configuration
- User: Flow username that can read and write in the environment.
- Password: Username password in the flow environment.
- Url: Flow server address
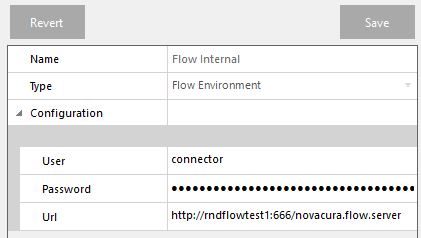
Generate Text Connector
The Generate Text Connector can be used to output text either to a file or over the network via HTTP or TCP. Flow variables can be used to compose the text to write.
Configuration
No configuration is required.
Utility
Database - IBM DB2
Get Started
- Install IBM Server Runtime Client version 10.5 with Fix Pack 9.
- Copy "msg" folder from IBM installation to Flow Server folder.
- Copy "db2app.dll" from IBM instllation BIN to Flow Server Bin folder.
Step 2-3 must be repeated after upgrading and patching.
Configuration
Same configuration as written in the general Database instructions.
In order to specify a specific database instance the following annotation can be used in "Database server" field: <ip>:<port>;Database=<database_name>
Get customer license
Customer license is a part of the business agreement between Novacura and our clients. It contains all the features required by your company.
In order to get the Customer license, please contact Novacura Support.
- By clicking here
- By sending an email on info@novacura.se
- By contacting your local Novacura sales representative.
Get demo license
To get your demo license please click on the "Create demo license" button, fill the required information and then press "Submit demo license request". Message with your license will appear shortly in the mailbox provided above.
Received key should be written into the field below and after pressing the "Create demo license" button your license will be created and stored on the server.
If you did not get a license key, please do the following:
- Check if the message was not put into the Spam folder. To prevent it next time, add Novacura to your mailbox trust list.
- Make sure you have provided a valid email address in the info section. If not, type the correct one and send the request once again.
- Make sure you are allowed to receive messages from Novacura. Contact your mailbox provider if it is blocked.
- In case of other problems, please contact Novacura Support.
If you requested your license before you will not get a new demo license - you can ask to extend your demo period using the previous license.
Active Directory Sync
Here you can set up syncing from Active Directory to Flow Users.
Click Add Group to add a new mapping, mapping is done from Active Directory group to Flow Role. When all groups have been added click Sync to begin syncing from Active Directory Users to Flow Users.
Everytime Sync is clicked all previous synced users are removed from Flow and new users are created to match current Active Directory status.
See Flow Script Active Directory Sync
Enter the relevant information for which AD that is to be used in the configuration and set the timing as to when the syncronization is to run. For Azure ID the id can be with our without domin. For customers with multiple domains, the inclue domain box should be ticked to avoid problems with users with the same name on differnt domains.
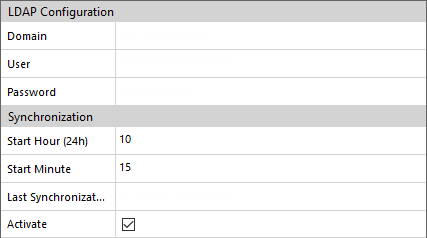
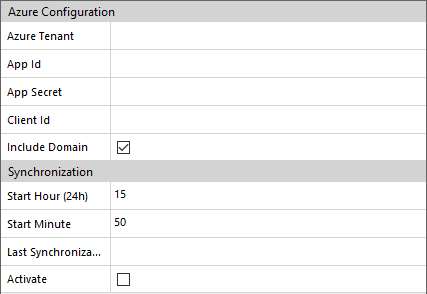
Connectors
With connectors can Flow integrate with different systems, databases and services.
When a connector is configured will it be used when creating workflows in the Flow studio and when executing workflows from a Flow client. For each type of connector there is a unique configuration that specifies how to connect to the specific system, database or service.
Update the Flow License
After ordering a connector license from Novacura or your local Partner, open the Flow Studio and go to Environment/License. Press the Update License button.
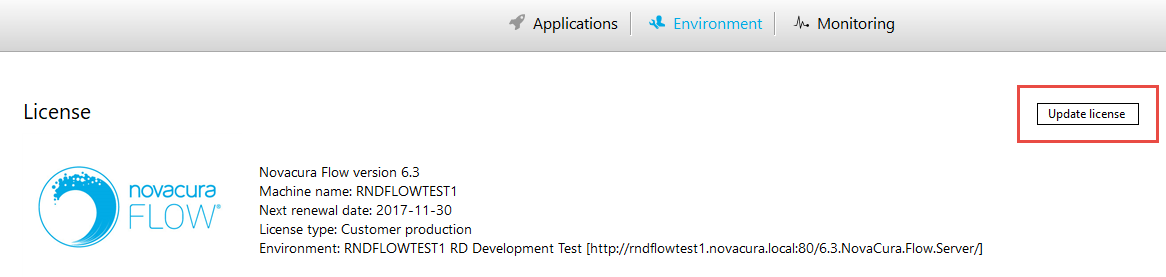
Make sure that the license is allowed in the list of connctors:
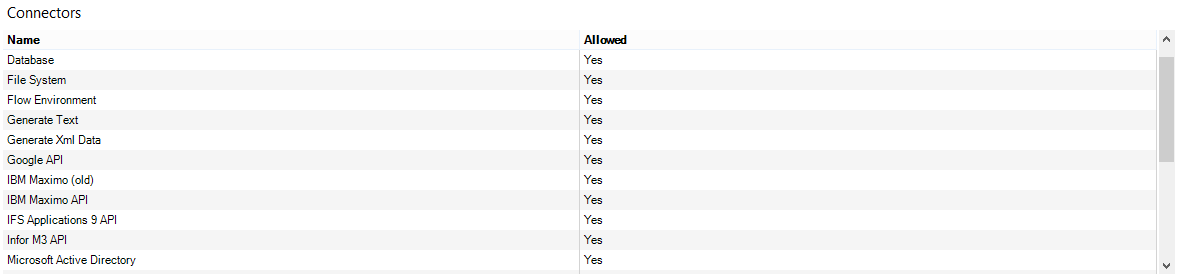
The connector is ready to be configured.
Setup a new connector
To add a connector click on Add in the top-right corner and choose type and enter a name of the connector.
See specific setup for the connectors under Connectors in the menu tree structure.
Read more about connectors here.
Devices
With the built-in Flow Basic Mobile Security Management all connected mobile devices can be overviewed and managed directly in the Studio or via a workflow.
If Device Management is enabled for the environment all new devices that tries to log in to the environment need to be approved before the user actually can log in to Flow via a mobile client. In the same way existing devices can be blocked if, for example, a device is lost or replaced.
Devices that are unhandled will have status New and an administrator can either Approve or Block the device. Every time a user logs in from an approved device will the Last User field be updated with the latest logged in user.

Until the device is approved the client user will get the message This device has yet to be approved by a system administrator.
If the device is blocked the client user will get the message This device has been blocked by a system administrator.
System event
With the system event Device Status Changed it is possible to automate some of the device management and for example alert administrators with an email if a new device is connected.
Use the Flow environment connector and the functions related to Device management to for example approve or block devices via a workflow.
Read more about system events here.
Common questions:
How to activate or deactivate device management?
Menu selection Device will only appear in the menu if device management is activated for the connected Flow server.
- Go to the Flow server installation folder
- Edit the web.config file
- Change the value of useDeviceManagement to true if device management should be used and false if device management should be turned off
Is device id the IMEI number?
No, the device id is generated from an OS-specific API made for the purpose.
Devices with iOS will generate a new device id if the Flow app is reinstalled.
Environment
The environment tab is used to adminstrate properties and values which is common for all workflows and creates a context in which the process platform can execute. Users with type AdministerBasicData can access this tab.
Languages
Flow administrators have access to add and remove languages. The added language can be used when designing workflows and can also be selected from the clients to get a preferred language on the whole client.
To add a new language, click on add and then select a language from the drop-down list.
To remove a language, click on an added language and then click on delete.
License
To be able to run Novacura Flow a license will need to be issued.
There are two types of licenses:
- Demo license - a trail license allows you to test and use all the features in Novacura Flow for a limited amount of time.
- Customer license - a regular license that includes the parts of Novacura Flow that is purchased.
Demo license
Request a demo license by clicking on the Create demo license button, enter the required information and click Submit demo license request. An email with the license key will be sent to the contact email adderss.
Enter the license key into the field and after pressing the Create demo license button the license will be created and stored on the server.
If you did not get a license key, please do the following:
- Check if the message was not put into the spam folder. To prevent it next time, add Novacura to your mailbox trust list.
- Make sure you have provided a valid email address in the info section. If not, type the correct one and send the request once again.
- Make sure you are allowed to receive messages from Novacura, contact your mailbox provider if it is blocked.
- In case of other problems, please contact Novacura Support, product.support@novacura.com.

Customer license
When the customer license key is recived, please do the following:
- Start the Novacura Flow studio and log in to the Novacura Flow server that should use the license key.
- Go to Environment -> License and click on Create customer license.
- Enter the received license key to the license key field and click on Create customer license.
- When a message License saved! appear is the license saved to the Novacura Flow sever.
About the license service
In the first of every month will the Novacura Flow service send a usage file with information about how many users that is used on the Novacura Flow server. The address https://home.novacuraflow.com need to be reachable from the machine where the Novacura Flow is installed, so the Novacura Flow service can call home and check if the license is valid. If it is not possible to open up for https://home.novacuraflow.com, the license will need to be manually updated through the Novacura Flow studio every month.
It is possible to enter as many users as wanted to Novacura Flow studio but if the license is exceeded a massage will be showed in the Novacura Flow studio and an email will be sent to Novacura with information that this license is exceeded. Novacura will control how many users that is used after the usage file have bin sent and if the license is exceeded will Novacura contact the customer. To buy more users and connectors please contact your Novacura sales contact.
Check the following when license is not updated automatically:
- Do the server have contact with Flow home? Run https://home.novacuraflow.com in a browser on the server.
- If the Flow logotype shows up then is the server connected. Jump to step 2.
- If there is no connection, then must internet connection be turned or opened up for Flow home to make the license service work.
- Is the server address correct in the Flow service config file? Open the .config file in the Service folder under the Flow installation. Make sure that the address is the correct Flow server address for the installation, copy the address and run it in a browser on the server to make sure that it works.
If the server address was incorrect, do:
- Change the address in the .config file to the correct address and remove the date and time for License_LastTime, save the .config file.
- Go to Services and find the Flow service and first stop and after that start it again. (the service have the same name as the environment).
- Wait some minutes, and open the service .config file and check of License_LastTime is updated with the current date and time. If it is updated, log in to Flow studio and check if the license is updated, next renewal date should be next month.
- If this is not working go to next step.

- Open the Service/log folder under the Flow installation, and send the logs to product.support@novacura.com to look at them (logs are only available from version 6.3).
- Change the address in the .config file to the correct address and remove the date and time for License_LastTime, save the .config file.
Properties
A defined property can be used from the Flow designer as a constant in the workflows and thereby be used to define different business logic depending from the value of the property.
A property can exist in two different scopes or contexts:
- Global: the property is valid for the Environment that the User logs in to.
- User: the property is valid for the logged in user.
Enter the value for the environment properties under Environment in the menu. Choose the environment you what to add properties to and press the cogwheel to modify the environment information. Go to tab Properties and fill in the environment data. Enter the value for the user properties under Users in the menu. Choose the user you what to add properties to and press the cogwheel to modify the user information. Go to tab Custom Properties and fill in the user data.
Roles
Roles is used to categorize users in different ways and could be used for different purposes in Flow.
Roles can for example be used to describe an organisational structure or to reflect different types of access group.
A User can be connected to one or many Roles. In order to separate different types of roles, many different Role Trees can be created.
There are two types of inheritance methods for each Role Tree; Inherit Children and Inherit Parent.
Select a role group from the list to view and edit the information or click on Add in the top-right corner of the roles list to add a new role group.
When a new role group is created, enter a Name (the role group name in Flow), Description (the description of the role) and check if the Role should Inherit Children (Inherit Parent is default).
Click on the + button to add a new Role, a new role named New role will appear, rename the role by double-click the new role.
System events
It is possible to connect a machine workflow to a specific event that occurs on the Flow server.
Examples of this can be when a user is added to Flow a machine workflow that sends an email to the user will be executed, or when a user steps over a log point in a workflow a machine workflow will be executed that commit the data to an appropriate data source. Connect a workflow to a system event by either Pick an already existing machine workflow or click on New to create and connect a new machine workflow. Choose a user that will be the executer of the machine workflow.
Observe that only machine users will appear in the list of users that can execute a system event.
Create system event workflows with the New button to get event specific parameters generated in the start step.
System events that is possible to connect a machine workflow to:
- Start workflow: The machine workflow will be executed when all workflows is started.
- End workflow: The machine workflow will be executed when all workflows is ended.
- Add user: The machine workflow will be executed when a user is added.
- Remove user: The machine workflow will be executed when a user is removed.
- Log point: The machine workflow will be executed when a log point is stepped over in a running workflow application, read more about log points here.
- Handover: The machine workflow will be executed when the workflow hands over to another swim lane.
- Device Status Changed: The machine workflow will be executed when a new device request is sent to the Flow environment, read more about device management here.
- Help Request: The machine workflow will be executed when a new help request is registered, read more about help request here.
Users
A Flow users can either have access level administor, designer or client. In combination with Type will the user have different limitations of running workflows.
Information about how many uses that is available can be found under license.
To add a new user click on Add in the top-right corner, it will appear a dialog to the right where it is possible to add the new user.
- Name: Enter the name of the user.
- E-mail address: Enter an e-mail address for the user.
- User id: Enter a user id.
- Access level: All userss can run applications but if the users should be able to administrate the environment or design workflows they need to have access level administrator and/or designer.
- Administrator: With this access level can the user administrate the environment and design workflows, for example add/edit users, roles, connectors and add/edit workflows.
- Designer: With this access level can the user create and edit workflows in the designer tool.
- Group: Group is used for grouping users in the users list.
- Type: Choose the type of the user.
- Full user: A full user can log in and run all licensed clients including the portal.
- Workflow user: A worklow user will only have permission to run specific granted workflows.
- Machine user: A machine user can only run machine workflows, read more about machine workflows here.
- Transaction user: For every workflow that is started will a transaction be counted.
- Portal user: A portal user will only have permission to log in to the portal client.
- Public user: A public user can run a workflow without the need to log in.
- App user: A user type for application packages.
- Password: If the user should have a specific Flow password then enter a password for the user in this field otherwise leave the field empty.
- Language: Enter a value to set the default language for the user. If the field is left empty the following language will be used:
- Andriod, iOS and UWP - device language
- Web and Portal - language depends on the browser:
- Chrome - Language is taken from the first language in the list of defined languages in the browser settings.
- IE/Edge - Language is taken from the display language set in Windows.
- Chrome - Language is taken from the first language in the list of defined languages in the browser settings.
Culture: This settings is for Portal and Web only; Enter a value to define which culture is to be used for date formats. If culture is left empty or set to Not Specified the formats will be based on the user language.
Andriod, iOS and UWP will use device settings for date formats regardless of Culture being set on the user or not.
- Role tags: Choose those roles the roles that the user should have permission to.
- Properties: Enter values for any properties, read more about properties here.
Connectors: Enter username and password for connectors, read more about properties here.
How do i find which version of flow i am running?
The version number are divided into four parts {Major}.{Minor}.{Service Pack}.{Revision}. Example: 6.1.7.26406
Flow server
- Navigate to the flow server URL on a web browser.
- The server version is displayed in the middle of the screen as seen below.
Flow Studio
- In the menu bar, navigate to Help-> About Novacura flow
- the server version is displayed as highlighted in the picture below.

Flow Android Client
- Navigate to Settings -> Programs -> Novacura Flow
- the server version is displayed as highlighted in the picture below.
Flow iOS Client
- Navigate to Settings -> General -> Storage and iCloud usage -> Manage Storage -> Flow Client
- the server version is displayed as highlighted in the picture below.
Flow Universal Windows Platform Client
- Navigate to the threebutton menu in the top right corner -> About.
- the server version is displayed as highlighted in the picture below.

Flow Windows CE Client
- Navigate to the top left avatar icon button in the ce client and click it.
- The server version is displayed as highlighted in the picture below.
For any further inquiries contact us at product.support@novacura.com
Advaned Functions
| Function | Description | Example Expression | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Split(input, delimiter) |
Divides the input string into substrings separated by the delimiter, returning a new table variable with a single value column containing the sub-strings. Note that the delimiter argument must be exactly one character long. | Split("2,89,16", ",") |
a table variable with one value column, containing three rows: value = 2, value = 89 and value = 16 |
IsNull(input, replacement) |
Replaces empty input values with the specified replacement value. If the input value is not empty will the value not be replaced. | IsNull("", 0) |
0 |
CSVFill(table(colA,colB,...),string,"delimiter") |
Creates a table variable from delimited text | CSVFill(table(partNo, qty, unit),decodedString,";") |
Creates a table variable with columns partNo, qty, unit based on the decodedString variable which was created using the DecodeText function |
DecodeText(input, encoding) |
Decodes text encoded as binary data (from a BLOB database column or a File Gallery interaction item). The second argument specifies the encoding from which to decode. Valid values for this argument can be found in the encodings system variable, which is available in all workflows. |
DecodeText(myFile.data, encodings.Windows1252) |
contents of myFile.data, decoded using the Windows 1252 Character Set |
Default(typeValue) |
Returns an empty record based on a type value (see Type Definitions). | Default($PurchaseOrders__RowType) |
<an empty record matching the type of the PurchaseOrders table variable> |
Empty(typeValue) |
Returns an empty table based on a type value (see Type Definitions). | Empty($PurchaseOrders__RowType) |
an empty table matching the type of the PurchaseOrders table variable |
The CASE/WHEN/THEN Construct
If you need an expression to return different values depending on the input, you can use the CASE-WHEN-THEN construct.
The example below returns the text "zero" if the value of variable x is 0, the text "negative" if x is less than 0 and the text "positive" in all other cases.
case when x = 0 then "zero" when x < 0 then "negative" else "positive" endThe IN Operators
The IN operator allows you to compare one left hand side value (L) with several right hand side values (R) at once. The result of the statement is TRUE if L is equal to any of the values in R.
firstName in ('James', 'Richard', 'Danny')Truth of Non-Boolean Values
FlowScript is fairly permissive when it comes to evaluating the truth of non-Boolean values. The following non-Boolean values count as true:
- All numbers except 0
- All strings except the empty string,
"0"and"FALSE"(including all upper- and lowercase variants)
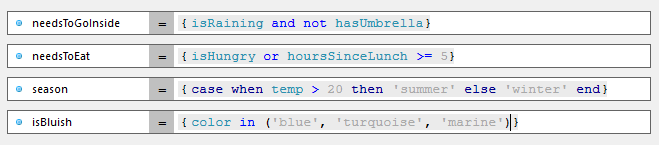
Examples
The JSON Module
The JSON module can be used to transform Flow variables (records or tables) into JSON data and vice versa.
JSON.Decode(data)
The generic Decode function takes a JSON record (as text) and decodes it as the specified type (T). Fields which are present in the type (T) but do not have a corresponding entry in the JSON data will be created with the default value. It is therefore recommended to specify default values for all type structures which will be decoded from JSON.
let data = '{"name" : "Richard", "age" : 28}';
type personType = [name = 'Not specified', age = 0, occupation = 'Unemployed'];
let myPerson = JSON.Decode<personType>(data); // Person will have occupation 'Unemployed' since the key is not present in the json data
return myPerson.age; // Returns 28JSON.DecodeTable
The generic DecodeTable function takes a JSON table (as text) and decodes it as a table of the specified type (T). Columns which are present in the type (T) but do not have corresponding entries in the JSON data will be created with the default value. It is therefore recommended to specify default values for all type structures which will be decoded from JSON.
let data = '[{"name" : "Richard", "age" : 28}, {"name" : "Samantha", "age" : 21, "occupation" : "Programmer" }]';
type personType = [name = 'Not specified', age = 0, occupation = 'Unemployed'];
let persons = JSON.DecodeTable<personType>(data);
return persons.First().name; // Will return "Richard"JSON.Encode
The generic Encode function takes any FlowScript record variable and encodes it as JSON.
let animal = [name: 'Cat', numberOfLegs: 4];
return JSON.Encode(animal); // Will return '{"name" : "Cat", "numberOfLegs" : 4.0 }'JSON.EncodeTable
The generic Encode function takes any FlowScript table variable and encodes it as JSON.
let animals = [name: 'Cat', numberOfLegs: 4] & [name: 'Millipede', numberOfLegs: 1000];
return JSON.EncodeTable(animals); // Will return '[{"name" : "Cat", "numberOfLegs" : 4.0}, {"name" : "Millipede", "numberOfLegs" : 1000.0 }]'Date Functions
| Function | Description | Example Expression | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Date(input) |
Explicitly converts the input to a date value. The input must be a string matching the format "YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS" | Date("2016-03-10 14:00:00") |
2016-03-10 14:00:00 (date) |
Now() |
Returns the current date and time | Now() |
(current date and time as a date variable) |
Format(x, pattern) |
Formats x as a string, using the given pattern. See Formats | Format(d, "yyMMdd") |
"160310" |
Example of the left side value (L) is a date and the right side value (R) is a number, the expression returns a new date representing L with R number of days added.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
now() + 1 |
A date variable representing tomorrow. |
now() - 1 |
A date variable representing yesterday. |
Functions
FlowScript has a number of built-in functions to transform or query the variables in your workflow. FlowScript uses a function call syntax identical to that of common programming languages such as C, Java and Visual Basic, where the function name is followed by an opening parenthesis, a commaseparated list of inputs (if required by the function) and a closing parenthesis:
{function(input1, input2)}Functions that require no parameters (such as the Now function, which returns today's date and time) must still be written with opening and closing parentheses, i.e. {now()}.
Functions in Flow never have side effects; that is, they never modify their input.
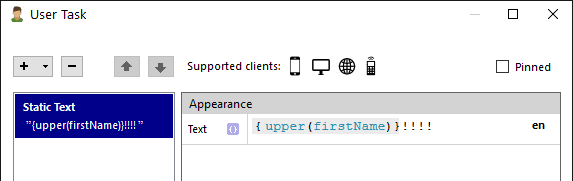
Screen shot: A User Task configuration dialog showing the user of the Upper function, which transforms the value of the variable "firstName" into uppercase. Note that the content of the firstName variable is not affected by this; all FlowScript functions return new values, leaving the input value(s) untouched.

Screen shot: The same User Task running in the web client. Note that the name "Richard" has been transformed to all-uppercase by the Upper function.
Another example is the Left function that returns the first N characters of the input text, where N is the value of the second parameter. If firstName has value "Richard" and lastName "Feynman" the result of this example would be "Your initials: R F".
Your initials: {left(firstName, 1)} {left(lastName, 1)}Number Functions
| Function | Description | Example Expression | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Min(a, b) |
Returns the lesser of a and b | Min(1, 2) |
1 |
Max(a, b) |
Returns the greater of a and b | Max(1, 2) |
2 |
Ceil(x) |
Returns the value of x rounded up to the nearest integer | Ceil(1.2) |
2 |
Floor(x) |
Returns the value of x rounded down to the nearest integer | Floor(1.5) |
1 |
Round(x) |
Returns the value of x rounded to the nearest integer | Round(1.8) |
2 |
Pow(x,y) |
Returns the result of x raising to the power y. | Pow(8,3) |
"512" |
Format(x, pattern) |
Formats x as a string, using the given pattern. See Formats | Format(0.33333333, "F") |
"0.33" |
Str(x) |
Changes the numeric variable x into a string value. This is rarely necessary as Flow automatically coerces numeric values into string value. | Str(7) |
"7" |
Val(x) |
Changes the string variable x into a numeric value. This is rarely necessary as Flow automatically coerces string values into numeric value. | Val(7) |
"7" |
Mathematical Expressions
FlowScript supports algebraic expressions using common mathematical operators and parenthesized expressions. For example, the expression:
{x + 1}...will print out as the value of variable x plus one (provided the variable x has a content which can be interpreted as a number).
Numeric literals (e.g. the 1 in the expression {x + 1}) can be positive or negative, integer or decimal. For decimals, always use the dot character, e.g. 1.5, whether or not your Flow environment is used in a language/region where the comma is used as decimal separator. Note, however, that the numeric content of variables (as opposed to literals) is interpreted less restrictively; both the comma and the period can be used as a decimal separator. This ensures that Flow works with user-input values in regions using a decimal comma (such as Scandinavia) as well as regions using a decimal point (such as the US).
Mathematical operators
The following listing contains all the algebraic operators available in FlowScript.
Plus (+)
Adds two numbers. If the left side value (L) is a date and the right side value (R) is a number, the expression returns a new date representing L with R number of days added.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
a + b |
If a is a number, the sum of variables a and b; if a is a date, a new date representing a plus b days. |
now() + 1 |
A date variable representing tomorrow. |
Minus (-)
Subtracts two numbers. If the left side value (L) is a date and the right side value (R) is a number, the expression returns a new date representing L with R number of days subtracted.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
a - b |
If a is a number, the difference between variables a and b; if a is a date, a new date representing a minus b days. |
now() - 1 |
A date variable representing yesterday. |
Multiplication and Division (* /)
Multiplies or divides two numbers.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
a * b |
a multiplied by b |
a * 1.5 * b |
a multiplied by 1.5 multiplied by b |
a / 10 |
a divided by 10 |
Text Functions
FlowScript text literals can be written either with a single or double quotes. Textual values can be concatenated using the & operator.
| Function | Description | Example Expression | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Len(input) |
Returns the length of the input. | Len("Hello") |
5 |
Left(input, count) |
Returns the first count characters of the string. | Left("Hello", 2) |
"He" |
Right(input, count) |
Returns the last count characters of the string. | Right("Hello", 1) |
"o" |
Mid(input, start, count) |
Returns the substring starting at start and continuing count characters. The start parameter is 0-based: the first character has index 0, the second 1 and so on. | Mid("Hello", 1, 3) |
"ell" |
Trim(input) |
Removes whitespace characters before and after the string. | Trim(" Hello ") |
"Hello" |
InStr(input, search) |
Returns the 0-based index of the first occurrence of the search string within input, or -1 if the substring is not found. | InStr("Hello", "e") |
1 |
Upper(input) |
Returns an all uppercase version of the input. | Upper("Hello") |
"HELLO" |
Lower(input) |
Returns an all lowercase version of the input. | Lower("Hello") |
"hello" |
Replace(input, search, replacement) |
Replaces all instances of the search string in input with replacement. | Replace("Hello", "e", "u") |
"Hullo" |
RegexMatch(input, pattern) |
Return a truth (Boolean) value indicating whether the given Regular Expression pattern matches the input. | RegexMatch("123", "\d{3}") |
TRUE |
RegexReplace(input, pattern, replacement) |
Performs a Regular Expression replace on the input string, returning the result. | RegexReplace("2hello1", "\d", "X") |
"XhelloX" |
Chr(code) |
Returns the given Unicode character code as a string. | Chr(9) |
<the TAB character> |
Guid() |
Returns a new Globally Unique Identifier: a random string with a very low chance of ever being returned again by subsequent calls to the same function. | Guid() |
<a unique identifier> |
Split(input, delimiter) |
Divides the input string into substrings separated by the delimiter, returning a new table variable with a single value column containing the sub-strings. Note that the delimiter argument must be exactly one character long. | Split("2,89,16", ",") |
<a table variable with one "value" column, containing three rows: value = 2, value = 89 and value = 16> |
IsNull(input, replacement) |
Replaces empty input values with the specified replacement value. If the input value is not empty will the value not be replaced. | IsNull("", 0) |
0 |
DecodeText(input, encoding) |
Decodes text encoded as binary data (from a BLOB database column or a File Gallery interaction item). The second argument specifies the encoding from which to decode. Valid values for this argument can be found in the "encodings" system variable, which is available in all workflows. | DecodeText(myFile.data, encodings.Windows1252) |
<contents of myFile.data, decoded using the Windows 1252 Character Set> |
Create Table and Insert/Update/Delete Rows
Create Table: The empty table statement
Sometimes it is necessary to create an empty table, containing only column names but no rows. This can be done by creating a Table Item with no rows in the workflow, or using a FlowScript expression.
let emptyOrderList = table(orderNo, price, isConfirmed);Converting a record to a table
To convert a record into a table, use the multiplier (*) unary operator.
let myTable = *myRecord;
let myOtherTable = *[a: 1, b: 2];Insert row: The table concatenation (&) operator
You can append a record to a table, or append a table to another table, using the & operator. The left hand side value (L) of the expression must be a table. The right hand side value (R) can either be a record or another table. R must contain all the columns/fields of L. Any fields/columns present in L but not R will be excluded from the output.
let newOrderList = orders & selectedOrder;
let allOrders = localOrders & centralOrders;
let orders = orders & [orderNo: orderNo, partNo: partNo, qty: qty];Download an example workflow from the Flow community (here)[http://community.novacuraflow.com/product/internal-table-example-flow/]. Observe that you need to log in to the Flow commnuity to be able to download the workflow
Update row: The WITH Keyword
WITH (described above) is also supported when working with tables. The example below updates the price column with new values.
let newItems = items with [price: price * 1.03];Delete rows: The EXCEPT Keyword
If you need to remove a record from a table (creating a new table variable with the record excluded), use the EXCEPT keyword. The except keyword takes a table on the left hand side and a record on the right hand side. Each row of the table is examined and compared to the record. Rows in which every named cell also present in the record is equal to the record's cell are excluded from the output. This means that the EXCEPT keyword can remove more than one row; if two duplicate rows exist in the table, or if the record to remove has fewer fields than the table, more than one table row may match the record.
let otherOrdersEx1 = orders except selectedOrder;
let otherOrdersEx2 = orders except [orderNo: 'ABC1234'];Delete rows: The EXCEPT WHERE Keyword
Sometimes a filtering expression becomes more readable if the logic is inversed. The EXCEPT WHERE keyword does the opposite of the WHERE keyword: it returns a new table excluding (rather than including) the rows matching the right hand side condition.
let valuableOrders = orders except where price = 0;Basic Table Functions
| Function | Description | Example Expression | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Count(table) |
Returns the number of rows in a table. | Count([col: "A"] & [col: "B"]) |
2 |
Any(table) |
Returns a truth (Boolean) value indicating whether the table has any rows. | Any([col: "A"] & [col: "B"]) |
TRUE |
Skip(table, n) |
Returns a table where first n rows have been excluded. | Skip([col: "A"] & [col: "B"] & [col: "C"], 1) |
<[col: "B"] & [col: "C"]> |
Take(table, n) |
Returns a table where first n rows are included in result. | Take([col: "A"] & [col: "B"] & [col: "C"], 2) |
<[col: "A"] & [col: "B"]> |
First(table) |
Returns a record representing the first row of a table. | First([col: "A"] & [col: "B"]) |
<[col: "A"] as Record> |
Sum(table.column) |
Returns the summarized value of the specified table column. | Sum([col: "4"] & [col: "7"]) |
11 |
The WHERE Keyword
You can use the WHERE keyword to create a filtered version of a table variable. Since this filtering happens locally on the device where the Flow client is run, it is not suitable for large amounts of data.
The WHERE keyword takes a table on the left hand side and a logical expression (with the scope of the table's columns) on the right hand side.
Since the WHERE keyword returns a new table, you can nest it in any table function, such as First, Any, Count, etc.
let orders = [id: 1, isConfirmed: 0, plannedDate: Now()] &
[id: 2, isConfirmed: 1, plannedDate: Now() + 1] &
[id: 3, isConfirmed: 0, plannedDate: Now() + 2];
let futureOrders = orders where isConfirmed and plannedDate > Now();
let nextOrderToProcess = first(orders where isConfirmed);
let numberOfOrder = count(orders where isConfirmed);The ORDER BY Keyword
ORDER BY sorts a table by one column and returns a new sorted table. As default the order is asending but by adding the keyword DESC the order can be changed to descending (ASC can be added for explicitly when sorting asending). Only simple types can used for sorting.
let items = [id: 1, price: 10, name: 'Soda'] &
[id: 2, price: 100, name: 'Burger'] &
[id: 3, price: 50, name: 'Fries'];
let cheapItem = First(items order by price);
let expensiveItem = First(items order by price desc);The SUM Function
The Sum function calculates the sum of the values in a numeric column in a table.
let projectedProfit = sum((orders where isConfirmed).value) - sum(expenses.cost);The JOIN Function
The Join function concatenates all values of a table column into a single textual value with a given separator.
In the example below, the orderNo column of the orders table is aggregated into a comma-separated string in the format <orderNo 1>, <orderNo 2>, <orderNo 3> etc.
let orderNumbers = join(orders.orderNo, ', ');The MAP-AS Construct
The Map-As construct is used to create a new table variable based on an existing table variable, changing the column names and adding or removing new columns. The syntax of the map-as construct is MAP <source table> AS <record literal>. The record literal to the right of the AS keyword has the scope of the table.
The example below shows an orderLines table being transformed, keeping the salesPart column but adding a new column called cost, which is calculated using the price and discountPercent columns of the orderLines table.
let newOrderLines = map orderLines as [salesPart, cost: price * discount];Variables
Flow variables come in three different categories: simple values, records and tables.
Simple values
A "simple value" (known as a "primitive type" value in some programming languages) is the most common variable type. A simple value variable can contain text ("string"), a number, a date, or a truth (Boolean) value. Internally, Flow keeps track of exactly which one of these sub-types a value currently has; however, as a user of the Flow Designer you rarely have to care about the exact type of a variable, since Flow will go to great lengths to automatically convert the types into something that makes sense in your workflow.
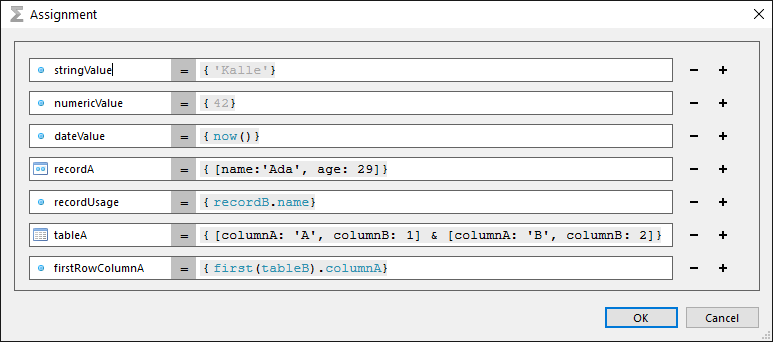
Assignment and usage example
See Assignment row 1-3 for different types of simple value assignment.
Records
A record (roughly equivalent to a "dictionary" or "object" in other programming languages) is a group of named values.
See Assignment row 4 where a new record with name recordA is assigned with a value for name and age. This record can later on be used just like recordB is used on row 5.
Tables
A table is a structure of columns and rows. Tables can be defined by one or more records (see row 6 in Assignment step above), there is many more ways to produce a table, for exmaple by using a Table step or Machine step.
Active Directory Sync Scripting
When syncing Active Directory groups to flow there are some additional functions available. Script will be executed for each user. User profile can be reached from record Profile.
Set User Property
User properties on user level can be set for each user. First argument is property name and second argument is property value.
exec SetUserProperty('Organisation', 'Novacura AB');Set Connector Login
If user should authenticate against a certain connector then at least a username should be set for each user. This can be configured with this function. First argument is connector name, second argument is username and last argument is password (should be empty string for enable password prompting).
exec SetConnectorLogin('IFS', Profile.Login, '');Get Ad Property
This function is used for accessing properties set in active directory.
let givenName = GetAdProperty('givenName');Set User Level
In order to set user level for user this function is used. Valid values are: Work/AdministerWorkflows/AdministerBasicData, as default user level will be set to Work.
exec SetUserLevel('AdministerBasicData');Set User Type
This function will set user type. Valid values are: FullUser/WorkflowUser/MachineUser/TransactionUser/PortalUser, as default user level will be set to FullUser.
exec SetUserType('WorkflowUser');Set AD Authenticate
This function will set whether the user should be authenticated against the active directory or if another system will handle the authentication.
exec SetAdAuthenticate(1);Other Functions
Additional functions:
exec SetLanguage('en');
exec SetGroup('Sales');
let enabled = GetAdProperty('Enabled');
exec SetActive(enabled);More about Flow Script
FlowScript
FlowScript is the built-in scripting language in the NovaCura Flow platform. FlowScript expressions are typically used to display the value of a variable to a user (in a User Task), but can also be used to perform simple or complex calculations and data transformations in a workflow. FlowScript statements can be used in some places where a single expression isn't enough, for example in Script Tasks.
 In the Flow Studio, fields where you can use FlowScript expressions are marked with the light blue FlowScript symbol, shown here to the left. FlowScript expressions always begin with an opening curly brace and end with a closing curly brace.
In the Flow Studio, fields where you can use FlowScript expressions are marked with the light blue FlowScript symbol, shown here to the left. FlowScript expressions always begin with an opening curly brace and end with a closing curly brace.
The simplest type of FlowScript expression simply refers to a variable which has been defined earlier in the workflow. Such an expression consists only of the opening curly brace, the name of the variable, and the closing curly brace:
{variableName}
The Flow Studio will automatically show a list of available variables when you type the opening curly brace; you can navigate this list with the arrow keys on the keyboard and accept the currently selected item using the Return key. To make the menu go away, press the Escape key or click anywhere outside the menu.
If your FlowScript expression refers to a variable which is not defined anywhere in the workflow, the Flow Studio will show a red line under your FlowScript expression.
Scope
The scope of a FlowScript means the collection of variables available to refer to in it. In most cases, the scope of a FlowScript expression is the set of variables available at the workflow step where the expression is used; however, in some cases the scope may be different. For example, the Large Row Text and Small Row Text properties of a List Selection item in a User Step has access to the columns of the selected table variable.
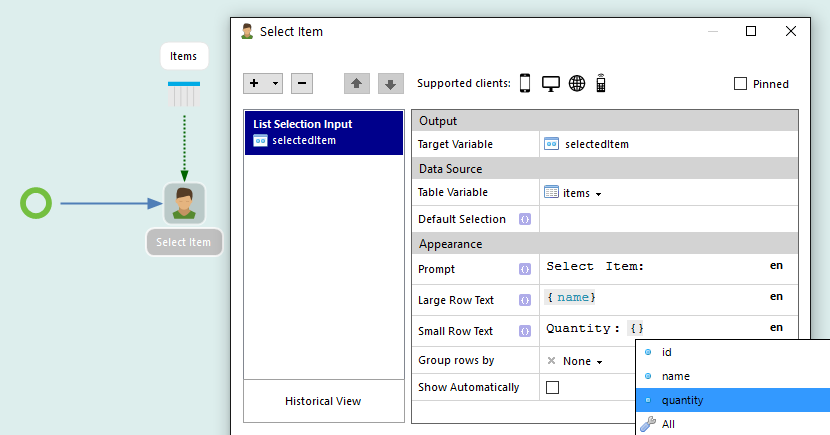
Screen shot: A User Task configuration dialog with a List Selection input. The Large Row Text and Small Row Text properties have FlowScript expressions referring not to variables in the workflow, but to cell values in the "items" table. The autocomplete menu shows the cells of the table at the top of the list, before the other variables in the workflow.
Formats
FlowScript supports converting numeric values and date times to string with a provided format string. This is performed with the format function.
Numeric Values
| Format | Description | Example (value: 1234.567) | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| "C" | A currency value.* | "C" (en-US) "C" (sv-SE) |
"$1,234.57" "1.234,57 kr" |
| "F" | Integral and decimal digits with optional negative sign.* | "F" (en-US) "F" (de-DE) |
"1234.57" "1234,57" |
| "Fn" (ex "F1") | Same as "F" with n precision (Number of decimal digits.)* | "F1" (en-US) "F3" (de-DE) |
"1234.6" "1234,567" |
| "N" | Integral and decimal digits, group separators, and a decimal separator with optional negative sign.* | "N" (en-US) "N" (ru-RU) |
"1,234.57" "1 234,57" |
| "Nn" (ex "N1") | Same as "N" with n precision (Number of decimal digits.)* | "N1" (en-US) "N3" (ru-RU) |
"1,234.6" "1 234,567" |
* Format is defined by the computer where the Flow Engine is executing.
Read more about .NET Date and Time format strings here:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dwhawy9k.aspx
Date and Time Format
| Format | Description | Example (date: 2009-06-15T13:45:30) | Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| "d" | The day of the month, from 1 through 31. | "d" | "15" |
| "dd" | The day of the month, from 01 through 31. | "dd" | "15" |
| "dddd" | The full name of the day of the week.* | "dddd" (en-US) | "Monday" |
| "M" | The month, from 1 through 12. | "M" | "6" |
| "MM" | The month, from 01 through 12. | "MM" | "06" |
| "MMM" | The abbreviated name of the month.* | "MMM" (en-US) | "Jun" |
| "MMMM" | The full name of the month.* | "MMMM" (en-US) | "June" |
| "yy" | The year, from 00 to 99. | "yy" | "09" |
| "yyyy" | The year as a four-digit number. | "yyyy" | "2009" |
| ":" | The time separator.* | "HH:mm" (en-US) "HH:mm" (ar-DZ) |
"13:45" "13.45" |
| "/" | The date separator.* | "yy/MM/dd" (en-US) "yy/MM/dd" (ar-DZ) |
"09/06/15" "09-06-15" |
| "\" | The escape character. | "\M M" | "M 6" |
* Language/format is defined by the computer where the Flow Engine is executing.
Read more about .NET Date and Time format strings here:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/8kb3ddd4.aspx
Operators
Comparison Operators
The following comparison operators can be used in FlowScript. The result of these expression are always a truth (Boolean) value:
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
a = b |
TRUE if a equals b, FALSE if a does not equal B or the types of a and b cannot be compared |
a != b |
TRUE if a does not equal b or the types of a and b cannot be compared, FALSE if a equals b |
a > b |
TRUE if a is greater than b, FALSE otherwise |
a < b |
TRUE if a is less than b, FALSE otherwise |
a >= b |
TRUE if a is greater than or equal to b, FALSE otherwise |
a <= b |
TRUE if a is less than or equals to b, FALSE otherwise |
Logical Operators
The following logical operators can be used in Flow Script. The result of these expressions are always a truth (Boolean) value.
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
a and b |
TRUE if both a and b are true, FALSE otherwise |
a or b |
TRUE if either a or b are true, FALSE otherwise |
not a |
TRUE if a is false, FALSE otherwise |
The IN Operators
The IN operator allows you to compare one left hand side value (L) with several right hand side values (R) at once. The result of the statement is TRUE if L is equal to any of the values in R.
firstName in ('James', 'Richard', 'Danny')Truth of Non-Boolean Values
Flow Script is fairly permissive when it comes to evaluating the truth of non-Boolean values. The following non-Boolean values count as true:
- All numbers except 0
- All strings except the empty string, "0" and "FALSE" (including all upper- and lowercase variants)

Examples
FlowScript statements
In a Script Step you can use the full range of FlowScript statements.
Variable declarations
Variables are declared using the let keyword and re-assigned using the set keyword. Because FlowScript is an implicitly typed language, you cannot declare a variable without also assigning it.
let x = 12;
set x = x + 1;
// x is now 13 letReturn statement
To return a value from a FlowScript, use the return keyword. The Flow Designer checks to make sure that each branch of a FlowScript returns a value.
return x * 16;Conditional statement
Conditional statements are written using the if/elseif/else keywords.
if quantity > 100 {
let discountPercent = 10;
let amount = quantity * price;
return amount - (amount * (discountPercent/100));
}
else {
return quantity * price;
}When the body of a conditional clause consists of only one statement, it is possible omit the curly braces and use the colon (:) sign instead.
if x > 0:
return "greater than zero";
elseif x < 0:
return "less than zero";
else:
return "zero";Loops
Loops are written using the for and in keywords. You can loop over table variables, strings (one iteration per character in the string) and numerical ranges.
Table example
let items = [name: 'soda', price: 4.1] & [name: 'pizza', price: 8.9];
let totalPrice = 0;
for item in items {
set totalPrice = totalPrice + item.price;
}String example
let barcode = 'A123522BA12332';
let number_of_a = 0;
for c in barcode {
if c = 'A':
set number_of_a = number_of_a + 1;
}In order to exit a loop prematurely, you can use the break; statement. In order to exit the current iteration and jump right into the next one, use the continue; statement.
If the body of a loop consists of only one statement, you can omit the curly braces and use the colon (:) sign instead.
for item in items:
set totalPrice = totalPrice + item.price;NOTE: To support backward compatibility with previous versions of Novacura Flow, the do and done keywords are also supported in lieu of the opening and closing curly braces.
Index loops
To loop over a range of indexes, use the range(start, count) function.
for i in range(0, 10) {
// statements
}Type declarations
It is possible to define types in FlowScript programs. A type defines the structure of a record (or table) variable. Types are defined like this:
type Person = [name, age];
// This creates a type named 'Person' with simple fields 'name' and 'age'.When creating a new record based on a type, use the following syntax:
type Person = [name, age];
let donaldDuck = Person[name: 'Donald Duck', age: 35];Types can have nested structures:
type Car = [model, year, engine: [power, torque]];
// This creates a type named "Car" with two simple fields (model and year) and a complex (record) field containing sub-fields "power" and "torque".
let myCar = Car[model: 'Volkswagen Golf', year: 2016, engine: [power: 170, torque: 184]];Types can also refer to other types:
type Car = [model, year, engine: [power, torque]];
type personWithCar = [name, age, car: Car];Types always define the structure of record variables. However, by adding the multiplier (*) unary operator, you can convert a type into the corresponding table type:
type Car = [model, year, engine: [power, torque]];
type PersonWithManyCars = [name, age, cars: *Car];The multiplier (*) unary operator can also be used when initializing a record:
type Point = [x, y];
type DotGraph = [points: *Point];
let mySingleDotGraph = DotGraph[points: *[1, 1]];It is possible to define default values for type fields. If a default value is given, the field does not have to be initialized.
type Customer = [name, email, phone = 'Not specified'];
let myCustomer = Customer[name: 'Acme Industries', email: 'info@acme.com'];
// myCustomer.phone will now be automatically initialized as 'Not specified'It is possible to use nil values for type fields which themselves are records. nil values are only permitted for such cases; simple or table values cannot be nil.
type Employee = [name, salary, manager: Employee];
let anEmployee = Employee[
name: 'Bob',
salary: 10000,
manager: Employee[name: 'Alice', salary: 20000, manager: nil]
];
if not anEmployee.manager.manager = nil:
error 'Didn't work';Automatic Types
Each record and table variable in a workflow can also be used as a type. This is useful when you need to programmatically create a record that matches the output from a machine step or some other workflow step. Automatic types are prefixed with the dollar sign ($$). For record a variable `myRecord`, the automatically created type will be named `$myRecord_type. For a table variablemyTable, the automatically created type will be named$myTable_rowtype`.
let newRow1 = $myTable_rowtype[a: 1, b: 2];
let newRow2 = default($myTable_rowtype) with [b: 2];Function declarations
Functions are declared using the let and function keywords.
let least = function(a, b) => {
if a < b:
return a;
else:
return b;
}For a single-parameter function, no parentheses are needed around the argument list. For a single-statement bodied function, the curly braces, as well as the return keyword, can be omitted.
let square = function x => x * x;If no parameter type is given for a function parameter, it is assumed to be a simple value. For complex values (records and tables), the syntax is similar to that of type definitions:
type Employee = [name, salary, position];
let employeesWorkingForFree = function(employees: *Employee) => {
return employees where salary = 0;
}
let distance = function(point1: [x, y], point2: [x, y]) => {
return sqrt(pow(point2.x - point1.x, 2) + pow(point2.x - point1.y, 2));
}
return distance([x: 3, y: 28], [x: 99, y: 0]);If no return type is declared for a function, Novacura Flow tries to infer the return type based on the function body. It is also possible to specify an explicit return type.
type Employee = [name, salary, position];
let employeesWorkingForFree = function(employees: *Employee) : *Employee => {
return employees where salary = 0;
}
// This function returns a table of Employee recordsIf recursion is required (i.e. a function that calls itself), return types MUST be explicitly specified. If such a function returns a simple value, the return type should be specified using the simple keyword.
let recursiveFunction = function(x) : simple => case when x > 10 then 999 else recursiveFunction(x + 1);NOTE: To support backward compatibility with previous versions of Novacura Flow, the do and done keywords are also supported in lieu of the opening and closing curly braces.
Errors
If you need to raise an error from a FlowScript, use the error keyword.
error "This is the error message";Parsing Example
The following FlowScript program example will take a table with one string column and parse it into a table with several columns. It will split columns based on a column delimiter and take the right side value by using a key-value delimiter.
let newTable =
[rowName:'id=1,price=10,name=Soda'] &
[rowName:'id=2,price=100,name=Burger'] &
[rowName:'id=3,price=50,name=Fries'];
let firstDelimiter = ',';
let secondDelimiter = '=';
let parseFunction = function(rowName, columnIndex, subColumnIndex) =>
rowName.Split(firstDelimiter).Skip(columnIndex).First().value
.Split(secondDelimiter).Skip(subColumnIndex).First().value;
return map newTable as
[id: parseFunction(rowName, 0, 1),
price: parseFunction(rowName, 1, 1),
name: parseFunction(rowName, 2, 1)];Monitoring
It can be good to monitor the crucial parts of the Flow server.
The parts of the Flow server that are recommended to monitor:
IIS components:
- Flow site
- Flow application pools
Windows service:
- Flow service
Troubleshooting
If there is problems with the Flow server, clients or other Flow related products, please contact us at product.support@novacura.com and attach log files or other related files.
App pool and sites
If the server stops responding there might be something wrong with the applications running on the app pools or something wrong with the site.
- Navigate to the IIS -> Servername -> Application Pools.
- Select the Novacura application pool(s), on the right side select recycle or start it up if it's not running.
- Navigate to Sites and select the site where the Novacura server is running, on the right side select restart if it's not responding or start if it's not running.
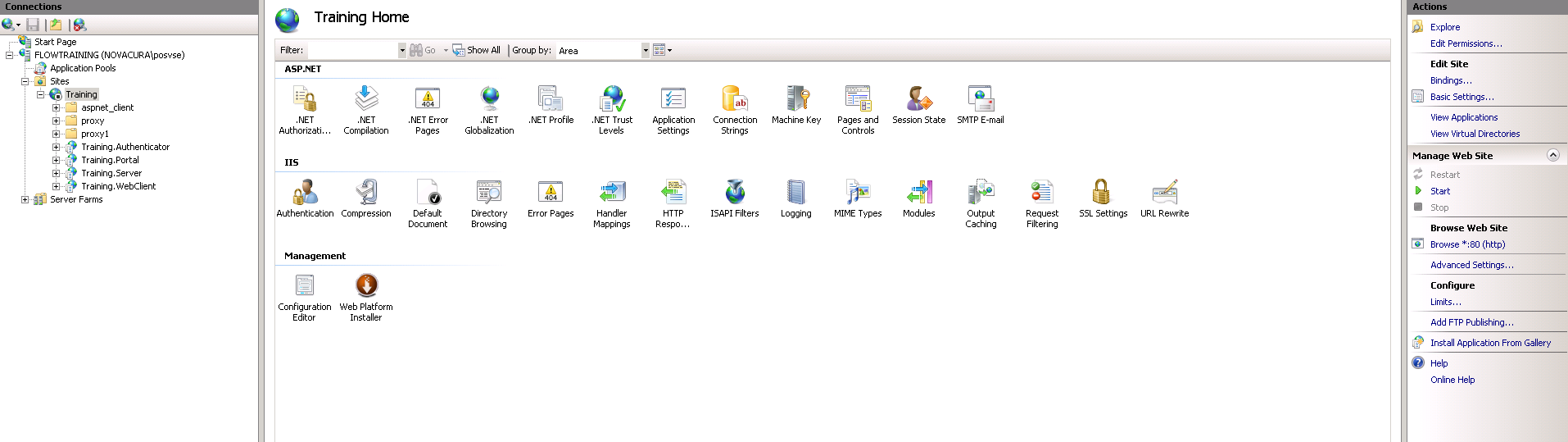
- Verify that the server is now up and responding again.
If the application pool stops regularly please contact us so we can investigate it. Meanwhile, a workaround is to raise the amount of errors the server can receive before it automatically stops the site by following these steps:
- Navigate to the IIS -> Server name -> Application Pools.
- Right-click on the application pool you wish to raise the amount of errors it can receive.
- Under "Rapid-Fail Protection" change the failure interval and maximum failures to how many failures during x amount of minutes you want the application pool to allow.
Fetch custom event views
If the server stops responding often, crashes or if the server is experiencing any other errors which are hard to specify the cause for, a log containing information about errors occurring could be useful.
To fetch a log containing crash dumps etc. follow these steps:
- Press windows button + R and type in "eventvwr.msc".
- Select custom views and click on create custom view.
- Logged - Specify in which time frame you want to fetch the logs from.
- Event Level - Select Error, Warning and Critical
- Select by source and choose all sources you want to fetch messages from, some relevant are: ".Net Runtime, Application Error, ASP.Net 4.0, MSSQL SQLexpress, MSSQL SQLexpress Audit". But it depends on what you wish to view, these mentioned above can help us investigating your error if you report it to us and attach the custom view file.
- Select the new custom event view you have created, click on "save all events in custom view as..."
- Choose a name for the file and save it as .evtx, attach this file to your issue when you report them to us if you're having server problems. It can both help us identify the problem and allow us to fix the problem faster.
Fetch a memory dump
If the logs from the IIS and Flow server aren't enough, you can also fetch a memory dump which can help us trace the root cause of the problem you are experiencing. By following the instructions in: Fetch memory dump you can fetch the memory dump and send it to us.
Be very careful to fetch the memory dump during the time the error occurs, and not after you have fixed the error or restarted the server etc..
If the bug does not exist in the current session when you fetch the dump, we will not see it.
Moving SQLITE Portal DB
If the portal database is located in the wrong directory will an upgrade not be possible.
To fix this:
- Locate the Portal database, go to the portal web.config and see tag datapath for the location.
- Open the Flow server tool and find the data storage for the installation to upgrade; click on the meny for the installation and take Open storage.
- Copy the Portal database to the installation location.
- Navigate to the portal web.config and change the datapath to the new data path and save the web.config.
Contact product support if above does not work for you
IIS user permission
Follow this instruction to give the IIS application pool user read and write permission in a folder
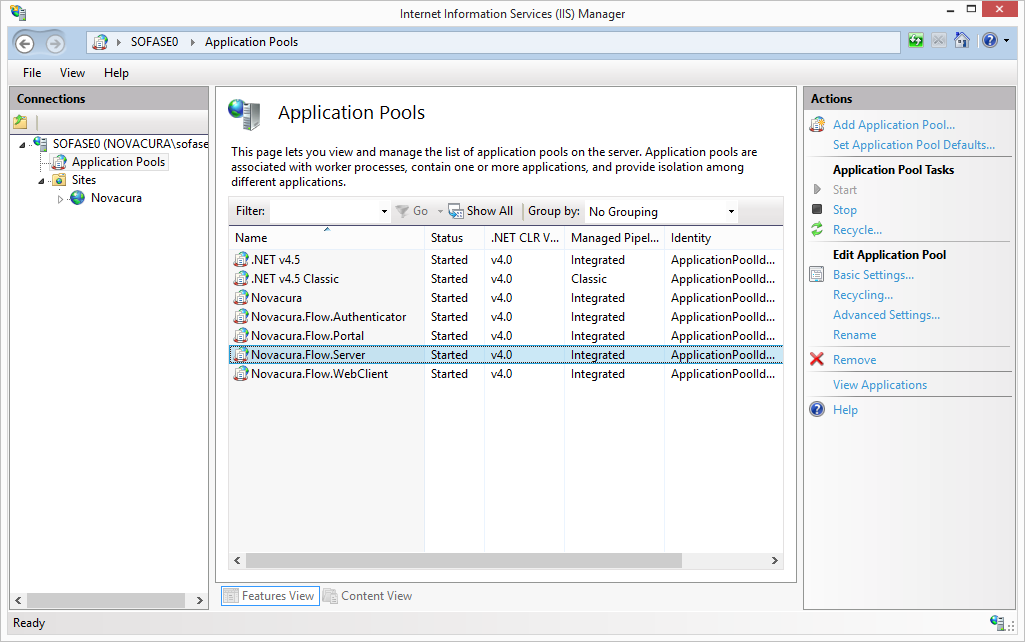
Right click on the folder where the application pool user should have permission. Choose Properties and tab Security, click Edit and then Add.
Enter IIS APPPOOL\"the name of the Novacura Flow server application pool" in the object name field.

Click on Locations and mark the local machine in the tree structure and click OK.
Click on Check Names, if the user name is correct and exists will it get a underline and be change to just the user name and click OK.
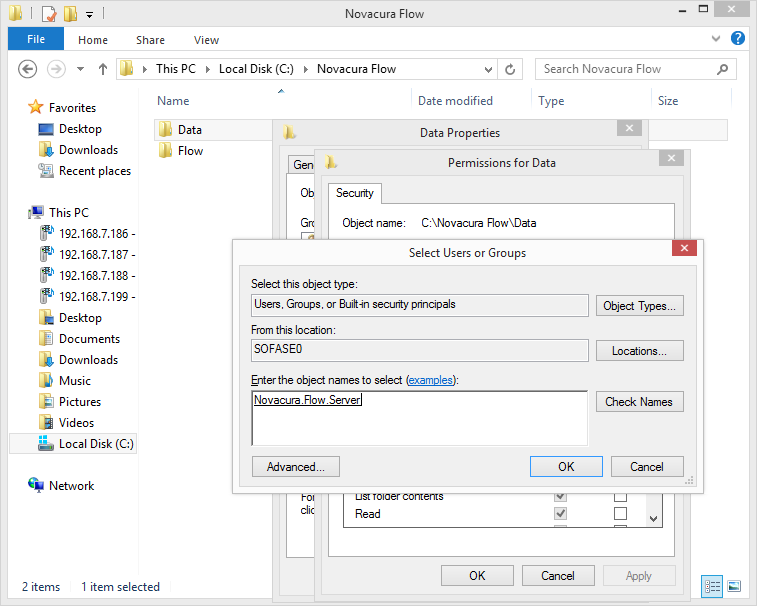
Mark the added Novacura Flow server application pool user and check Write and Read permission, click OK.
Now have the Novacura Flow server application pool user permission to Read and Write in the folder.
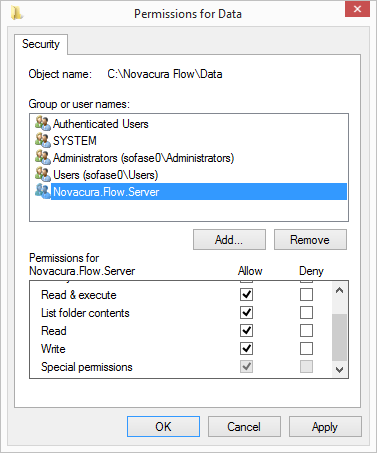
Moving SQLITE Portal DB
If the portal database is located in the wrong directory will an upgrade not be possible.
To fix this:
- Locate the Portal database, go to the portal web.config and see tag datapath for the location.
- Open the Flow server tool and find the data storage for the installation to upgrade; click on the meny for the installation and take Open storage.
- Copy the Portal database to the installation location.
- Navigate to the portal web.config and change the datapath to the new data path and save the web.config.
Contact product support if above does not work for you
Novacura Flow Add Component
Before you start the installation make sure the System Requirements are fulfilled and that https://home.novacuraflow.com is accessible from the server.
The installation can either be done online or offline.
Online: The installation files will automatically be downloaded by the Novacura Flow Server Manager tool.
Offline: The installation files need to be downloaded separately and added manually in the Novacura Flow Server Manager tool. Observe this is only necessary if for any reason https://home.novacuraflow.com can not be accessible.
1. Open the Novacura Flow Server Manager
- Click on the menu for the installation that the component/s should be added to.
- Choose Add Component...
- Choose the component/s that should be installed.
- Click Install.
If connection to Novacura Flow home is not available, then it will be possible to do an offline installation. Download the offline packages and enter each package for the component/s that should be installed.


2. The installation is done and the component/s is added to installation
- If the Novacura Flow Web Client was installed. Open the Novacura Flow Web Client. The page should show a log in prompt.
- If the Novacura Flow portal was installed, open the portal application to to finish the portal installation. The portal database will be created when the portal application is open for the first time. When the installation is done will the login page appear.

Contact product.support@novacura.com for support if the installation fails.
Novacura Flow Apply Service Pack
The system will be unavailable when the apply service pack is done.
Recommendation is to restart server prior to applying service packs.
1. Stop site and service and take a backup
- Open the IIS and stop the Novacura Flow 6 site and do a recycle on the application pool.
- Open Services and stop the Novacura Flow service, the service have the same name as the Novacura Flow environment.
- Take a backup of the installation folder with all file for all components of Novacura Flow.
2. Open the Novacura Flow Server Manager
- Click on the menu for the installation that should be updated and choose Apply service pack....
- Click on Apply to start the update, when message Upgrade successful shows is the service pack applied.

### Problems If the upgrade process results in a corrupt state, which it can't rollback automatically, an error message "Entry is incorrect. Fix errors or remove entry" will be displayed on the environment instance. This can often be recovered manually by: - Go to the installation folder and change the name of the data backup that the installation tool have done.
- Remove the underscore and date from the folder name of each component installation folder (see example image below).
- Start the site and service from IIS Manager.
- Open the Novacura Flow server page to see that it is up and running.
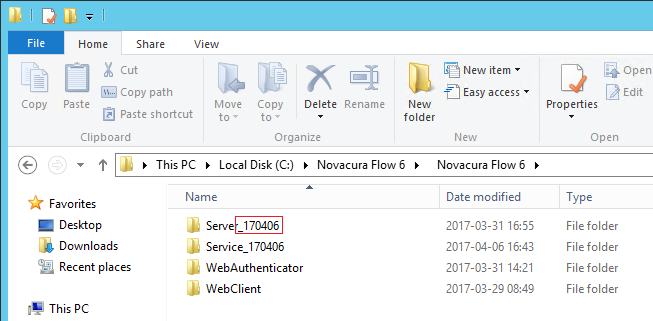
Contact product.support@novacura.com for support if the upgrade fails.
Event Log
As of Flow 6.6 system security events will be logged and possible to view in the Windows Event Viewer.
A log, NCFLog, is created under Applications and Services Logs.
The following applications are supported:
- Flow Studio Application
- Client - Web Application and Mobile Applications (iOS, Android, UWP)
- Portal Application
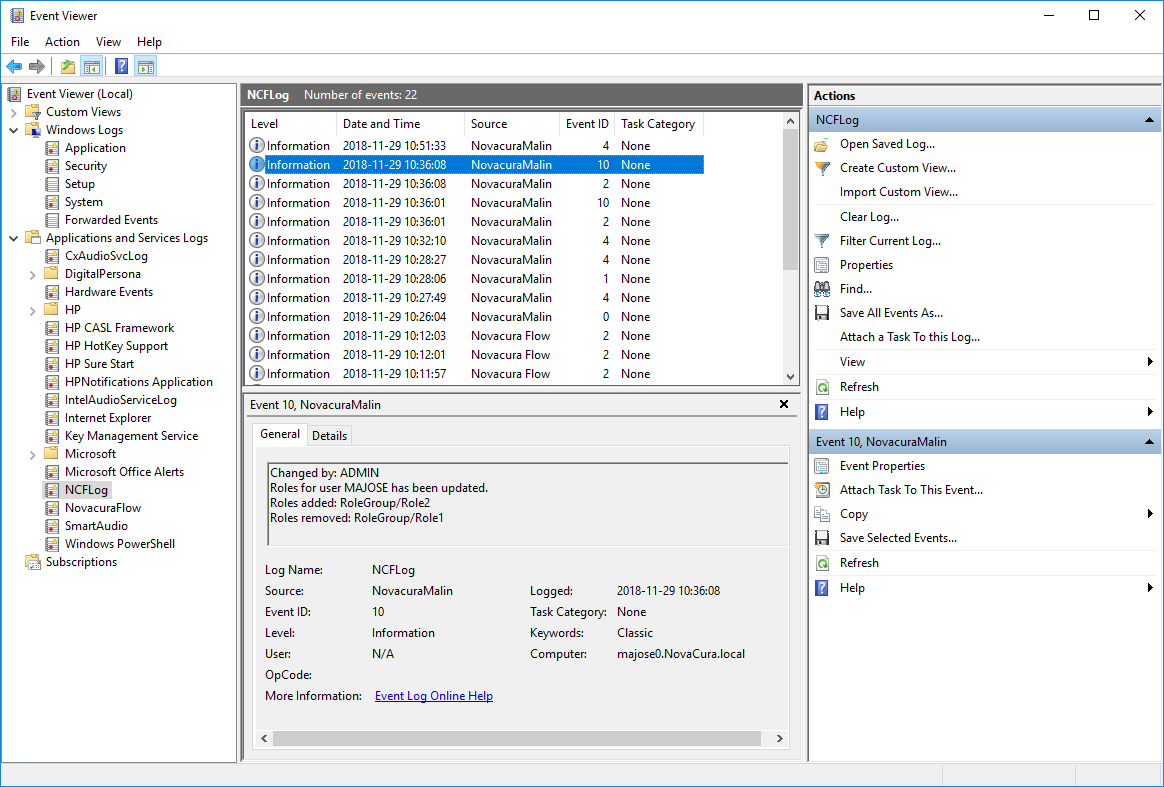
Types of Events
The following types of events will be logged:
- USER_CREATED
- Event Id - 1
- Parameters: Login, Access Level, Type, Roles
- USER_UPDATED
- Event Id - 2
- Parameters: Login, Access Level, Type, Roles
- USER_DELETED
- Event Id - 3
- Parameters: Login
- USER_LOGGED_IN
- Event Id - 4
- Parameters: Login
- USER_LOGGED_OUT
- Event Id - 5
- Parameters: Login
- ACCESS_DENIED
- Event Id - 6
- Parameters: Login
- DEVICE_APPROVED
- Event Id - 7
- Parameters: Device Id, Device Name, Last user login
- DEVICE_BLOCKED
- Event Id - 8
- Parameters: Device Id, Device Name, Last user login
- MENU_CHANGE
- Event Id - 9
- Parameters: Menu name, Roles
- ROLES_CHANGE
- Event Id - 10
- Parameters: Login, Roles
- PASSWORD_CHANGE
- Event Id - 11
- Parameters: Login
Novacura Flow New Installation
Before you start the installation make sure the System Requirements are fulfilled and that https://home.novacuraflow.com is accessible from the server.
The installation can either be done online or offline.
Online: The installation files will automatically be downloaded by the Novacura Flow Server Manager tool.
Offline: The installation files need to be downloaded separately and added manually in the Novacura Flow Server Manager tool. Observe this is only necessary if for any reason https://home.novacuraflow.com can not be accessible.
1. Download the Novacura Flow Server Manager
- Go to http://community.novacuraflow.com/downloads/.
- Download the Novacura Flow Server Manager and Novacura Flow Studio, and place the installation files on the machine where Novacura Flow Server should be installed.
- If Novacura Flow needs to be installed offline download the installation packages for the version you want to install.
- Run the installation for the Novacura Flow Server Manager Installer.exe.
2. Create an installation folder
- Create a folder named Novacura, for example under: C:\. (all Novacura Flow binaries will be placed under this installation folder)
- In the Novacura folder, add a folder named Data.
(in the Data folder will the Sql Lite database be stored, this folder can be placed where data storage is most suitable)
3. Open the Novacura Flow Server Installer Manager
- Click on the menu in the top right corner and choose Install new.
- Choose what Novacura Flow version to install.
- Choose the component/s that should be installed.
- Click Next.
If connection to Novacura Flow home is not available, then it will be possible to do an offline installation. Download the offline packages and enter each package for the component/s that should be installed.
It is possible to add component/s after the installation is done read more here.
Read about the Web authenticator here.
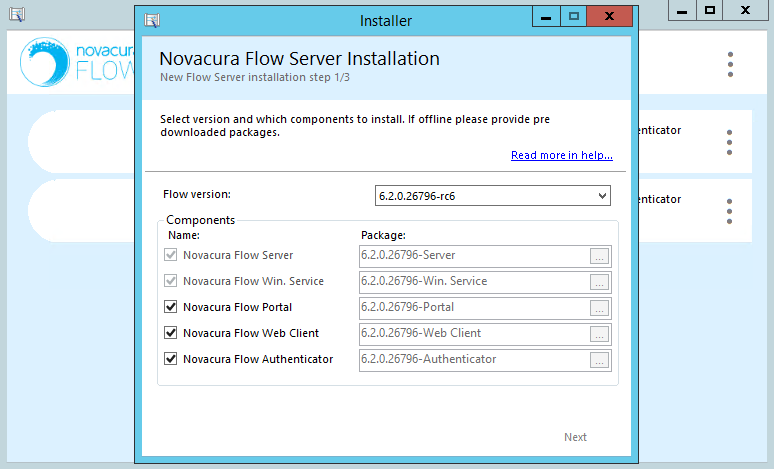
- Create a new Site in the Internet Information Services (IIS) by clicking on New....
- Enter a name for the site, for example: Novacura.
- Enter a port for the site, for example: 80 (open the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager and control so the port that is entered is free to use).
- Enter Environment name, for example: Flow.
- Recommended name standard; for test and dev installations include Test or Dev in the beginning of the environment name, such as "Test Flow" or "Dev Flow", so the different environments are easy to distinguish for the end-user.

- For Install directory, browse to the Novacura folder that was created earlier.
- For Storage directory, browse to the Data folder that was created earlier.
- Click Next.
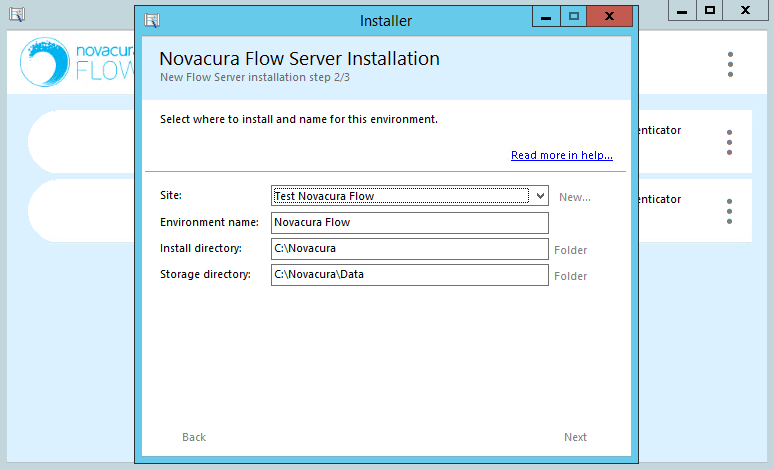
- The External URL should already be filled in.
- The Server name should already be filled in.
- Enter a Help e-mail address, the e-mail could be to a technical person who is responsible for the Novacura Flow installation.
- Enter a Admin user name, use this user to log in to the Novacura Flow Studio.
- Enter a Password for the Admin user.
- Check any of the security options Use Device Management, Force Web Login, Block Flow Studio requests... if needed. You can also change these settings, using the action menu Edit Installation Settings on the installation, at any time after the installation is made.
- Use Device Management: Having this option checked will force all devices to be approved before a User can log in. It will also enable Device Management in the Flow Studio, where new devices can be approved or denied and existing devices can be Blocked.
- Force Web Login: Having this option checked will force Users to log in every time they access Novacura Flow through the Web Client.
- Block Flow Studio requests outside the local network: Enabling this option will prevent all external access to the Flow Studio. Only requests from the local network will be accepted. You can however define exceptions in order to allow requests from specific IP addresses. If needed, these addresses should be listsed in the Exception list.
- Click Install.

4. The installation is done and all installations will be listed in the Novacura Flow Server Manager
- Open the Novacura Flow Server page. The page should show the version, bar code and pin code.
- Open the Novacura Flow Web Client. The page should show a log in prompt.
- Install Novacura Flow Studio and connect to the Novacura Flow Server. Log in with the admin user that was enter during the installation. When logged in to the Novacura Flow Studio go to Environment -> License and request either a demo license or a customer license, read more here: License.
- If the Novacura Flow portal was installed, open the portal application to to finish the portal installation. The portal database will be created when the portal application is open for the first time. When the installation is done will the login page appear.

The Novacura Flow Server Manager will list each installation on the machine. If another installation is needed click on Install new and follow the installation guide again. Use the Novacura Flow server manager to upgrade the Flow server to a new version or apply service packs.
Contact product.support@novacura.com for support if the installation fails.
Novacura Flow Installation and Upgrade
Use the Novacura Flow server management tool to do new Flow server installation, upgrade and apply service packs.
The differnce between an upgrade and a service pack is that can upgrade is between minor version like 6.2 to 6.3 and a service pack is always within the minor release like 6.2.3 and 6.2.7.
Upgrade
An upgrade includes new features and corrections and can change the structure of the Flow database. All Flow clients need to be updated to the same version as the Flow server.
Service pack
A service pack only includes corrections that is suitable for patching. A patch will for example not change the database structure of the internal Flow database.
Migration tool upgrading Novacura Flow Portal 5 to Portal 6
This tool is required if you have migrated your portal from flow 5 to flow 6, but your flow 6 environment differs from flow 5.
It supports migrating Connectors, Workflows, Roles, News Viewer Comments
1. Complete a portal migration by following the steps in: Upgrade
2. Open the Migration Tool folder
Set up the Migrate5To6.exe.config file with:
- Appsettings
- ssoCommonSecret: enter {ssoCommonSecret} found in your novacura flow server web.config file.
serverLogin value: flow user with portal admin rights".
- ConnectionStrings
- Data Source: Path to the the 5 Portal sql server.
- Initial Catalog: Name of the 5 Portal database.
- user id: login to access database.
- password: password to the user id.
The second connection string also needs to be configured, it works the same way but it's the receiving end. Which means here you type in the portal 6 server/database.
- Client
Endpoint address: change everything before /PortalAPI to your novacura flow server e.g "http://myserver/Novacura.Flow.6.Server/PortalAPI/PortalUsersAccessService.svc"
Do the same for both endpoint addresses in Client and save your modified .config file
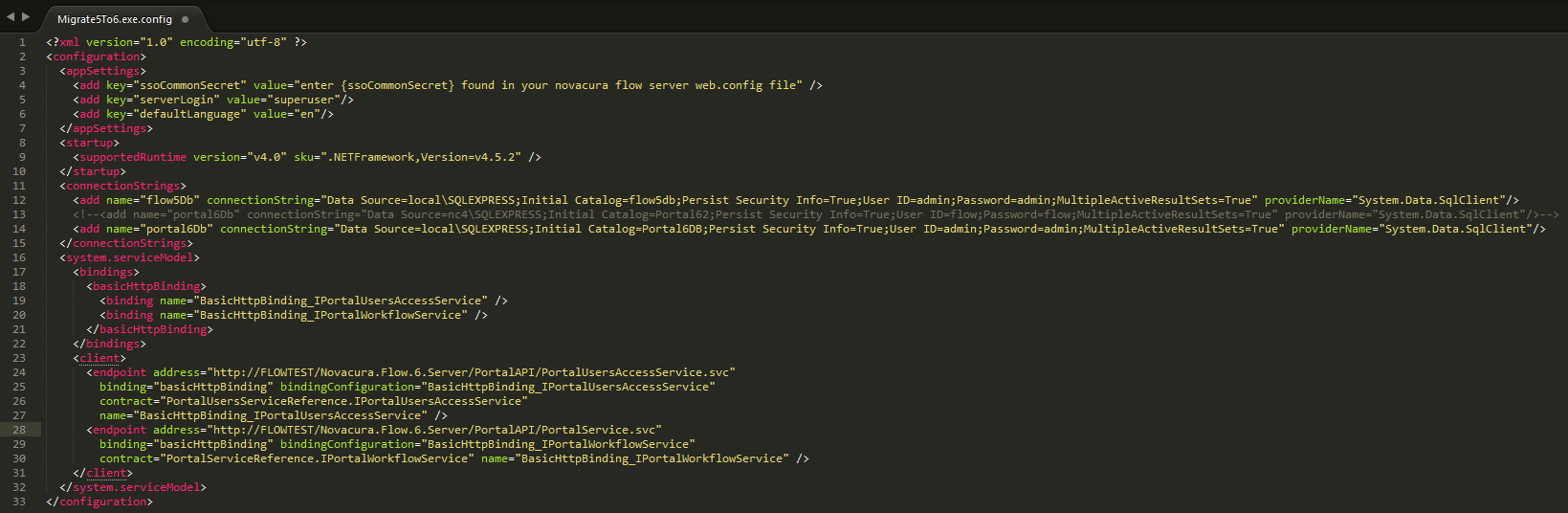
Configuration Example
3. Migrate portal 5 to portal 6
Run the Migrate5To6.exe tool
Click on Test flow 5 DB and Test Portal 6 db to make sure the .config file is set up correctly.
Migrating Connectors
- Click on Load Flow 5 Connectors And Load Flow 6 Connectors
- Choose the flow 5 connector that is being used somewhere in the flow 5 portal.
- Choose the corresponding flow 6 connector that should be used in the flow 6 portal.
- Click on the >> button to map the connectors.
- Repeat this for every connector you wish to migrate and map to flow 6.
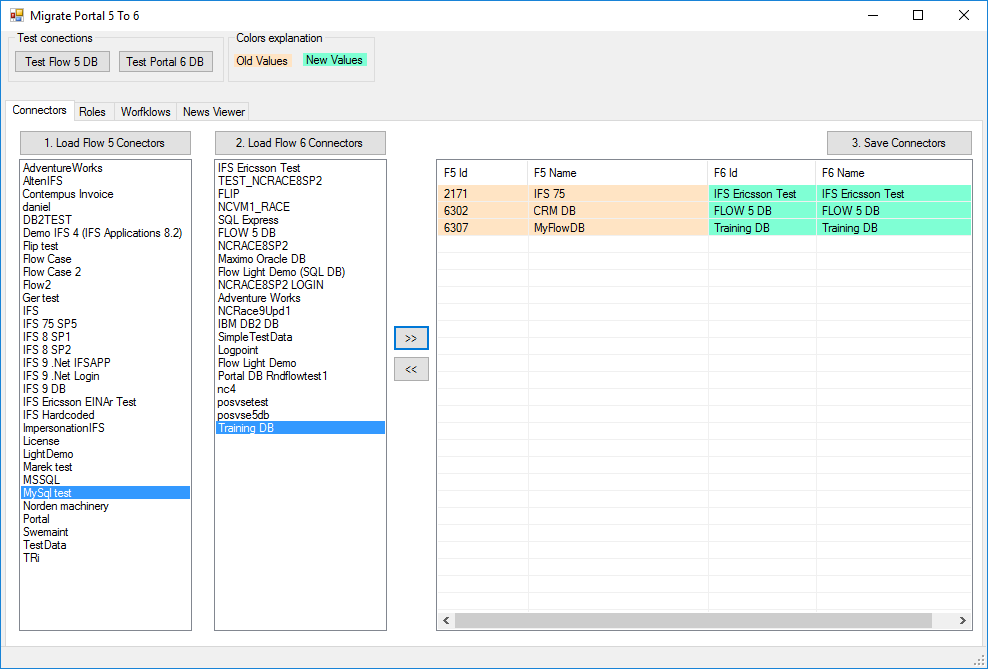
Connector Migration Example
Migrating Roles
- Click on Load Flow 5 Roles And Load Flow 6 Roles
- Choose the flow 5 role that is being used somewhere in the flow 5 portal.
- Choose the corresponding flow 6 role that should be used in the flow 6 portal.
- Click on the >> button to map the roles.
- Repeat this for every role you wish to migrate and map to flow 6.
Role Migration Example
Migrating Workflows
- Click on Load Flow 5 portlets.
- Click on Load Flow 6 Workflows.
- Select a portlet to display the workflows used by the portlet.
- Select and input which kind of flow 5 workflow and it's parameters in the corresponding text box.
- Select which flow 6 workflow that corresponds to that operation press the >> button which will fill the necessary text boxes with information.
- Click on Save Workflows for selected portlet.
Workflow Migration Example
Migrating News Viewer Comments
- Click on Find users
- Click on Save comments users, it can only map when the user names match between environments.
Contact product.support@novacura.com for support if the upgrade fails.
Novacura Flow Portal Installation
The Novacura Flow Portal server feature HTTP Activation found under .Net Framework 4.5 Features -> WCF Services.
1. Open Novacura Flow Server manager installer and either create a new installation or click on the option button to the right of an already installed flow server and press "Add Component"
Select Portal and follow the installer instructions.
2. Modify the Novacura Flow Portal web.config (Optional)
Go to the Novacura Flow Portal binaries folder and edit the web.config file.
Portal database connection string, replace the bold text with correct information and copy the connection string and replace #{Portal.ConnectionString} with the connection string:
Data Source=Enter Microsoft SQL server name; Initial Catalog=Enter the Portal catalog name;Integrated Security=true
Example: Data Source=localhost; Initial Catalog=Novacura_Flow_Portal;Integrated Security=true
If you have a brand new flow server installation the step above altering the connection string is not required.
3. Completing the portal installation
Enter the URL to the newly installed portal, an progress bar regarding the installation is now shown.
After this the portal is installed and ready to be used!
Contact product.support@novacura.com for support if the installation fails.
Novacura Flow Upgrade To New Version
Before you start the upgrade installation make sure the System Requirements are fulfilled, and that https://home.novacuraflow.com is accessible from the server.
The system will be unavailable when the apply service pack is done.
Recommendation is to restart server prior to upgrade.
The installation can either be done online or offline.
Online: The installation files will automatically be downloaded by the Novacura Flow Server Manager tool.
Offline: The installation files need to be downloaded separately and added manually in the Novacura Flow Server Manager tool. Observe this is only necessary if for any reason https://home.novacuraflow.com can not be accessible.
1. Latest version of the Novacura Flow Server Manager
Use always the latest version of the Novacura Flow Server Manager.
Online:
- From version 6.2 is the Novacura Flow Server Manager self updating. When Novacura Flow Server Manager is started will it check for new avaliable versions and show a dialog where it is possible to download and install the latest version.
Offline:
- Go to http://community.novacuraflow.com/downloads/.
- Download the Novacura Flow Server Manager and Novacura Flow Studio, and place the installation files on the machine where Novacura Flow Server should be installed.
- Download the installation package for the version you want to install.
- Run the installation for the new version of Novacura Flow Server Manager Installer.exe.

2. Take a backup of Novacura Flow
- Take a backup of the database files; find the database files by clicking on the menu and choose Open storage for the installation that should be upgraded, copy the files to a backup folder.
- Take a backup of the binaries; find the binaries by clicking on the menu and choose Open folder for the installation that should be upgraded, copy the files to a backup folder.
3. Upgrade to new version
- Click on the menu for the installation that should be updated and choose Upgrade....
- Click on Upgrade to start the update, when message Upgrade successful shows is the upgrade done.
- Browse to the the Novacura Flow server page to see that it is up and running.
If connection to Novacura Flow home is not available, then it will be possible to do an offline upgrade. Download the offline packages and enter each package for the component/s that should be upgraded.

After the upgrade is done, make sure the mobile clients (iOS, Android, Windows) are updated to the latest version. If not the users won't be able to log into the client
Novacura Flow portal upgrade to 6.3 and later
Regarding portal upgrades from Flow versions earlier than 6.3, contact product.support@novacura.com for more information.
Problems
If the upgrade process results in a corrupt state, which it can't rollback automatically, an error message "Entry is incorrect. Fix errors or remove entry" will be displayed on the environment instance. This can often be recovered manually by: - Go to the installation folder and change the name of the data backup that the installation tool have done.
- Remove the underscore and date from the folder name of each component installation folder (see example image below).
- Start the site and service from IIS Manager.
- Open the Novacura Flow server page to see that it is up and running.

Contact product.support@novacura.com for support if the upgrade fails.
Windows Authentication for Novacura Flow Web Client or Portal
The Novacura Flow User Id need to be the same as in the Active Directory to be able to use Windows Authentication. Use the Active Directory Sync in the Environment part of the Novacura Flow Studio to easily import users from the Active Directory.
1. Enable Windows Authentication
- Click on the Web.Authenticator application under the site
- Double click on Authentication
- Enable Windows Authentication and disable all other authentications
If Windows Authentication is missing in the list of authentications; go to the Server Manager and click on Add roles and features. Click on Next until the Server roles tab, extract Web Server (IIS), Web Server, Security and check Windows Authentication, click on Next until installation.
2. Control the configuration of the Web Authenticator
- Open the folder for the Web Authenticator (C:\Novacura\Novacura Flow 6\WebAuth)
- Right click and edit the Web.config file
- Change the value for key flowServerAddress to the full Flow Server address, for example:
<add key="flowServerAddress" value="http://servername:80/Novacura.Flow.6.Server/">
- Open the folder for the Web Client and/or portal
- Right click and edit the Web.config file
- Change the value for key flowWebAuthenticator to the Flow Web Authenticator address, for example:
<add key="flowWebAuthenticator" value="http://servername:80/Novacura.Flow.Client.Web.Authenticator">
- Save the changes and close the files
3. The installation of the Windows Authentication for the Novacura Flow Web Client / Portal is now done. The users can log on with Windows Authentication in the Novacura Flow Web Client / Portal if they click on Sign in with your Microsoft Windows domain account.
OpenID Connect
OpenID Connect 1.0 (OIDC) is an identity layer on top of the OAuth 2.0 protocol. It allows Clients to verify the identity of the end user based on the authentication performed by an Authorization Server, as well as to obtain basic profile information about the end user.
Set up Studio
Requirements:
In order to be able to access the OIDC Configurations in the clients, the firewall needs to be opened to the following three methods:
- FlowServerContact - method to get the connection to the Flow Server and downloads necessary data to be able to sign in to Flow
- GetExternalCredentials - method to get the credentials required for the user to sign in to Flow and other connected systems
- GetOpenIdConfigurations - method to get the OpenID configurations for the user, these are needed to know where and what the user needs to sign in to
The OpenID server must allow the specific callback URL: novacura://openid.
OIDC is configured in the flow Studio under Environment - External Authentication.
- Name - the name of configuration
- Authority Address - the address the client will browse to and sign in to OIDC
- Client ID - the client id used in the OIDC server
- Client Secret - the client secret used in the OIDC server
- Scope - the scope the connection should be valid for
- Primary Configuration - set the configuration should be used when communicating with the Flow server to the primary one. If set to true, the Flow client will send the Bearer Token in the Request Header in each request to the Flow server.
- Authentication Flow - Authorization Code or Hybrid
- Require Authorization Code Hash - The code hash is included in ID tokens only when the ID token is issued with an OAuth 2.0 authorization code. It can be used to validate the authenticity of an authorization code.
- Require Access Token Hash - The access token hash is included in ID tokens only when the ID token is issued with an OAuth 2.0 access token. It can be used to validate the authenticity of an access token.
- Client Type - All, Native or Web; Applications can implement a web client (confidential) which runs on a web server, a native client (public) installed on a device.
- Do Not Validate Discovery Endpoint - The discovery endpoint can be used to retrieve metadata about your IdentityServer - it returns information like the issuer name, key material, supported scopes etc.
- Use Access Token as Bearer - if true access token is used bearer token, if false ID token is used
- Flow Roles Which Uses OIDC to Log In - in the screenshot set up, all users connected to the role NovaCura will be required to sign in using OIDC before it will be possible to log on to Flow
It is possible to set up multiple OIDC Configurations, but there can only be one Primary Configuration.
Once OIDC Configuration are completed, they can be used as variables in Workflows. This means that a user can sign in to multiple OIDC servers and access different systems that requires different OIDC credentials.
The OIDC configuration variable name is:
{openIdLogins."your config name".access token/id token/refresh token}Applications
To be able to monitor an application in the Applications sub tab, tick the Monitored checkbox in the metadata panel.

In Monitoring tab, user can select Applications sub tab and select workflow by clicking Choose application dropdown.
Application process Ids will be registered and displayed in table with Start Time and End Time details. The process ID is a link, that pressed will bring User to specified process in Tasks overview.
Clicking button: ? Refresh, user will reload results and get actual data ? Open Workflow, user will open selected workflow in Application main tab.
Help requests
When working with offline workflows in the iOS, Android or Windows10 Flow clients, all transactions that are produced by the workflow are put in a queue. This queue can be found in the Offline Data section, under MY WORK. The transactions are executed automatically in the background when the device have access to internet.
Normally these transaction executes without any problems and disappears from the queue. However, if a workflow transaction has failed, the User is able to send a Help Request to an Administrator, so that the problem can be fixed. The Administrator can then either correct the problem in the back-end system or correct the data in the workflow transaction. When the problem is fixed, the Help Request can be sent back to the User and the transaction can be executed again.
The Administrator can view all requests in the Help Request tab under Monitoring.

The help request table contains eight columns:
- Request ID: Unique id for the Help request
- Login: Username of the user who made the Help request
- Workflow name: From where the transaction is created
- Time stamp: Time when the request was created
- Status: Request status
- Error message: The error message for the failed transaction
- Instance name: The name of the workflow instance
- Transaction name: The task name set for the handover
The Administrator can in the right side panel edit and view the details of the request, such as the name of the workflow that has failed, the user id, comment from the sender, status etc. In order to resolve the transaction issue, the Administrator can edit any variable from the workflow transaction, add an optional comment and send the solution back to the user. If the cause of the error is only related to data or logic in the back end system, the Administrator can fix the root cause and directly send the request back to the User. The Administrator can also cancel the request.
The Help Request is being tracked by the following statuses:
- New: New unhandled request
- In progress: The transaction is changed by the Administrator
- Sent back: The Help request is sent back to the User
- Retried: Retried by the User without errors
- Retried with errors: Retried by the User with errors
- Resolved: Resolved of the change done by the Administrator
- Cancelled by user: The User has deleted the request
- Cancelled by administrator: The Administrator cancelled the request
- Session was closed: The User logged out from the app
Changes done by an administrator are sent to the user as a notification on the mobile device. The status is refreshed after clicking on the notification or clicking the Refresh button.
When the fix is delivered, will the user see the message: Retry updated transaction! and can then click on the green TRY AGAIN button to execute the transaction again.
The User will receive notifications when the Help request changes status, from New to In progress and from In progress to Sent back.
System Event
To get a notification about new requests, can the System Event Flow functionality be used, which can be found in the System Events panel under the Environment tab. Read more about system events here.
Tasks
Monitoring in Flow studio tracks the inbox tasks that are assigned to users. The Administrator can track who the task is assigned to, when the task was created, the run time from when the task first was started and how long the task has been in the inbox. This can help the Administrator to get a clear overview of how many tasks are being executed, who is responsible for each task and if the task is assigned to someone who cannot work with it, the Administrator can also reassign or remove the task.
Tasks Overview
Task Overview contains eight columns:
- Task Name: Displays the name of the running task.
- Assignee: Shows which user that is assigned to the current task.
- Application: The name of the application where the task is placed.
- Process ID: A unique identifier string.
- Waiting Time: Measures how much time has passed since the task was created.
- Created: MM/DD/YYYY HH:MM:SS Date and Time when the task was created.
- Work Started: Displays when the assignee first started with the task.
- Run Time: Measures for how long the task has been running since it was started.
It is possible to select a task from the list to display details about the task.
Details
Details allows the administrator to Reassign, kill processes and see detailed information about the selected task.
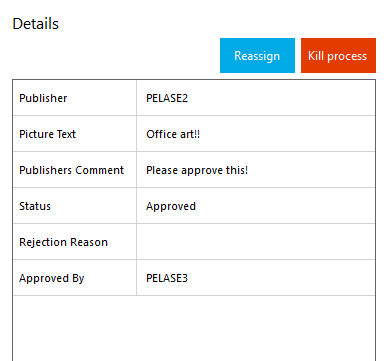
Reassign User 1. Select which task to reassign. 2. Click on reassign. 3. Choose which user to reassign the task to (make sure the user has a suitable role). 4. Click confirm reassignment.
Kill Process 1. Select which taskprocess to kill. 2. Click on Kill Process. 3. Confirm in the new confirmation window that you wish to kill the selected process.
Monitoring
server test
Novacura Flow System Requirements
For Novacura Flow Server and Novacura Flow Web Client
Software Requirements
Operating System
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
Server roles and features
- .NET Framework 4.6.1
- Internet Information Services (IIS) v7.5 or higher
- Web Server (IIS) -> Web Server -> Application Development:
- .NET Extensibility 4.5
- Application Initialization
- ASP
- ASP.NET 4.5
- HTTP Activation (found under .Net Framework 4.5 Features -> WCF Services)
- Microsoft Visual C++ 2010 Redistributable
Hardware recommendations
The hardware required for a Novacura Flow installation depends on many factors, including the number of concurrent processes, the amount of data processed by the workflows, and the frequency of calls to third-party systems.
Memory
The amount of RAM used by the Flow Server or Web Client varies depending on usage. The software depends on RAM caches to speed frequent look-up operations; a high RAM for the server process is not necessarily a sign that more memory needs to be added.
Recommendation: 4 to 8 GB. (Up to 16 GB if Web Client and Server are installed on the same machine.)
Disk
A fast disk will speed up some operations in the Novacura Flow Server and Web Client. This is true especially for workflows that handle large data sets or files. There may be some delay before disk space is freed, so it is normal to see a build-up of disk space usage in the initial stage of Novacura Flow Server usage.
Recommendation: 20+ GB of disk space available.
CPU
The Novacura Flow Server and Web Client are hosted in Microsoft IIS, making use of its threading and process model. Performance scalability is improved as clock speeds and number of cores increases.
Recommendation: At least 2 GHz clock speed, at least 4 cores (8 if Web Client and Server are installed on the same machine).
License requirements
The address https://home.novacuraflow.com need to be reachable from the machine where the Novacura Flow is installed, so the Novacura Flow service can call home and check if the license is valid. If it is not possible to open up for https://home.novacuraflow.com, the license will need to be manually updated through the Novacura Flow studio every month.
Clients
- Android Client, requires Android version 5.0 - 7
- iOS Client, requires any of the latest two major versions of iOS.
- Web Client, requires IE 10 or newer, Google Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge browser
- Windows CE Client, requires version 5.0 or newer with .NET Compact Framework 3.5
- Windows 10 Client, requires computers, tablets or mobile phones running Windows 10.
- Portal, requires IE 10 or newer, Google Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge browser
Scanning Devices
Definition of support:
- FULL SUPPORT: We can scan in all applicable controls (text inputs, list selections, etc.). The workflow moves forward automatically when appropriate.
- LIMITED SUPPORT: We can scan in text inputs. The workflow does not move forward automatically, and scanning may not work in list selections and other non-textual controls.
- NO SUPPORT: Scanning will not work at all.
Support for different kind of scanners:
- Android
- Honeywell CT50: FULL SUPPORT
- Zebra scanning devices supported in fig 1: FULL SUPPORT
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge with semicolon character as pre-and postfix and send the scanned characters as key events: FULL SUPPORT.
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge: LIMITED SUPPORT.
- iOS
- Linea Pro: FULL SUPPORT.
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge (scanning into any application): LIMITED SUPPORT.
- Other scanners which do not support keyboard wedge: NO SUPPORT
- Windows CE
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge with a configurable pre- and postfix: FULL SUPPORT.
- Scanners with keyboard wedge but no configurable pre- and/or postfix: LIMITED SUPPORT.
- Web
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge with return/carriage return as postfix and send the scanned characters as key events: FULL SUPPORT
- All scanners which support keyboard wedge: LIMITED SUPPORT.
Device/Os Compability chart for Zebra for Android scanning
The following devices has been tested by Symbol/Zebra and is officially supported according to: Zebra Support Site
| Device | Android KitKat | Android Lollipop | Android Marshmallow | Android Nougat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC5000-10 | x | |||
| ET5X | x | x | ||
| MC18 | x | x | ||
| MC32 | x | |||
| MC33 | x | |||
| MC40 | x | x | ||
| MC67 | x | |||
| MC92 | x | |||
| TC20 | x | |||
| TC25 | x | |||
| TC51 | x | x | ||
| TC55 | x | |||
| TC56 | x | x | ||
| TC70 | x | x | ||
| TC70x | x | x | ||
| TC75 | x | x | ||
| TC75x | x | x | ||
| TC8000 | x | x | ||
| VC80x | x | |||
| WT6000 | x |
fig 1
All devices requires at least version 6.7.10.1010 or higher of Zebra EMDKSERVICE on the device. Lower versions of EMDKSERVICE than this has limited scanning usability. Also note that Novacura Flow Android Client requires Android Lollipop or higher, which means supported Android KitKat devices will work with other scanning but will not run Novacura Flow client.
From version 6.10 for Zebra, the Data Wedge is used to control and execute scanning.
If upgrading to 6.10 and using the flow client preferences for scanner specific settings, please note that these must be moved to the data wedge application.
Novacura Flow System Requirements
Hardware recommendations
Application/Web Server
| Type | Minimum Recommendation |
|---|---|
| CPU | Xeon E5-2665 (8core) |
| Memory | 16GB |
| Disk | 60GB |
| LAN | GBit |
Proxy Server (in case of external access)
| Type | Minimum Recommendation |
|---|---|
| CPU | Xeon E5-2620 (6core) |
| Memory | 16GB |
| Disk | 60GB |
| LAN | GBit |
Software requirements
Operating System
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Server 2012 R2
Server roles and features
- IIS 7 or later including ASP.NET
- .NET Framework version 4.6 and 4.0
- Application development
License requirements
For the license to work and be able to call home and check if it is valid, the address https://home.novacuraflow.com needs to be reachable from the machine where the Novacura Flow Server is installed.
If it is not possible to open up for https://home.novacuraflow.com, then the license will need to be manually updated through the Novacura Flow Studio every month.
Clients
- Android Client is certified from Android 4.1 up to Android 7
- iOS Client, requires versions 7 - 10
- Web Client, requires IE 10 or newer, Google Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge browser
- Windows CE Client, requires version 5.0 or newer with .NET Compact Framework 3.5
- Portal, requires IE 10 or newer, Google Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge browser
The Novacura Flow portal needs a Microsoft SQL server database for the Flow portal configuration
Troubleshooting Server Issues
If you are having troubles with the flow server, clients or other flow related products, please contact us at product.support@novacura.com and attach log files or other related files.
Services
When the service is stopped, the novacura server won't work. Follow these steps to start/restart the service:
- Press windows button + R and type in "services.msc".
- Scroll down until you find the novacura service.
- Right click the service and press start/restart, the service should now start up.
App pool and sites
If the server stops responding there might be something wrong with the applications running the app pool or something wrong with the site.
- Navigate to the IIS -> Servername -> Application Pools.
- Select the Novacura application pool, on the right side select recycle or start it up if it's not running.
- Navigate to Sites and select the site where the novacura server is running, on the right side select restart or start if it's not running.
- Verify that the server is now up and responding again.
Fetch custom event views
If the server stops responding often, crashes or if you are experiencing any other errors which are hard to specify the cause for a log containing information about errors occuring could be useful.
To fetch a log containing crash dumps etc. follow these steps:
- Press windows button + R and type in "eventvwr.msc".
- Select custom views and click on create custom view.
- Logged - Specify in which timeframe you want to fetch the logs from.
- Event Level - Select Error, Warning and Critical
- Select by source and choose all sources you want to fetch messages from, some relevant are: ".Net Runtime, Application Error, ASP.Net 4.0, MSSQL SQLexpress, MSSQL SQLexpress Audit". But it depends on what you wish to view, these mentioned above can help us investigating your error if you report it to us and attach the custom view file.
- Select the new custom event view you have created, click on "save all events in custom view as..."
- Choose a name for the file and save it as .evtx, attach this file to your issue when you report them to us if you're having server problems. It can both help us identify the problem and allow us to fix the problem faster.
Fetch a memory dump
If the logs from the IIS and Flow server aren't enough, you can also fetch a memory dump which could help us tracing the root cause of the problem you are experiencing. By following the instructions in: Fetch memory dump you can fetch the memory dump and send it to us.
Be very careful to fetch the memory dump during the time the error occurs, and not after you have fixed the error or restarted the server etc..
If the bug does not exist in the current session when you fetch the dump, we will not see it.
Monitoring flow events
If the site, service or any kind of crucial part of your flow server stops responding/working you might want to get notified.
Some relevant parts of flow server which you might want to monitor includes: Flow Service, Flow Site, Flow applications pools.
Also server cpu and memory usage might be handy if you are experiencing performance issues.
 Novacura Flow Help
Novacura Flow Help
This is the Novacura Flow Help.
The Novacura Flow Help can be reached offline from the Novacura Flow Studio.
When the Novacura Flow Help opens from the Novacura Flow Studio it will first try to open the online help, if no internet connection is available the offline help will be opened. The offline help will be updated for every new version of Novacura Flow 6 and the online version will be updated continuously.
Launcher
The Studio launcher supporting launching of different Flow studio versions depending on environment, it is easy to connect to different Flow servers, even though the Flow servers have differnet versions. As a Designer or Administrator, you don't even have to know which version you are connecting to, the Studio launcher takes care of all this, including downloading new versions and updates of the Flow Studio. The Flow Studio launcher can be used with Flow version 6.4 or later.
Download the Studio launcher from here.
Lgoin or create an account to download the Studio launcher.
Installation
Click on Install in the studio to be able to see which versions of the studio that are installed, uninstall or update a current version or install a new one. The installation can be done both with and without internet connection.
Install a new version Click on Install under preferred flow studio version to install a new version.A user will be notified when logging in with a server address which doesn't match a version that are installed. Click yes to install and log in with the new version and no to log in with the current version. The user must be an administrator to do the installation.
Update a current version Click on update under preferred flow studio version to update an already installed version.
A user will be notified if a new version is available when logging into the studio. Click "yes" to install and log in with the new version and no to log in with the current version.
Uninstall a current version Click on uninstall under preferred flow studio version to uninstall a current version.
Install package manually Click on install package manually to install a version of flow studio manually. Choose your package and click open.
Login
Login to a Flow environment by enter server url or server pin code followed by your credentials. When leaving the Server input field a inital connection will be established and url/pin will be replaced by server instance name.
To save a server address, enter the address and click on the star icon and click Save. To remove saved server addersses, open the list of saved server addresses and hover over the address you want to delete and press the Delete-button on the key board.
Check "Remember me next time" if the credentials should be stored until next login.
It is possible to run multiple instances of Flow studio and server instance name is shown in title bar.
Login Screen
Novacura Flow Studio
With the brand new Novacura Flow Studio we have created a true power tool for creating efficient, user-friendly and integrated apps providing increased growth, higher efficiency and simpler administration.
And as usual, everything is based on step-by-step workflows. Now you can create multi-user applications, run tasks in parallel, use sub-workflows, send push notifications, get an activity live-feed, create parts of workflows that can be reused and much more. You can even test run your apps directly inside Novacura Flow Studio, something that will radically shorten the time from idea to implementation.
With the simplicity of Novacura Flow Studio, you can go from zero to app in just minutes, as long as you know what you want to achieve - or discover potential achievements you weren't even aware of!
The Novacura Flow Help can be reasched offline from the Novacura Flow Studio. When the Novacura Flow Help opens it will first try to open the online help, if no internet connection is available the offline help will be opened. The offline help will be updated for every new version and the online version will be updated continuously.
Example screens from Flow Studio
 User Step
User Step
A user step contains a sequence of interaction items, like input controls, lists and static texts. Each interaction item type has a number of properties and preferences. Extend User step in the tree beside to read about all of the different user controls.
Multi exits
A user step can have multiple exits that will appear like buttons in the clients. There is no restriction on how many exits that it is possible to have, but too many buttons in the client (especially in the mobile clients) can look messy, therefore it can sometimes be better to use a sub workflow instead of a button.
If a user step got one exit step it's automatically set to default but when having more than one exit you have to manually set one exit to default, otherwise no exit will be selected automatically when using enter or scanning in a workflow.


The first exit button is set to default in the Web Client and the priority of the buttons is set to show in which order they should be displayed.

Always enabled exit
Tick the box Always Enabled if an exit should be available even if mandatory data in the user step is missing.
If data is partly entered in the user step from which an always enabled exit is used, the data is not cleared but can be used later in the workflow. The workflow designer should take care so an always enabled exit is not used when the next step requires mandatory data.
Pinned user steps
A pinned user step are an information
It is only possible to use Header, Static Text, Labeled Static Text, Link and List Presentation in pinned user steps, this because a pinned user step is only a way to show the user information.

The pinned user step will show up in the side of the screen, and the user need to tap/click on the icon to extend or colaps the pinned user step. In the below picture is the pinned user step to the left and the regular user step to the right. If there is more then one pinned user step in the workflow, will the pinned user step be replaced when the user steps over another pinned user step.

History
From the user step it's possible to edit the text that is displayed in the historical view in the clients.
Click on historical to configure the historical view. Then enable show in history to be able to see the text in the clients. Enter the preferred text into the text, title and value field.

In Universal windows client the configured history step looks like this:

Designer
The designer allows for drag-and-drop interaction with the user step. The user can simply drag one item on the left bar and drop it inside the design area. The designer allows for 1, 2, 3 and 4 columns to be added in one row. The web client will expand or shrink depending on the amount of columns added in the designer step.
